MATERNAL & CHILD: POST PARTUM
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
__________ - It begins immediately after childbirth, as the nurse assists the new mother in caring for herself and her baby during the 6-week puerperium.
- This period is filled with changes, major adjustments, and adaptations for the family.
- Parenting starts here, and a positive, loving relationship with the newborn promotes emotional well-being and affects the child's growth and development.
Postpartum care
_____________ - begins within an hour after the woman gives birth and continues through discharge.
This ASSESSMENT includes vital signs and psychosocial assessments.
Although the exact protocol may vary among facilities, postpartum assessment typically is performed as follows:
During the FIRST hour: every __________
During the SECOND hour: every __________
During the FIRST 24 hours: every ___________
AFTER 24 hours: every __________
- During each assessment, keep in mind RISK FACTORS that may lead to complications, such as _____________, during the recovery period.
- Comprehensive nursing assessment
During the FIRST hour: every 15 minutes
During the SECOND hour: every 30 minutes
During the FIRST 24 hours: every 4 hours
AFTER 24 hours: every 8 hours
- infection or hemorrhage
What are the Postpartum assessment of the mother typically includes?
vital signs,
pain level,
"systematic head-to-toe review" of body systems.
The acronym ______________ — Breasts, Uterus, Bladder, Bowels, Lochia, Episiotomy/perineum, Sexual, Homan's, and Emotional status, Bonding and Spiritual
— can be used as a guide for this "head-to-toe review".
BUBBLE-SHEBS
Vital Signs: TEMPERATURE
- During the first 24 hours postpartum, the mother's temperature is usually normal, though a slight fever up to 38°C (100.4°F) may occur due to _____________ from labor.
- After 24 hours, the temperature should return to _________ once fluids are replaced.
- A temperature above 38°C at any time, or an abnormal temperature after the first 24 hours, may indicate ___________ and must be reported. Continued monitoring is required until infection is ruled out.
- dehydration
- normal
- infection
Vital Signs: PULSE
- Postpartum changes in blood volume and cardiac output may cause relative ____________, with a pulse ranging from "50-70 bpm", returning to pre-pregnancy levels within 10 days.
______________ - may signal anxiety, fatigue, pain, excessive blood loss, infection, or cardiac issues, and should be investigated further to rule out complications.
- Bradycardia - (a slow heart rate)
- Tachycardia - (Fast heart rate / a heart rate over 100 beats a minute)
Vital Signs: RESPIRATION
- Respiratory rate in the postpartum woman should remain within the normal _________ breaths per minute.
- Any rate outside this range may indicate ____________________ and must be reported.
- Lungs should remain clear on auscultation.
- 16-20
- pulmonary edema, atelectasis, or pulmonary embolism
Vital Signs: BLOOD PRESSURE
- Postpartum blood pressure should be compared with the predelivery baseline to detect deviations.
- An increased BP may be caused by pain or anxiety, and a BP of 140/90 mm Hg or higher may indicate - _____________.
- A decreased BP may suggest ______________ from excessive bleeding.
- BP varies with position, nurse should watch for ______________ when the woman stands up quickly.
- Pre-eclampsia
- dehydration or hypovolemia - (body loses fluid)
- orthostatic hypotension - (form of low blood pressure might cause dizziness, lightheadedness or fainting when rising from sitting or lying down)
Vital Signs: __________ - fifth vital sign
- Postpartum orders often include ________________ for afterbirth pains rather than waiting for the woman to feel discomfort.
- The goal is to keep pain between ____________, especially after breastfeeding, through frequent assessment and preventing pain by giving analgesics as needed.
- PAIN
- routine premedication
- 0 to 2
Components of a Postpartum Assessment BUBBLESHEBS:
BREAST:
- Assess the breasts by inspecting __________ (everted, flat, or inverted), __________ (soft, filling, or firm), and X ___________ (warm, pink, cool, or red-streaked).
- Check for size, contour, asymmetry, engorgement, erythema, and nipple damage such as cracks, fissures, or bleeding, which may indicate improper latch.
- ______________ - the breasts to determine tissue firmness and identify nodules, masses, or areas of warmth, which could suggest a plugged duct or risk of mastitis.
- For non-breastfeeding women, palpate gently to AVOID __________. Ask about nipple discomfort and document findings, noting engorgement or firmness as milk comes in.
- nipple shape, breast tissue, breast tissue
- Lightly palpate
- stimulating milk production
Components of a Postpartum Assessment BUBBLESHEBS:
UTERUS
- Assess location: _____ to right or left side.
_________ - is the return of the uterus to its pre-pregnancy size and condition.
_________ - one hand on the lower segment to stabilize, the other to palpate the fundus with the woman in supine position and the bed flat or as low as possible.
A "boggy or relaxed uterus" indicates - ___________ -- Causes include bladder distention (displacing the uterus upward and to the right) or retained placental fragments, both of which increase risk of hemorrhage.
- midline or deviated
- Involution
- Use a two-handed approach
- uterine atony - (failure of the uterus to contract adequately after childbirth)
ASSESSMENTS OF THE UTERINE FUNDUS AND NURSING ACTIONS:
NORMAL: Fundus firmly contracted
ABNORMAL: Fundus is soft, "boggy," uncontracted or difficult to locate.
- NURSING ACTION WHOULD BE?
NURSING ACTION
- Support lower uterine segment.
- Massage until firm
ASSESSMENTS OF THE UTERINE FUNDUS AND NURSING ACTIONS:
NORMAL: Fundus remains contracted when massage is discontinued
ABNORMAL: Fundus becomes soft and uncontracted when massage is stopped.
- NURSING ACTION WOULD BE?
NURSING ACTION
- Continue to support lower uterine segment.
- Massage fundus until firm; then apply pressure to express clots.
- Notify health care provider, and begin oxytocin or other drug administration, as prescribed, to maintain a firm fundus
ASSESSMENTS OF THE UTERINE FUNDUS AND NURSING ACTIONS:
NORMAL: Fundus located at level of umbilicus and midline
ABONRMAL: Fundus located at level of umbilicus and midline
- NURSING ACTION WOULD BE?
NURSING ACTION
- Assess bladder elimination.
- Assist mother in urinating, or catheterize, if necessary, to empty bladder.
- Recheck the position and consistency of fundus after bladder is empty
Components of a Postpartum Assessment BUBBLESHEBS:
BLADDER:
- Assess the _____ by noting the last time the patient emptied it (spontaneously or via catheter), whether it is _____, and the color, odor, and ______.
- Postpartum diuresis may reach up to _________ for several days but usually decreases by day three.
- Many women may not sense the need to void, especially if they received _________, which can cause bladder distention and difficulty voiding until sensation returns.
________ - It is NORMAL due to progesterone effects, edema, prolonged labor, forceps use, analgesia, or anesthesia.
- Assess for voiding problems by asking about urination, burning, difficulty, incomplete emptying, signs of infection, urinary control, or leakage.
- bladder, palpable, amount of urine
- 3,000 mL
- regional anesthesia
- Decreased bladder tone
It is displaces the uterus above and to the right of the umbilicus, can cause uterine atony and lead to hemorrhage.
Overdistended bladder - (a stretched, swollen bladder that occurs when it is unable to empty completely, leading to a buildup of urine)
Components of a Postpartum Assessment BUBBLESHEBS:
BOWEL:
- Gastrointestinal activity ________ soon after childbirth, often causing hunger and thirst due to prior food and fluid restrictions.
__________ - during pregnancy depress bowel motility.
__________ - contribute to constipation during early puerperium.
- Bowel movements are usually delayed until the _________postpartum.
- Hemorrhoids, perineal trauma, and episiotomy may cause ___________.
- increases
- Relaxing and progesterone
- Relaxed intestinal and abdominal muscles
- second or third day
- painful defecation
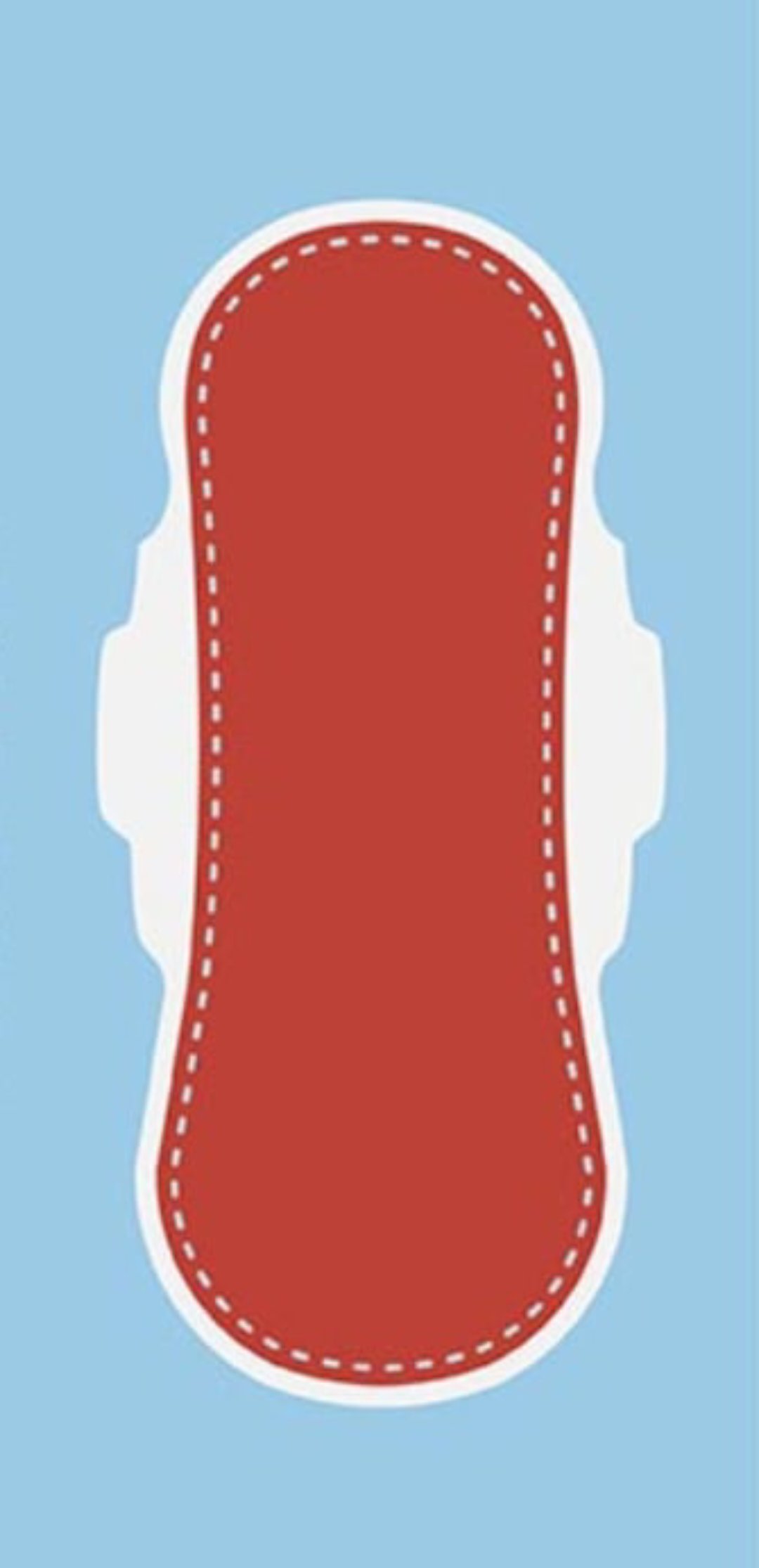
Occurs first few days postpartum.
Mostly blood, giving a red color.
Contains amnion, chorion, decidua, vernix, lanugo, meconium.
Causes fleshy odor.
Abnormal discharge: large clots, saturated pads, foul odor.
Lochia rubra
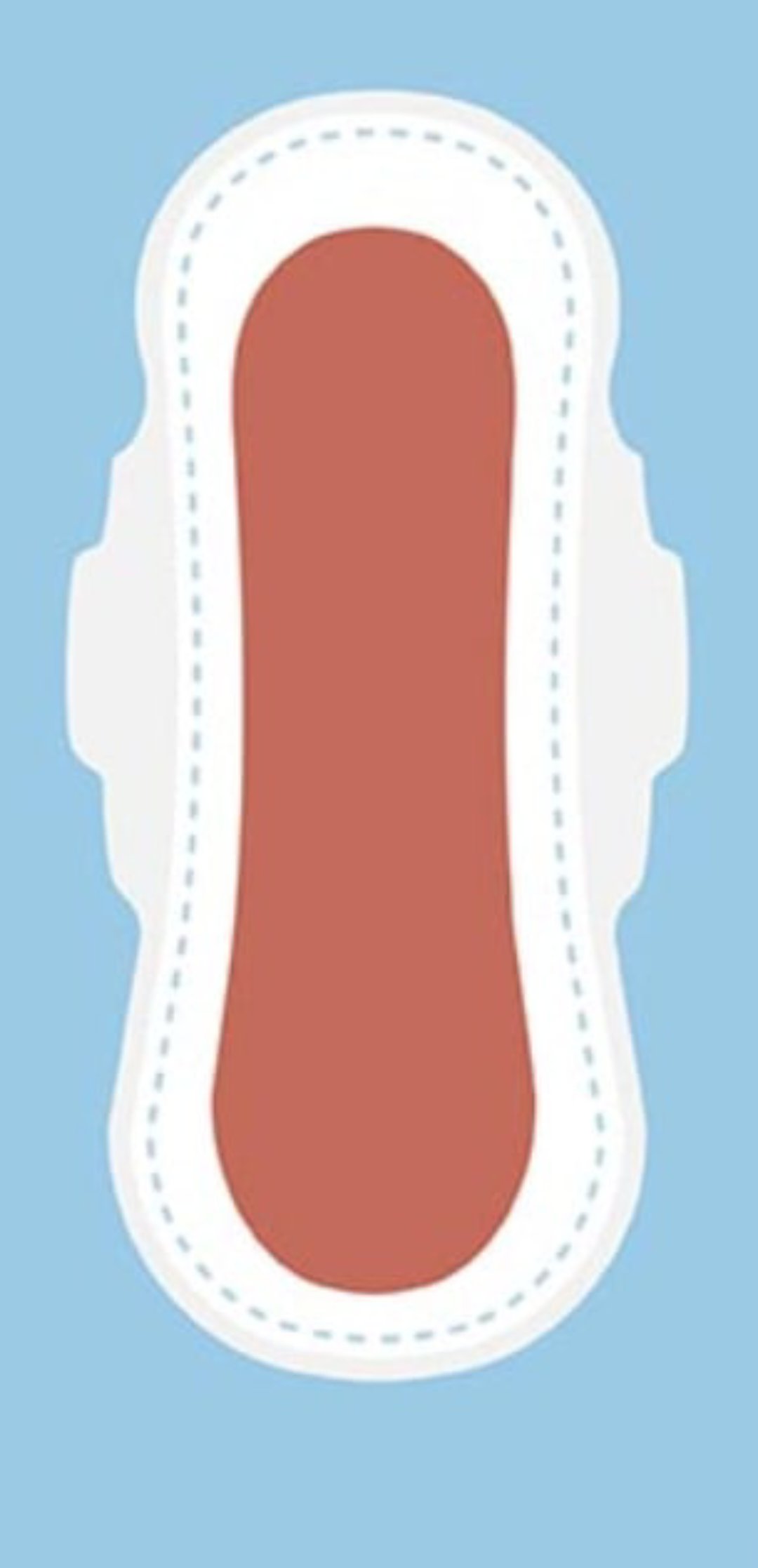

Appears after 3-4 days.
Pinkish-brown, contains blood, wound exudates, erythrocytes, leukocytes, cervical mucosa.
By 10-14 days, mostly leukocytes and reduced fluid content.
Abnormal discharge: excessive amount, foul smell, continued/recurrent reddish color.
Lochia serosa
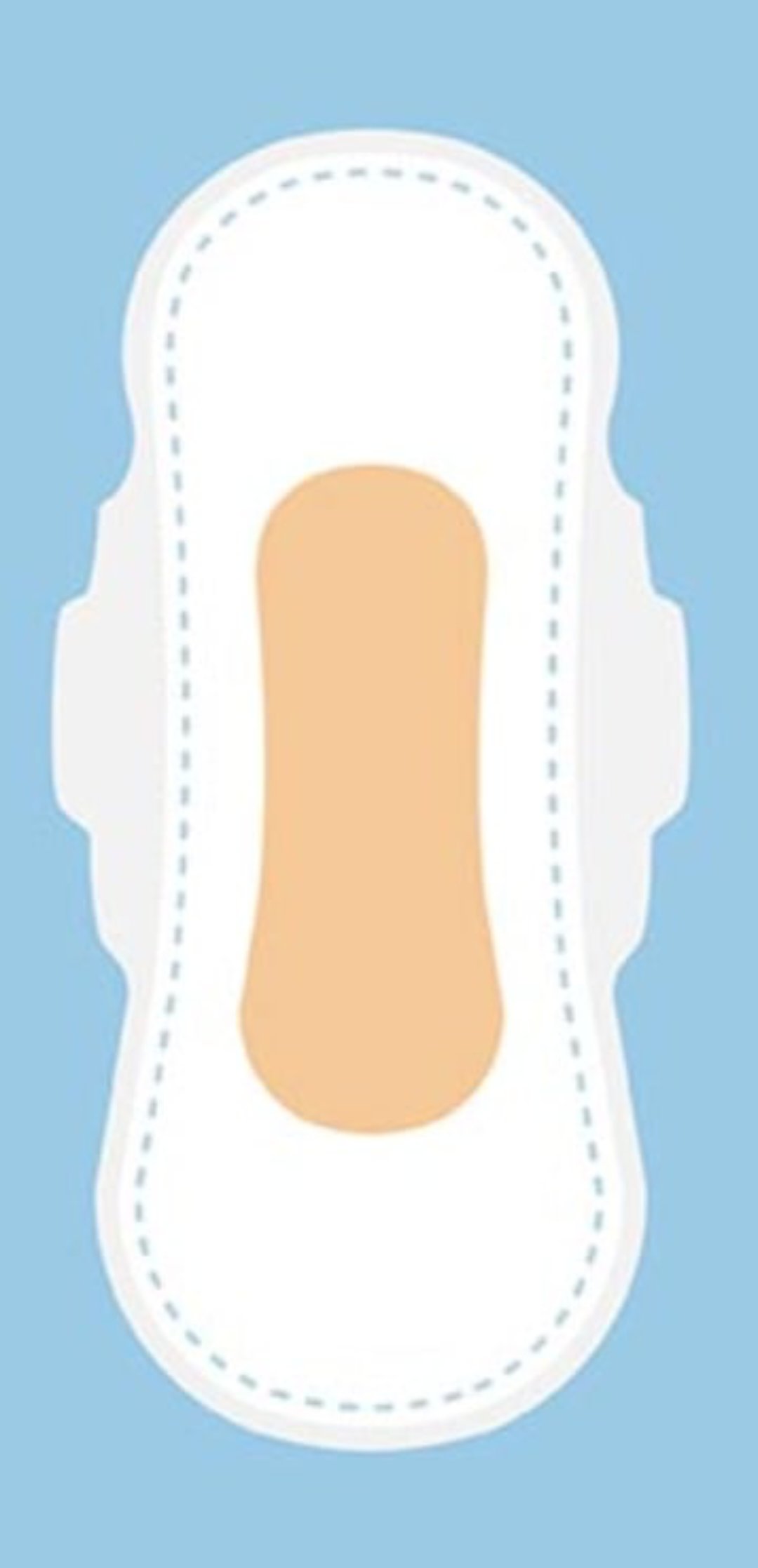
White or yellow-white thick discharge.
Contains decidual cells, mucus, bacteria, epithelial cells.
Present until about third week, may persist up to 6 weeks.
Abnormal discharge: persistent lochia serosa, return to lochia rubra, foul odor, prolonged discharge.
Lochia alba
LOCHIA
Total volume: approximately _________ (8-9 oz), decreasing daily.
240-270 mL
Components of a Postpartum Assessment BUBBLESHEBS:
Episiotomy / Laceration:
- Assess type of episiotomy and other tissue trauma (lacerations, etc.) using _____.
- Episiotomy: ________ surgical incision in the perineum to enlarge the vaginal opening before birth.
Perineal lacerations classified by degree:
________: superficial vaginal mucosa or perineal skin.
________: vaginal mucosa, perineal skin, fascia, and muscles of perineum.
________: same as second-degree but extends into or through the external anal sphincter.
________: extends through anal sphincter and into rectal mucosa.
- REEDA
- 1-2 inch
- First-degree - Forth-degree
A tear involving perineal muscles
Second degree tear
A tear with partial anal sphincter involvement
Third degree tear
A tear with complete tear of anal sphincter involving bowel lining
Fourth degree tear
- Used in assessment for deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in the leg.
Assessment procedure:
Patient's legs extended and relaxed, knees flexed.
Examiner grasps the foot and sharply dorsiflexes it.
Positive Homans' sign: elicited calf pain.
Homan's Sign
- New mothers may experience mixed emotions: happiness, sadness, insecurity, and mild depression.
- These emotional fluctuations are normal during the early puerperium.
Emotional Changes After Birth
Provide ___________ by listening and allowing the mother to share her labor experience.
emotional support
- Providing parents with a caring, supportive environment during labor, birth, and early postpartum strengthens bonding.
- creates the foundation for nurturing behaviors that influence the child's long-term development.
Bonding
- Women intensify prayers to God for protection, safe delivery, and blessings.
- Pregnant women explore all spiritual and traditional options to ensure spontaneous delivery.
- Prayer increases faith, hope, and confidence in having a safe delivery.
Spiritual Practices During Pregnancy
Systemic Changes during Puerperium:
- Uterine contractions cause _______ (return to pre-pregnancy size).
- Afterpains are common in multiparas; may require _______.
- __ from breastfeeding enhances involution
- Fundus descends one fingerbreadth per day.
- By day 7-9, the fundus is no longer _______.
UTERUS
-Involution
-analgesics
-Oxytocin
-Palpable
_________ - Postpartum vaginal flow progresses in "stages":
- LOCHIA
- Lochia rubra → serosa → alba.
Returns nearly to pre-pregnant state through soft tissue healing and cicatrization (scar formation).
VAGINA
- Returns around 6 weeks postpartum in non-breastfeeding mothers.
- Returns up to 24 weeks in breastfeeding mothers.
- Important teaching: Ovulation can occur before menstruation, so breastfeeding is NOT a reliable contraceptive method.
MENSTRUATION
- Soft and flabby immediately after birth; tone gradually returns.
- May have diastasis recti (muscle separation).
- Gentle postpartum exercises help strengthen abdominal muscles.
- Usually returns to normal by 6 weeks postpartum.
ABDOMINAL WALL
BREASTS
- After placenta expulsion, ___________ then activates; ___________ stimulates milk production.
Breastfeeding mothers:
__________ - from the posterior pituitary causes let-down reflex and milk ejection.
Non-breastfeeding mothers:
No SUCKLING → decreased __________________ → milk production stops.
- Breast engorgement occurs on day 2-3 in both breastfeeding and non-breastfeeding mothers, due to vasodilation before lactation.
- luteinizing hormone, prolactin
- Oxytocin
- oxytocin and prolactin
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
- Postpartum women often experience _________, needing nourishment to replace calories, protein, and fluids lost during labor.
___________________ - may occur due to:
- Fear of pain from hemorrhoids/episiotomy
- Decreased food intake during labor
- Reduced bowel motility
Management:
Increase fiber, fluid, and exercise
Physician may prescribe stool softeners, suppositories, or enemas
First stool: usually occurs within ________ postpartum
Normal bowel elimination patterns return by ________ after birth
- hunger and thirst
- Constipation and abdominal distention
- 2-3 days
- 8-14 days
BLOOD VOLUME & CARDIAC OUTPUT
- Blood volume returns to pre-pregnant levels in _________.
- Cardiac output _________ in the first postpartum hours due to blood shifting back from the uteroplacental circulation.
- Cardiac output declines by _____% within 2 weeks and returns to normal by 6-12 weeks.
- 3 weeks
- increases
- 30%
- Occurs during the first 2-5 days postpartum.
- Helps reduce excess extracellular fluid.
- Results in ~3 kg weight loss.
- Failure to ________ can lead to pulmonary edema and cardiac complications.
DIURESIS
CLOTTING FACTORS
__________ - they will increase during the first postpartum week.
- Elevated clotting factors increase the risk of _________.
- If DVT develops, treatment may include heparin → warfarin (Coumadin).
- Early ambulation has reduced the incidence of postpartum thrombophlebitis.
- Fibrinogen and platelet levels
- thrombus formation
- Leukocytosis common: WBC count may rise up to 30,000/mm³ after long labor.
- WBCs return to normal within 6 days postpartum.
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
- Hemoglobin and RBC levels ________ around the 4th postpartum day.
________ - may temporarily rise due to fluid loss (hemoconcentration).
- returns to pre-pregnancy levels by 4-6 weeks postpartum.
- Decrease
- Hematocrit
Urinary output ___________ from the 2nd to 5th postpartum day.
- Causes of diuresis include:
- Large amounts of IV fluids given during labor
- Declining oxytocin, reducing its antidiuretic effect
- Extra fluid retention during pregnancy
- Decreased aldosterone production, leading to increased urine formation
increases
Pregnancy causes ______________, leading to small, frequent voiding and possible retention.
Women who received:
__________ → reduced sensation to void
__________ → antidiuretic effect are at risk for bladder distention and incomplete emptying.
- diminished bladder tone
- Anesthesia
- Oxytocin
It focuses on physiologic safety of the mother (discussed previously), comfort measures, bladder elimination, and health education.
CARE IN THE IMMEDIATE POSTPARTUM PERIOD
Vital Signs:
Monitor vital signs regularly.
_________ - is expected in postpartum clients.
- Temperature > 100.4°F (38°C) for 2 consecutive days (after the first 24 hrs) → possible ____________.
_________ - may occur after hemorrhage or trauma.
If infection is suspected:
Obtain lochia cultures and order diagnostic tests.
Administer prescribed antibiotics and antipyretics.
- Bradycardia
- puerperal infection
- Fever
- Assess pain level.
- Administer analgesics as prescribed (e.g., afterpains caused by uterine contractions, especially in multiparas).
Pain Management
Fundal Assessment:
- Ensure the client empties _________ before assessment.
_________ - fundus for firmness, height, and location.
Fundus should be firm, midline, and descend _____________ per day.
Boggy fundus = ________ → massage until firm to prevent hemorrhage.
- bladder
- Palpate
- 1 fingerbreadth (1-2 cm)
- uterine atony
- Monitor color, amount, clots, and odor.
- Foul odor indicates infection → report deviations immediately.
Lochia Monitoring
- Assess for breast __________
- Encourage wearing a support bra 24/7, even during sleep.
- Apply ice packs between feedings (if breastfeeding).
- Use warm soaks or warm showers before feeding to promote milk flow.
- Administer analgesics if non-pharmacologic measures are insufficient.
Engorgement - (is the painful swelling of breasts caused by milk overfilling the mammary glands)
PERINEAL CARE:
Perineal Swelling & Discoloration
- Apply _________ during the first 24 hours to reduce swelling.
- After 24 hours: use _________ for comfort and healing.
Episiotomy / Laceration Care
- Assess using ___________
- Instruct mother on proper perineal hygiene after each void.
- Encourage use of analgesic sprays as prescribed.
- Provide systemic analgesics if pain persists.
- ice packs
- warm sitz baths
- REEDA:Redness, Ecchymosis, Edema, Discharge, Approximation.
- Assess bowel sounds at each shift.
- Notify physician/midwife if bowel sounds are faint or absent.
- Assess for constipation: ask when the last bowel movement occurred.
- Administer stool softeners as per orders.
Bowel Status
- Encourage _________ to prevent blood stasis.
- Maintain _________ and notify healthcare provider if signs of thrombophlebitis appear (e.g., redness, warmth, tenderness in legs).
- early ambulation
- bed rest
______________ - is the healthiest form of milk for babies
- There are few exceptions, such as when the mother is taking certain drugs or is infected with human T-lymphotropic virus, HIV, or has active untreated. tuberculosis.
Human breast milk
__________ - promotes health and helps to prevent disease.
__________ - is associated with more deaths from diarrhea in infants in both developing and developed countries.
- Breastfeeding
- Artificial feeding
FACTORS INFLUENCING THE BREASTMILK
NUTRITION
POSITION
NUTRITIONAL STATUS
ATTITUDE OF THE MOTHER
PRIVACY
GENETIC FACTORS

Lie on one side
Use pillows
Tummy to tummy
Baby's mouth in line with nipple
This position happen when:
➤ Cesarean birth
➤ Uncomfortable sitting
➤ No assistance for latch on in sitting
SIDE-LYING POSITION

- Infant legs are under mother's arm, with hand at the base of the head and neck.
- Use pillows Help infant in latching on
This position happen when:
➤ Cesarean birth
➤ To see the latch on position
➤ Large breast Small baby
➤ Infant is sleepy
THE FOOTBALL POSITION

- Hold the infant in upright position on mother's lap
- Infant head in crook of mother's elbow on the same side close to the breast, the neck is slightly extended.
- Infant ear, shoulder and hips in straight line
- Tummy to Tummy
- Chest to chest of mother and infant
THE CRADLE POSITION

Same of cradle position but just the opposite hand was used to support the infant and the same side hand was used to hold the breast
THE CROSS CRADLE POSITION

- Mother holds the baby in upright position on her lap.
- Mouth is wide open and the chin touches the breast.
- Mother guide the nipple and areola into the baby's mouth for effective milk transfer
- Peristaltic action from the tip of the tongue to the base.
LATCH ON
◆Mouth wide open
◆Lower lip is turned outside
◆Chin touching the breast Black part of the breast not visible below the lower lip Large black portion of breast and nipple including milk collecting ducts are inside baby's mouth
◆Tongue under the teat
Signs of Correct Attachment
SIGN OF SUCCESSFUL BREAST FEEDING
Urination:
____ - wet diapers during the first few days.
____ - wet cloth diapers (or 5-6 wet disposable diapers) per day after initial days.
Bowel Movements:
At least _____ bowel movements every 24 hours.
Feeding Frequency:
______ feedings per 24 hours.
Baby's Behavior & Physiology:
Swallowing sounds are audible during feeding.
Gains 120-210 g per week after the fourth day of life.
Appears healthy with good color, firm skin, and steady growth in length and head circumference.
Shows sound sleep followed by feeding.
- 1-2
- 6-8
- 2-5
- 6-10
- Mothers suffering from HIV infection
- Mothers with open pulmonary tuberculosis
Contraindications of Breast Feeding
It is the painful swelling and tightness of breasts that occurs when milk, blood, and lymph build up in the mammary glands
Breast engorgement
Getting the child to latch on well from the first breastfeeding, and nursing very often — at least every _____________
2 to 3 hours
What is the primary duty of a mother?
Breastfeeding
Area between urethra and anus, includes vaginal opening.
Perineum
- A clean cut, may heal better than a tear.
- to speed up delivery.
Episiotomy
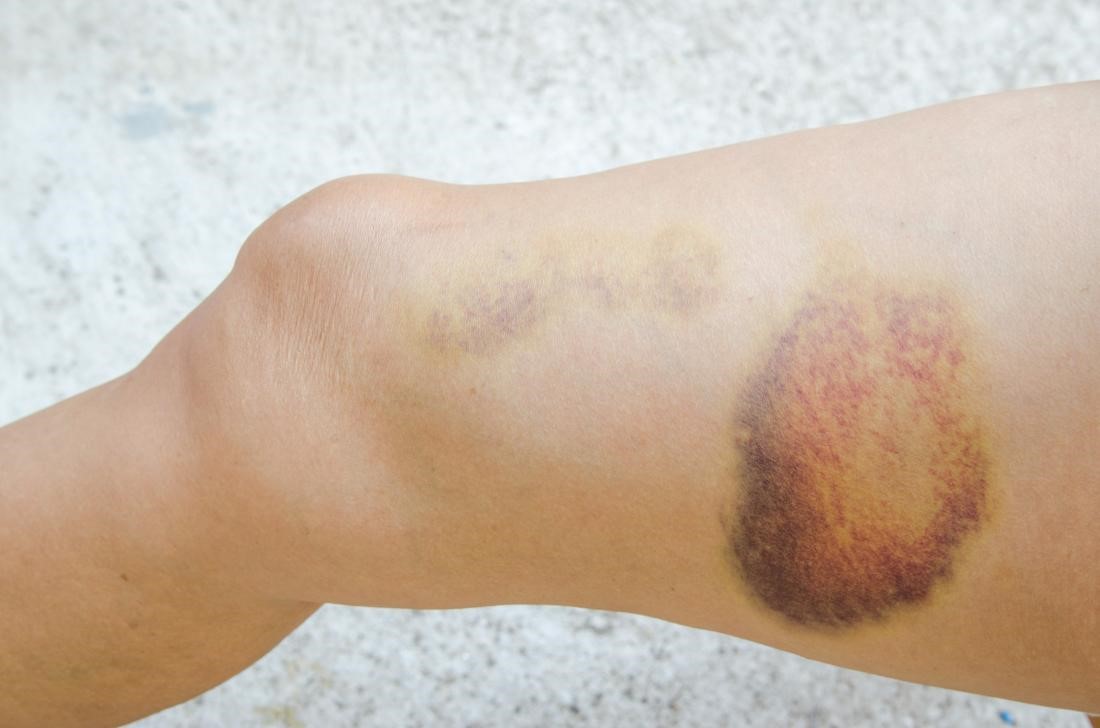
Injury to the vagina and the perineum during delivery may cause swelling, bruising, or a collection of blood under the skin called?
Hematoma - (a localized collection of blood outside of blood vessels, typically caused by an injury or surgery that damages a blood vessel)
What type of Perineum Care at Home is this?
Keep perineum clean after delivery.
Change pads frequently; lochia may last up to 4 weeks.
Take a bath or shower 1-2 times daily.
Hygiene
- Hemorrhoids may bleed after bowel movements; usually resolve naturally.
- Painful hemorrhoids: steroid suppositories may help.
Hemorrhoid Care
Comfort Measures:
- Use an inflatable "_________" cushion when sitting/lying to reduce pressure on episiotomy scar.
- Perform _________ to strengthen pelvic muscles and reduce perineal pain.
- _________ is especially helpful for episiotomy and uterine pain.
- doughnut
- Kegel exercises
- Ibuprofen
When Should You See a Doctor for Post Partum Perineal Problems?
• Bad-smelling discharge from your vagina
• Burning pain with urination
• Passing urine more frequently than usual
• Urge to pass urine frequently, but only going a small amount
• Vaginal bleeding, like spotting or heavy vaginal bleeding (soaking through more than one pad every hour)
• Severe pain in your perineum, pelvis, or lower abdomen
• High fever when you are not sick otherwise
- Early ambulation reduces risk of thromboembolism and strengthens muscles.
- Women should incorporate exercise gradually, starting slowly and increasing over several weeks.
- Routine exercise promotes well-being, muscle tone, and helps return to prepregnant size and shape.
Benefits of regular exercise:
Lose pregnancy weight.
Increase energy to cope with new responsibilities.
Provide an outlet for stress.
Promoting Physical Activity
- Recognize the need for rest and realistic expectations.
Strategies to promote rest:
- Nap when the infant sleeps.
- Reduce outside activities and limit visitors.
- Adjust infant's sleep-wake cycles to increase night sleep.
- Eat a balanced diet to promote healing and energy.
- Share household tasks with family members.
- Ask father or family to provide nighttime infant care occasionally.
- Cluster daily activities to conserve energy.
Rest & Sleep
Exercise Guidelines:
- Start __________ on the first postpartum day.
- Progress to abdominal, buttock, and thigh-toning exercises by the second week.
- ______ is excellent early exercise; avoid jarring/bouncing movements (joints stabilize 6-8 weeks postpartum).
- Avoid exercising too much too soon → may cause more ________ or return of ________.
- Kegel exercises
- Walking
- bleeding
- bright red lochia
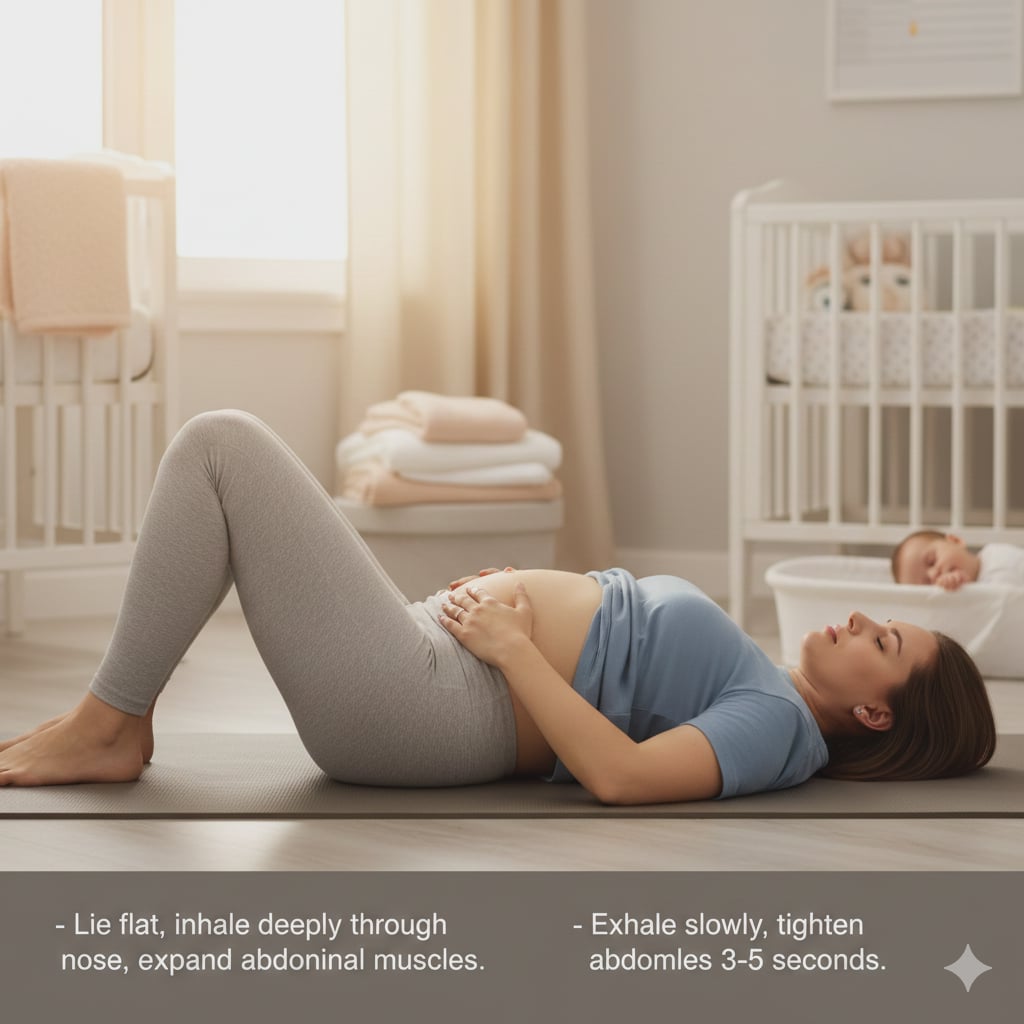

- Lie flat, inhale deeply through nose, expand abdominal muscles.
- Exhale slowly, tighten abdominal muscles 3-5 seconds.
- Repeat several times.
Abdominal Breathing

- Lie flat, knees flexed, feet on surface.
- Lift head, tuck onto chest, hold 3-5 seconds.
- Relax and return to start.
- Repeat several times.
Head Lifting

1. Lie on your back on a firm surface with knees bent and feet flat on the bed
2. Pull your tummy in, tilt your bottom upwards slightly while pressing the middle of your back into the bed and hold for two seconds
3. Let go slowly
4. Repeat ten times daily
Pelvic tilting
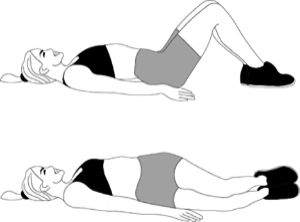
1. Lie on your back on a firm surface with knees bent and feet flat on the bed
2. Pull your tummy in and, keeping your knees together, slowly roll them from side to side
3. Repeat ten times
Knee rolling
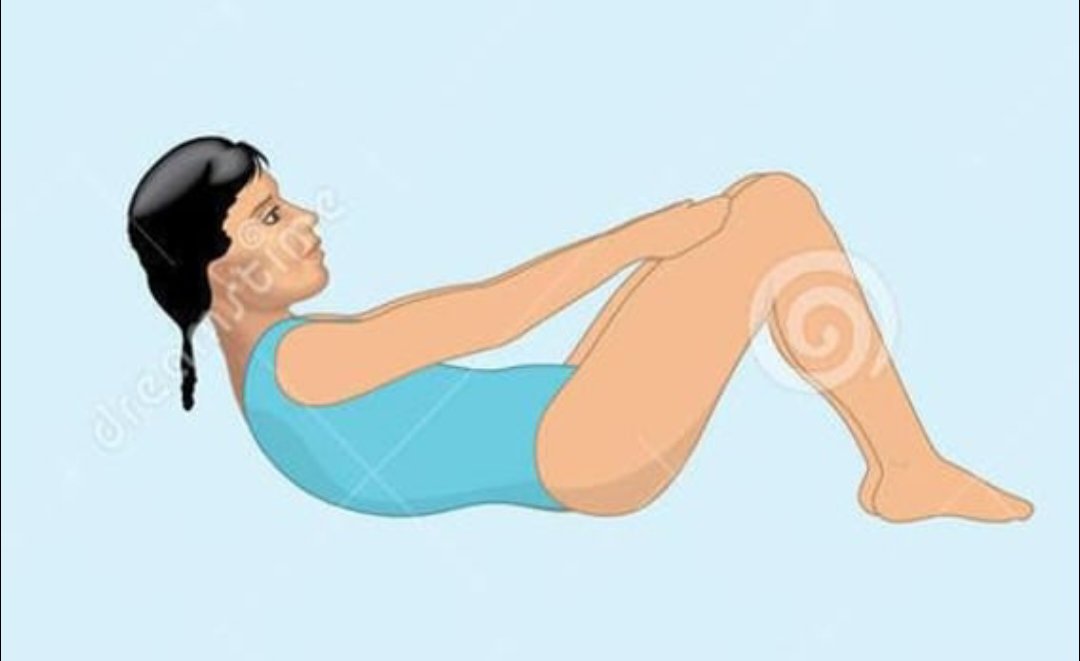
1. Lie on your back on a firm surface with knees bent and feet flat on the bed
2. Place your hands on the front of your thighs and pull your tummy in
3. Lift your head off the pillow
4. Hold for three seconds, then slowly return to starting position
5. Repeat ten times daily
Abdominal sit ups
Couples can begin intercourse as early as ________ after giving birth
2 weeks
Contains synthetic estrogen and progestin, similar to hormones normally produced by ovaries.
Called "combination oral contraceptives."
Effectiveness:
99% if used perfectly.
Realistically about 91% due to missed pills (9 out of 100 users get pregnant each year).
Proper use: Following pill-taking schedule and starting packs on time improves effectiveness.
Pill (Combination Oral Contraceptives)
- Small, thin pouch made of latex, plastic (polyurethane, nitrile, polyisoprene), or lambskin.
- Covers penis and collects semen, preventing sperm from entering the vagina.
Effectiveness:
- 95% if used correctly.
- In reality, 15 out of 100 users get pregnant per year due to improper use.
Advantages:
- Only birth control method that helps prevent STDs.
- Blocks contact with bodily fluids, reducing disease transmission.
- Recommended to use even if on the pill for added protection.
Condom