Hess's Law
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
What does Hess’s law state?
The total enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the route taken from the reactants to the products.
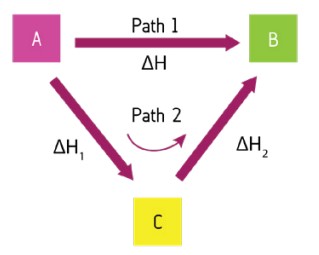
Explain Hess’ law.
Path 1 shows a direct route for converting reactants to products and Path 2 shows an indirect route via the formation of an intermediate, C.
Hess’s law states that the total enthalpy is independent of the route, so Path 1 must equal Path 2: ΔH = ΔH1 + ΔH2
Can you use to enthalpy changes of combustion and formation to calculate the overall enthalpy change of a reaction?
Yes.
The enthalpy changes of combustion and formation can be used to calculate the overall enthalpy change of a reaction.
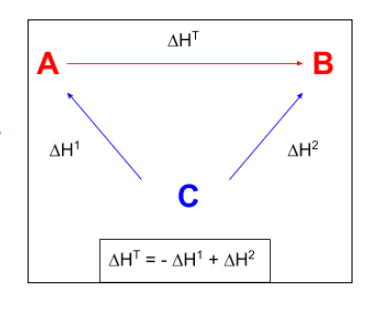
How can the overall enthalpy change of a reaction be calculated using enthalpies of formation?
When setting up the triangular diagram, the arrows UP point from C as both A and B are formed from the elements C.
The left hand arrow goes in the opposite direction to the reaction so ΔH1 is subtracted.
ΔH = -ΔH1 + ΔH2
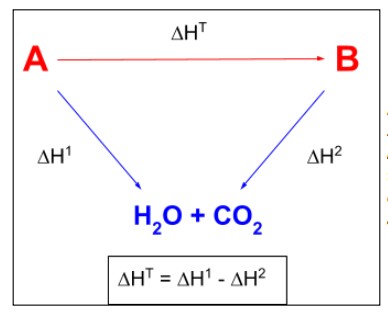
How can the overall enthalpy change of a reaction be calculated using enthalpies of combustion?
When setting up the triangular diagram, the arrows point DOWN to the central products (which is always carbon dioxide and water).
The right hand arrow goes in the opposite direction to the reaction so ΔH2 is subtracted.
ΔH = ΔH1 - ΔH2