2.10 - Opioids
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
MOR: Agonist, Antagonist, Endogenous Opiod Peptides, Pharmacological Effects:
Agonist: Morphine
Antagonist: Naloxone
EOPs: Beta-Endorphins, Endomorphin 1&2
PEs: Analgesia, Constipation, Reward, Respiratory Depression
DOR: Agonist, Antagonist, Endogenous Opioid Peptides, Pharmacological Effects:
Agonist: Morphine
Angtagonist: Naloxone
EOPs: Met-Enkephalin, Leu-Enkephalin
PEs: Analgesia, Affective Disorders, Seizures
KOR: Agonist, Antagonist, Endogenous Opioid Peptides, Pharmacological Effects:
Agonist: Morphine
Antagonist: Naloxone
EOPs: Dynorphins
PEs: Analgesia, Diuresis, Sedation, Dysphoria, Psychotomimetic Effects
Structure of all opioid receptors
7 transmembrane spanning GPCRs
Amino acid sequences between opioid receptors are 65% identical, what are the highest and lowest sequence similarities between them?
Highest:
-7TM spanning regions
-intracellular loops responsible for G-protein coupling
Lowest:
-Amino and carboxyl terminus
-2nd and 3rd extracellular loops responsible for ligand affinity
Opioid agonists bind in a pocket defined by the __________; antagonists further depend on ______ to bind respective receptors
Opioid agonists bind in a pocket defined by the extracellular loops; antagonists further depend on extracellular tail to bind respective receptors
Which G-proteins are associated with opioid receptors?
Gi and Go
All signaling from opioid receptors is:
Inhibitory, neurons hyperpolarized
Opioid receptors are activated by______ which then _____ adenyl cyclase activity
Gi, inhibits
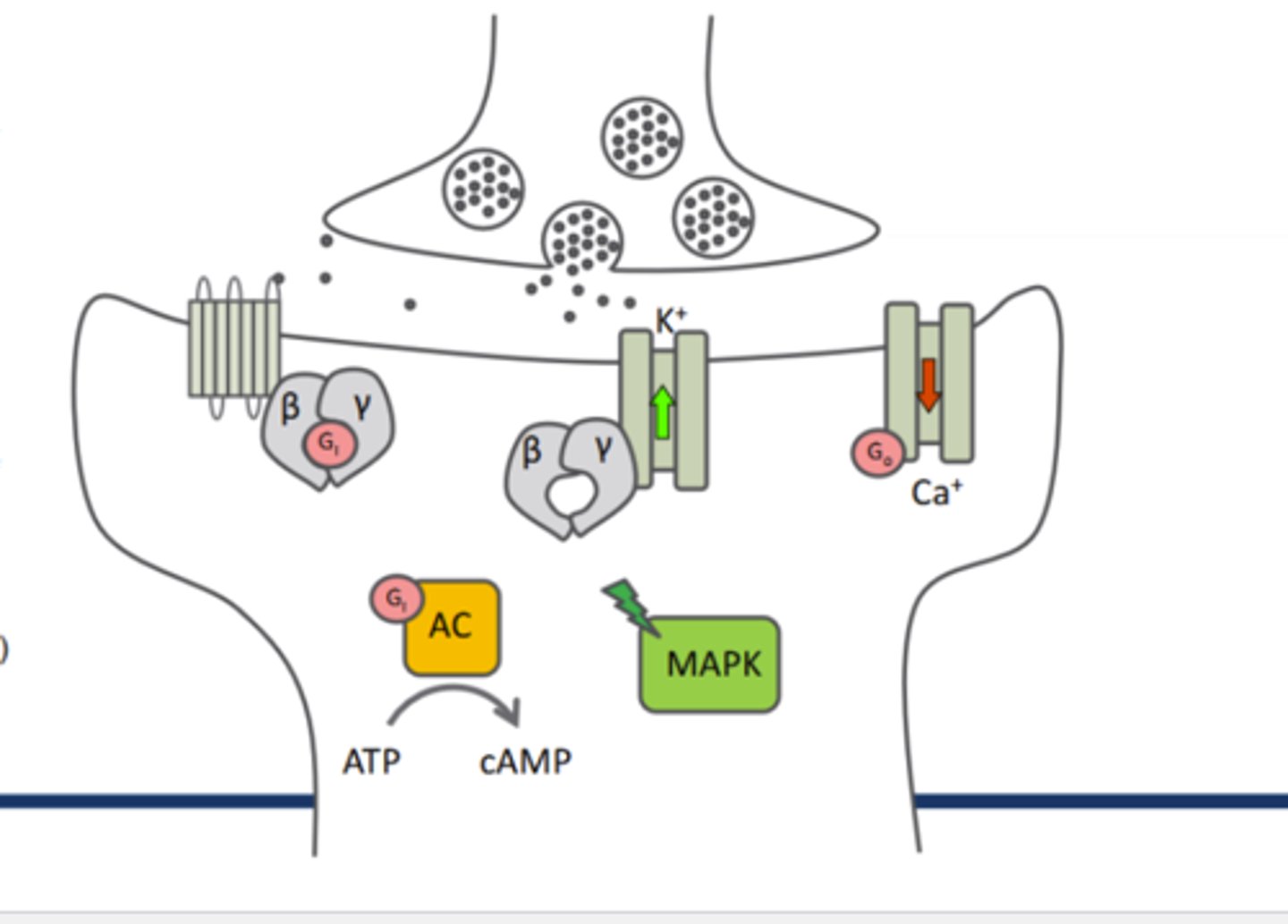
beta-gamma complex and Go on opioid receptor ion channels:
_____K+ efflux and ____Ca2+ channels
increases K+ efflux, Go inhibits Ca2+ channels
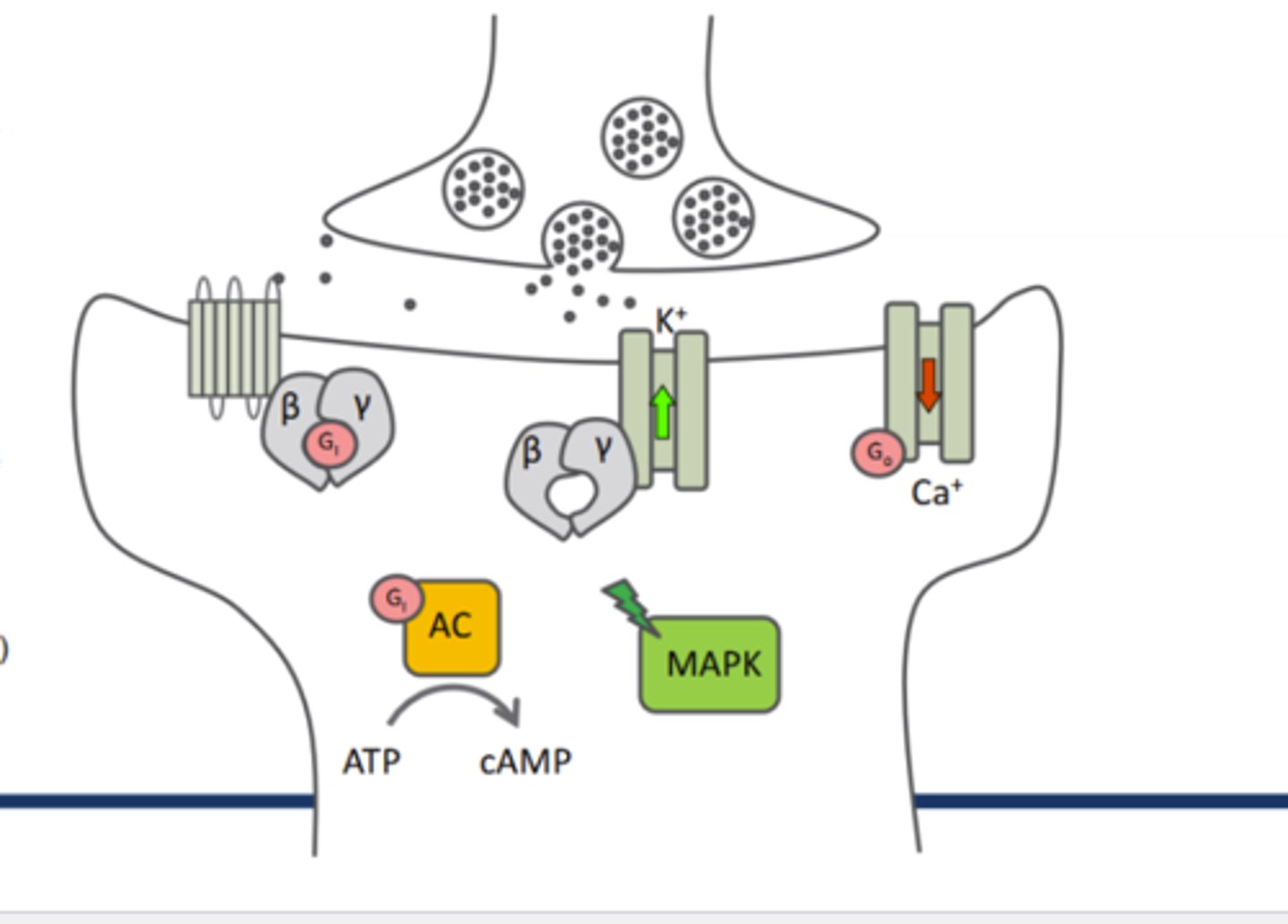
Activation of opioid receptors results in the activation of ____ which then inhibits_____
MAP Kinase cascade, inhibits other cascades (PKC,PLC,IP3 cascade wtc)
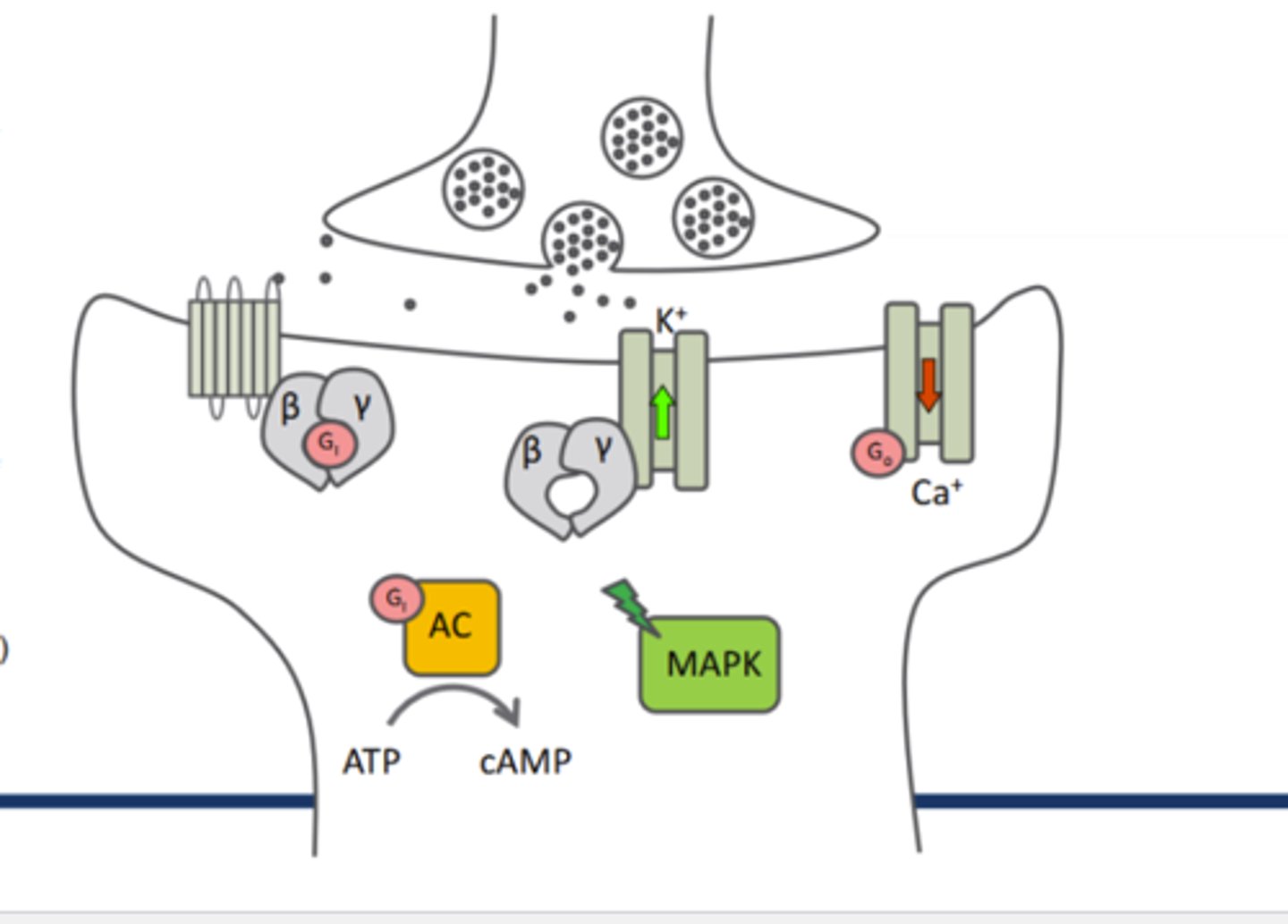
Endorphin synthesis
1)cell specific DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase enzymes
2)mRNA exists nucleus and is translated into precurser proteins in ER
3)Precursor polypeptides are then transported through ER and become packaged in vesicles which are collected at the synaptic terminal
4)Precursor peptides are longer than endorphin peptides so specific peptides are derived from enzymatic cleavage of each distinct precursor protein by cell-specific enzymes
5)Endorphins are released into the synapse upon AP

Once released into the synaptic cleft, what happens to endorphins
endorphins cannot re-enter the cell THERE ARE NO OPIOID TRANSPORTERS; endorphins do NOT undergo reuptake
Endorphin signaling is rapidly terminated by metabolism
Metabolism of Endorphins
Extracellular peptidases rapidly degrade opioid peptides
Enkephalins are the product of what peptide which is the product of what gene?
Enkephalins are the product of the precursor peptide proenkephalin which is the product of the proenkephalin (PENK) gene
Two types of enkephalin peptides cleabed from proenkephalin:
Met-Enkephalin
Leu-Enkephalin
(cleaved at a ratio of 5Met:1Leu-Enkephalin
Enkephalins bind to which opioid receptors?
Preferentially bind to DOR, but also bind to MOR as well (and KOR less so)
Enkephalins are metabolized by:
enkephalinases: aminopeptidase N (APN) and neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (NEP)
Enkephalins are primarily found in:
shorter interneurons pervasively throughout the CNS and PNS
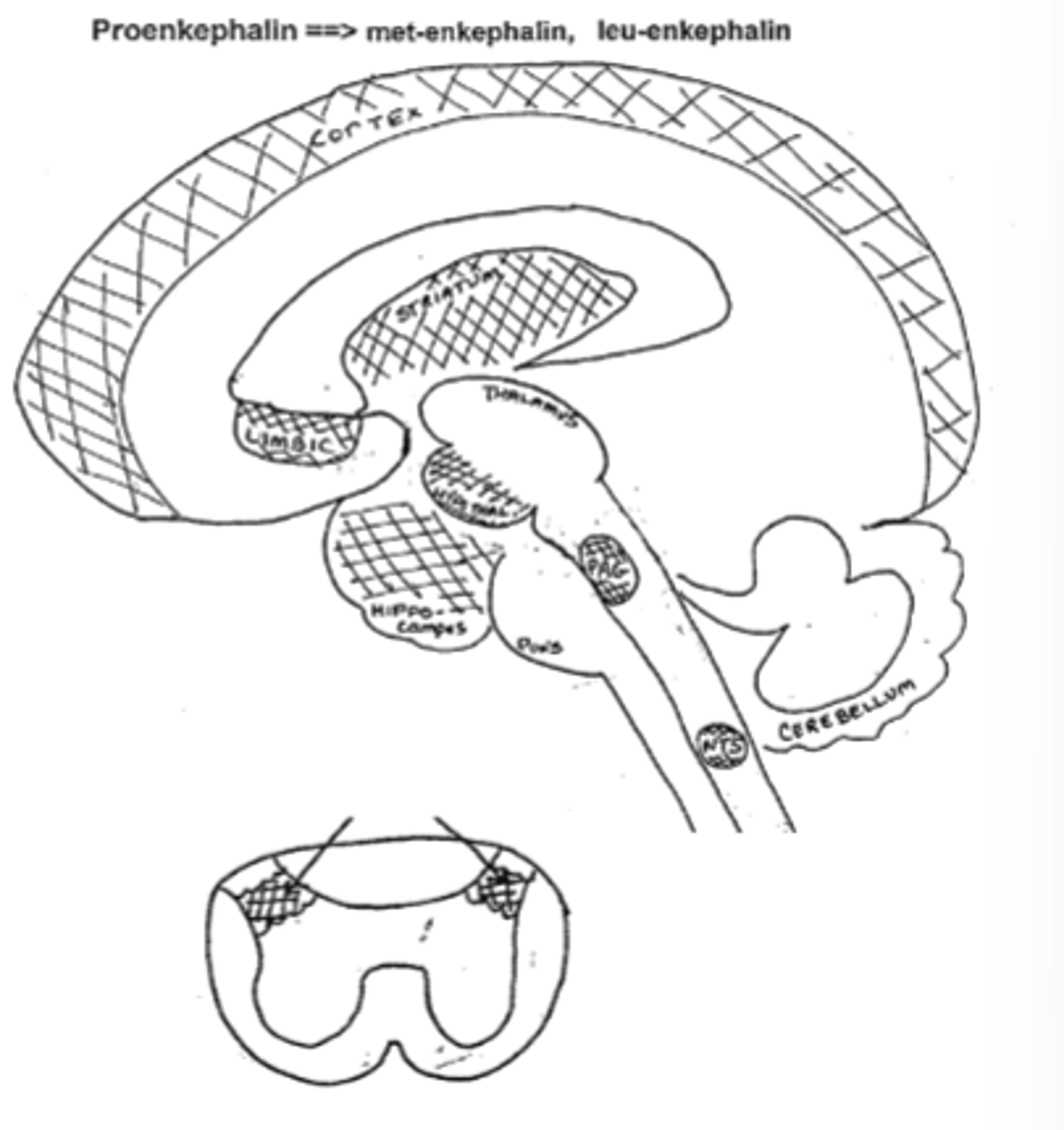
Enkephalins are found in areas of the CNS related to:
-pain perception
-modulation of affective disorders
-autonomic nervous functions
-neuroendocrinological functions
Name the specific regions of the brain where Met and Leu-Enkephalin are found and what the region is associated with
-Hypothalamus (endocrine system)
-Periaquetal grey, substantia gelatinosa (pain)
-Cortex, hippocampus, limbicc system (mood/emotions)
-Nucleus tractus solitarius (autonomic reflexes)
-Striatum (motor rigidity)
-Nucleus Accumbens (euphoria, addiction)
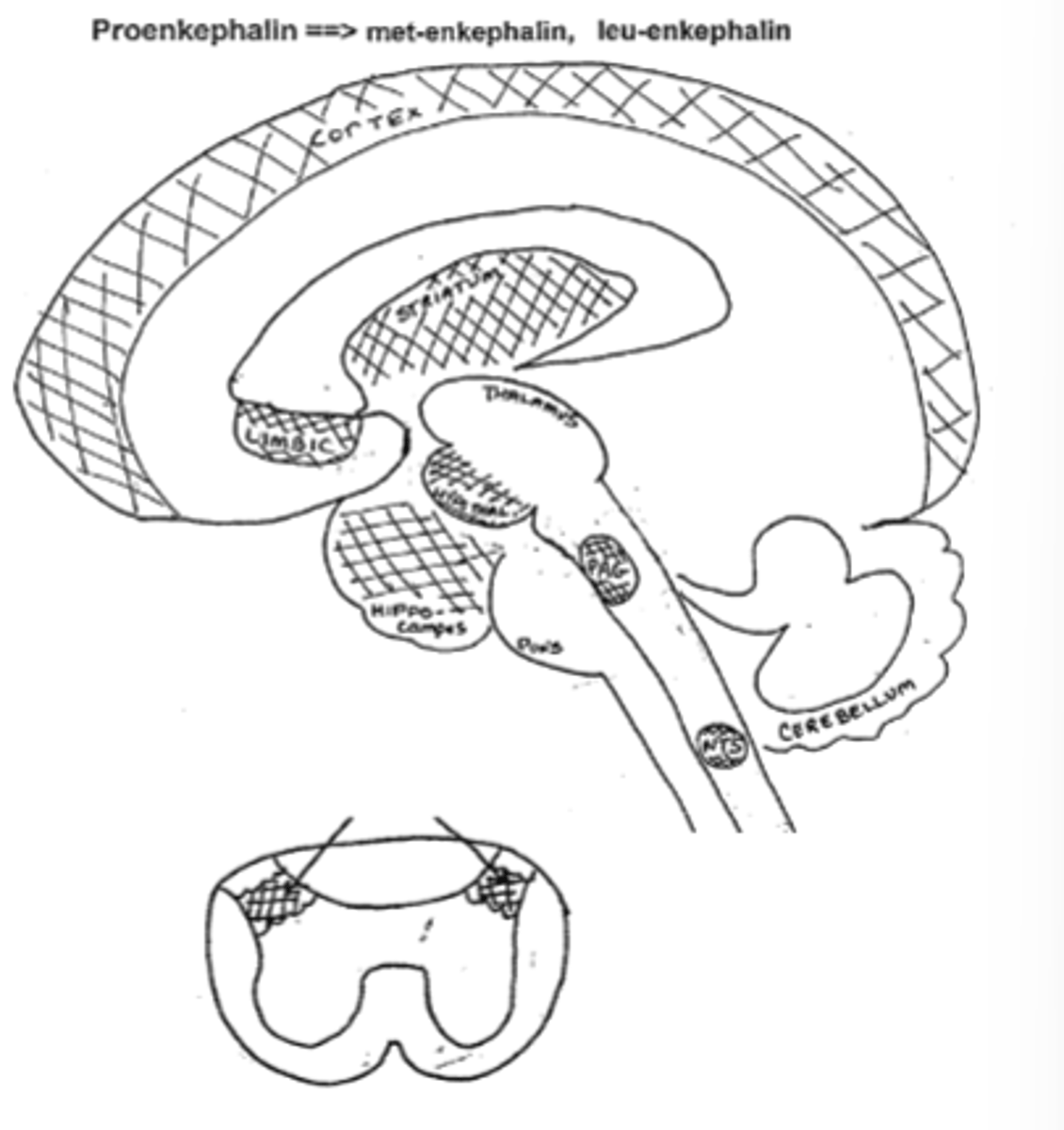
What effect would an enkephalinase inhibitor have at the synapse?
It would prolong enkephalin signaling by preventing its degradation.
What is Beta-Endorphin?
a 31 amino acid peptide
What gene is beta-endorphin derived from?
pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)
***Although included in POMC, met-Enk is NOT a primary product
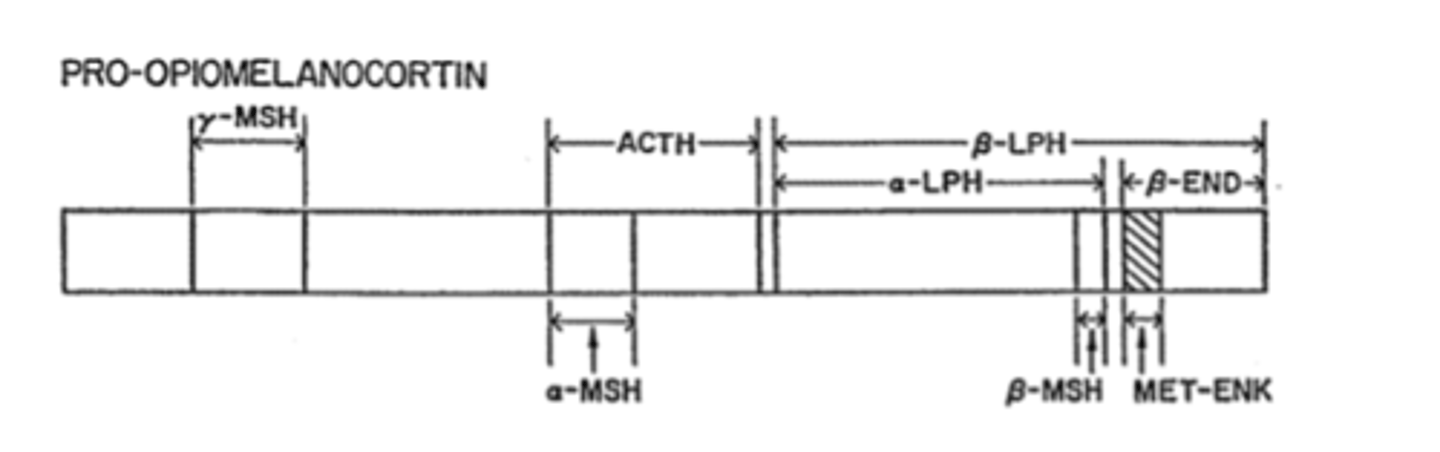
What other, non-opioid precurser is derived from POMC other than Beta-Endorphin?
ACTH
Which endorphin is a Potent analgesic and important in homeostasis and alleviating stress; produces "runner's high"
Beta-Endorphin
Metabolism of Beta-Endorphin
Metabolism by hydrolysis is carried out by a wide variety of enzymes.
Betap-Endorphin is primarily found in
longer projection neurons
High POMC levels in:
-arcuate nucleus
-projecting to limbic, brainstem, and spinal cord
Neurons carrying Beta-Endorphin project from the arcuate Nucleus to which brain regions, and what is each region associated with
-Hypothalamus (stress)
-Periaquetal grey, raphe nucleus (pain)
-Nucleus tractus solitarius (autonomic reflexes)
-Striatum (motor rigidity)
-Nucleus accumbens (euphoria, addiction)
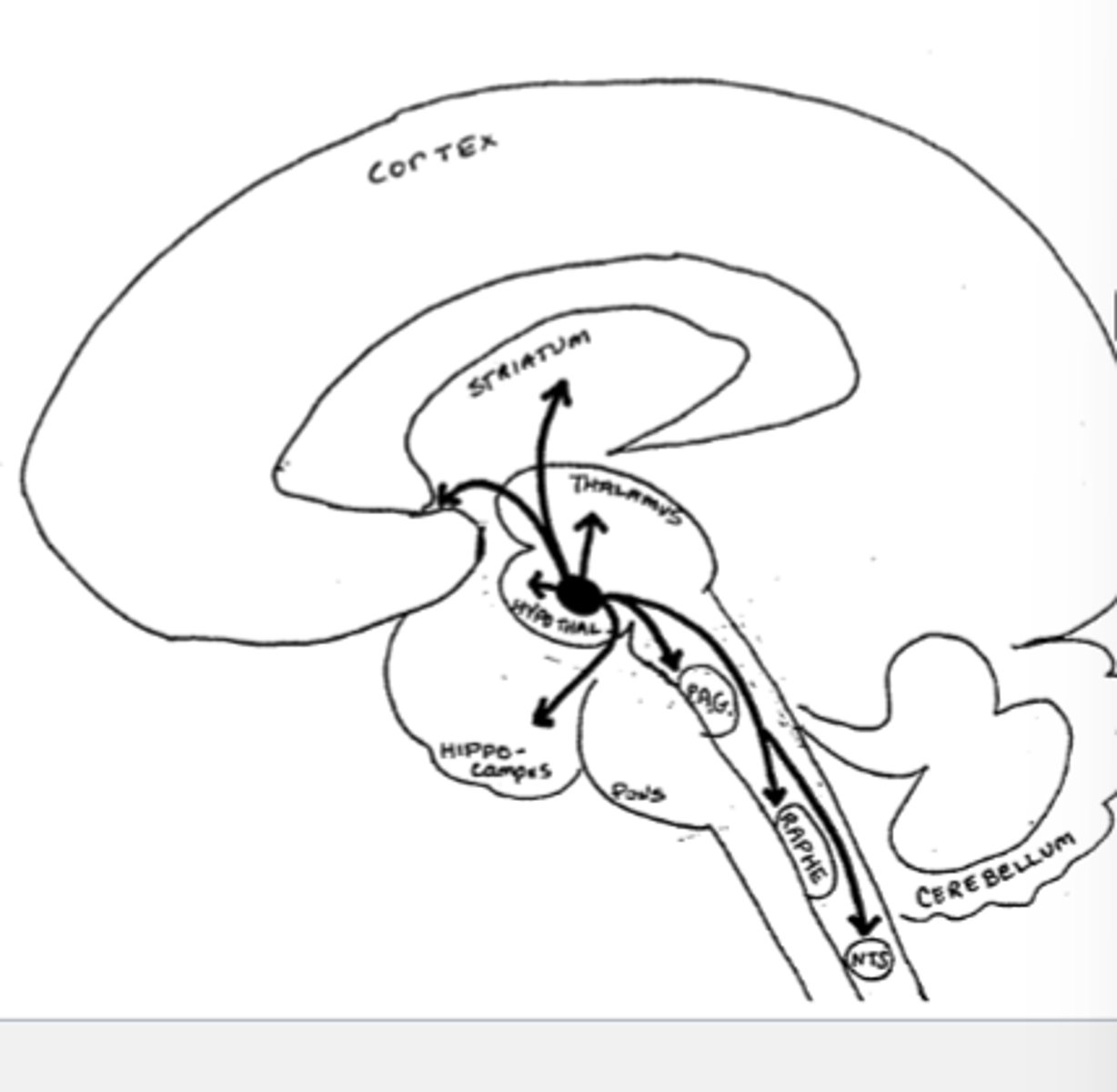
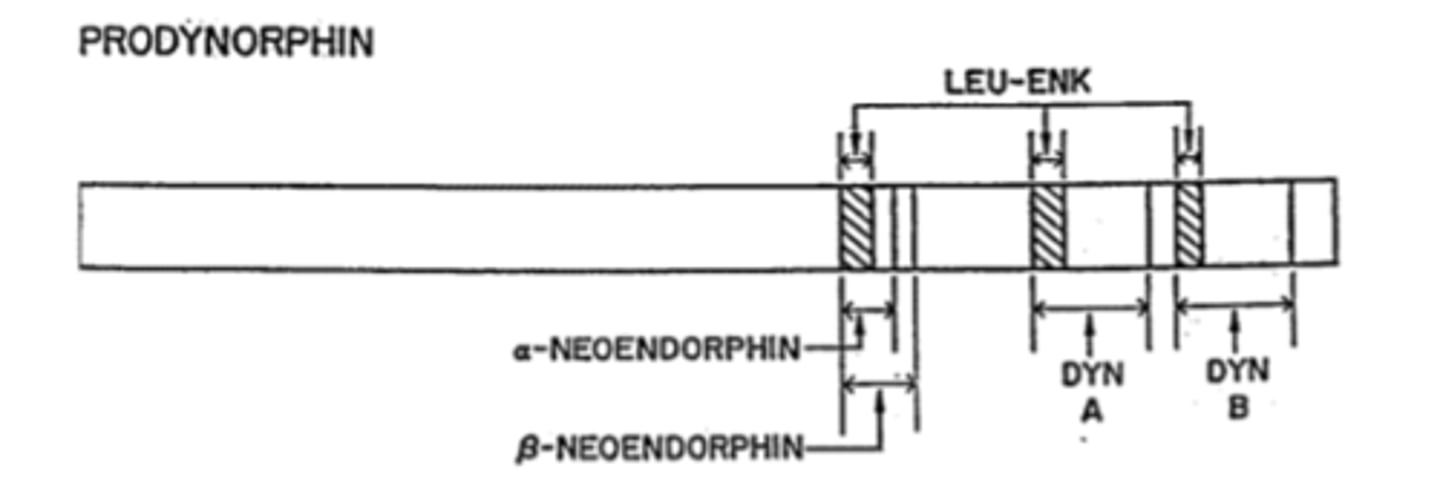
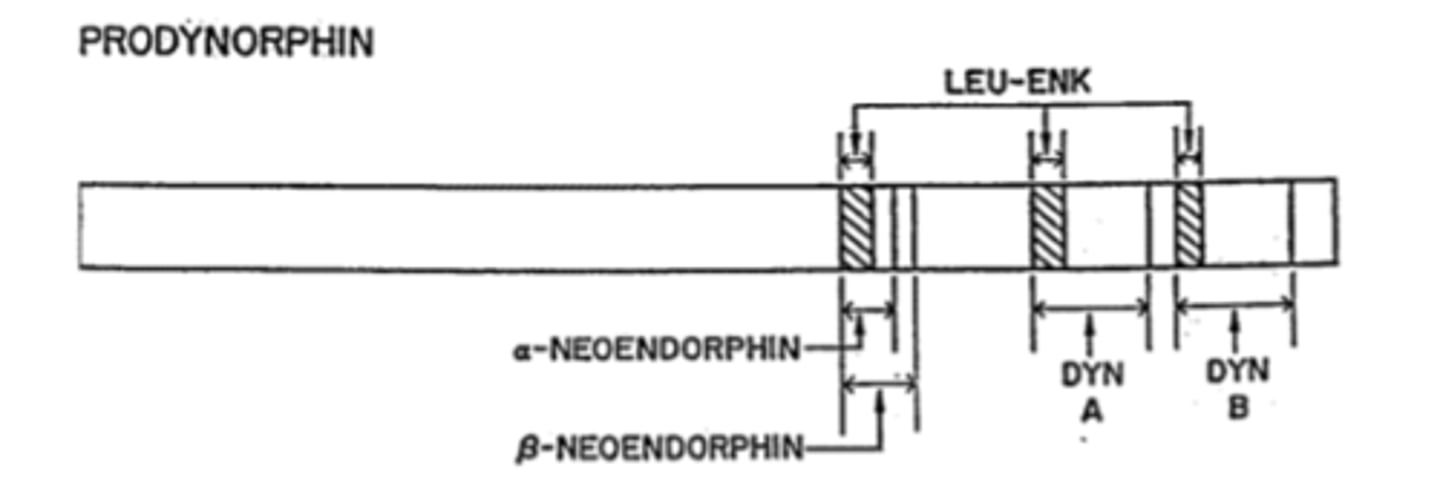
Dynorphins are a family of peptides from what gene
Prodynorphin gene (PDYN)
Big Dynorphin is an ___ amino acid peptide
32
Synthesis of Dynorphins
Proprotein convertase 2 cuts Dyn A (1-17)+DynB
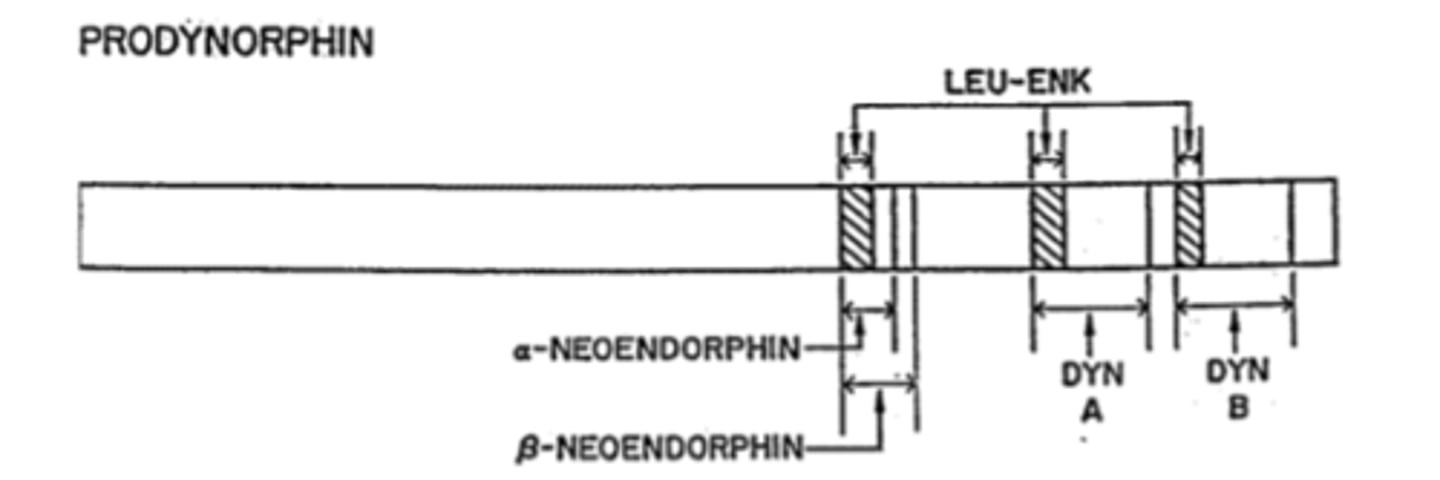
Other weak opioids in addition to Dynorphins that are included in PDYN gene
neoendorphins
Metabolism of Dynorphins
Metabolism by a number of enzymes on the C-terminal end stqpwise reduce DynA length
-Metabolites retain significant opioid activity: Dyn A(1-17)->DynA(1-13)->DynA(1-8)->DynA(1-7)
DynA peptides bind to which opioid receptors
Preferentially bind to KOR (MOR and DOR less so)
Which endorphin is describes as a Good analgesic (see first lecture), but associated with mood disorders and dysphoria
Dynorphins
Dynorphins are Found widely throughout CNS; frequently found in:
interneurons with the enkephalins.
These two endorphins are Found together in areas of the CNS related to the perception of pain, modulation of affective disorders, locomotion, reward and neuroendocrinological functions:
Enkephalins and Dynorphins
Specific brain regions where Dynorphins are found and there actions
-Hypothalamus (endocrine response)
-Striatum, substantia negra (motor rigidity)
-Nucleus accumbens (dysphoria-KOR agonsists NOT abused)
-Limbic System (mood and emotions)
-Ventral SPinal cord (pain)

Two types of Endomorphins
Endomorphin-1
Endomorphin-2
Shortest of endorphins; metabolized into inactive forms by cleaving off Tyr residue
Endomorphins
Precursor for Endomorphins
Precursor not yet known! Discovered by working backwards from synthesized combinatorial librariesscreened across the μ-opioid receptor, then isolating natural peptides
Endomorphins bind to which opioid receptors
ndomorphin peptides preferentially bind Mu Opioid Receptors (~0.1 nM affinity); DOR and KOR far less
Which Endorphins are decribed as Potent analgesic, but associated with less reinforcement and respiratory depression (in animal testing)
Endomorphins
Endomorphins are found in which areas of the CNS that control pain and sedation and their functions:
-Periventricular hyopthalamus (endocrine response)
-Dorsomedial hypothalamus (endocrine response, sleep, feeding)
-Nucleus of the solitary tract (autonomic regulation, pain)
Most selective to least selective for endorphins; MOR
Endomorphin 1+2>>Beta-Endorphon>Met-Enkephalin=Leu-Enkephalin>DynorphinA
Most selective to least selective endorphins: DOR
Met-Enkephalin=Leu-Enkephalin>Beta-Endorphin>Dynorphin A> Endomorphin 1+2
Most selective to least selective endorphins: KOR
Dynorphin A>>Beta-Endorphin>Met-Enkephalin=Leu-Enkephalin>Endomorphin 1+2
Opioid Adverse Effects on Respiration
Respiratory depression - Produced by activating μ medulla in brain.
Potentially lethal adverse effect
- Effects dose dependent, with lethal effects (3-4 breaths/min) at 50-fold analgesic doses
- ↓ respiration when μ agonists inhibit medulla CO2 feedback control; results in toxic build up of [CO 2] in blood
» Significance worsens as tolerance to analgesics effects necessitates increasing dose for relief
- First sign of acute opioid intoxication is decreased respiration.
Opioid adverse effects on reward
μ opioid agonists produce euphoria, and are among the most addictive agents known.
Activation of μ and δ receptors in striatum inhibits (inhibitory) GABA interneurons, causing ↑ Dopamine
- κ receptors are located on dopamine neurons in striatum.
κ agonists thus inhibit DA neurons, causing dysphoria
» Suggestion that κ agonists may block acute substance intoxication, but may induce depression
Opioid adverse effects on pupils
Pupil constriction
Miosis mediated by activation of μ andκ receptors in Edinger-Westphal nucleus- Second sign of acute opioid intoxication is pinpoint pupils.
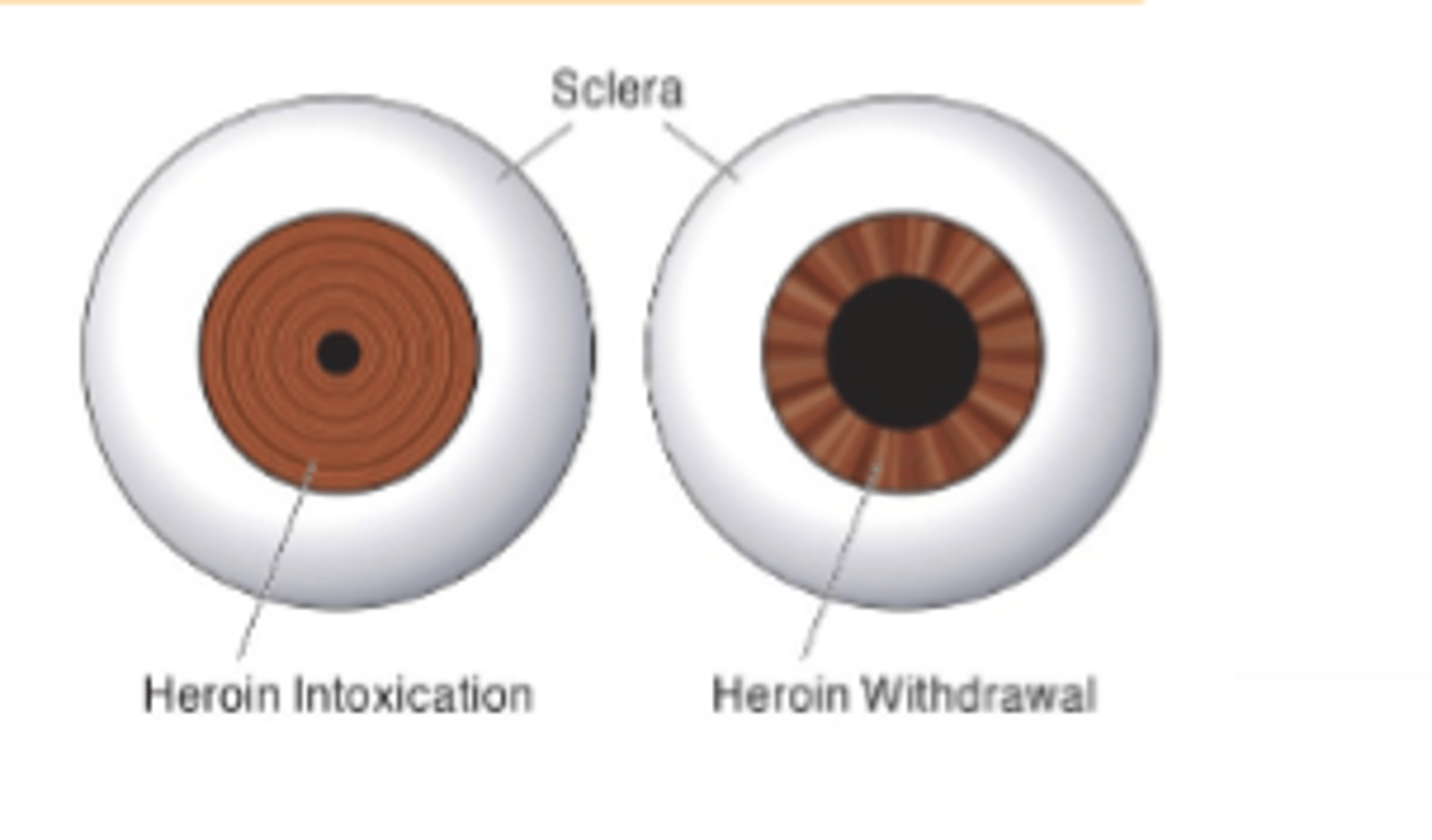
Opioid Adverse Effects: Nausea and emetic effects
μ agonists may induce vomiting and nausea! Two causes:
1) (direct) activation of μ receptors in Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone in medula oblongata ↑ sensation of nausea
2) (indirect) Vestibular component: hyperpolarization of inhibitory neurons on semicircular canals results inhypersensitization to movement; nausea
» Opioid users remain still to avoid this effect, but chronic users show tolerance to this effect- Another sign of opioid abuse: bad teeth (when repeated vomiting causes stomach acid to rot teeth
Opioid Adverse Effects: Convulsions
Activation of δ receptors produce seizures via disinhibition of inhibitory motorneurons in brain stem
Opioid Adverse Effects: Cardiovascular
No direct effects on heart rate or blood pressure. HOWEVER:
-increased histamine indirectly causes peripheral vasodilation (a problem in cases of shock, trauma)
-Results in postural hypotension and hypovolemia (fainting) upon rapid movement
Opioid Adverse Effects: Smooth muscle constriction
Mediated by μ and δ receptors, but indirectly by histamine. In addition to GI tract
Bronchial: ↑ constriction indirectly, by μ agonist release of histamine, closing airways + lungs (worsens asthma)
Uterus: μ agonists inhibit the effects of oxytocin, prolonging labo
Opioid Adverse Effects on skin
Indirect effects, mediated through histamine release. (Antihistamines can alleviate these effects)
↑ Flushing: indirect effect of histamine, opening vasodilation of capillary beds
Pruitus: ↑itching. #2 patient complaint; can be a significant issue as scratching causes unrecognized damage
Third sign of opioid intoxication is itching and bad skin. (Typically more common with chronic use)
Opioid Adverse Effects on Endocrine System
Activation of μ receptors in hypothalamus inhibit gonadotropins
Opioid Adverse Effects: Tolerance and Physical Dependence
Complex series of events, seem to start with desensitizationof the on the receptor/signaling level, with transitions occurringup to behavioral responses.
Oddly, rates of tolerance and dependence vary by opioid effect. Analgesia, euphoria quick; constipation slow
Very generally: μ agonists show faster tolerance, and κ seems to show the slowest rate (many exceptions)
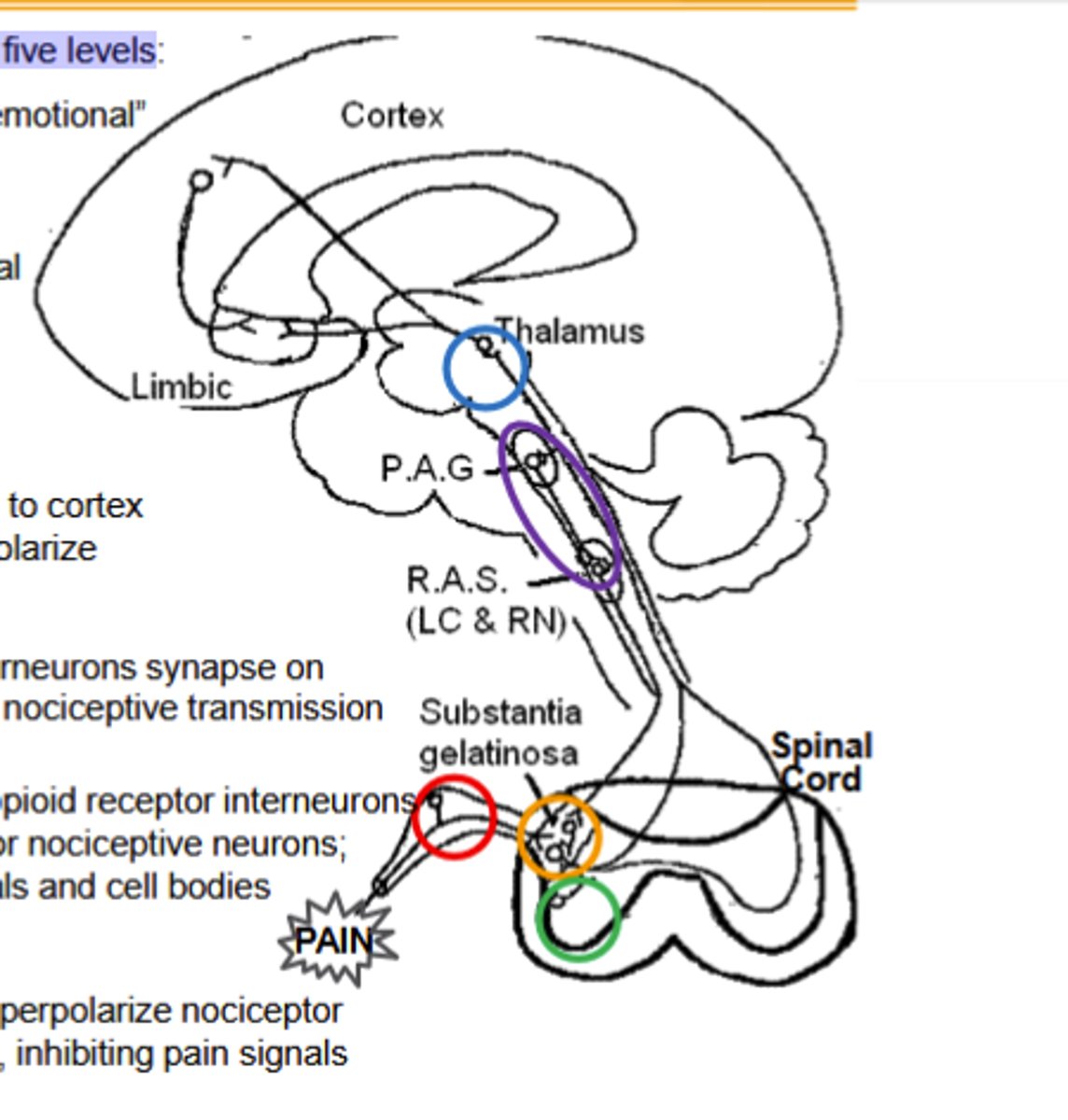
Opioid agonists inhibit nociceptive transmission at five levels, Limbic system elements ____ and _____ agonists regulate "emotional"content of pain
MOR and KOR
Opioid agonists inhibit nociceptive transmission at five levels:
1)Dorsal root ganglia (DRG)
2)Spinal cord and dorsal horn
3)spinal cord and ventral horn
4)Thalamus
5)Activation of the decending inhibitory pain pathway
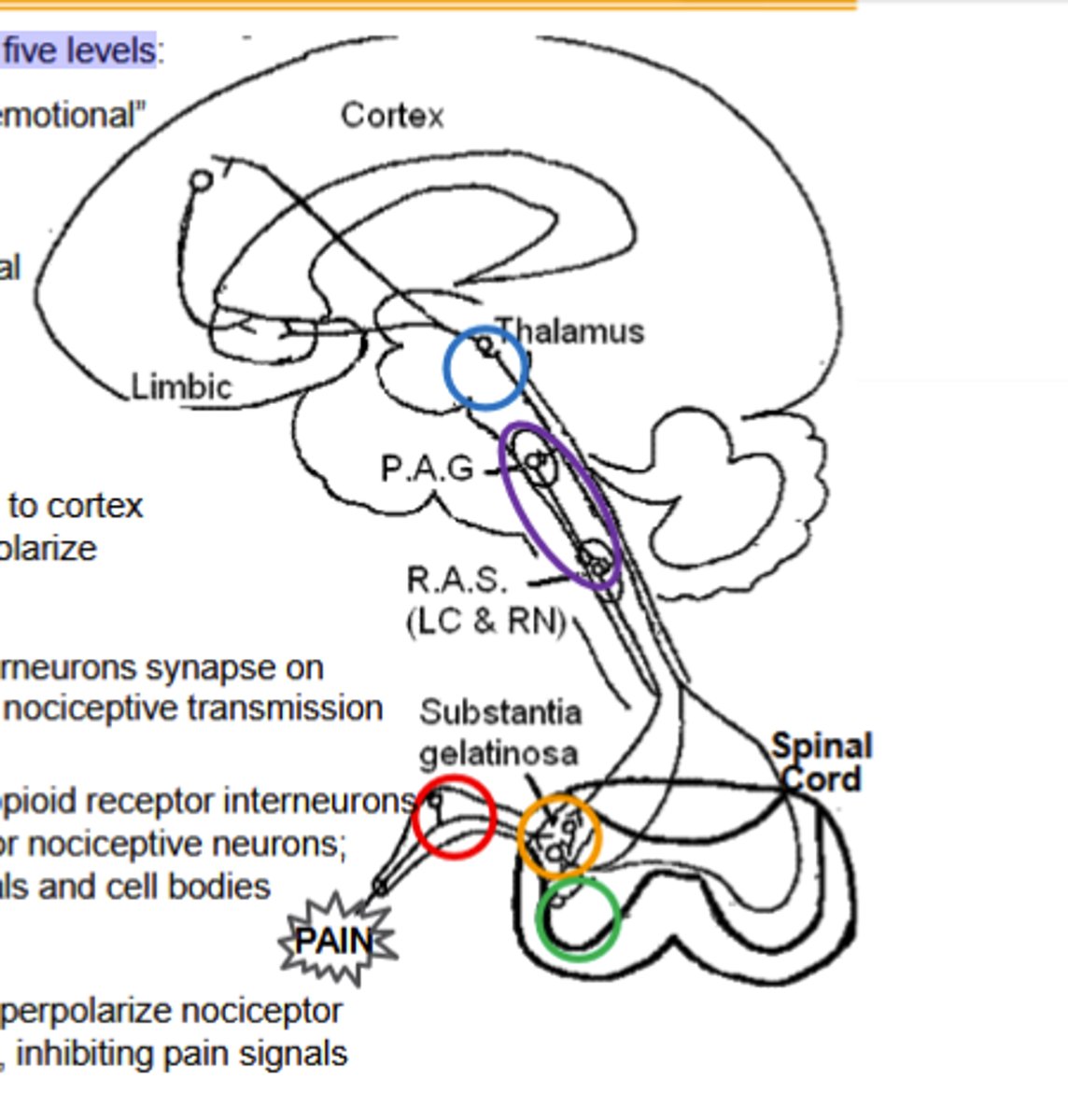
Dorsal Root Ganglion Pathway of Opioid agonists noiciceptive transmission inhibiton:
κ and δ agonists hyperpolarize nociceptor neurons from the periphery along the spinal cord, inhibiting pain signals(Site of peripheral inhibition)
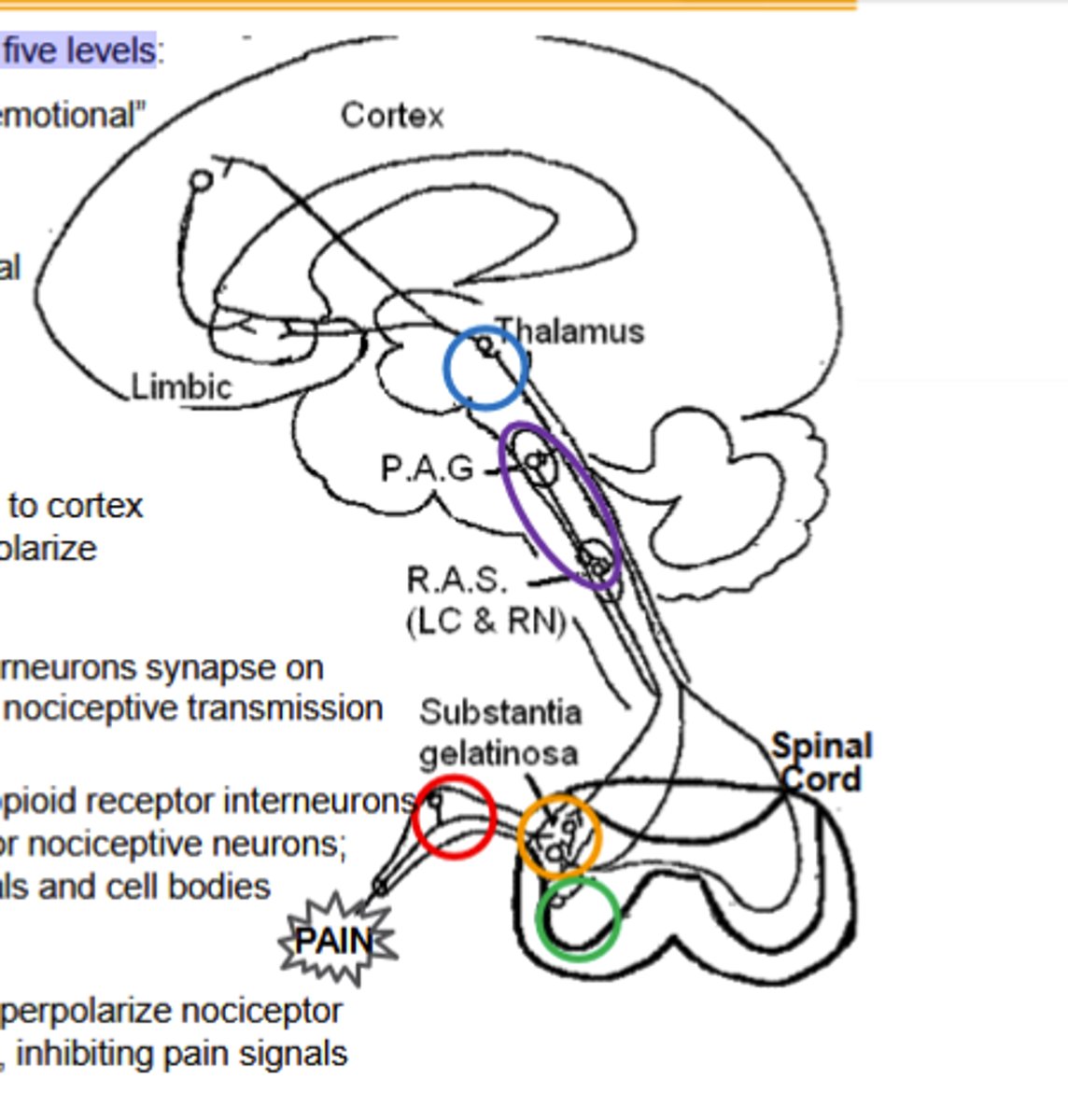
Spinal cord dorsal horn pathway of opioid agonist noiciceptive transmission inhbiton:
Outer layers contain opioid receptor interneurons Substantia gelatinosa: primary afferent terminal for nociceptive neurons;Enkephalin (δOR) interneurons synapse on terminals and cell bodies
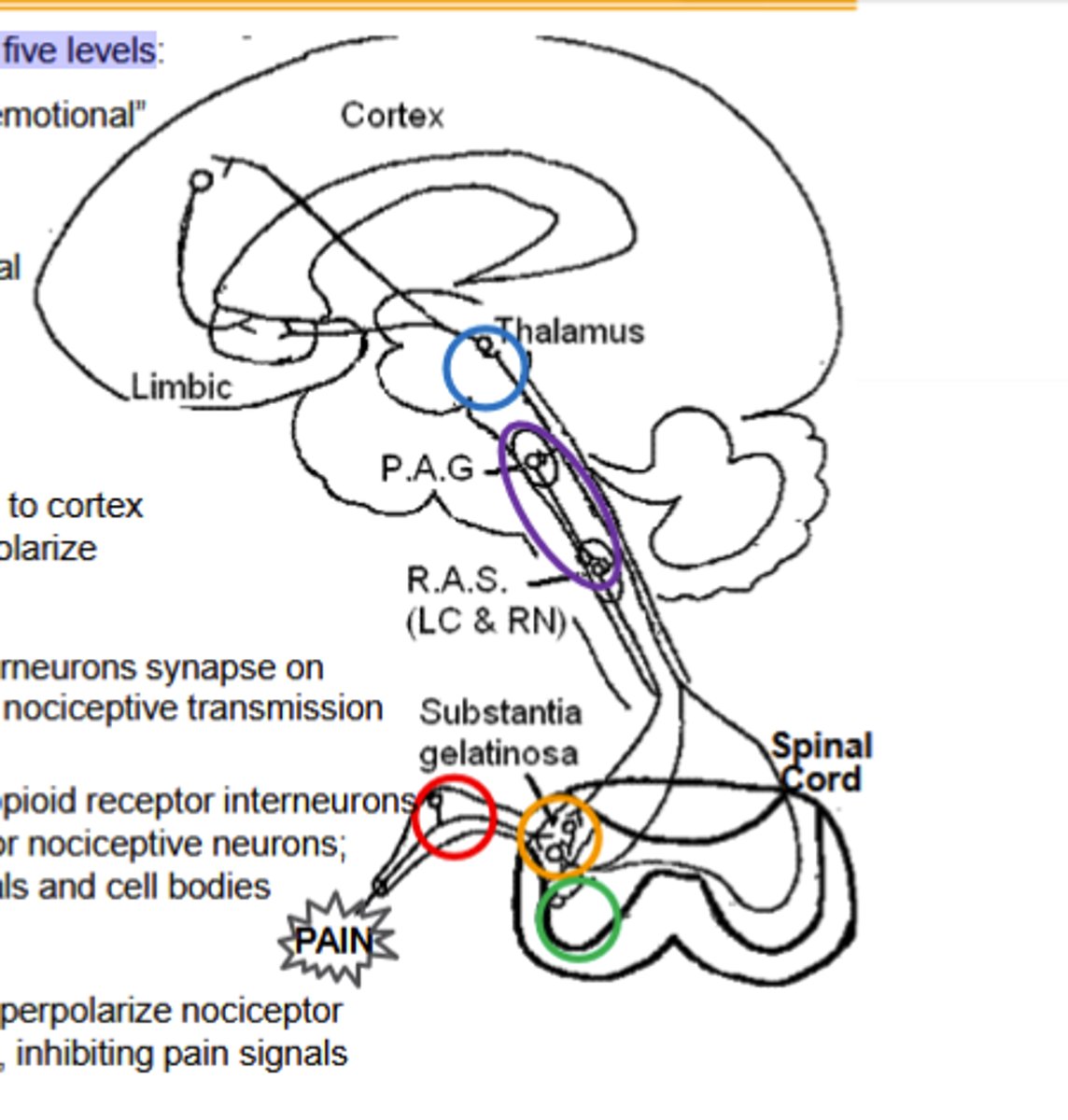
Spinal cord and ventral horn pathway of opioid agonist noiciceptive transmission inhibition
Dynorphin (κOR) interneurons synapse on Spinothalamic axons, inhibiting input to decrease nociceptive transmission
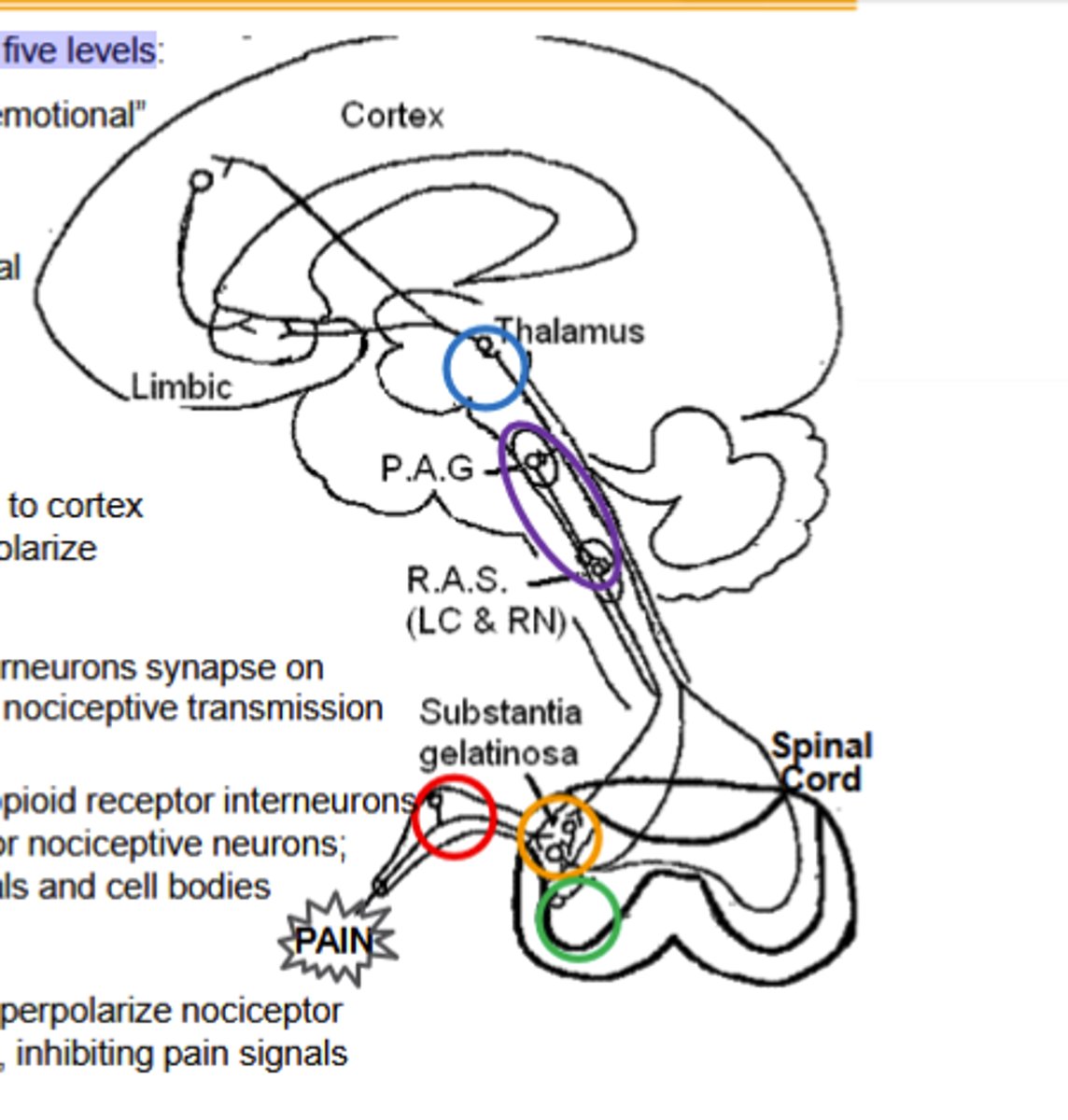
Thalamus pathway of opioid agonists noiciceptive transmission inhibition
Spinothalamic neurons connect here to cortex and limbic system. μ agonists (and μOR) hyperpolarize nociceptive neurons, "gating" pain signals.
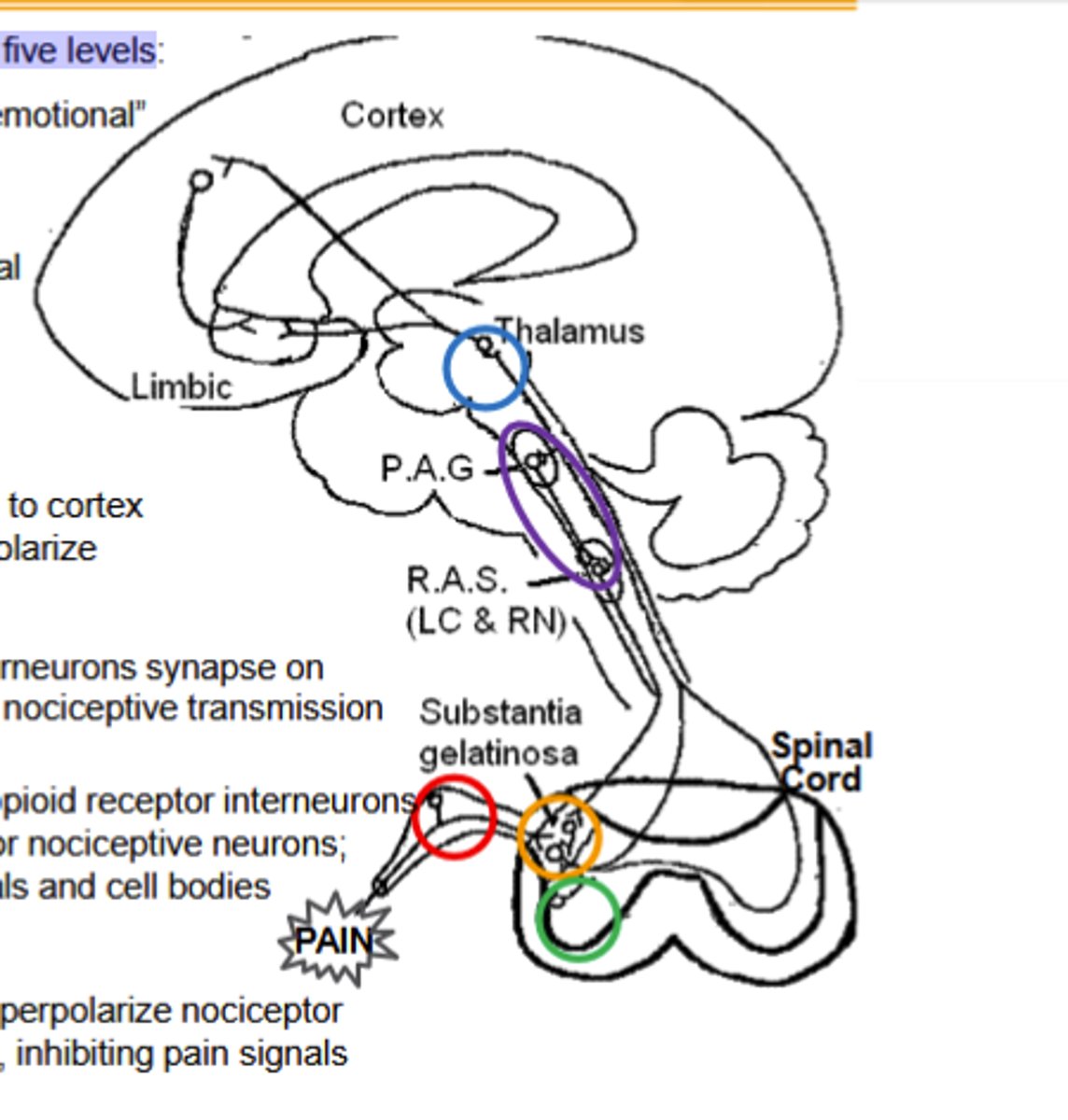
Activation of decensing inhibitory pathway by opioid agonists to inhibit noiciceptive transmission
μ agonists (and μOR) in Periaqueductal Gray inhibit GABA interneurons, releasing the descending pathway (RAS) to inhibit the ascending pain pathways.
Morphine, Hydromorphone (Dilaudid), Oxymorphone (Numorphan) mechanism of action
Full μ agonist, but at 10-fold higher doses will be agonist at δOR and κOR (δ > κ).
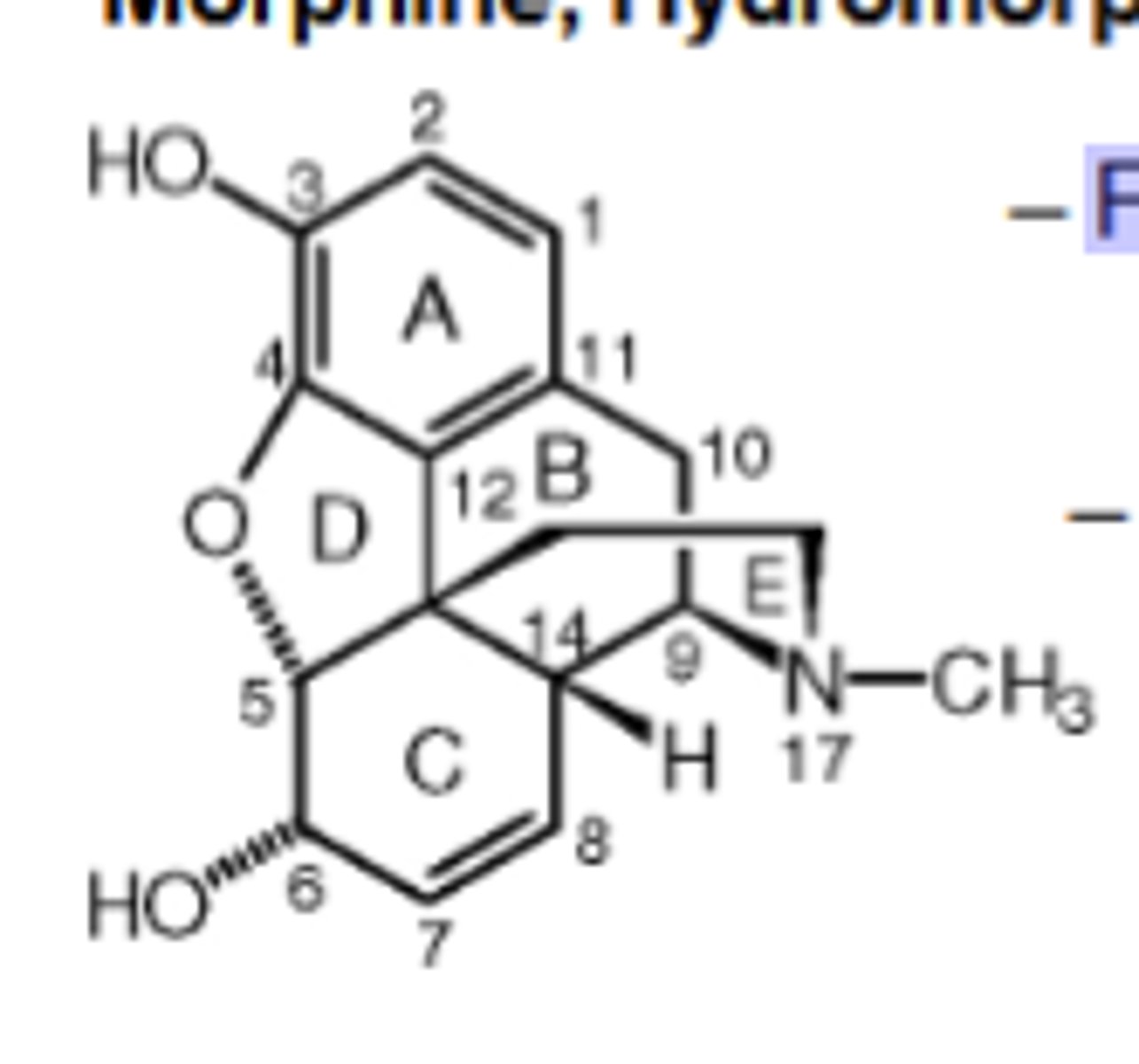
Pharmacokinetics of Morphine, Hydromorphone (Dilaudid), Oxymorphone (Numorphan)
Low oral absorbance: ~40% enters CNS
» ½ life = 2 hr; duration = 4-5 hr
Morphine (and similar structures) is primarily metabolized in ______via glucuronidation into morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G; 60%) and morphine-6 glucuronide (M6G; 10%)
liver
Morphine Metabolites
M3G is inactive; M6G is a μ agonist with twice the potency ofmorphine
Which Opioid Drug is descibed as maximally efficacious; still the gold standard for analgesia. Highly addictive
Morphine
Which opioid drug is described as a Schedule 1 drug; illegal. "Diacetyl morphine"; hydrolyzed to 6-MAM, then to morphine (<30 min)
Heroin
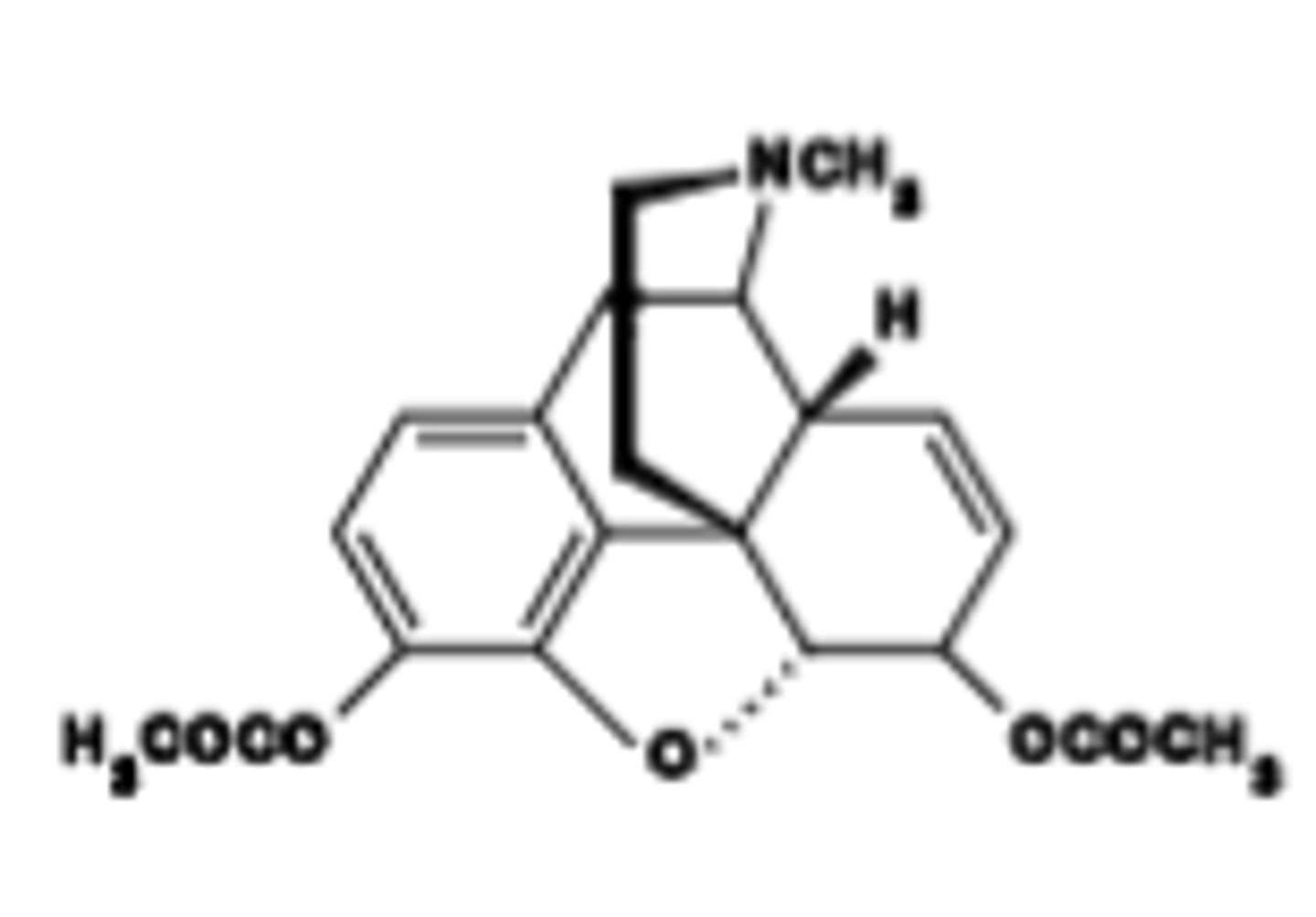
Heroin mechanism of action
Full μ agonist. Good oral : parenteral potency ratio.
Heroin Pharmacokinetics
ood oral : parenteral potency ratio.
After i.v. admin: very fast acting; reward/euphoria within seconds to a minute
Very lipophilic; facilitating ready crossing over the BBB\Effective as analgesic (as morphine); analgesia lasts ~4-5 hr
Which opioid drug is described as Remarkably addictive: perhaps one of the most addictive drugs in animal studies
Heroin
Which specific opioid drug is described as: Although not as effective analgesic vs. morphine by dose, still a full μ agonist.
Codeine, Oxycodone (Oxycontin), Hydrocodone (Drocode)
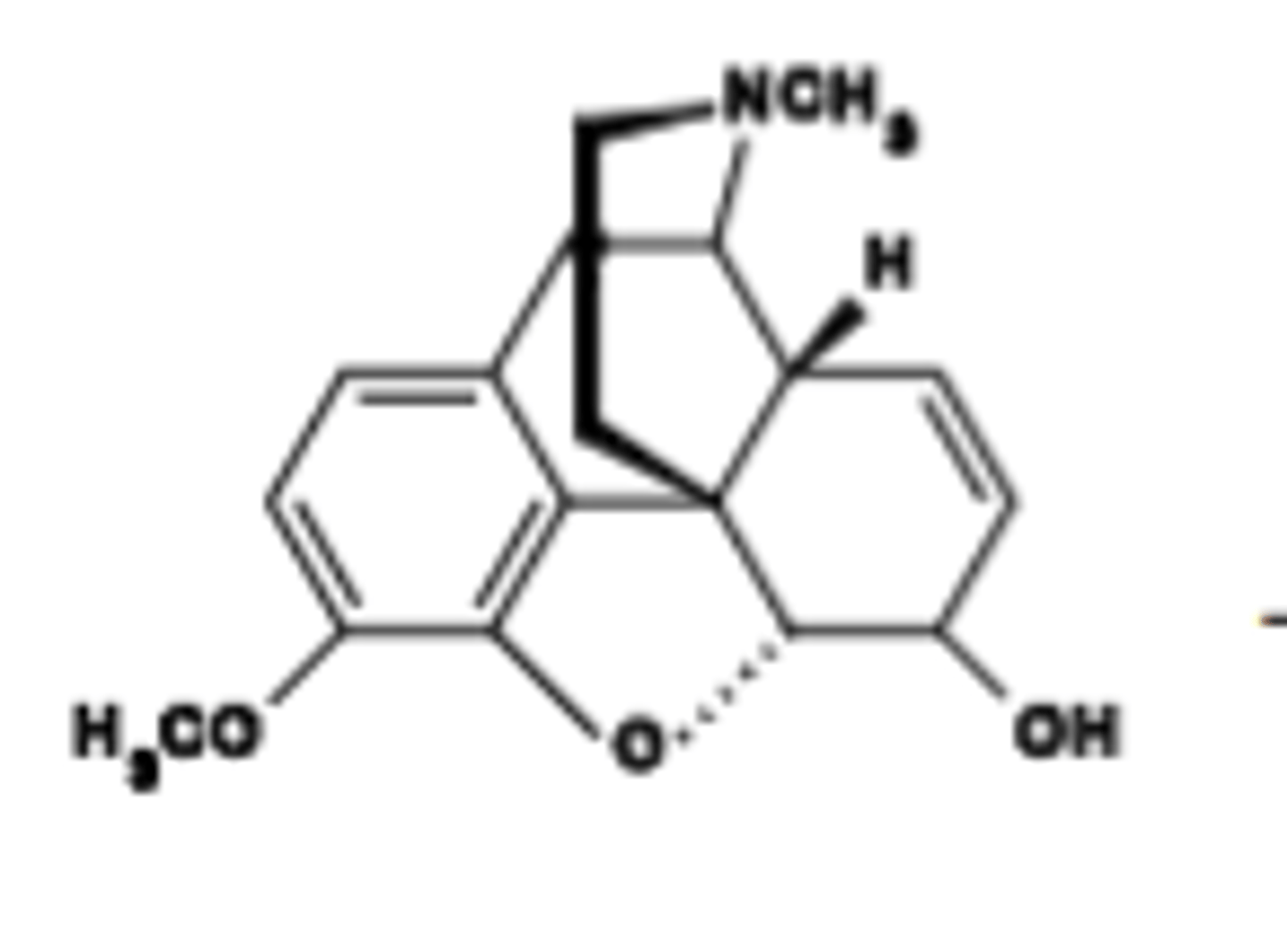
Pharmacokinetics of Codeine
Less first pass metabolism due to C3 OH-methylation.
Duration of Codeine
Duration = 3-4 hr. 10% of codeine converted to morphine after oral administration.
Which specific opioid drug is Often mixed with NSAIDs to give improved, synergistic analgesia (30 mg in Percocet)
Codeine
15 mg (subanalgesic dose) works well to suppress cough (dextromorphan site?)
Which specific opioid drug is described as:
Synthetic; a phenylpiperdine. A drug of abuse
Not orally active (but transdermal)
Fentanyl (Sublimaze), Sufentanil (Sufenta), Remifentanyl
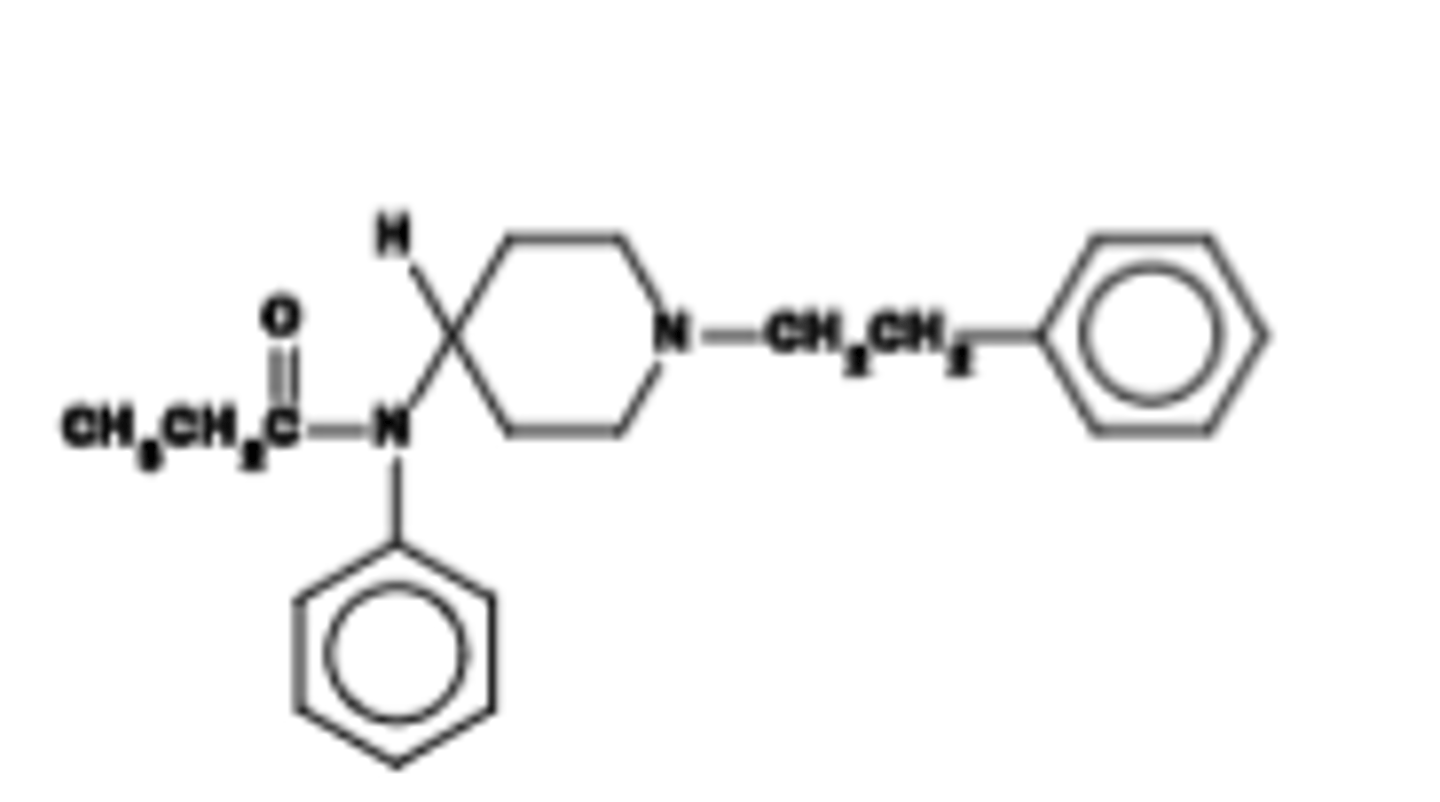
Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl
Very fast onset of action (~5 min)\Rapidly cleared; duration of action = 1-1.5 h. (Reminfentanyl: >15-30 min)
Full μ agonists, 80-100 times more potent than morphine!
Which specific opioid drug has a Key use: post-operative pain management due to fast PK. Primaryanesthetic for surgery; epidural.
Fentanyl
Which specific opioid drug is described as: Releases less histamine (reason unknown), but must be monitored carefully due to high potency.
Fentanyl
Which specific opioid drug is described as: Antagonists produce none of the effects described: NO analgesia. But vital to reverse agonist overdose.
Naloxone (Narcan)
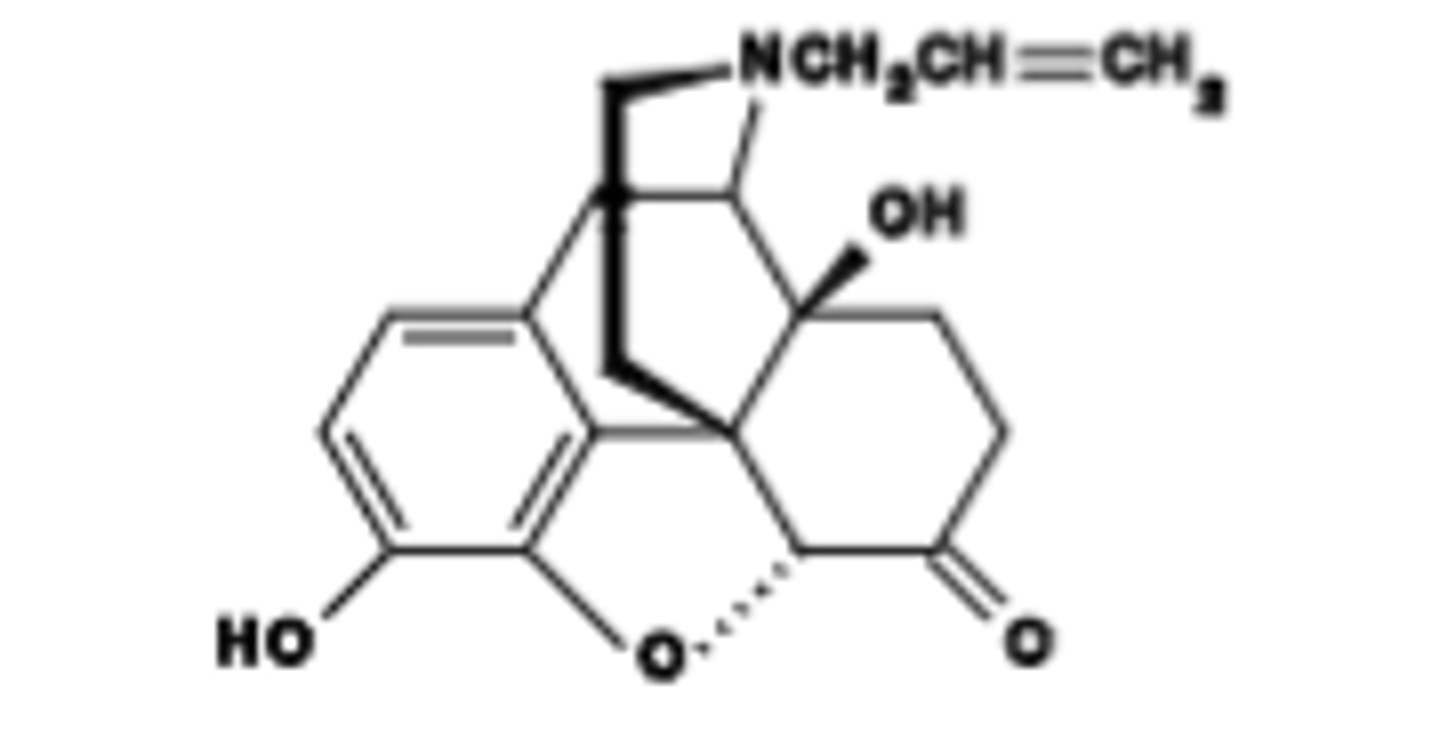
Pharmacokinetics of Naloxone
Fast acting (1-2 min)
First pass metabolism is very high; i.v. adminstration used to circumvent
½ = 1 hr; short duration of action (1-2 h). Must often re-administe
Which specific opioid drug is described as: Competitive, potent nonselective μ, δ and κ antagonist (highest affinity for μOR
Naloxone
Which specific opioid drug has a Key use: reverse opioid overdose and counteract opioid toxicity.
Naloxone
Which specific opioid drug Will induce withdrawal in opioid physically-dependent subjects.
Naloxone
Which specific opioid drug at a Low dose (0.15 mg/kg s.c.) reverses μ-opioid agonist-induced constipation with few/no CNS effects.
Naloxone
Which specific opioid drug is described as Synthetic. Good oral : parenteral potency ratio. More potent than naloxone.
Naltrexone (Revia, Vivitrex)
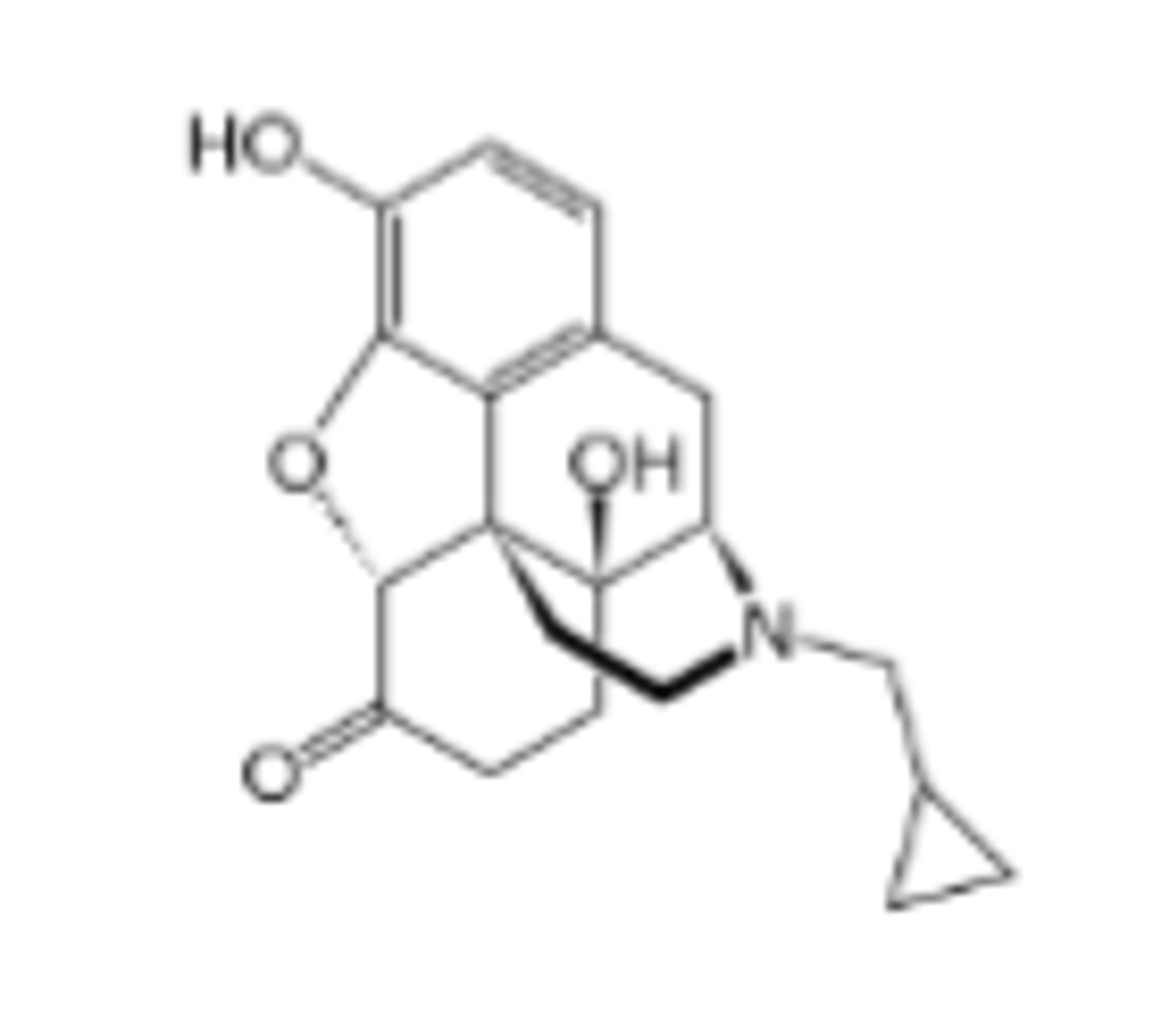
Pharmacokinetics of Naltrexone
Fast (1-2 min)
Less first pass metabolism; longer duration ~24 hr; peak effect @ 1-2 h
Metabolized in liver to 6-naltrexol, a weaker antagonist but w/ t ½=13 h
Competitive, potent nonselective μ, δ and κ antagonist
Which specific opioid drugs has a Key use: reverse opioid overdose and counteract opioid toxicity.
Naltrexone
Which specific opioid drug is described as: Decreases cravings in alcoholics; used as abstinence medication. Not abused.
Naltrexone
Which endorphin: Endogenous agonist for μ-opioid receptors. Potent analgesic, produces "runner's high"
Beta-Endorphin
Which endorphin: Endogenous agonist for δ-opioid receptors. Important endogenous analgesic
Met and Leu-Enkephalin
Which endorphin: Endogenous agonists for κ-opioid receptors. Endogenous nalgesic, but dysphoric.
Dynorphin A Peptides
Morphine
Natural agonist for μ-opioid receptors. WHO med. Potent analgesic, but highly addictive.
Heroin
μ-opioid receptor agonist. One of the most addictive substances known
Codeine
μ-opioid receptor agonist. WHO med. Useful analgesic due to oral activity; also suppresses cough
Fentanyl
Synthetic μ-opioid receptor agonist. 100-times more potent analgesic than morphine; addictive
Naloxone
Non-selective opioid receptor antagonist. Used to treat opioid overdose