CA1 - DEVPSYCH 3 (LEARNING THEORIES)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Session 3 - Learning Theories
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
(3) Behaviorism Precursors
E.L. Thorndike
John Watson
B.F. Skinner
E.L. Thorndike
BEHAVIORISM PRECURSORS
the proponent of the concepts of rewards (satisfiers) and punishments (annoyers)
John Watson
BEHAVIORISM PRECURSORS
this proponent stated that human behavior can be studied objectively; made experiments to prove Thorndike’s theory
B.F. Skinner
BEHAVIORISM PRECURSORS
this proponent insisted that human behavior should be studied scientifically
(2) Kinds of Conditioning
Classical
Operant
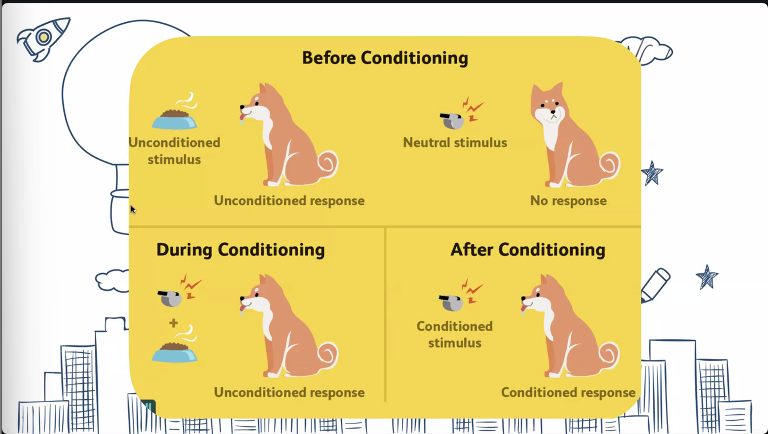
Classical Conditioning
KINDS OF CONDITIONING
a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus a number of times until it is capable of bringing about a previously unconditioned response
Operant Conditioning
KINDS OF CONDITIONING
involves concepts such as:
shaping
reinforcement
punishment
Shaping
OPERANT CONDITIONING
procedure in which the experimenter first rewards gross approximations of the behavior, then close approximations, and then finally, the desired behavior itself; gradually shapes the final complex set of behaviors
Reinforcement
OPERANT CONDITIONING
strengthens the behavior and rewards the person
Positive Reinforcement
something pleasant is added to reinforce the behavior
Negative Reinforcement
something unpleasant is removed to reinforce the behavior
Punishment
OPERANT CONDITIONING
does not strengthen a response, although it does not weaken it because its effect is less predictable; no accuracy is possible
(4) Schedules of Reinforcement
Fixed-ratio
Variable-ratio
Fixed-interval
Variable-interval
Fixed-ratio
SCHEDULE OF REINFORCEMENT
reinforced every after nth response
Variable-ratio
SCHEDULE OF REINFORCEMENT
reinforced after the nth response on the average
Fixed-interval
SCHEDULE OF REINFORCEMENT
reinforced after a designation period of time
Variable-interval
SCHEDULE OF REINFORCEMENT
reinforced after the lapse of random or varied periods of time
Albert Bandura
stated we can learn through observation; vicarious learning; proponent of Social Cognitive Theory
Observational Learning
observation allows people to learn without performing any behavior
Modeling
adding and subtracting from the observed behavior
Chance Encounter
unintended meeting of persons unfamiliar to each other
Fortuitous Event
environmental experience that is unexpected and unintended
Self-Efficacy
people’s beliefs in their capability to exercise some measure of control over their own functioning and over environmental events
(4) Sources of Self-efficacy
Mastery Experiences
Social Modeling
Social Persuasion
Physical and emotional states
Mastery Experiences
SOURCE OF SELF-EFFICACY
past performances
Social Modeling
SOURCE OF SELF-EFFICACY
vicarious experiences provided by other people
Social Persuasion
SOURCE OF SELF-EFFICACY
persuasion from others
Physical and Emotional States
SOURCE OF SELF-EFFICACY
people’s physiological and emotional states
Lawrence Kohlberg
stated that the basis of moral behavior is justice and fairness; gave morally ambiguous situations to determine stages of development; Heinz Dilemma; proponent of Moral Development Theory
(6) Stages of Moral Development
Level 1: Preconventional Morality (2 to 10 years old)
Stage 1: Obedience and Punishment Orientation
Stage 2: Instrumental-Relativist Orientation
Level 2: Conventional Morality (9 years and older)
Stage 3: Good Boy/Good Girl Orientation
Stage 4: Law and Order Orientation
Level 3: Postconventional Morality (12 years and older)
Stage 5: Social Contract Orientation
Stage 6: Principled Conscience-Driven Orientation
Stage 1: Obedience and Punishment Orientation
STAGES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT
moral judgements are driven by a need to avoid punishment; under Level 1: Preconventional Morality (2 to 10 years old)
Stage 2: Instrumental-Relativist Orientation
STAGES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT
moral judgements are driven by the desire to meet personal needs; under Level 1: Preconventional Morality (2 to 10 years old)
Stage 3: Good Boy/Good Girl Orientation
STAGES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT
driven by a need to be accepted by others; under Level 2: Conventional Morality (9 years and older)
Stage 4: Law and Order Orientation
STAGES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT
driven by a desire to adhere to the law or the authorities; under Level 2: Conventional Morality (9 years and older)
Stage 5: Social Contract Orientation
STAGES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT
adherence to laws that are set up as social contracts for the common good; under Level 3: Postconventional Morality (12 years and older)
Stage 6: Principled Conscience-Driven Orientation
STAGES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT
arise from adherence to personal principles; under Level 3: Postconventional Morality (12 years and older)
Carol Gilligan
stated that basis of moral behavior is care and empathy; proponent of Ethics of Care; believes that it is normal for women to have care and empathy which makes them faster to have progress on stages over men
(3) Stages of Ethics of Care
Empathy and the ability to care
Level 1: Pre-conventional
Level 2: Conventional
Level 3: Post Conventional
Level 1: Pre-conventional
STAGES OF ETHICS OF CARE
only the needs of the self are recognized
Level 2: Conventional
STAGES OF ETHICS OF CARE
the needs of other are prioritized, and the needs of the self are denied
Level 3: Post Conventional
STAGES OF ETHICS OF CARE
balance between the needs of the self and the needs of others
Jean Piaget
proponent of Stages of Moral Reasoning
(3) Stages of Moral Reasoning
Stage 0: Premoral Development (until around 4 years old)
Stage 1: Heteronomous Stage (4-10 years old)
Stage 2: Autonomous Stage (around age 10 or 11)
Stage 0: Premoral Development (until around 4 years old)
STAGES OF MORAL REASONING
unaware that rules exist
Stage 1: Heteronomous Stage (4-10 years old)
STAGES OF MORAL REASONING
rules are inviolate and unalterable; egocentric in their use of rules; ignore intentions and focus only on consequences; immanent justice
Stage 2: Autonomous Stage (around age 10 or 11)
STAGES OF MORAL REASONING
rules as human conventions; well-developed notions of fairness and appropriate justice; belief in immanent justice also diminishes