Cholinergic Neurotransmission
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
The main targets for drug action are
Receptors
Enzymes
Transporters
Ion channels
General steps in neurotransmission
1. Choline (neuron) is taken into the cholinergic neuron (transmitter precursor) via carrier-mediated transport
2. Acetylcholine (transmitter) synthesised
3. Acetylcholine stored in vesicles (via carrier-mediated active transport)
4. Depolarization by action potential → Ca2+ influx
5. Acetylcholine released by Ca2+ mediated exocytosis (vesicle-SNARE proteins (synaptobrevin) & target SNARE proteins (syntaxin) form a complex
6. Acetylcholine binds to receptors (nicotinic/muscarinic) on the post-synaptic cell
7. Acetylcholine action is broken down by acetylcholinesterase into choline & acetate & is reuptaken
What is the rate-limiting step for acetylcholine production
Step 1: Neuron takes up transmitter precursor (choline uptake by cholinergic neuron)
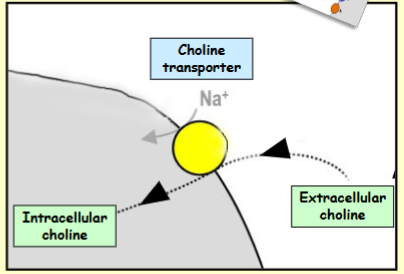
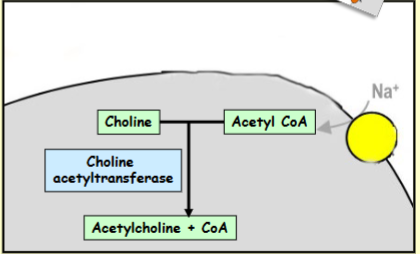
How is Acetylcholine synthesised
Choline is acetylated using acetyl coenzyme A as a source of acetyl groups
This is catalysed by the synthetic enzyme, choline acetyltransferase
Name the 3 subtypes of nicotinic receptors
Muscle-type nicotinic
Ganglion-type nicotinic
CNS-type nicotinic
Name the 5 subtypes of muscarinic receptors
Muscarinic M1
Muscarinic M2
Muscarinic M3
Muscarinic M4
Muscarinic M5