Group 2, Alkaline Earth Metals
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
what ions do group 2 elements form
+2 ions
trend in atomic radius down group 2
increases, more shells
trend in 1st ionisation energy down group 2
decreases
why does 1st ionisation energy decrease down the group
extra shells added as we go down
= more shielding = weaker attraction between nucleus and outer electrons
atomic radius increases = weaker attraction
easier to remove the outer electron so less energy is needed
overrides increase nuclear charge
trend in melting point down group 2
decreases
describe the structure of group 2 elements
metallic structures, where you have positive metal ions attracted to a sea of delocalised electrons
why does melting point decrease down group 2
size of metal ions increases, but number of delocalised electrons stays the same, 2+ charge stays the same too
larger ions = larger distance between positive nuclei and delocalised electrons = weaker attractive force
easier to break bonds
exception to the melting point trend in group 2?
magnesium, it decreases due to a structural difference compared to other group 2 metals
what do group 2 elements react with water to form
bases (metal hydroxides)

trend in reactivity down group 2 with water
reactivity increases down the group

why does reactivity increase with water down group 2
atom gets larger and electron is further from nucleus
easier to remove and hence more reactive
more shielding
exception in group 2 reactions with water
magnesium, it reacts slowly with cold water
what does magnesium react more vigorously with, what does this produce
steam, producing magnesium oxide instead of a hydroxide
trend in solubility of group 2 metal surfaces down group 2
decreases down the group
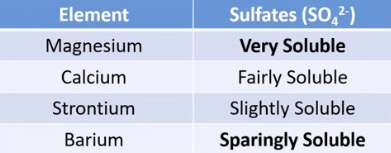
as an anion has a double charge they become ? as we go down the group
less soluble
trend in solubility of group 2 hydroxides down group 2
increases going down group 2

if the anion has a single charge, what happens to solubility of hydroxides
more soluble
reagent used to test for sulfates
barium chloride
how to test for sulfates
add HCL to remove carbonates
add barium chloride
observation for a positive sulfates test
white precipitate, observed because barium sulfate formed is insoluble

why is it important to add hydrochloric acid before a sulfate test
to remove any carbonates which could precipitate out after adding barium chloride
how can group 2 elements be used
to neutralise acids:
acidic soil neutralised
antacids
also barium meal
ionic equation for neutralisation
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) → H2O (l)
what can be used to neutralise acidic soils
calcium hydroxide, slaked lime
Ca(OH)2
what can be used as antacids
magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2
neutralises excess stomach acid
what is barium meal and what is it used for
barium sulfate is used to help identify problems with the digestive tracts,
patient drinks barium sulfate then goes through an x-ray
why do we use barium sulfate as a barium meal
dense, so can be picked up on an x-ray
coats lining of soft tissue
x-rays are absorbed by barium sulfate so soft tissues will show up on an x-ray
insoluble so will not be absorbed into the blood
potential risk of barium sulfate
barium sulfate is toxic,
but it is insoluble so can’t be absorbed into the blood
what group 2 element is used to extract titanium from its ore
magnesium
step 1 of extraction of titanium

why do we heat titanium ore with carbon AND chlorine
need to heat with chlorine so carbon doesn’t react with titanium, which would form titanium carbide which is brittle
step 2 of extraction of titanium
titanium (IV) chloride produced in step 1 is passed through a fractional distillation column to increase the purity
step 3 of extraction of titanium
purified TiCl4 is reduced using magnesium in 1000°c furnace
reaction between titanium (IV) chloride with magnesium
titanium is reduced
magnesium is the reducing agent

uses of titanium
it is light weight but strong, and is commonly used in planes
what is used to remove sulfur dioxide emissions
calcium carbonate and oxide
importance of removing sulfur dioxide, how is it produced
burning fossil fuels for electricity produces the POLLUTANT. sulfur dioxide
what process is used to neutralise sulfur dioxide in flue gases
wet scrubbing
describe wet scrubbing process
involves dissolving calcium carbonate or oxide instead water and spraying it on acidic sulfur dioxide gas,
produces calcium sulfate which can be used for the production of plasterboard
use of calcium sulfite produced in wet scrubbing
production of plasterboard
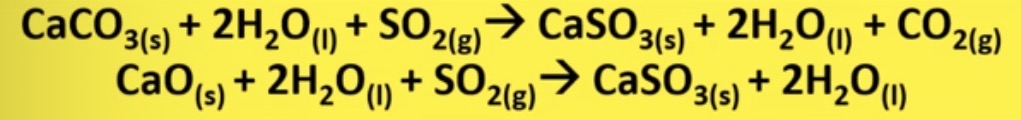
wet scrubbing equations
CaCO3 (s) + 2H2O (l) + SO2 (g) → ?