Meiosis Study Guide with Flashcards on Genetic Variation and Disorders
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the main function of meiosis?
creation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) which gives rise to four haploid (23) daughter cells
Where does meiosis occur?
sex cells- ovaries, testes
Why does meiosis reduce the number of chromosomes from 46 to 23?
It allows to restore the original number of chromosomes in a zygote when fertilization (egg and sperm fuses together) happens.
How does meiosis create genetic variation?
due to recombination and independent assortment in meiosis, each gamete contains a different set of DNA
Are the four daughter cells produced by meiosis identical or unique?
unique (different)
What happens during interphase in meiosis?
cell growth (G1), DNA duplicates (S), cell prepares for division (G2)
What happens during prophase I in meiosis?
a. homologous chromosomes pair up, forming a tetrad, crossing over (recombination) can occur.
b. nuclear envelope breaks apart
c. chromosomes condense

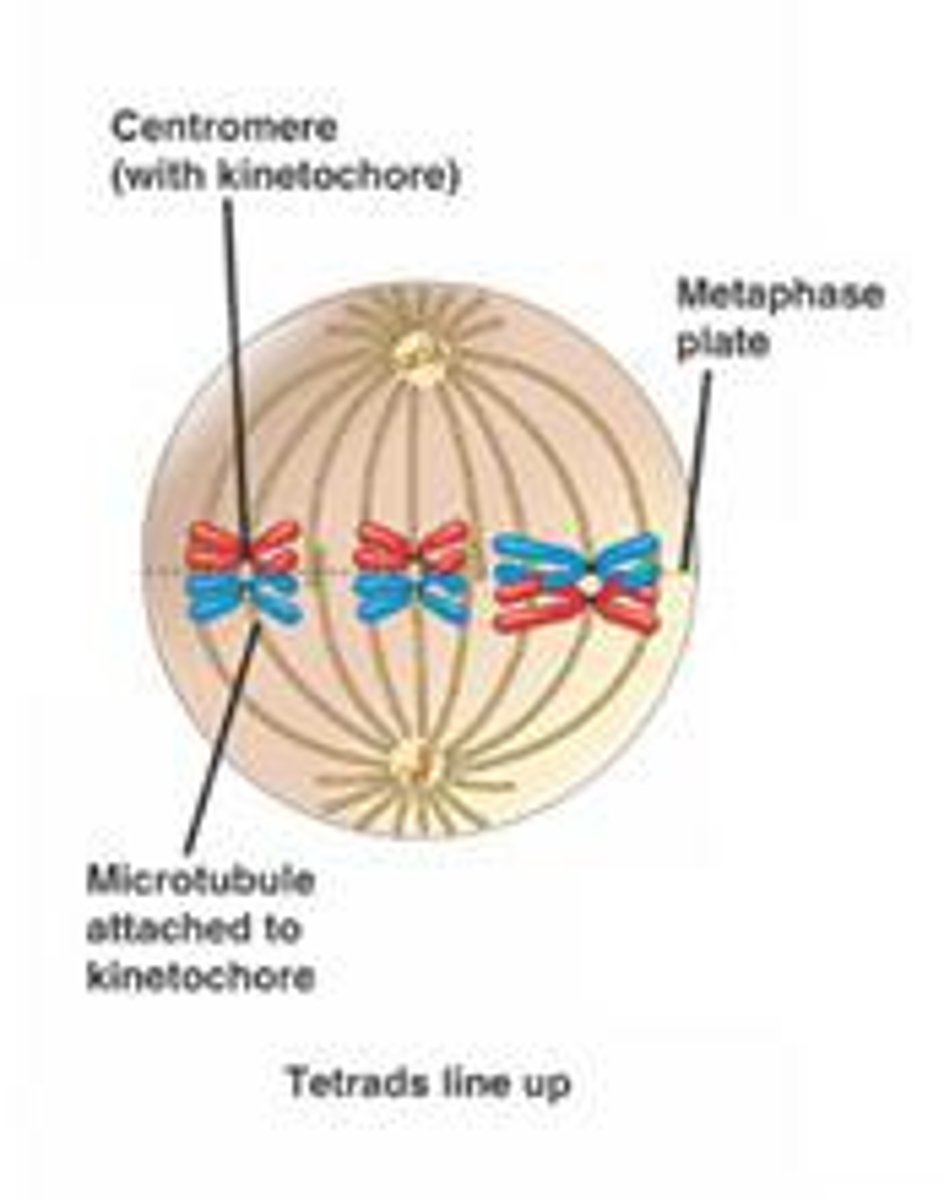
What happens during metaphase I?
a. homologous pairs line up in the middle of the cell
b. spindle fibers attach to centromeres
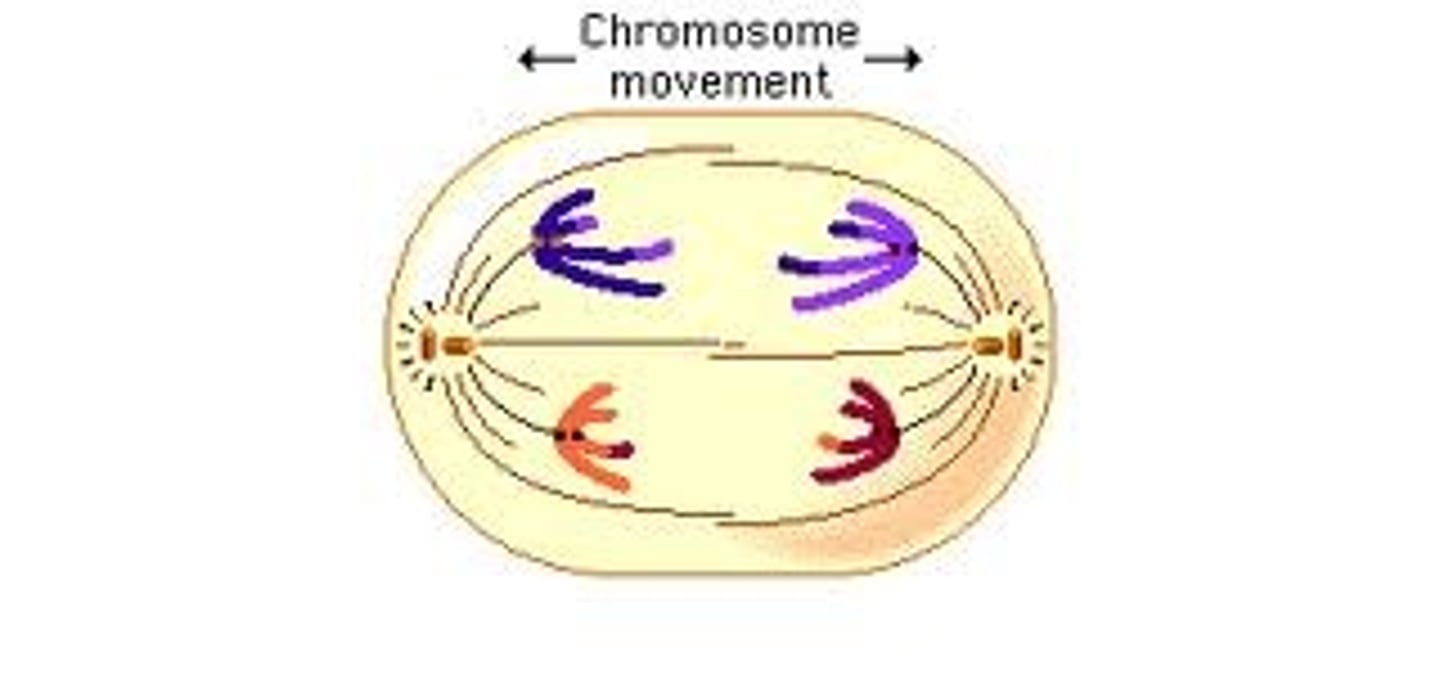
What happens during anaphase I?
spindle fibers pull each homologous chromosome pair toward opposite ends of the cell
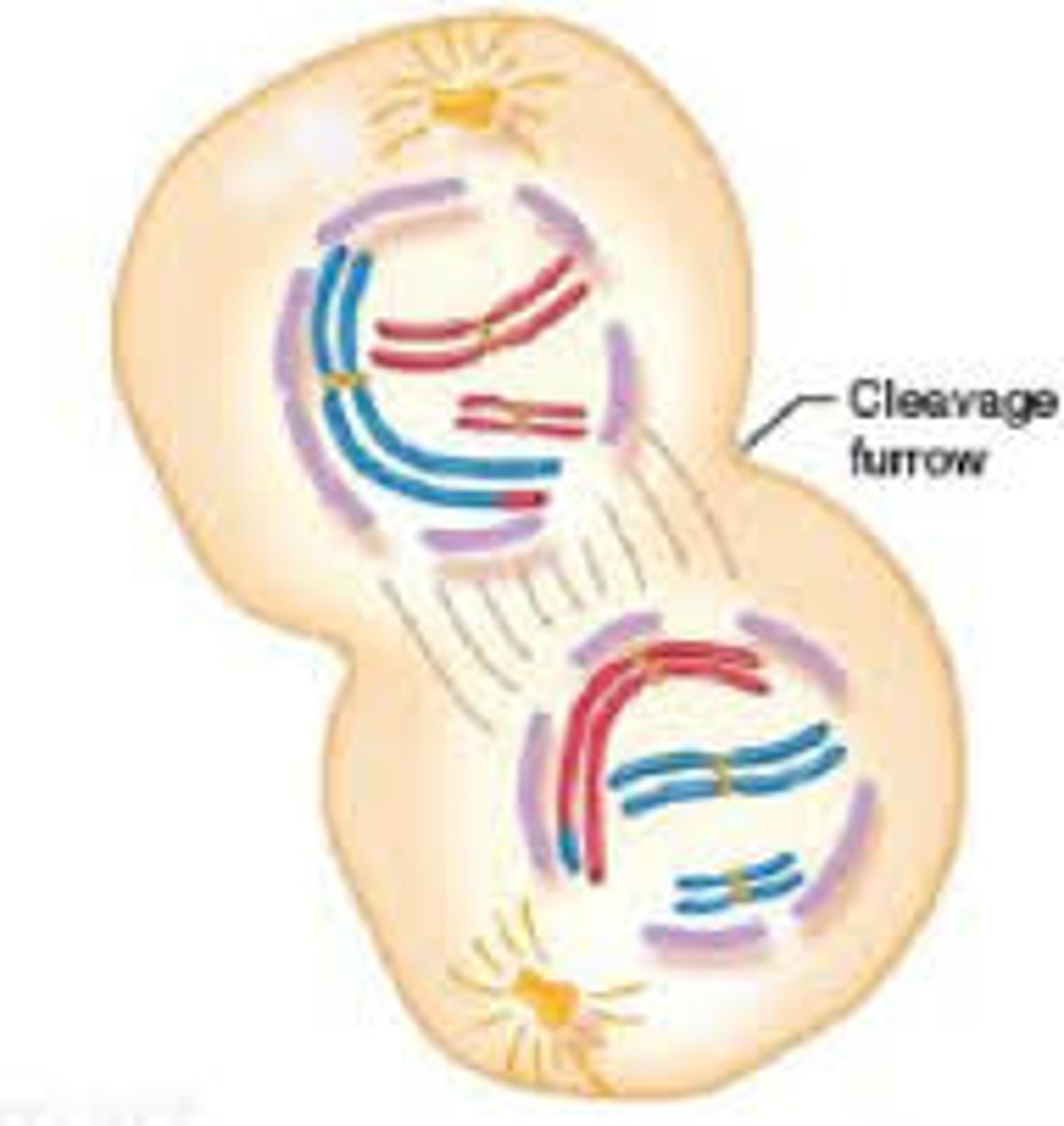
What happens during telophase I?
Cleavage furrow forms.
Nuclear membranes form.
The cell separates into two cells.
What happens during prophase II?
1. Chromosomes condense
2. spindles form in each new cell

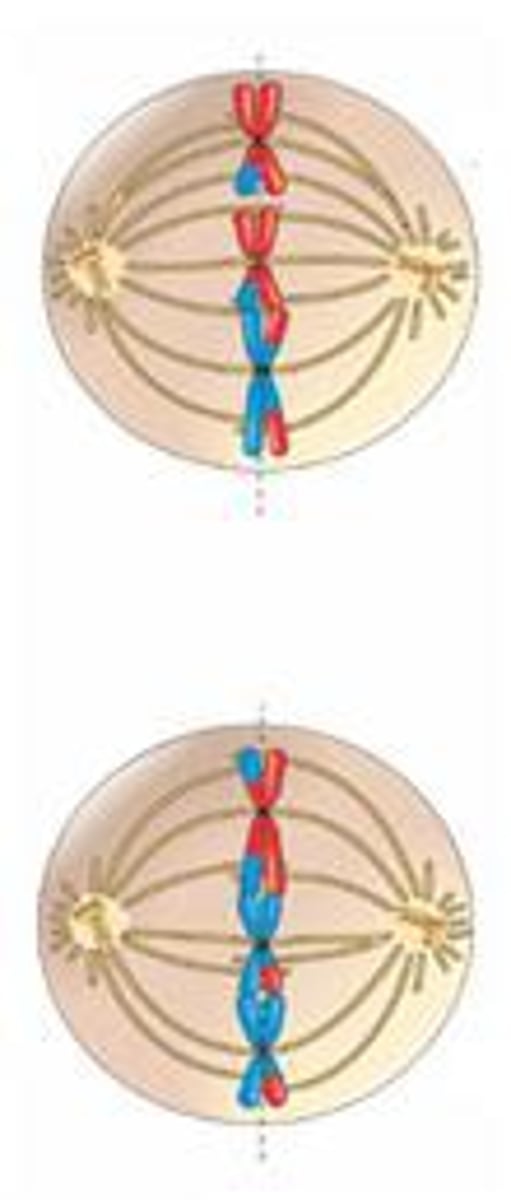
What happens during metaphase II?
1. The chromosomes (sister chromatids) line up in the middle of the cell
2. spindle fibers attach to centromeres
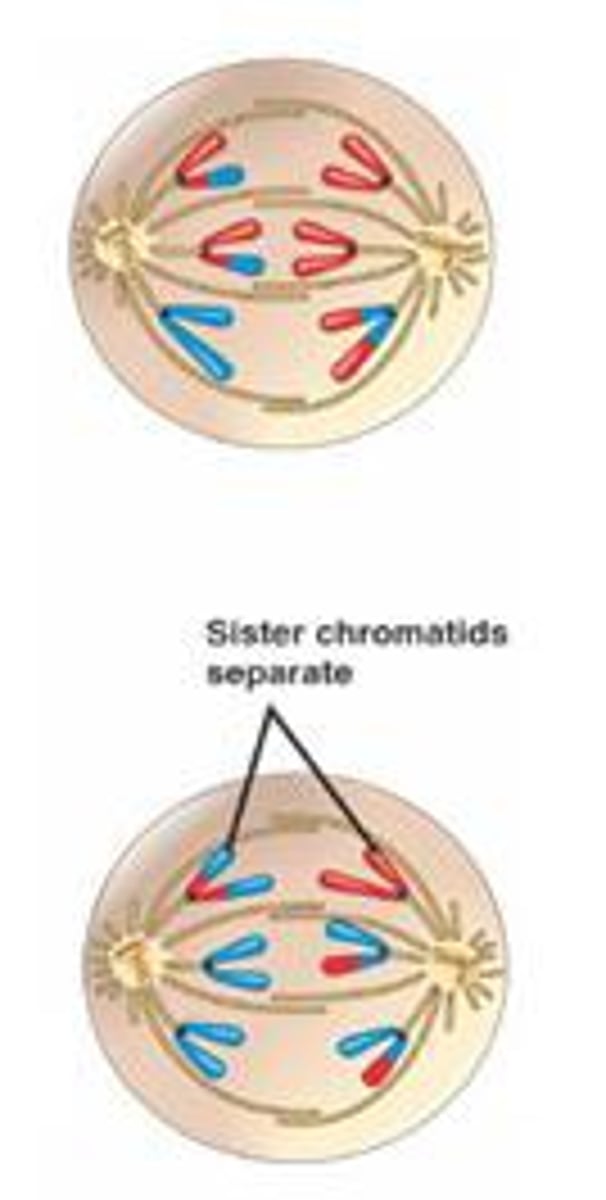
What happens during anaphase II?
sister chromatids are pulled apart
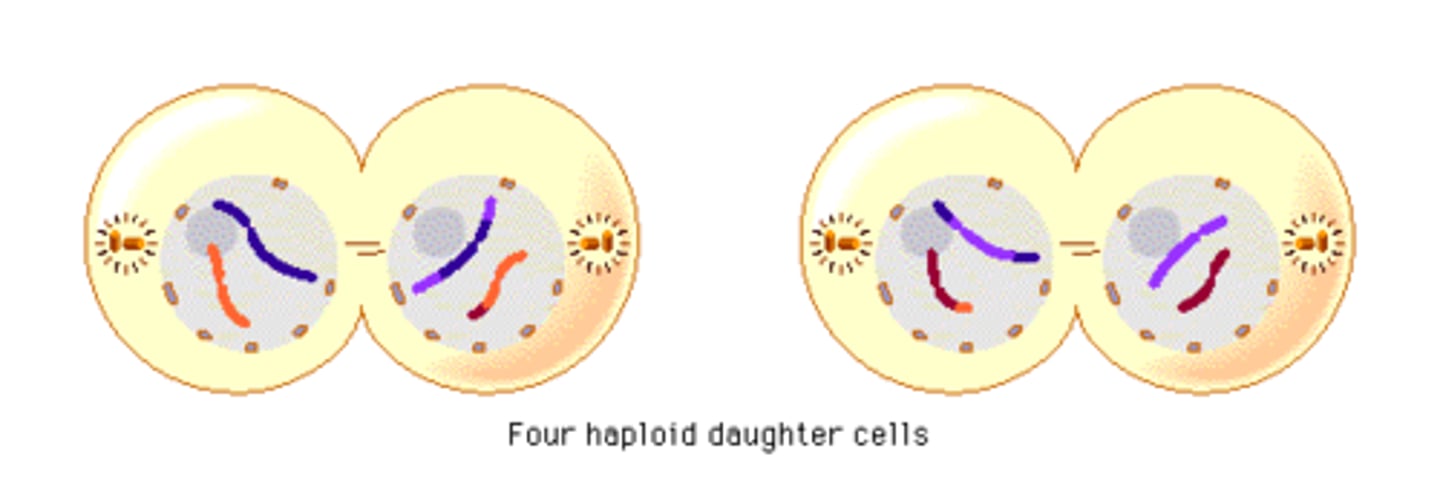
What happens during telophase II?
1. cleavage furrow forms
2. chromosomes reach the poles
3. nuclear membrane and nuclei reform
4. four daughter cells are produced
What is crossing over (recombination)?
the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring.
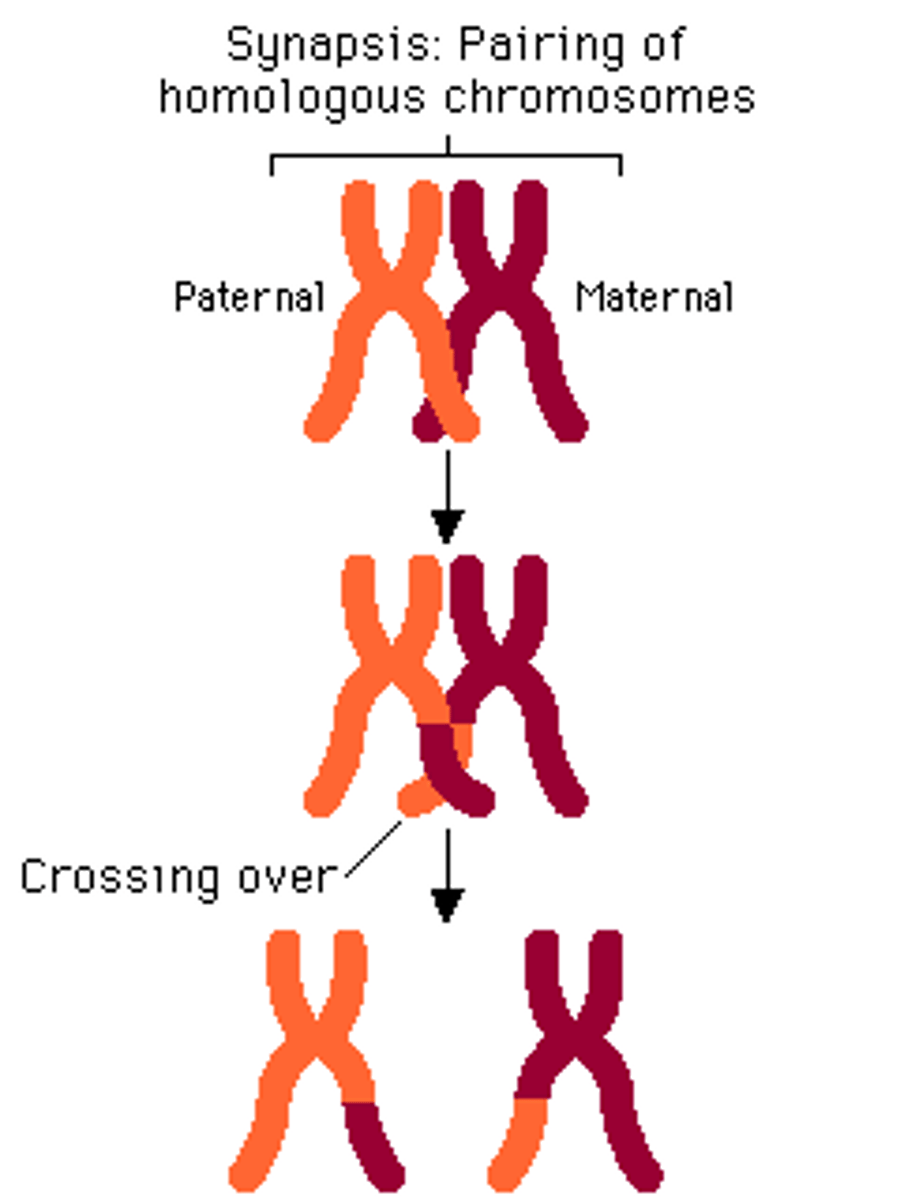
When does crossing over occur?
prophase I of meiosis
What happens when nondisjunction happens during meiosis?
Each cells would get an extra chromosome which would lead to a lot of genetic disorders
In which stage in meiosis does nondisjunction occur?
Anaphase I (worse)
Anaphase II
What genetic disorder causes down syndrome?
trisomy 21 (due to nondisjunction)
Why does miscarriage occur?
a miscarriage happens when the fetus has an abnormal number of chromosomes which causes genetic abnormalities.