Alcohols
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what is an alcohol?
An organic compound that contains an -OH functional group
general formula for alcohols?
CnH2n+1OH
functional group in the alcohol homolohous series?
hydroxyl group, -OH
what is a primary alcohol?
An alcohol in which the carbon with the -OH group has only one R group (alkyl) attached to it
what is a secondary alcohol?
An alcohol in which the carbon with the -OH group has only two R groups attached to it.
what is a tertiary alcohol?
An alcohol in which the carbon with the -OH group has three R groups attached to it.
2 production processes of alcohols?
Alcohols are produced industrially by hydration of alkenes in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Ethanol is produced industrially by fermentation of glucose.
hydration and fermentation
(alchols can also be dehydrated to form alkenes)
process of hydration to form alcohols?
acid-catalysed hydration:
electrophilic addition of the proton (or acid) to the double bond to form a carbocation intermediate.
Addition of water in the second step results in formation of an oxonium ion, which, upon deprotonation, gives the alcohol
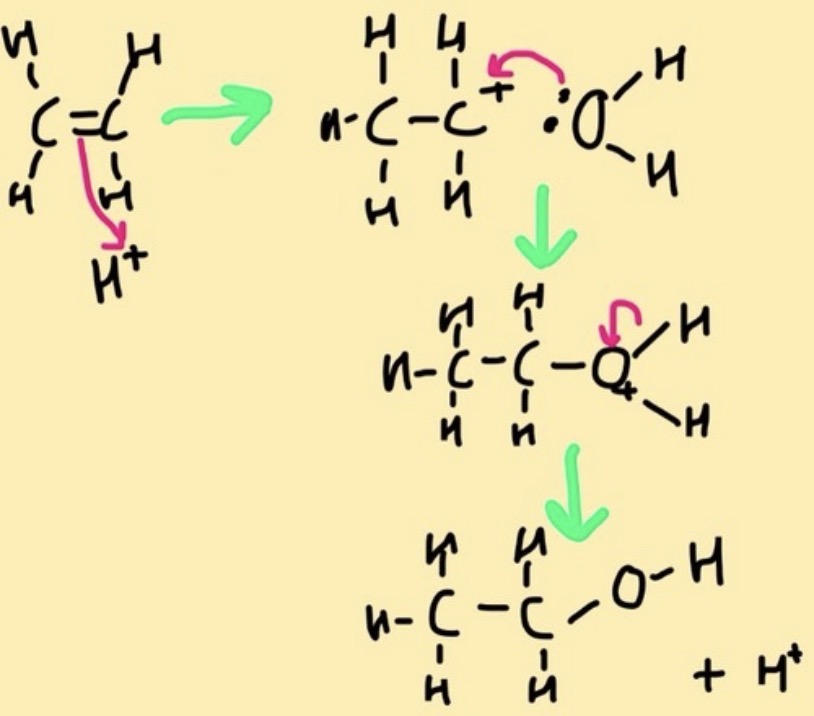
conditions required for hydration to form alcohols?
hydration of alkenes in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst, under aqueous conditions at 300 *c and high pressure
why is hydration favoured as an industrial process?
high percentage yield as ethanol is the only product, and water is easily accessible
process of fermentation to produce ethanol?
enzymes break down starch by amylotic enzymes from crops into glucose, yeast converts glucose/sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide
Ethanol produced industrially by fermentation is separated by fractional distillation and can then be used as a biofuel.
conditions required for fermentation?
absence of oxygen (yeast fermentation is anaerobic) (if 02 is present, ethanol is oxidised into ethanoic acid)
aqueous conditions (dissolved in water)
warm (37c)- optimum temp for enzymes - NOT HIGH
Yeast (enzyme=zymase)
waste product of fermentation of ethanol?
carbon dioxide
negatives of fermentation to produce alcohol?
starch has to be fermented in batches = a much slower process with a lower % yield
lower % yield as ethanol isnt the only product
Ethanol produced industrially by fermentation is separated by fractional distillation and can then be used as a biofuel.
ethanol is a biofuel, what is a biofuel?
a fuel derived/produced from renewable biological sources
> Ethanol produced industrially by fermentation is separated by fractional distillation and can then be used as a biofuel.
how is chemical energy of a biofuel calculated?
calorimetery
environmental (including ethical) issues linked to decision making about biofuel use?
Biofuels development should not be at the expense of people's essential human rights, including food, health, and water.
Biofuels should be environmentally sustainable.
Biofuels should be carbon neutral
Biofuels should adhere to fair trade principles.
is fermentation to produce ethanol carbon neutral?
yes, carbon given out when burned = carbon taken in my crops during the growing process
what does carbon neutral mean?
An activity that has no net annual carbon emissions to the atmosphere:
carbon given out when burned = carbon taken in my crops during the growing process
what is oxidation?
addition of oxygen, loss of electrons/hydrogen
how is oxidation, addition of oxygen, /oxidant represented in oxidation of alcohols?
[O]
what does oxidation of a primary alcohol produce?
aldehyde (partial oxidation)
e.g. ethanol + [O] -> ethanal + water
conditions required to oxidise primary alcohols to make aldehydes?
heated in the presence of acidified potassium dichromate and distilled to produce aldehydes
when heated under reflux, what do primary alcohols further oxidise to produce?
carboxylic acids (complete oxidation at this stage)
e.g. ethanal + [O] -> ethanoic acid + water
what do secondary alcohols produce when oxidised?
ketones cant be oxidised easily, so even prolonged refluxing wont produce anything more
e.g. alcohol + [O] -> ketone + hydrogen has (H2 g)
e.g. alcohol + [O] -> ketone + hydrogen has (H2 g)
conditions required for oxidation of secondary alcohols?
heated in the presence of acidified potassium dichromate
potassium dichromate is an oxidising agent, what is an oxidising agent?
is reduced as alcohols are oxidised
how to test for primary and secondary alcohols?
1 add alcohol to potassium dichromate (oxidisng agent)
2 if present, solution will change from orange to green
negatives with this test?
it doesnt tell you if its a primary or secondary alcohol, only that it is or isnt tertiary
what further test do we do to distunguish between primary and secondary alcohols?
tollens' reagent is reduce to a silver mirror when warmed with an aldehyde, but not with a ketone
Why don't tertiary alcohols undergo oxidation?
As it would require C-C bonds to break which is unfavourable and the alchol carbon doesnt have any removeable hydrogen atoms
why dont tertiary alcohols change potassium dichromate from orange to green?
they arent easily oxidised, K2Cr2O7 is an oxidising agent
what is the only process that will oxidise tertiary alcohols?
burning them
what is distillation of primary alcohols used to produce?
goal is to produce an aldehyde through the partial oxidation of primary alcohols
what is acid reflux used to produce?
goal is to produce a carboxylic acid from the full oxidation of primary alcohols
explain how the method used to oxidise a primary alcohol determines whether an aldehyde or carboxylic acid is obtained
1 gently heating ethanol with potassium dichromate and sulfuric acid in a test tube produces ethanal, however its trickly to control the heat and the aldehyde further oxidises to COOH
2 to get just the aldehyde: use distilling apparatus to prevent further oxidation, so the aldehyde (which has a lower b.p than the alcohol) is immediatley distilled off
3 to produce the carboxylic acid: alcohol has to be vigorously oxidised, it is mixed with excess oxidising agent and heated under acid reflux
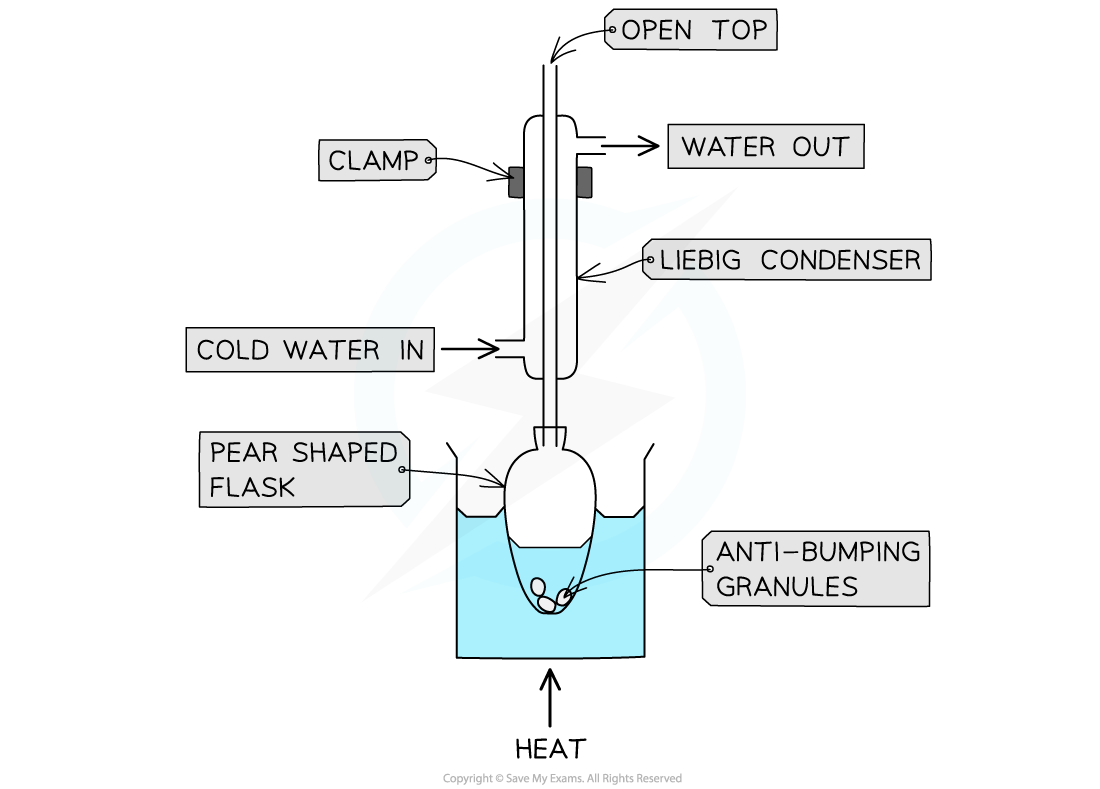
why do we heat under reflux?
You can increase the temperature of an organic reaction without losing volatile solvents, reactants, or products.
Any vaporised compounds cool, condense and drip back into the reaction mixture, so the aldehyde stays in the reaction mixture and is oxidised to carboxlylic acid
what is acid reflux used for generally?
used to heat a solution at a constant temperature without losing any liquid
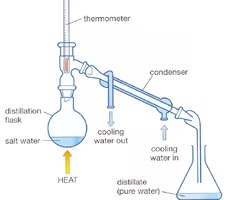
distillation process?
the process of vaporizing a liquid, condensing the vapor, and collecting the condensate.
heating under reflux process?
1 heated, vapourised, condensed by cold water -> liquid and goes back into the flask - no waste
what is formed from dehydration of alcohols?
alkenes and water
Alkenes can be formed from alcohols by acid-catalysed elimination reactions.
is dehydration of alcohols elimination or additon?
elimination
conditions required for dehydration of alcohols?
excess of hot sulfuric acid is added and aluminium oxide is used as a catalyst in order to remove water
elimination reaction mechanism for dehydration of alcohols?
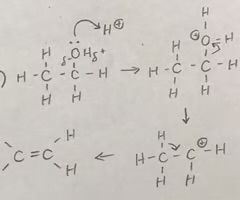
how are H+ ions seen to act as a catalyst in this reaction?
H+ ions are reformed in the reaction, showing how they act as a catalyst
environmental benefit from dehydration of alcohols to produce alkenes?
Alkenes produced by this method can be used to produce addition polymers without using monomers derived from crude oil.
how do fermentation and dehydration of alcohols work together?
fermentation produces the primary alcohol, which is then dehydrated to produce an alkene in the production of addition polymers