Unit 3 Depression - PollEv
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What are medications that cause depression?
isotretinoin
beta blockers
oral contraceptives
benzodiazepines
What are the risk factors for depression?
being divorced
females
age 45-65
unemployment
low income
What is the most dangerous class of antidepressants?
TCAs
block Na+ channels
lead to coma, seizures (brain)
arrithymias, death (heart)
What drug class is associated with hepatotoxicity (liver disease)?
SARI
Which drug classes are associated with seizures?
TCAs
NDRIs
Which drug classes cause sexual dysfunction?
SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, MAOIs
Which drug class causes weight loss?
NDRI
Which drug classes improve sleep?
NaSSA, SARI, TCA
Which drug classes improve nerve pain?
SNRI
TCA
Which drug classes cause HTN?
SNRI
NDRI
What goes in the subjective area of SOAP note?
history of what brought patient in
diagnosis of diabetes
symptoms
What goes in the objective section of the SOAP note?
labs
rating scales
What is the goal of treating depression?
remission, or the absence of depressive symptoms
What is the criteria to be diagnosed with depression?
5 target symptoms must have them for 2 weeks and must include depressed mood or anhedonia
The primary hypothesis for depression is the monoamine hypothesis. Why is this theory flawed?
(Antidepressants increase monoamines) According to the monoamine hypothesis of depression, a deficiency in serotonin, norepinephrine and/or dopamine leads to depression. Thus, an increase in these neurotransmitters should cause a return to a normal state. In general, all antidepressants boost the synaptic action of one or more of the monoamines, in most cases by blocking presynaptic transporters. In this figure, an antidepressant is blocking the norepinephrine transporter (NET), thus increasing synaptic availability of norepinephrine and theoretically reducing symptoms of depression.
AB is a 20 year old male who is having the first episode of depression. He started on an SSRI today. How long should he take the SSRI?
a minimum of 1 year
AB is now having a second episode of depression and his doctor initiates an SNRI antidepressant today. How long should he use the antidepressant and why?
2 prior episodes: 70% will experience a future episode - treat 4 to 9 months after response + 12 weeks (initially) = 1 year
AB is now having a third episode of depression. He is initiated on an NRDI. How long do you recommend that he take this drug?
Three or more prior episodes: 90% will experience a future episode – treat indefinitely
How long does it take for antidepressants to treat depressive symptoms?
4-6 weeks (some may require up to 8 weeks)
first week: decreased anxiety, improvement in sleep, appetite, and energy
1-3 weeks: increasing activity, sex drive, self care, concentration, memory
2 to 4 weeks: relief of depressed mood, decreased or abolished feelings of hopelessness
Which rating scale is clinician rated?
Hamilton Depression Scale (HAM-D)
MADRS
GDS
QIDs
A PHQ-9 score of 25 is associated with:
20-27 severe depression
15-19 moderately severe depression
10-14 moderate depression
5-9 minimal symptoms
<5 symptoms absent
Which of the following medications can cause symptoms of depression?
beta blockers
benzodiazepines
oral contraceptives
isotretinoin (acne)
What is a risk factor for developing depression?
females
middle aged (age 45-65)
divorced
unemployment
low income
What kind of information is placed in the subjective portion of a soap? What kind of information is placed in the objective portion of a soap?
subjective
demographics
chief complaint
history of present illness
FH
SH
allergies
objective
vital signs
rating scales
current medication list
OTC’s and herbal supplements
include pase medications
labs
Suicidal thinking is a potential adverse effect that must be managed for which of the antidepressants?
All of them
Which are the most dangerous class of antidepressants in overdose?
Tricyclic Antidepressant (TCAs)
block Na+ channels in the brain cause coma, seizures
block Na+ channels in the heart cause arrhythmias and death
Which antidepressants initially make anxiety worse in the first week of use, but treat anxiety for a long-term use?
SSRIs and SNRIs initially making anxiety, worse, but treat anxiety, long-term
Which of the following drug classes has an antidepressant that can lead to hypertension?
Serotonin norepinephrine uptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
Which of the following drug classes is associated with hepatotoxicity?
Serotonin antagonist reuptake inhibitors (SARIs)
Which PHQ-9 score is associated with severe depression?
20-27
How to treat depression?
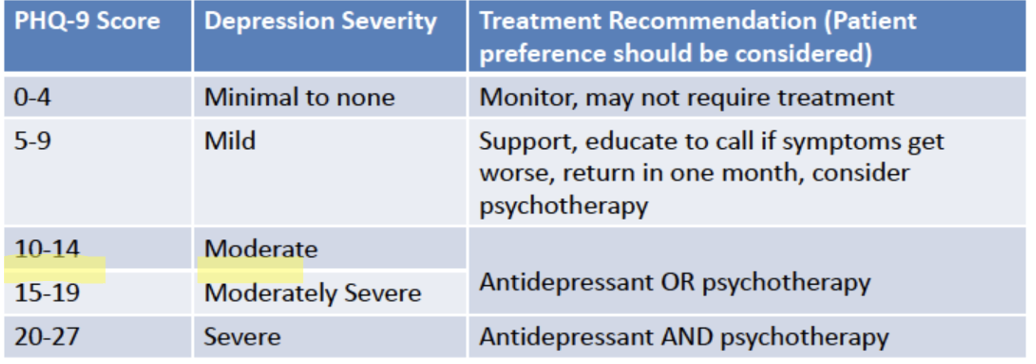
Which PHQ-9 score is associated with moderate depression?
10-14
Which of the following antidepressants have histamine activity?
TCAs
SARIs
NaSSA
Which of the following effects is caused by antagonism of muscarinic (acetylcholine) receptors?
blurred vision, dizziness, confusion, sedation
tachycardia
urinary retention
dry throat, constipation
Which of the following antidepressant classes is associate
Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRI)
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
An increase in norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft leads to which of the following adverse effects?
Vasoconstriction (HTN)
Which of the following antidepressants causes sexual dysfunction?
SSRIs
SNRIs
TCAs
MAOIs
Which of the following antidepressants causes weight loss?
-NDRI
Which of the following antidepressants causes improved sleep?
TCAs
SARIs
NaSSAs
Which of the following antidepressant classes improves nerve pain?
SNRIs
TCAs
Which of the following drugs block reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine?
NDRI
Which of the following antidepressant classes causes hypertension?
SNRIs
If you think someone is depressed and might be considering suicide, which of the following should you consider doing?
Ask directly whether they are feeling suicidal
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and specific serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) cause which mutual adverse effects when taking an overdose?
CNS depression
Seizures
QT prolongation
Treatment should last at least one urine patients who have how many episodes of depression?
1 prior episode: 50% will experience a future episode
Treat 4 to 9 months after response [response time is 12 weeks] (acute and continuation)
2 prior episodes: 70% will experience a future episode
Treat 4 to 9 months after response [response time is 12 weeks] (acute and continuation)
Feelings of purposelessness is most closely related to which of the following?
suicidal thinking
What is the best treatment for mild depression?
Psychotherapy
Which PHQ-9 score is associated with a mild depression?
5-9
Which of the following parameters should be monitored for drug efficacy?
degree of danger to self and others
other mental disorders, including alcohol and other substance use disorders
side effects of treatment
adherence to treatment plan
Impatient taking Nonadrenergic Specific Serotonergic Alpha-2 Adrenergic Antagnoists (NaSSAs) clinicians should monitor which of the following?
Hypertriglyceridemia
A patient comes into your emergency room after eating a Reuben and french fries at a local restaurant. The patient complains of a fever, headache, stiffness, and sweating. He is taking a beta blocker, a statin and an MAIO. What do you suspect?
pickled or fermented food-sauerkraut (HTN crisis)
Expect a severe drug interaction if you use the pain medication tramadol with which antidepressant class?
MAOIs
Which adverse effects is common to both TCAs and NDRIs?
seizures
The three most common adverse effects of serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) include?
headache, nausea, anxiety
A norepinephrine dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) can help which symptoms in a patient with depression?
weight loss, insomnia
NDRIs do not cause sexual dysfunction and may be added to other antidepressants or they may replace an antidepressant when a patient finds this side effect intolerable
Men have a greater risk of completing suicide than any other group?
True
There is a 90% risk of reoccurrence after how many episodes of depression?
3 episodes
It takes five months to see, which of the following would the use of antidepressants depress
The median time between the onset of symptoms and recovery, which is no symptoms is 20 weeks with adequate treatment of antidepressants
Untreated episodes can last six months or longer
Rank the ethnic group with the greatest risk of suicide to the least risk of suicide.
white men, Native American men, black men, asian/pacific island men
Female gender is a risk factor for which of the following
depression
You must have one of two symptoms to be diagnosed with depression according to DSM-5-TR. What are the two symptoms?
(1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure
Which antidepressant is dangerous in overdose?
SSRI: well tolerate; frequently no results in no symptoms
SNRI, TCAs, MAOIs
Name three common causes of death from suicide
firearms, poison, hanging, autohide, jumping
What percentage of patients discontinue their antidepressant prematurely?
50%
What percentage decrease in depression rating scales is associated with response?
50%
What is the best way to assess efficacy of an antidepressant?
•Rating scales such as the PHQ-9 or QIDS are recommended to monitor symptoms. Measurement-based care has been associated with greater response and remission rates
What does the etiology of depression include?
genetics
The HAM-D is the “Gold Standard” for Depression Rating Scales?
True
Oldest and most used depression rating scale
Have the most research and data concerning it's used patient with depression
If a patient is on an MAOI, what side effects would you monitor for?
Blood pressure, pulse (postural hypotension)
blurry vision, dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation (anticholinergic effects)
assess severity and impact on quality of life (sexual dysfunction)
body weight (weight gain)
sleep problems (sedation/insomnia)
What would you monitor if a patient is taking an MAOIN you think they may be experiencing a hypertensive crisis?
Autonomic function (blood pressure, pulse, temperature) neuromuscular function