AP gov ch 1/2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
democracy
the rule of the many
direct/participatory democracy
a government in which all or most citizens participate directly
representative democracy
a government in which leaders make decisions by winning a competitive struggle for the popular vote
elite
persons who possess a disproportionate share of some valued resource like money or power
class view
view that the government is dominated by capitalists
power elite view
view that the government is dominated by a few top leaders, most of whom are outside of government
bureaucratic view
view that the government is dominated by appointed officials
pluralist view
the belief that competition among all affected interests shapes public policy (group based policy making)
unalienable
a human right based on nature or god
articles of confederation
a weak constitution that governs America during the Revolutionary War
emphasized state power; not unified
no executive/judicial
cannot raise taxes or army
amendments required all 13 states approval
equal representation (1 vote/state)
states had own currency
constitutional convention
a meeting in Philadelphia in 1787 that produced a new constitution
Shay’s Rebellion
a 1787 rebellion in which ex-Revolutionary War soldiers attempted to prevent foreclosures of farms as a result of high interest rates and taxes
Virginia Plan
proposal to create a strong national government
New Jersey Plan
proposal to create a weak national government
Great Compromise
Plan to have a popularly elected House based on state population and a state-selected Senate, with two members for each state
republicanism
a government in which elected representatives make the decisions
judicial review
the power of the courts to declare laws unconstitutional
federalism
government authority shared by national and local governments
enumerated powers
powers given to the national government alone
reserved powers
powers given to the state government alone
concurrent powers
powers shared by the national and state governments
checks and balances
authority shared by three branches of government
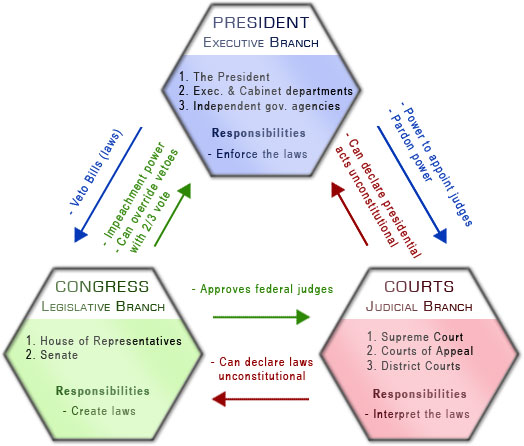
separation of powers
constitutional authority is shared by three different branches of government
faction
a group with a distinct political interest
federalists
those who favor a stronger national government
antifederalists
those who favor a weaker national government
coalition
as alliance of factions
bill of rights
first ten amendments to the constitution
habeas corpus
an order to produce an arrested person before a judge
bill of attainder
a law that declares a person without a trial to be guilty of a crime
ex post facto law
a law that makes an act criminal although the act was legal when it was committed (constitution protects against it)
amendment
a new provision in the constitution that has been ratified by the states
line-item veto/presidential veto
an executive’s ability to block a particular provision in a bill passed by the legislature
natural rights
life, liberty, property; fundamental rights and liberties that belong to all people and can’t be taken away
social contract
people establish government to protect rights but give up some freedom to maintain that social order
popular sovereignty
the people are the source of governmental power; “consent of the governed”
limited government
government cannot do whatever they want. the constitution limits our government
declaration of independence
why colonies should break apart from britain
emphasized popular sovereignty, natural rights, social contract, limited gov., taxation w/o representations; power to the states
federalist 10
by james madison
pure democracy —> majority will always win, no protection for minority views
dangers of FACTIONS (group of citizens that dominate gov. to impose their interests on society, threatening ppls liberties)
two solutions: destroy causes or effects
causes - destroying freedom to create faction or making everyone have same opinion (bad, not possible)
effects - a large republic —> less probable that a majority/FACTION will form and take over gov
multiple factions = all in competition w. one another —> creates compromises NOT in the interests of a group, but for the GOOD of society
advocates for federalism (so representatives aren’t always focused on local issues)
federalist papers
john jay, james madison, alexander hamilton (federalists) write essays to support the ratification of the constitution and convince the public; addressed several concerns
federalist 51
james Madison
if people were “angels” we wouldn't need a gov. —> ppl r inherrently selfish
create a gov powerful, but doesn't violate liberties —>
SEPARATION OF POWERS + CHECKS AND BALANCES!! (lim. gov)
dividing legislature (strongest branch) into two houses
federalism (states + fed gov get powers)
large Republic
brutus 1
antifederalist (DID NOT support constitution); anti strong fed gov
SMALLER republic: can tend better to interests of ppl
Elastic clause —> gov. will abuse its power and weaken power of states!!
Supremacy Clause —> will weaken power of states; fed, gov will overrule state laws!!
commerce clause
An enumerated/expressed power written in the Constitution
Allows Congress to regulate trade between states (interstate commerce, not INTRAstate) and between USA and other countries
necessary and proper clause/elastic clause
Congress may make new laws to carry out expressed powers and responsibilities
resulted in expanded fed. gov power/role
threat to anti-federalists
first amendment
freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, petition
fifth ammendment
protection from self-incrimination (right to remain silent, protection against self-incrimination), double jeopardy (being tried twice for same crime), due process (fair treatment under law/fair trial)
tenth amendment
federal gov only has powers listed in constitution; all others are given to states/citizens
fourteenth amendment
citizenship to all people born in US, equal protection of laws for all ppl, states cannot infringe of citizens rights
seventeenth amendment
direct election of senators
three-fifths compromise
slaves count as 3/5 of a person to state pop.
full faith and credit clause
States must recognize the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state
Privileges and Immunities Clause
Citizens of one state must be treated equally to citizens of another state when in that state
Establishment Clause
Federal government cannot establish official religion or favor a religion
Free Exercise Clause:
Federal government can’t interfere with your ability to practice a religion (pending obvious exceptions)
supremacy clause
federal laws override any state laws about the same thing
amendment process
article V
amendment process;
propose an amendment: ⅔ vote by congress or ⅔ of state legislatures request congress to call a convention (latter option has never happened)
ratify and amendment: ¾ by state legislatures or ¾ approval by state conventions (latter option only happened with 21st amendment)
baron de Montesquieu
separation of powers —> no risk of another tyrant
assoc. w/ declaration of independence, constitution
james madison
federalist, large Republic, checks and balances, strong central gov., federalism
john locke
social contract, natural rights, consent of the governed, limited gov.
thomas hobbes
people are inherently selfish and driven by self-interest —> we must have a strong gov., social contract
hyper-pluralist
in a pluralist democracy, groups have a big impact on government (ex: interest groups). A hyper-puralist democracy means groups continuously clash, leading to a lack of legislation from the government