08.E BIO Sexual Reproduction & Meiosis (PART E)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
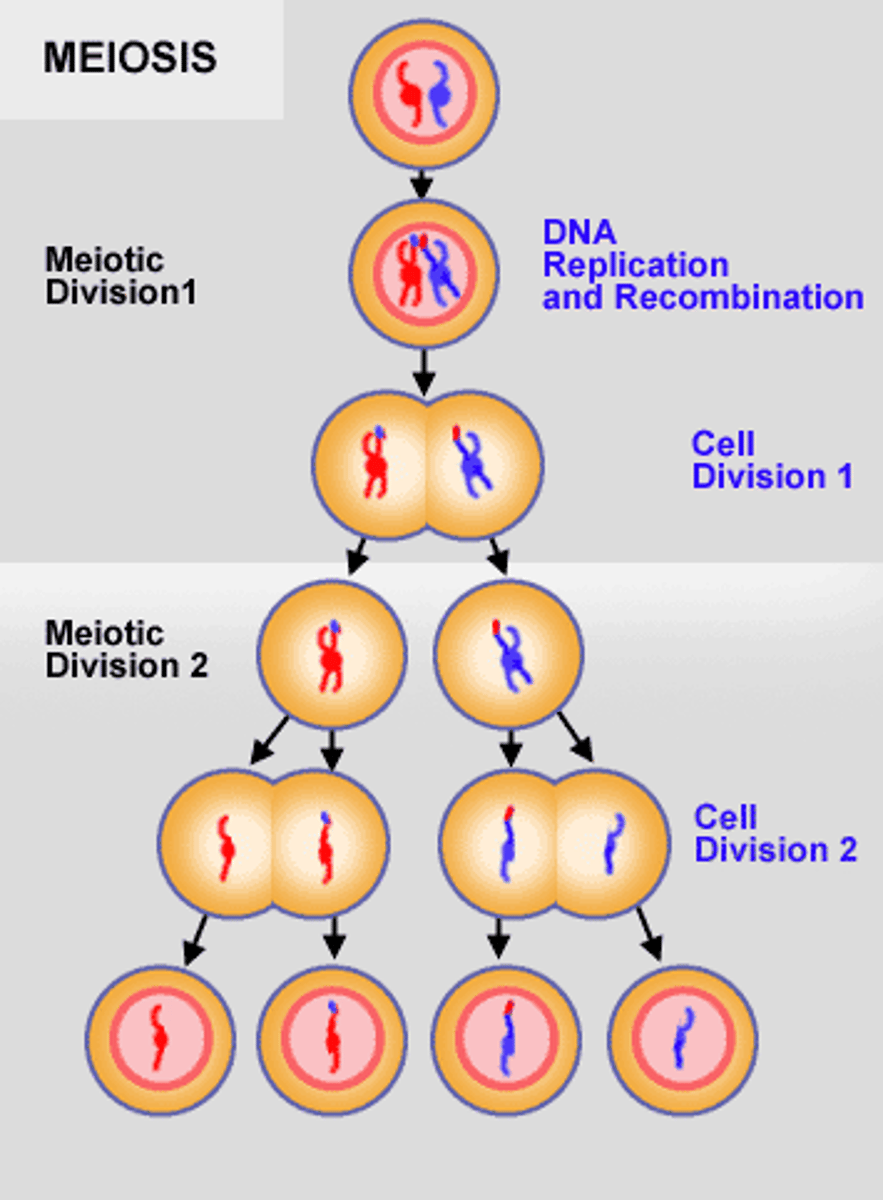
Meiosis
A type of cell division that forms gametes, sperm (male) and egg (female) with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores; duplication of DNA followed by two consecutive cell divisions
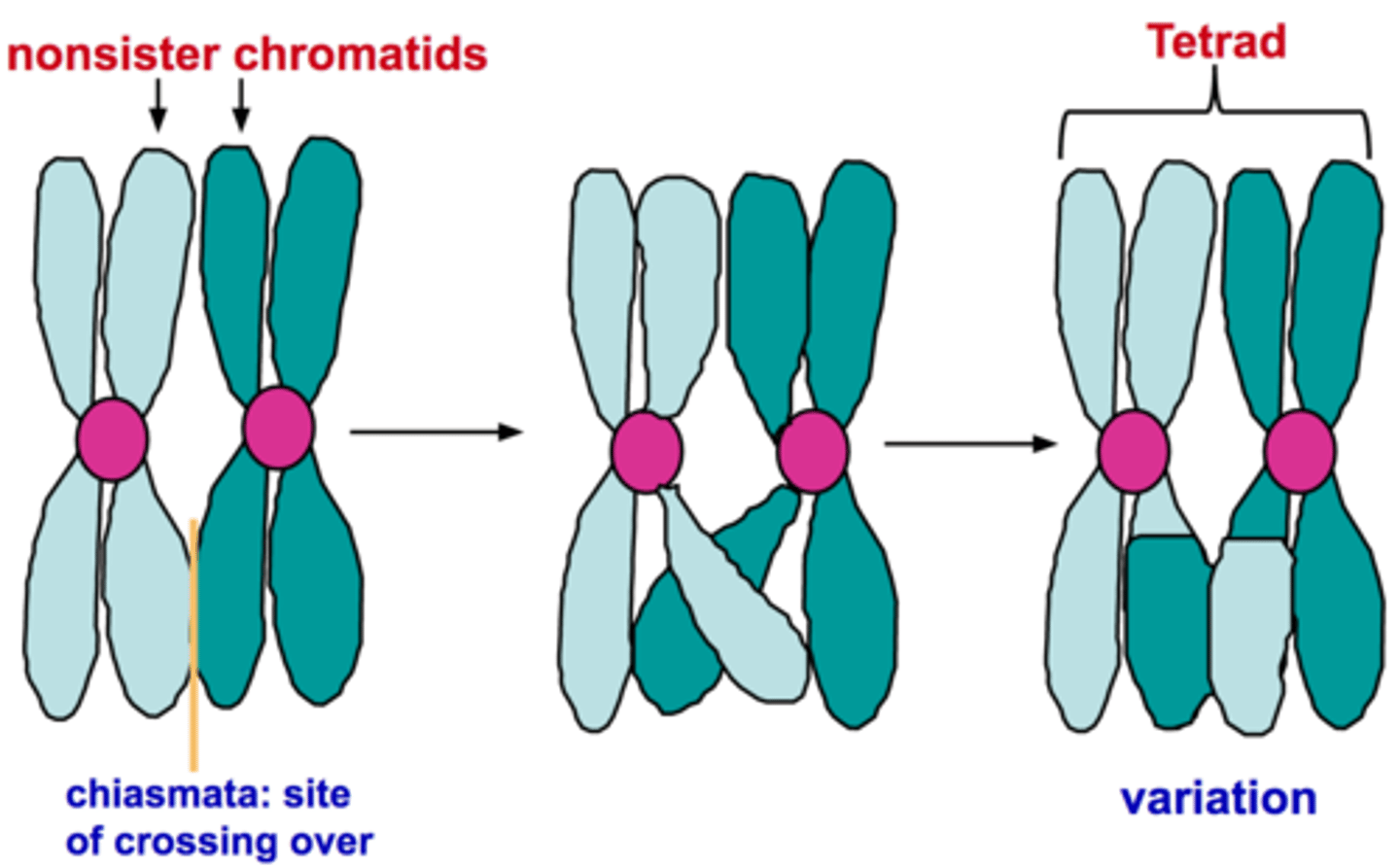
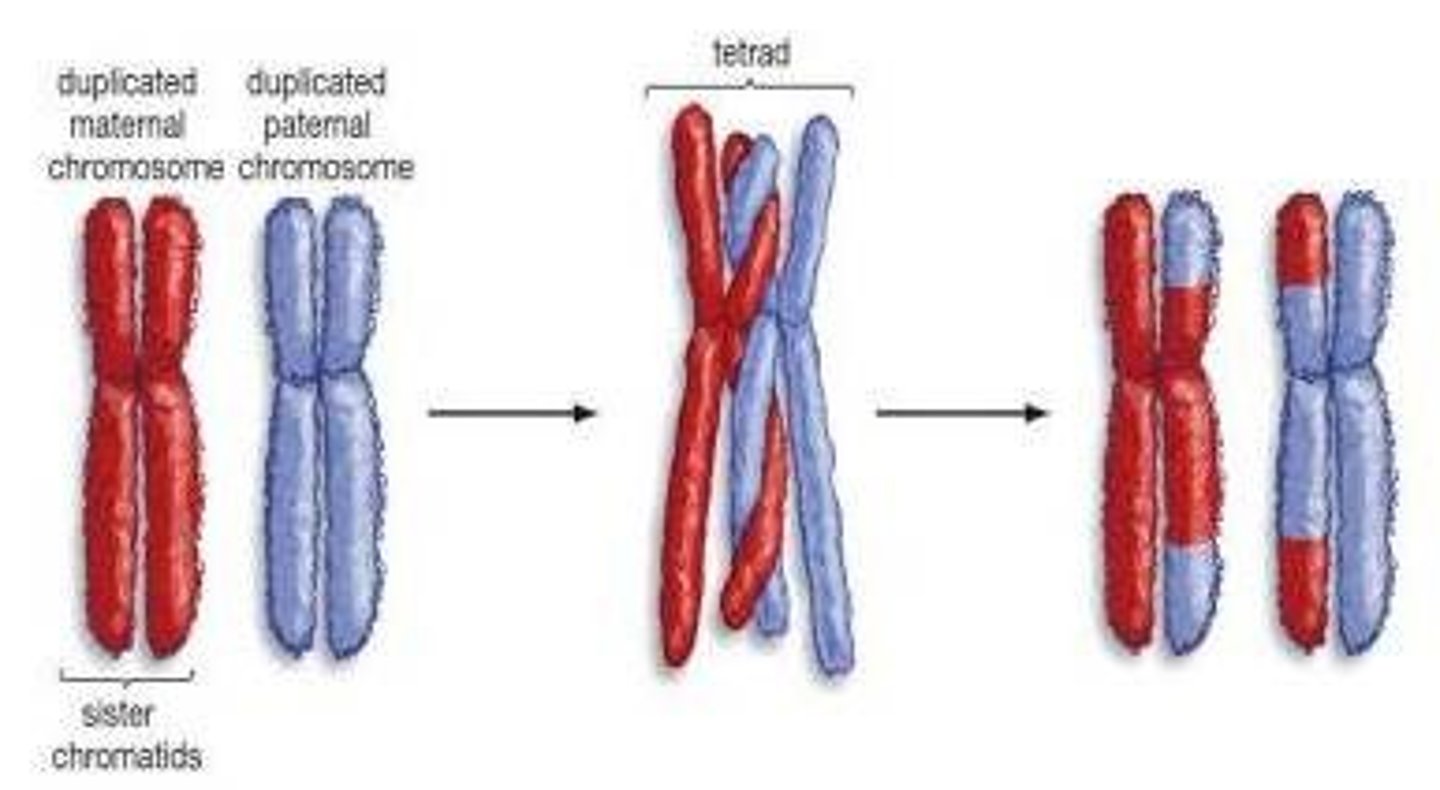
Crossing Over (Description)
The process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during prophase I of meiosis
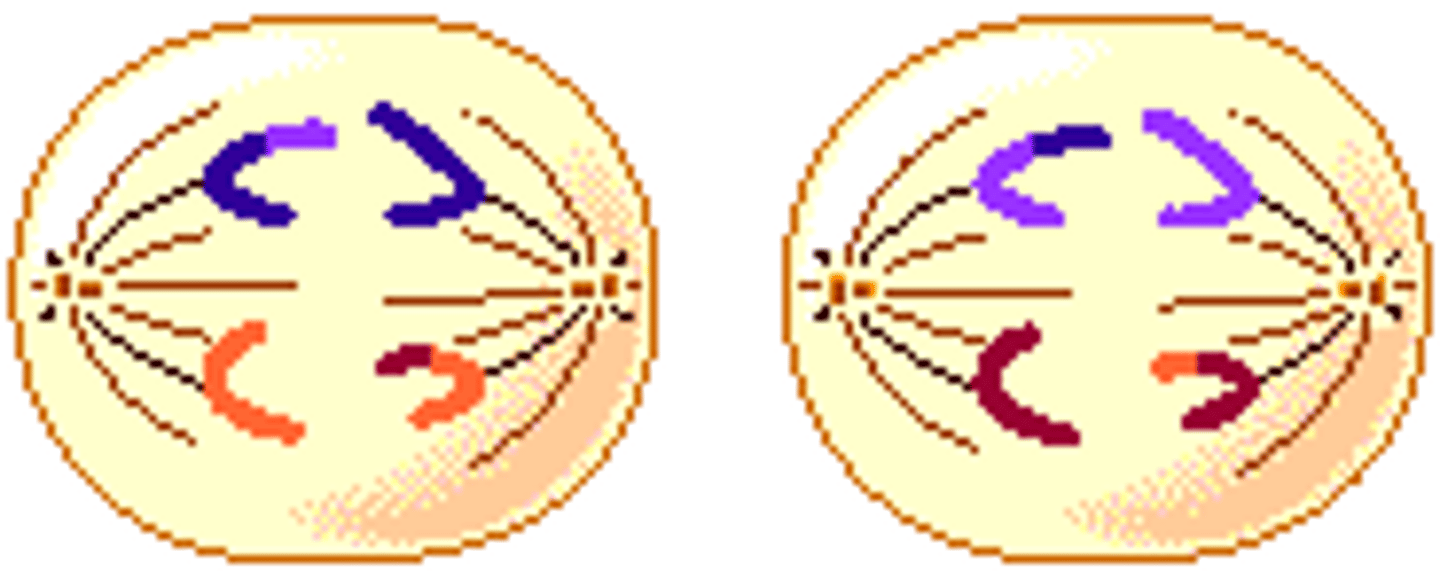
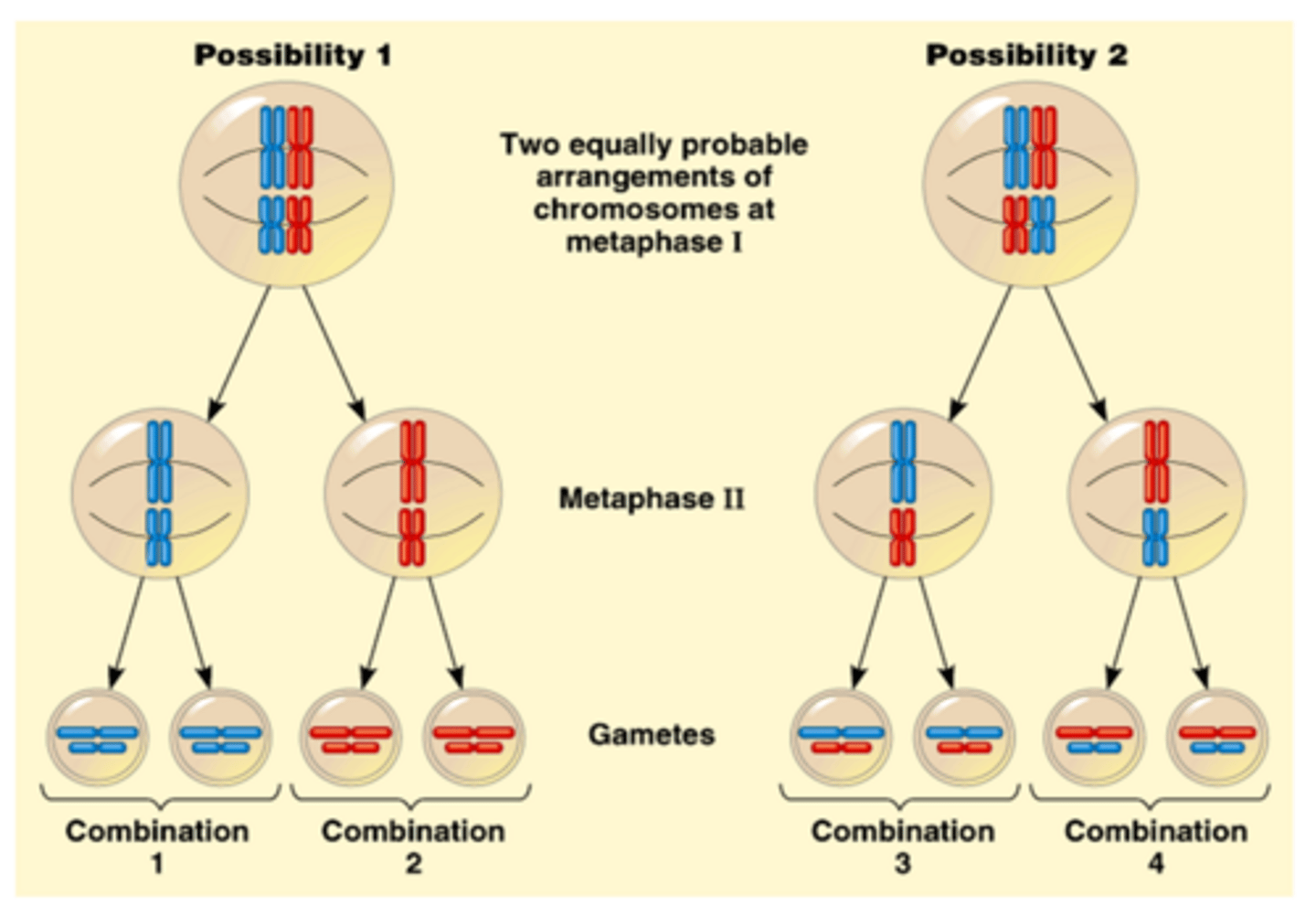
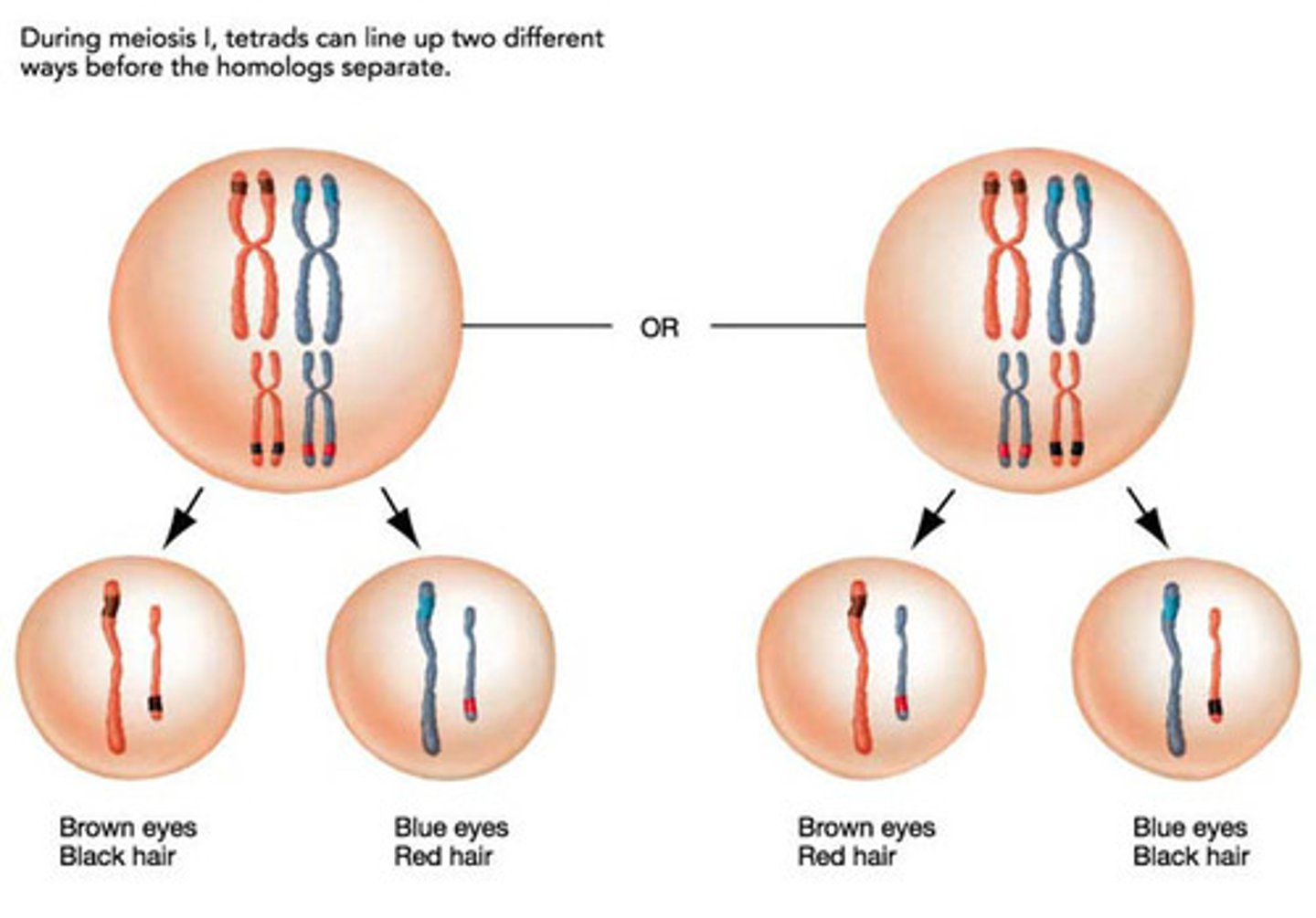
Independent Assortment (Description)
The random distribution of genes on the homologous chromosomes that occurs during metaphase I of meiosis; creates genetic variation
Genetic Variation (Description)
Genetic variation refers to diversity in gene frequencies. Genetic variation can refer to differences between individuals or to differences between populations. Mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation, but mechanisms such as sexual reproduction and genetic drift contribute to it as well.
Interphase I (Meiosis)
Similar to mitosis interphase; nucleus and nucleolus visible; chromosomes replicate during S phase of interphase; each duplicated chromosome consist of two identical sister chromatids attached at their centromeres; centriole pairs also replicate
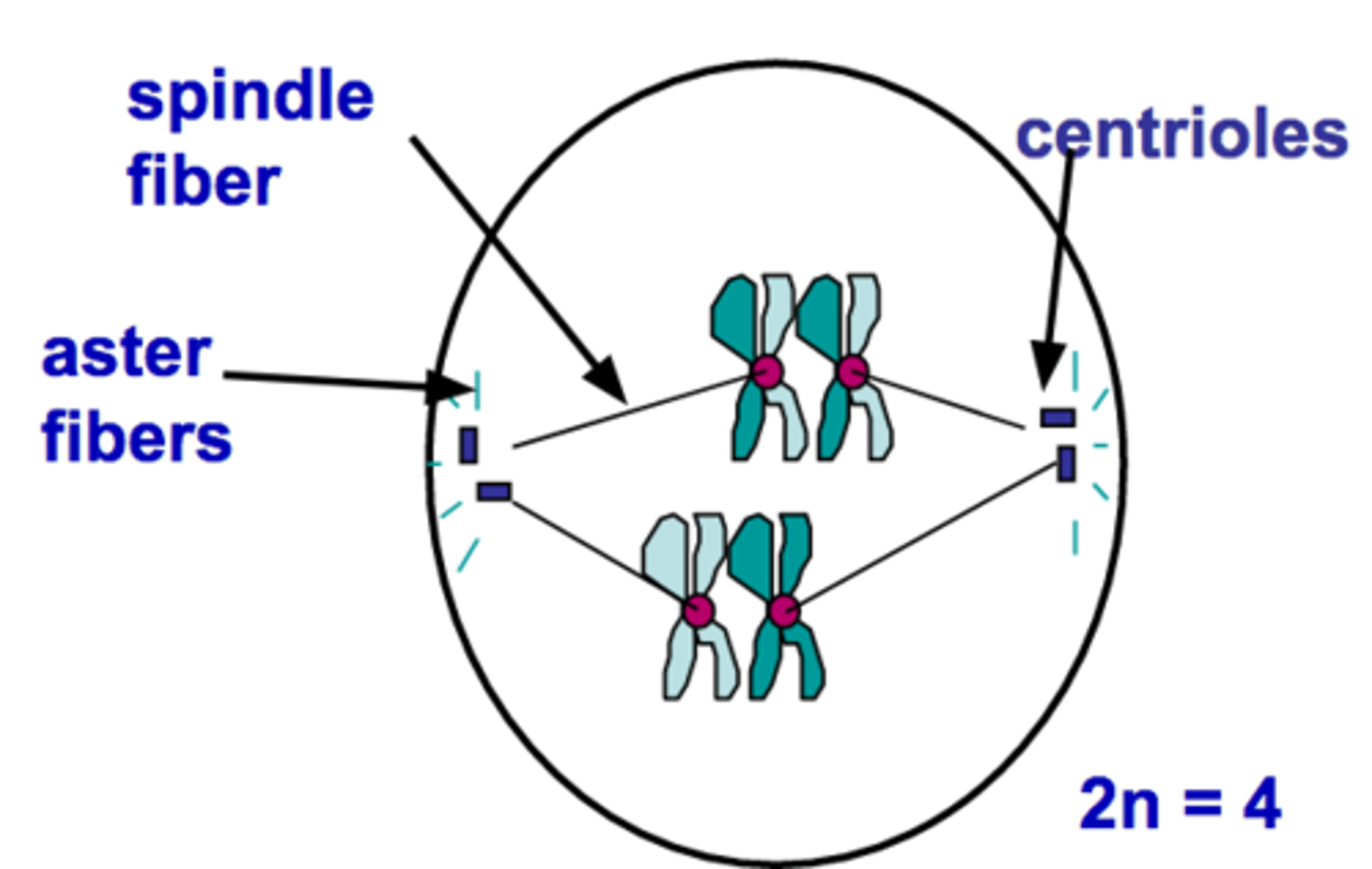
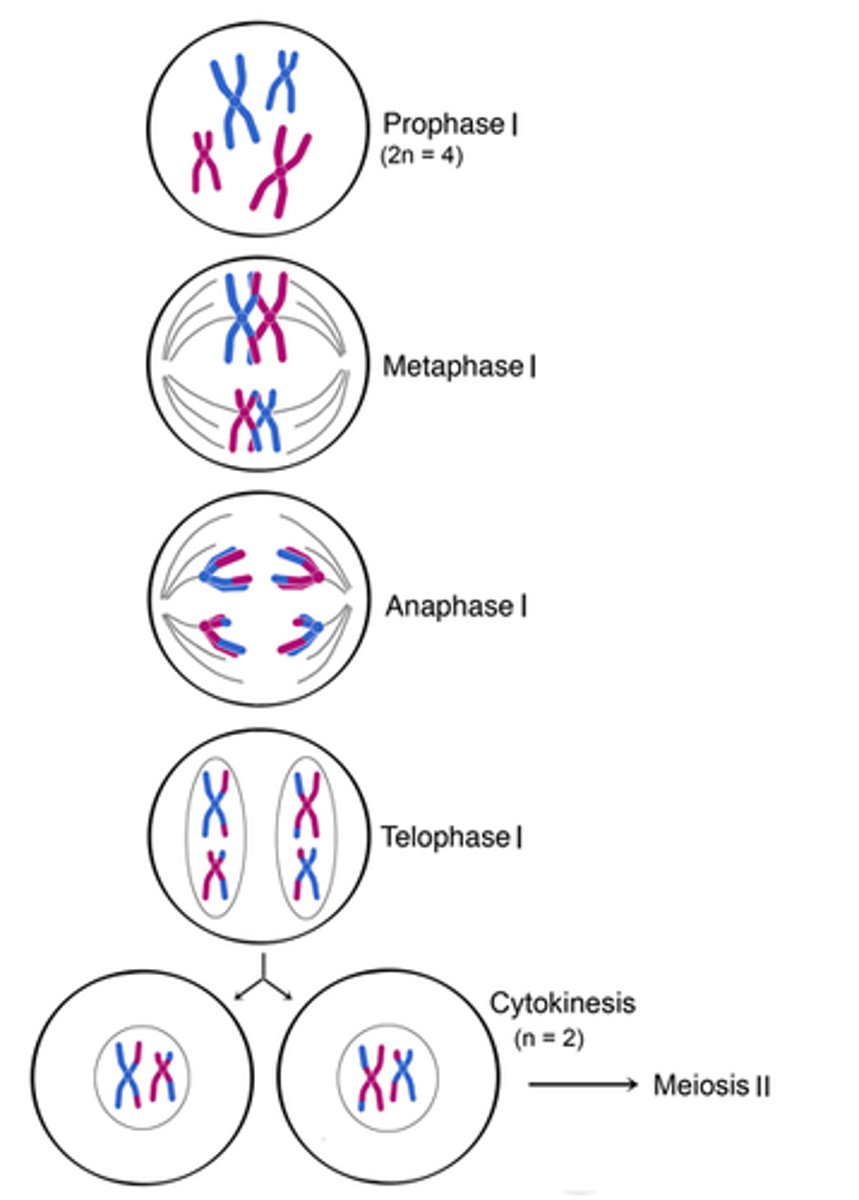
Prophase I (Meiosis)
Longest, most complex phase of meiosis; 90% of the meiotic process is spent in this phase; chromosomes condense; synapsis occurs and homologous chromosomes come together to form a tetrad; during synapsis, crossing over occurs and genetic material is exchanged between non-sister chromatids at site of crossover called chiasmata
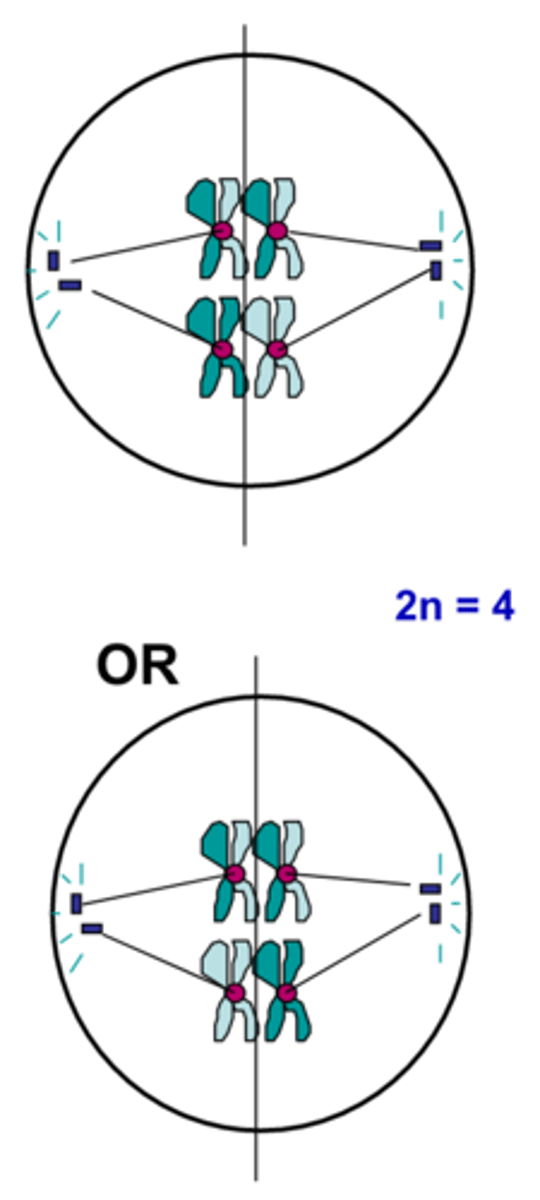
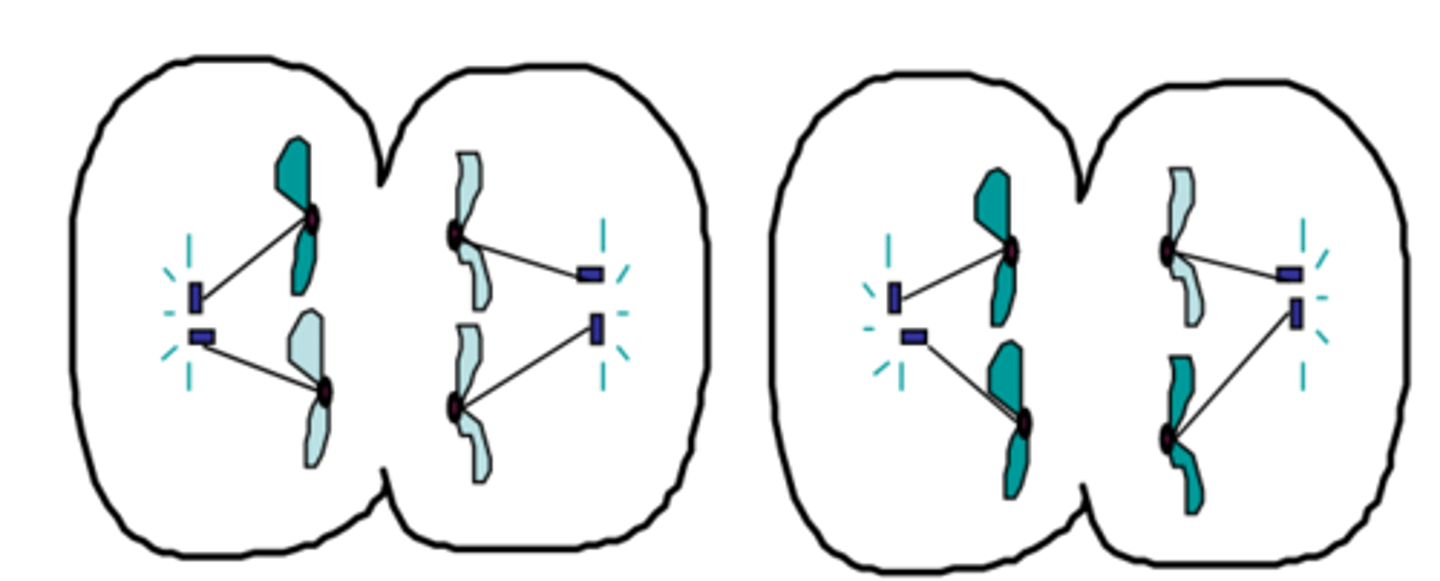
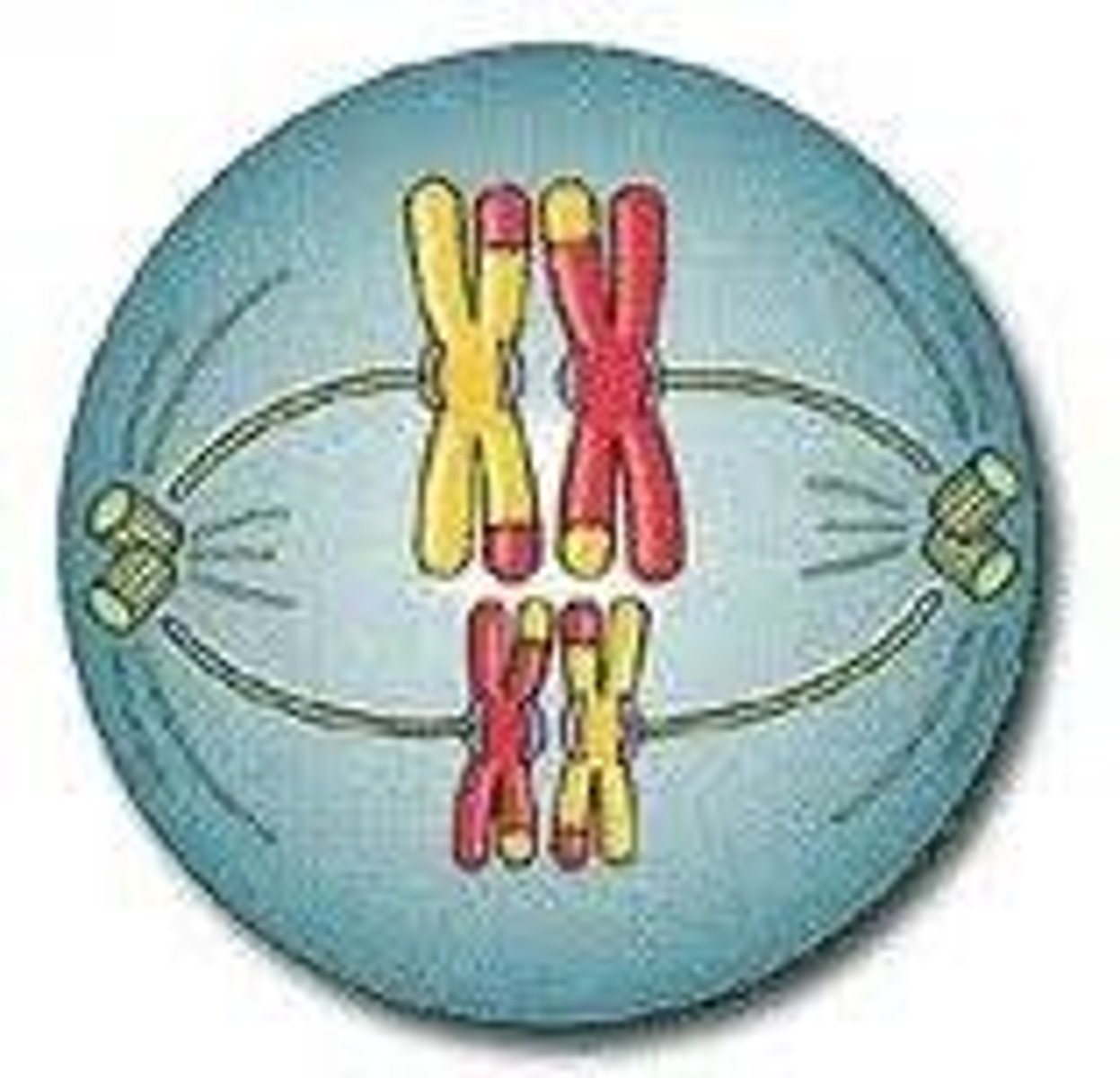
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
The shortest phase of meiosis; tetrads align on the equator randomly resulting in independent assortment; creates genetic variation
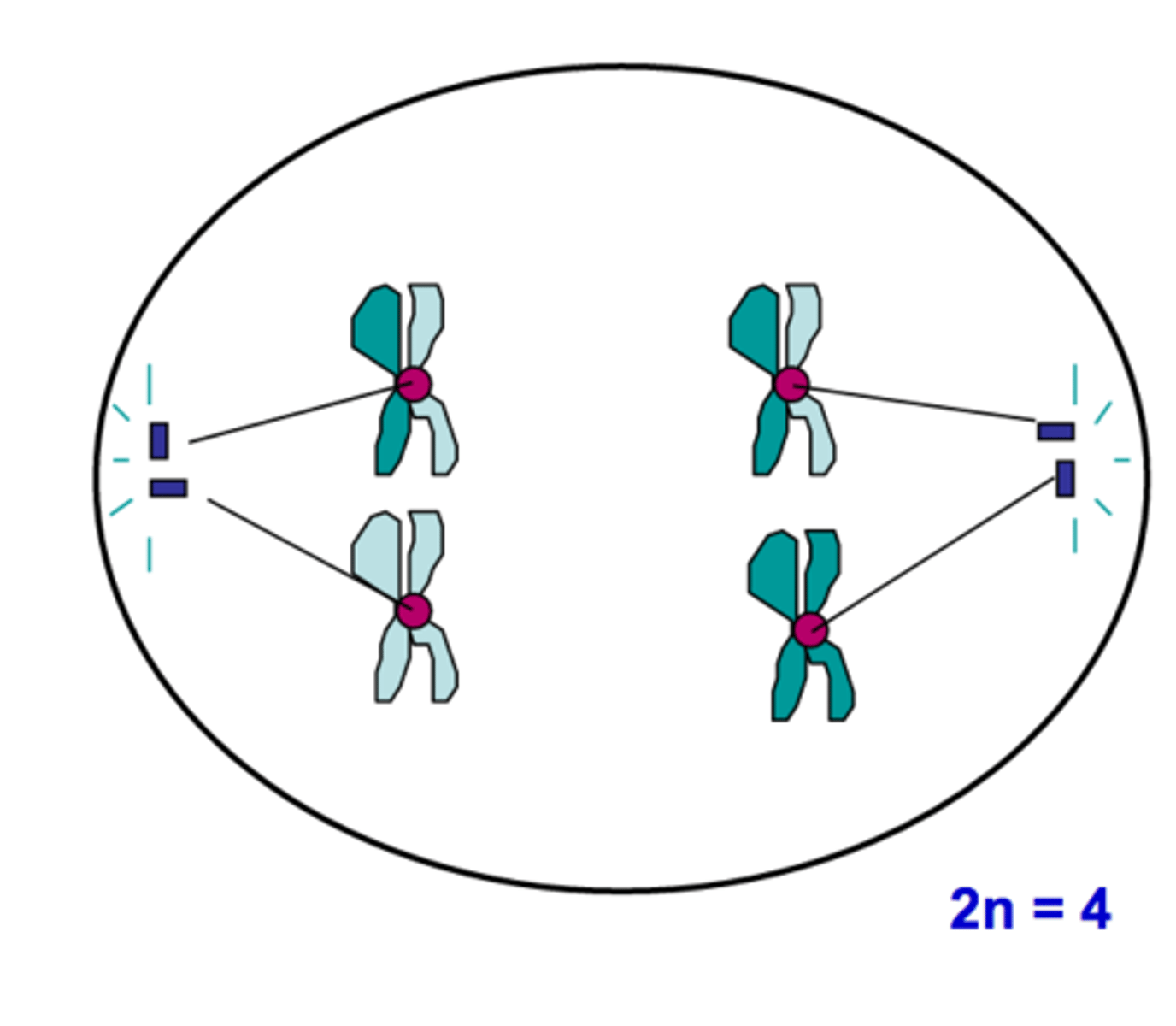
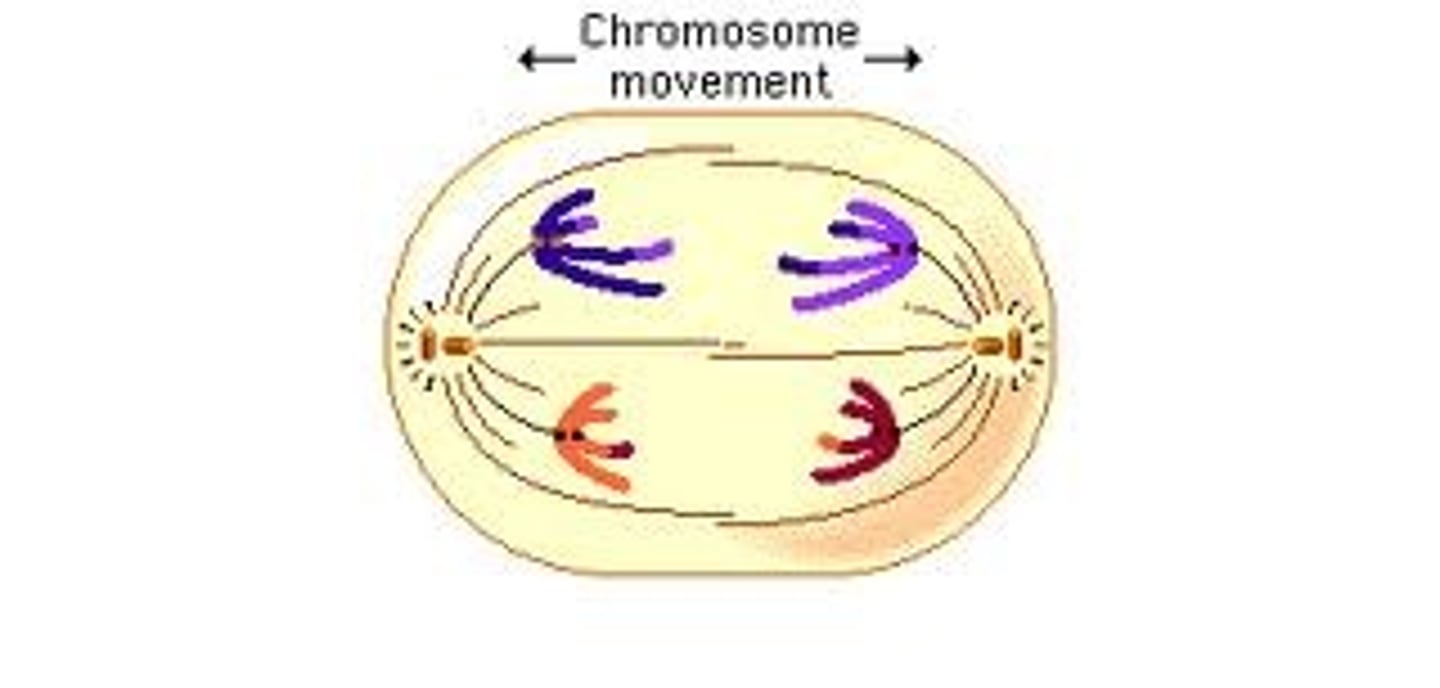
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
The phase of meiosis in which homologous chromosomes separate and move towards the poles; sister chromatids remain attached at their centromeres
Telophase I (Meiosis)
The phase of meiosis in which each pole has diploid set of chromosomes; remember the chromosomes were duplicated before entering Meiosis I
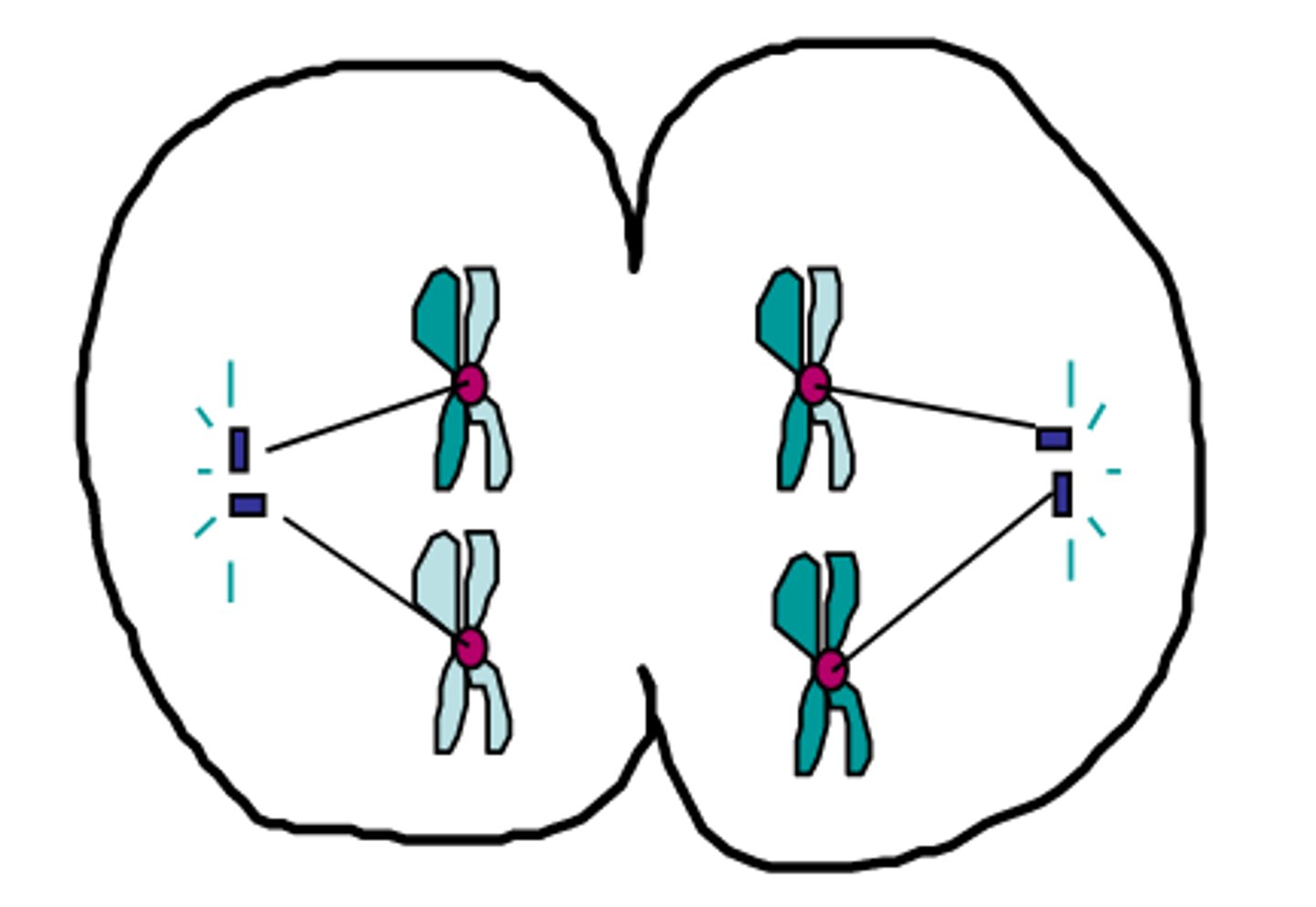
Cytokinesis
The phase in meiosis in which two daughter cells are formed each containing a diploid number of chromosomes
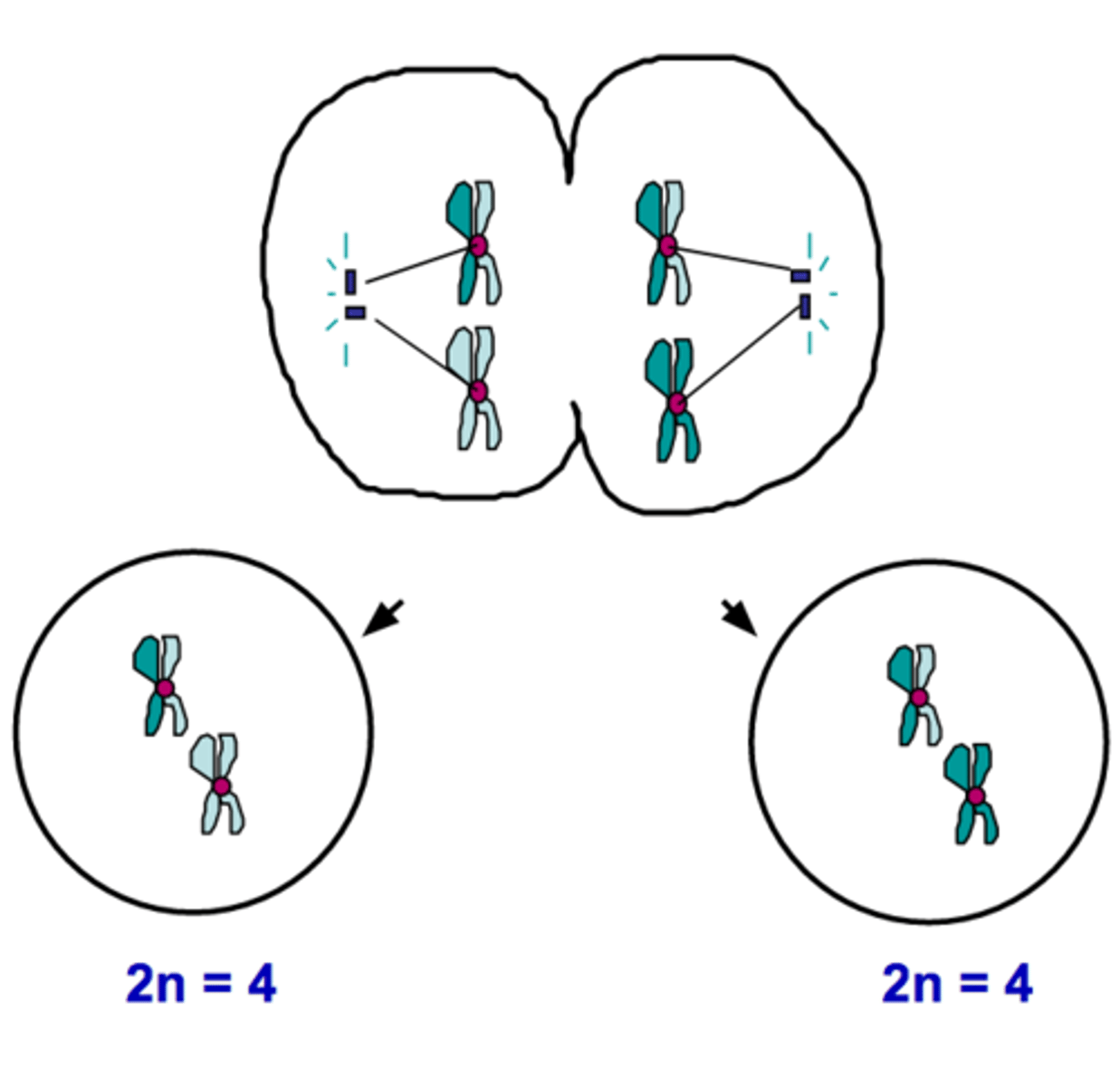
Meiosis I
The first division of a two-stage process of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms in which homologous chromosomes undergoing crossing over, independent assortment and ultimately separating into two different cells
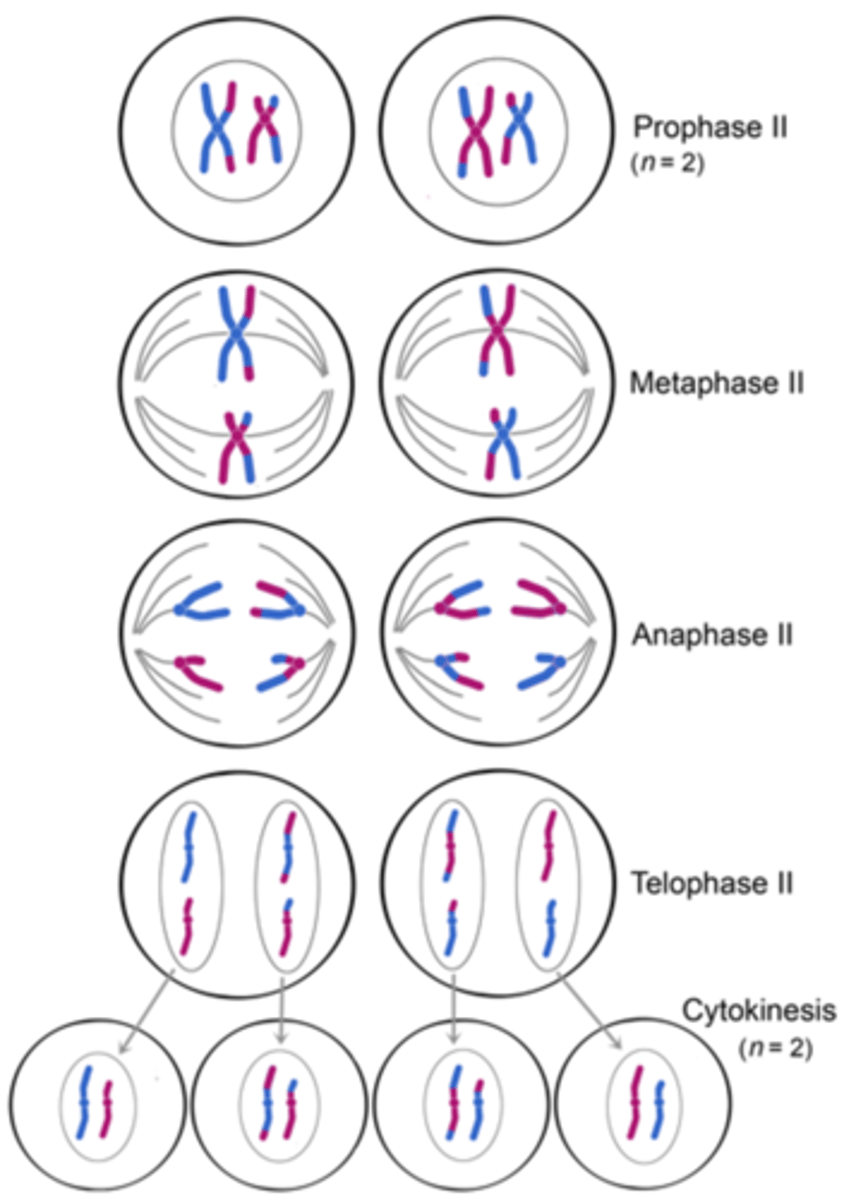
Meiosis II
The second division of a two-stage process of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms in which chromatids separating resulting in cells with half the chromosome number of the original cell
Interphase II
During Meiosis II there is no Interphase II or it is very short; there is also no replication of DNA between Meiosis I and Meiosis II
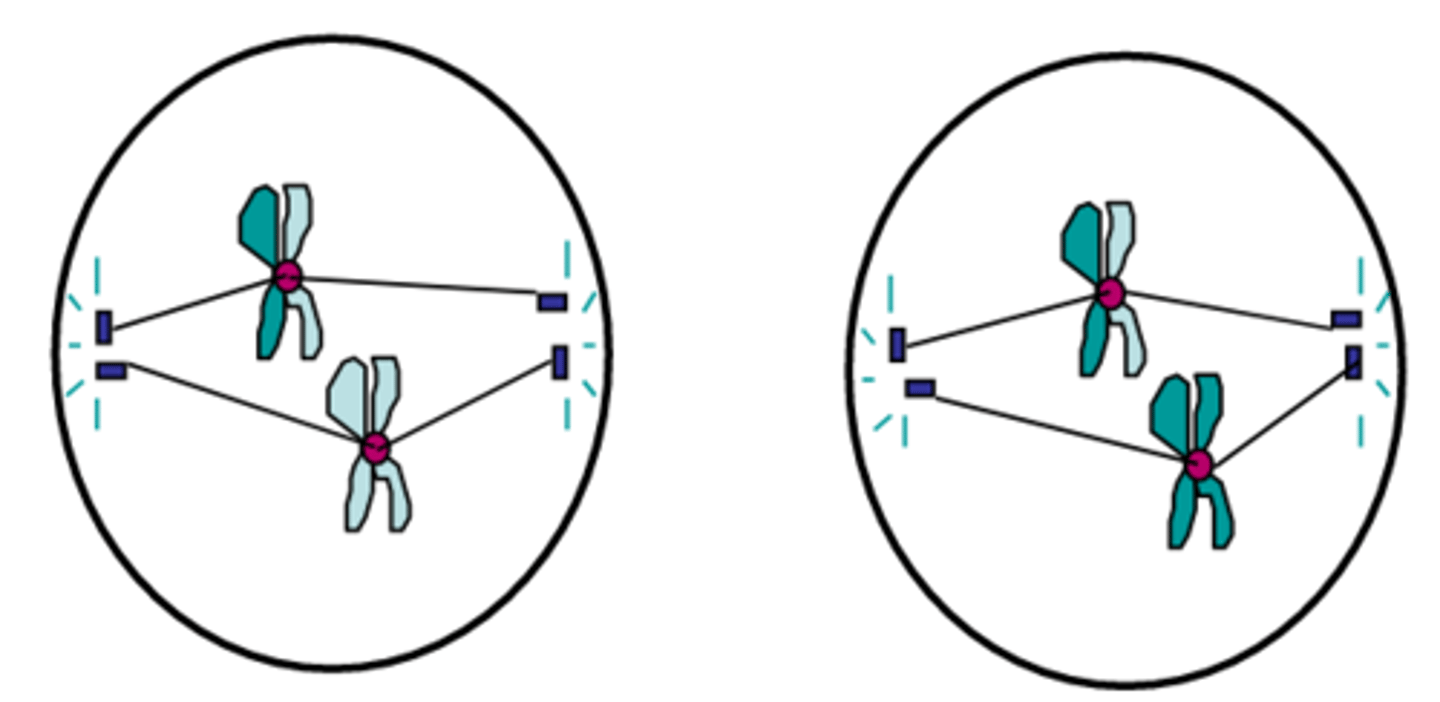
Prophase II
The first phase of meiosis II in which centrioles appear, spindle fibers form and chromosomes begin migrating to the midline of the cell; identical to mitotic prophase except in meiosis I the number of chromosomes was reduced by half
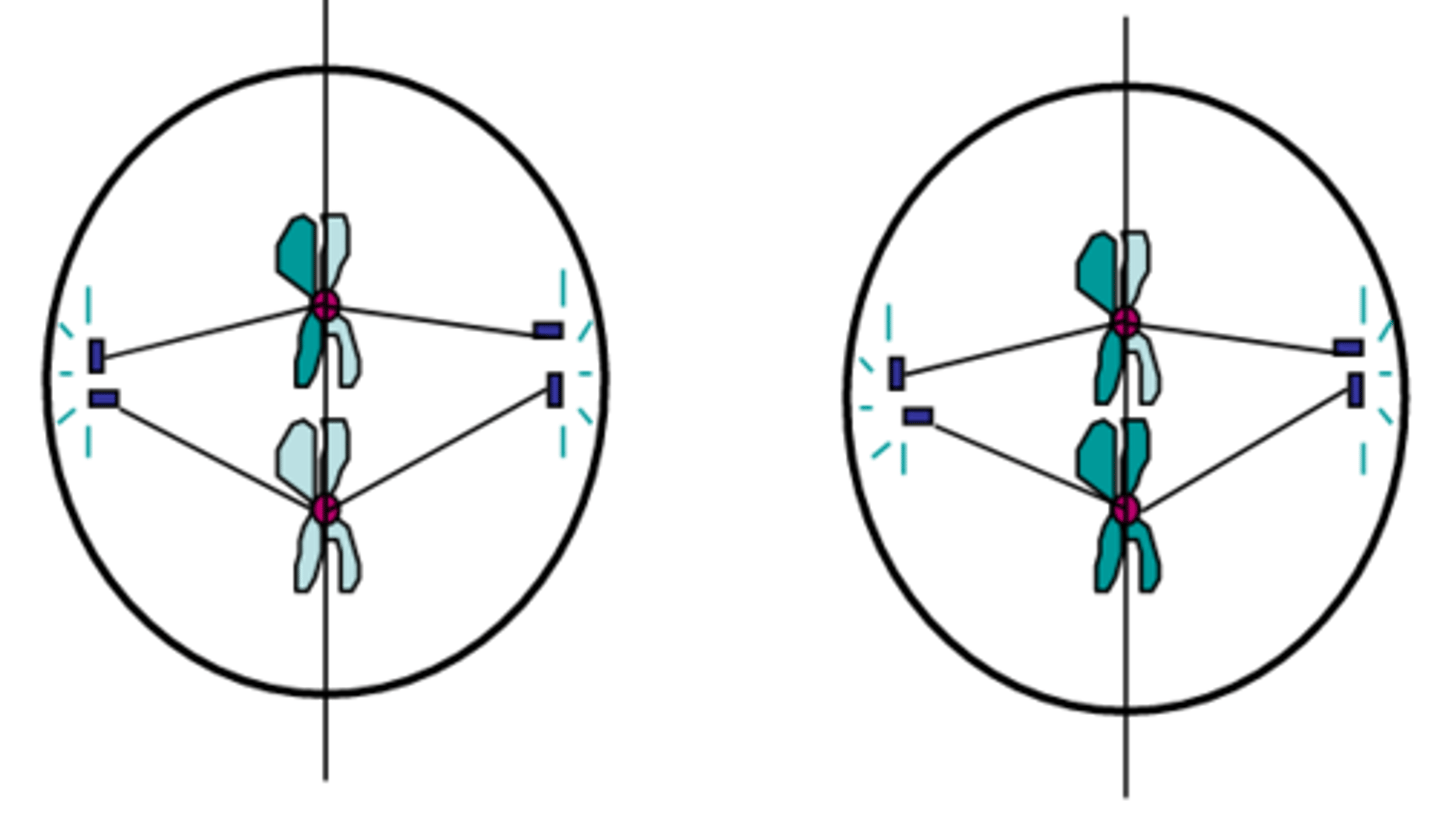
Metaphase II
The second stage of meiosis II; chromosomes made up of two sister chromatids line up across the centre of the cell; spindle fibres from the opposite poles of the cell attach to one of each pair of chromatids; identical to mitotic metaphase except in meiosis I the number of chromosomes was reduced by half
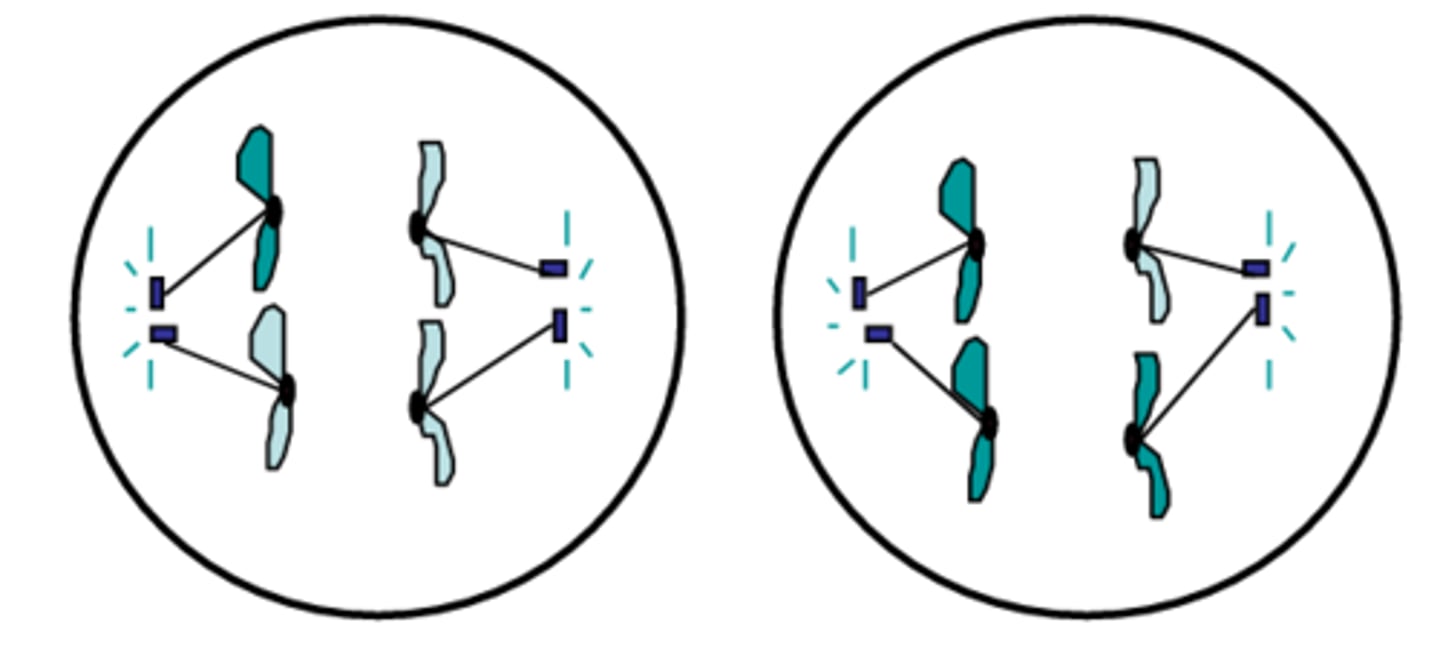
Anaphase II
The third phase of meiosis II in which the sister chromatids are finally separated at their centromeres and pulled to opposite sides of the cell; identical to mitotic anaphase, except in meiosis I the number of chromosomes was reduced by half
Telophase II
The fourth phase of meiosis II in which the chromosomes decondense, the nuclear envelope reappears and centrioles disappear ; identical to mitotic telophase except the number of chromosomes was reduced by half
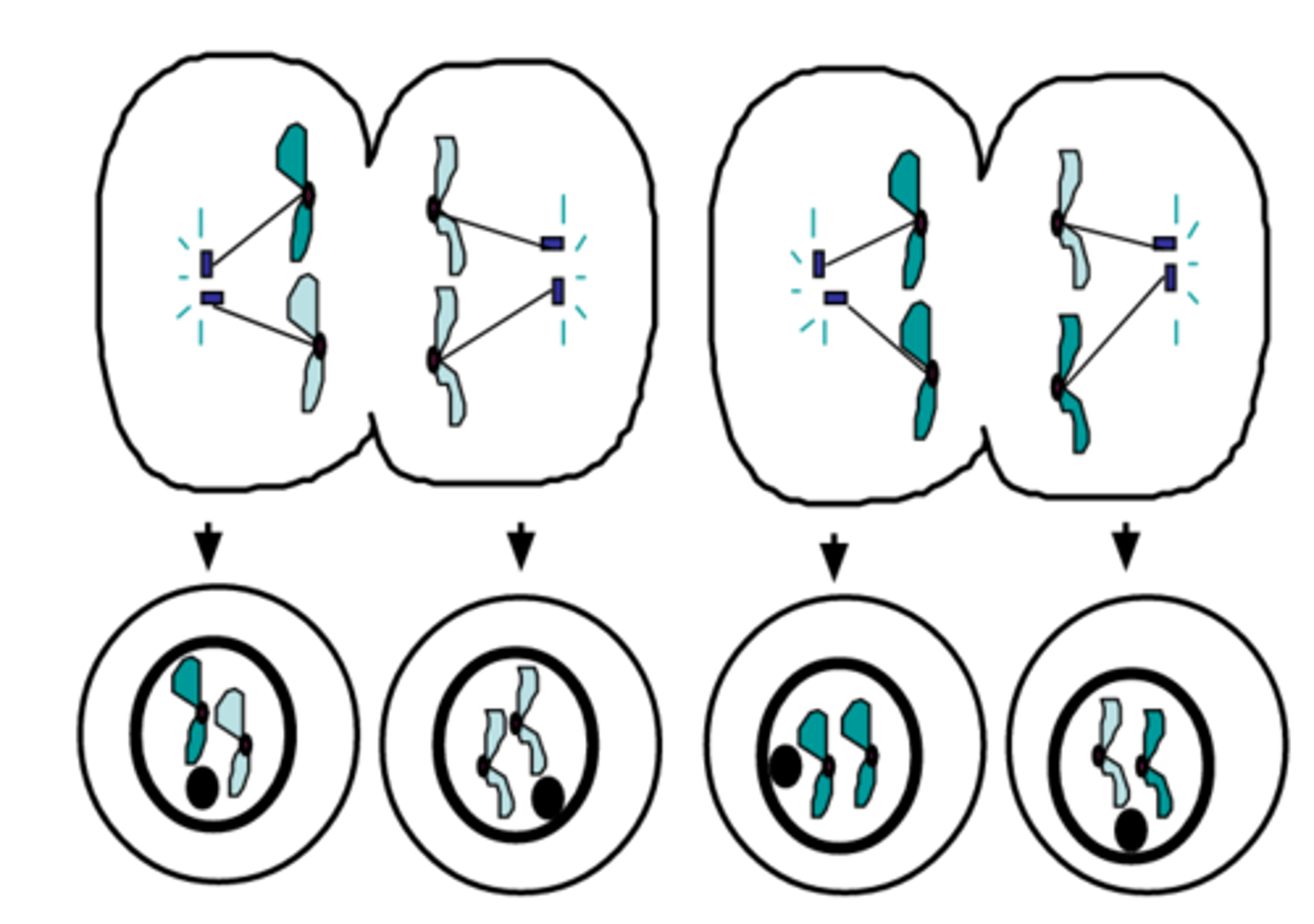
Cytokinesis II
The final stage of meiosis II in which cell division occurs resulting in four haploid cells; each containing half the number of chromosomes
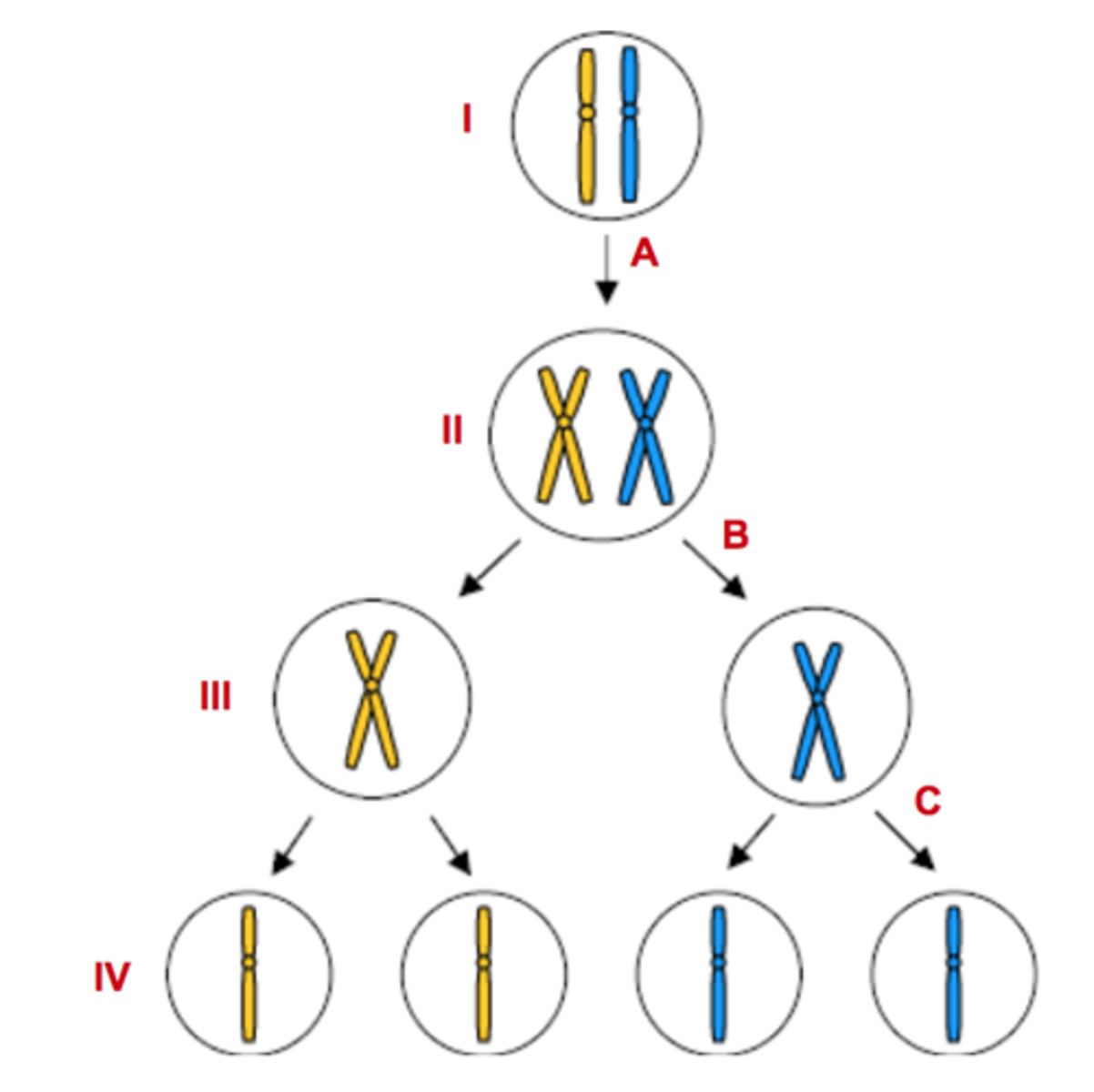
Letter A
Represents DNA Replication
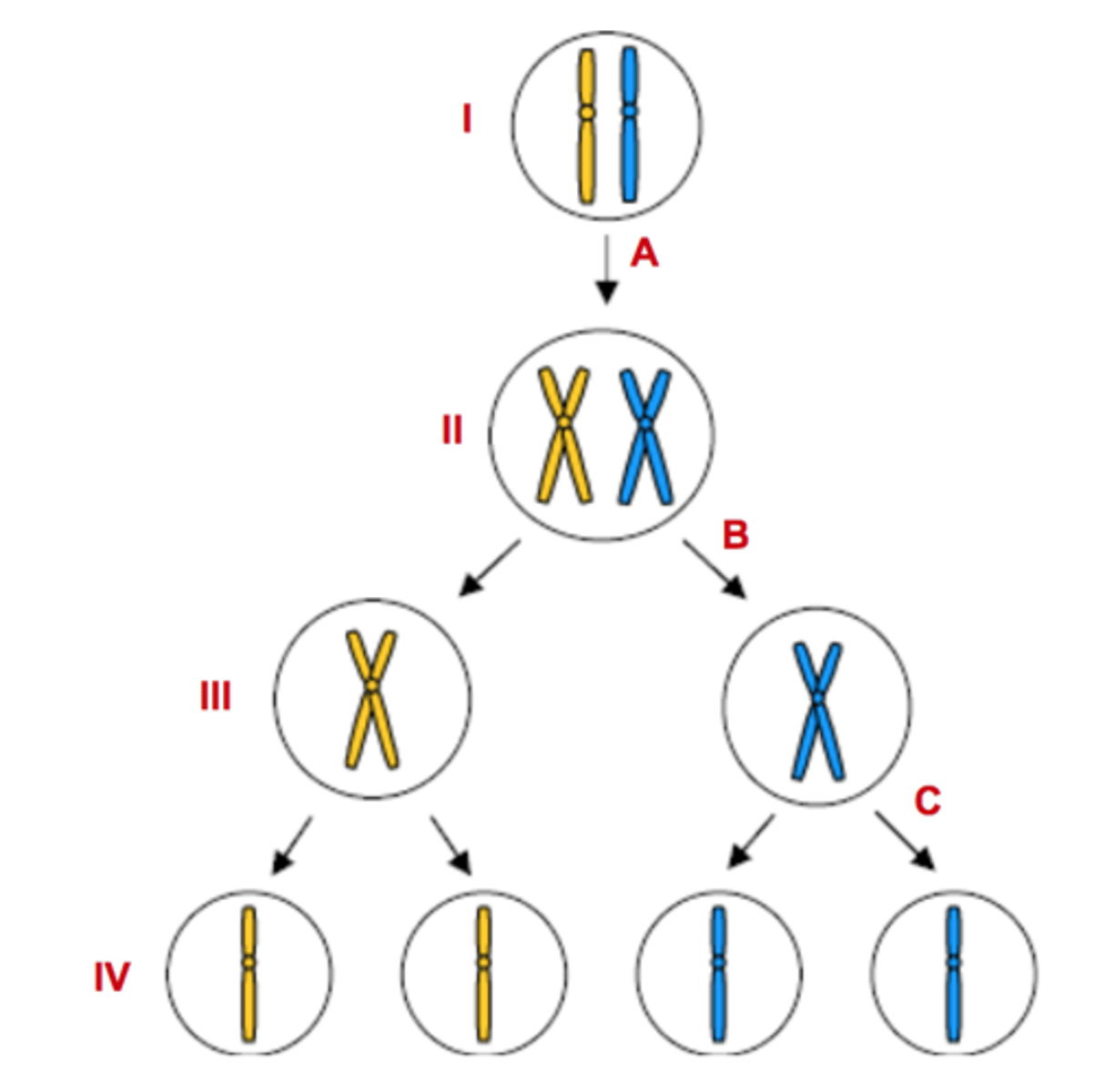
Letter B
Represents Meiosis I
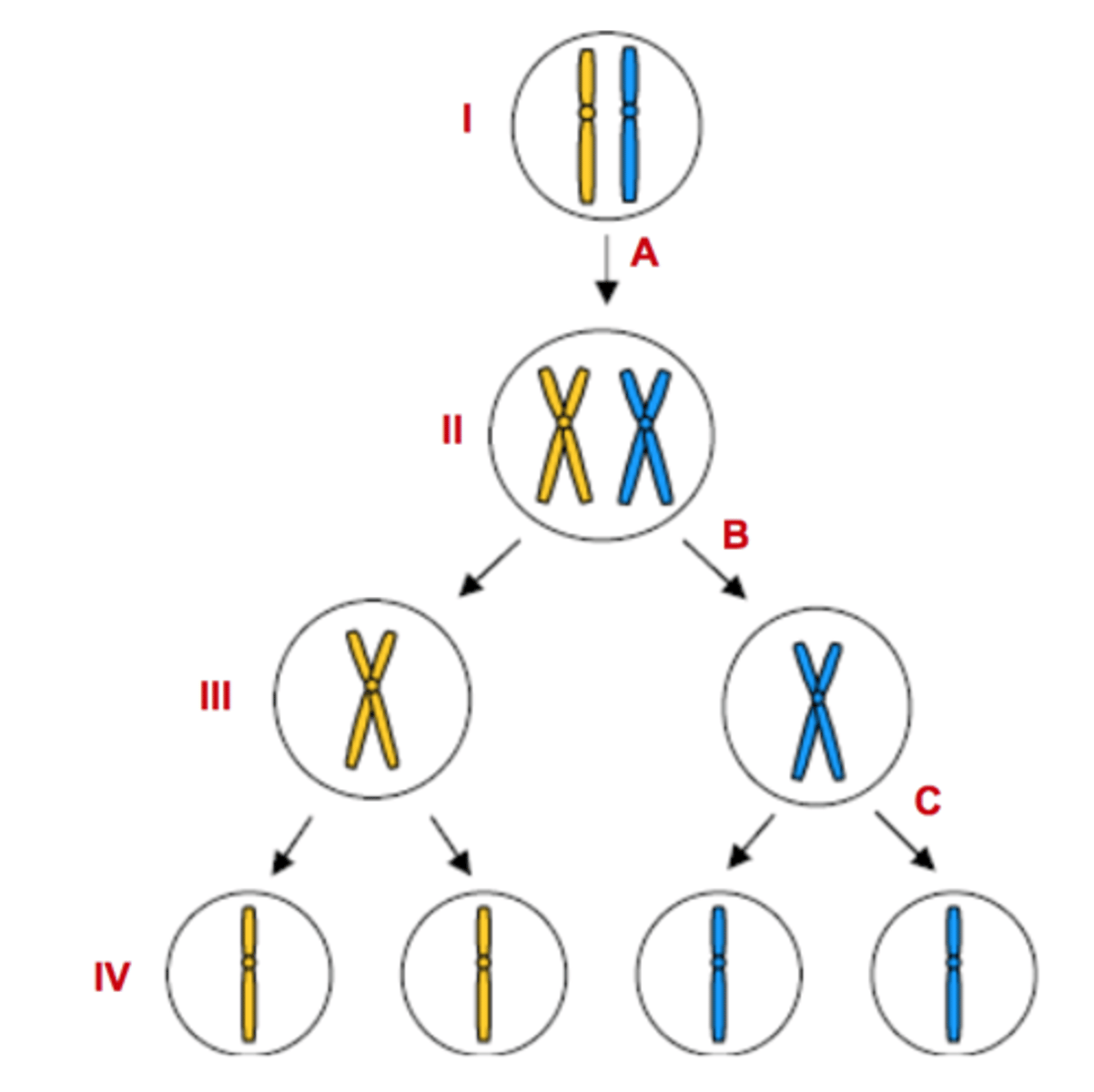
Letter C
Represents Meiosis II
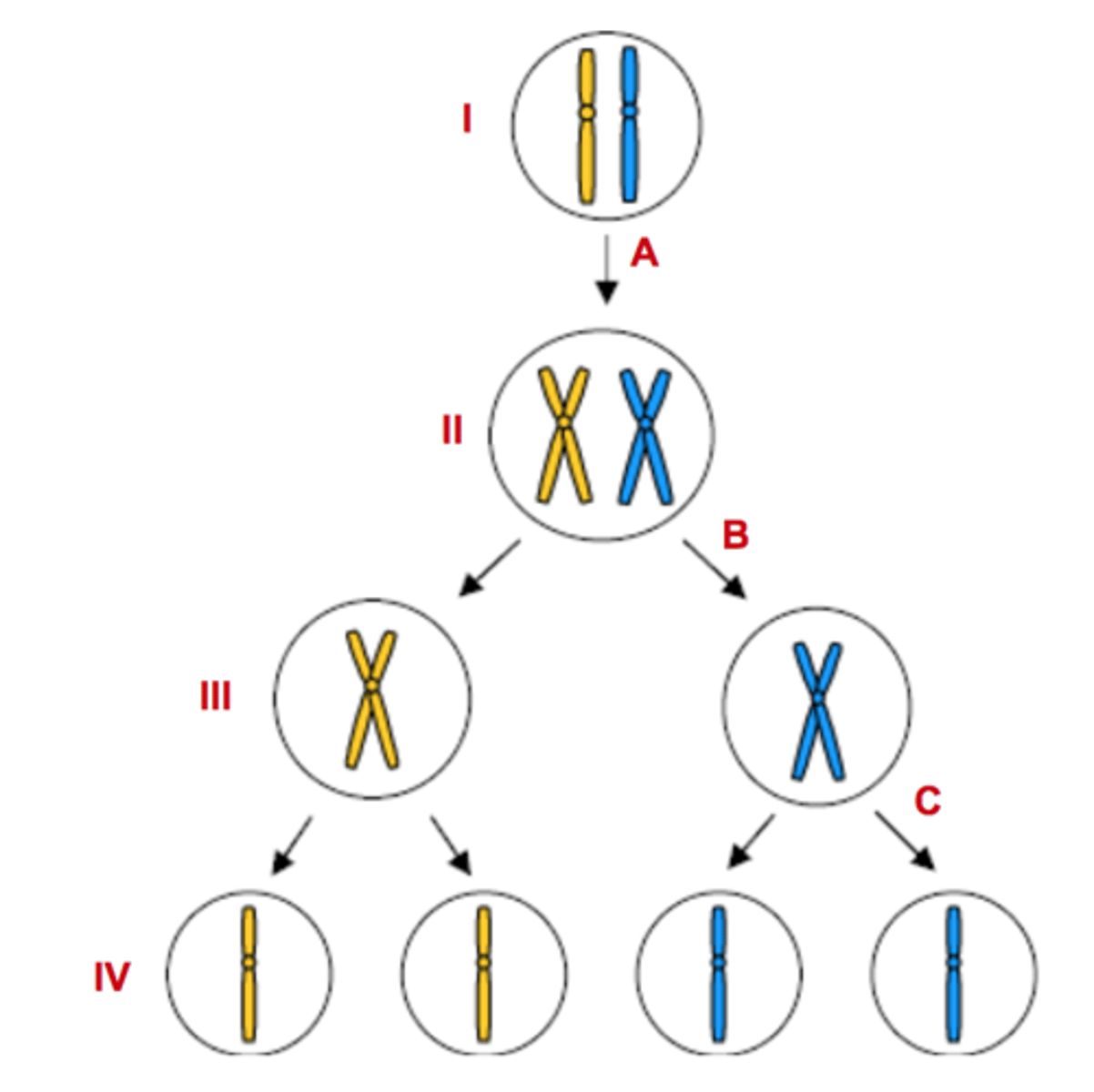
Numbers III & IV
Represents haploid cells
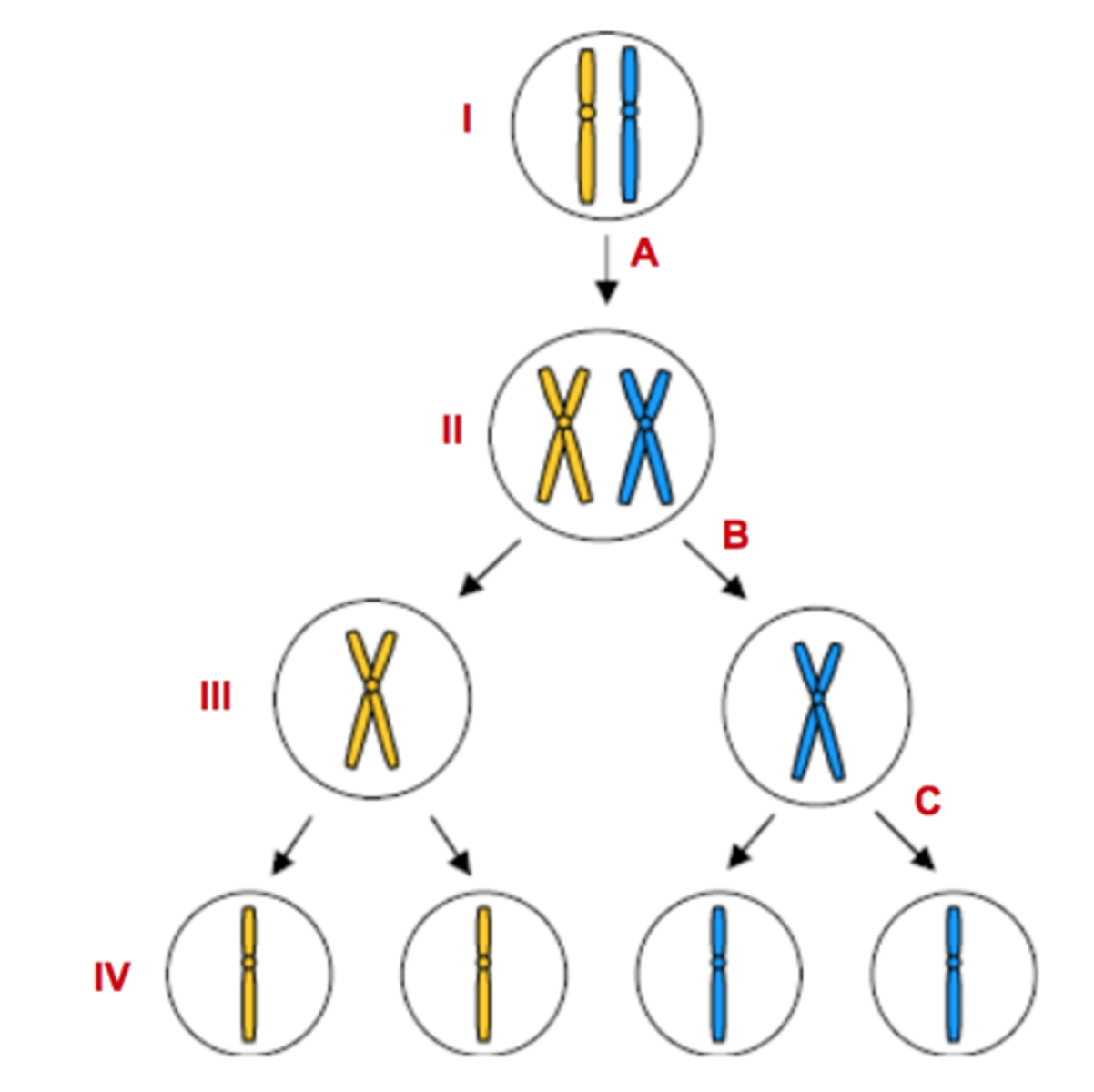
Numbers I & II
Represents diploid cells
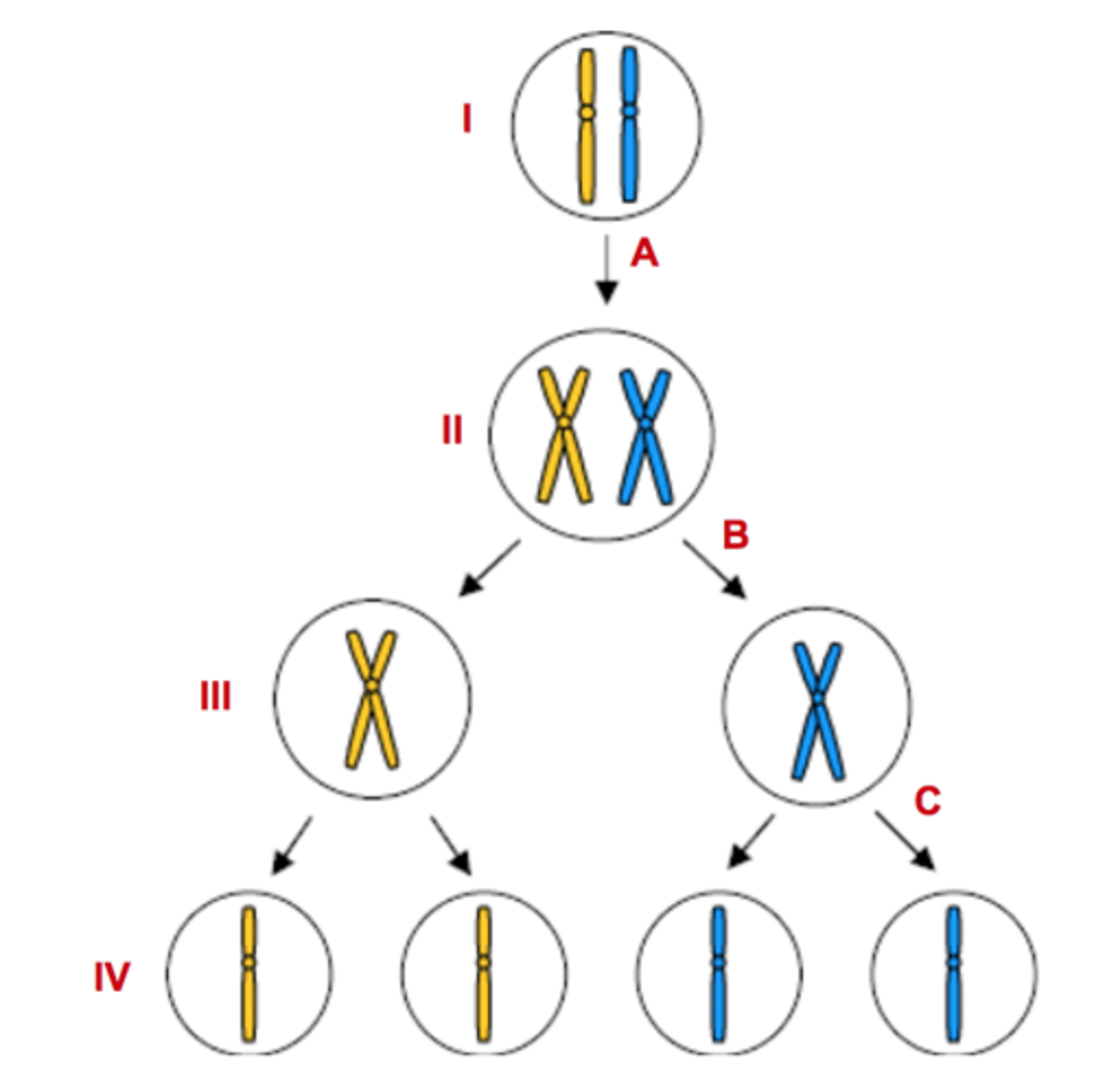
Number II
Tetrad forms
Sexual Reproduction (Causes of Genetic Variation)
Crossing over
Independent Assortment
Fertilization
Crossing Over (Phase)
Occurs during Prophase I
Independent Assortment (Phase)
Occurs during Metaphase I
Metaphase I (Chromosomes)
Tetrads Align on Equator
Anaphase I (Chromosomes)
Homologous pairs separate
Prophase I (Chromosomes)
Homologous pairs come together

Anaphase II (Chromosomes)
Sister chromatids separate