BIOL 1442 Exam 3 Sixth Extinction Questions and other stuff
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is an ammonite?
a type of zooplankton (small aquatic heterotroph)
a hard-shelled mollusk closely related to a squid
a small dinosaur
a type of phytoplankton (small aquatic photoautotroph)
a hard-shelled mollusk closely related to a squid
Name the key biological concept that "did not crop up during the Middle Ages or during the Renaissance..." but rather came to light during the 1700s, as a means to explain the existence of certain fossils.
uniformitarianism
transmutation
taxonomy
extinction
extinction
In this story, the "luck of the ammonites" was
No answer text provided.
neither good nor bad
good luck
bad luck
bad luck
Match each scientist with his perspective or historical contribution.
1, Georges Cuvier
2. Jean Baptiste Lamarck
3. Charles Lyell
4. Carl Linnaeus
catastrophism
transmutation (transformisme)
uniformitarianism
binomial nomenclature and taxonomic categories
An extinct flightless bird that Kolbert nicknamed "the original penguin" is actually called
a kiwi
an auk
a dodo
a puffin
an auk
The "original penguin"
was the only species known to survive a mass extinction event
was thought to be extinct, until a remnant population was recently rediscovered.
was overhunted to extinction by humans.
went extinct with the non-avian dinosaurs.
was overhunted to extinction by humans.
Ammonites
were thought to be extinct until a remnant population was recently discovered.
were overhunted to extinction by humans
survived the mass extinction event that killed the non-avian dinosaurs.
went extinct with the non-avian dinosaurs
went extinct with the non-avian dinosaurs
Identify the creature locally celebrated in the town of El Valle, Panama (where an institute called EVACC was established to prevent the extinction of this animal and its close relatives).
the golden frog
a rare type of crow
a flightless bird called an auk
a type of coral
the golden frog
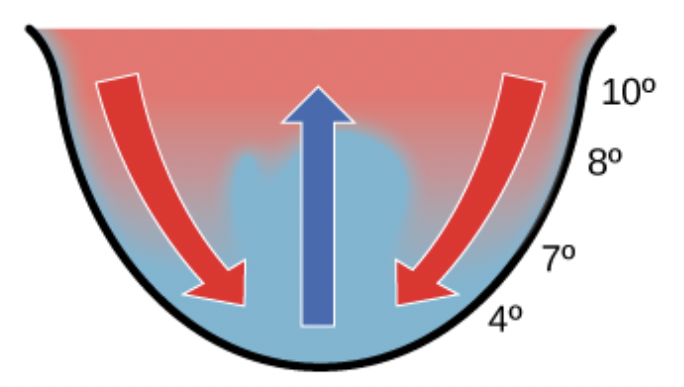
Choose the most appropriate description for this image.
ocean upwelling
bioaccumulation
seasonal turnover in a lake
biomagnification
seasonal turnover in a lake
What do the “Out of Africa” hypothesis & “Frog Leg Soup” hypothesis have in common?
toxic pollution
climate change
habitat destruction
an invasive species
an invasive species
This man discovered extinction but disagreed with "the notion that animals could change their body types when convenient."
Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Carl Linnaeus
Charles Lyell
Georges Cuvier
Georges Cuvier
Elizabeth Kolbert recalls her visit to an unusual natural phenomenon at Castello Aragonese in the Gulf of Naples: "When we get close enough, I start to see bubbles rising from the sea floor, like beads of quicksilver. Beds of seagrass wave beneath us." Identify the gas that produces the bubbles described by the author:
Oxygen
Methane
Nitrogen
Carbon Dioxide
Hydrogen Sulfide
Carbon Dioxide
Castello Aragonese in the Gulf of Naples provides a natural experiment where scientists can study the effects of differing pH levels on the biology of the local marine ecosystem. Kolbert claims that "Here it is possible to swim... in the seas of tomorrow today." What does she mean by this? Why would the pH of the oceans change dramatically in many places across the world?
Human activities are accelerating the Carbon Cycle, causing an average increase in global temperatures.
Invasive species are causing unprecedented change in marine systems.
Deforestation is resulting in unprecedented rates of soil erosion.
Human activities are causing unprecedented levels of acid precipitation.
Agricultural pollution is resulting in nutrient run-off and eutrophication.
Human activities are accelerating the Carbon Cycle, causing an average increase in global temperatures.
Which group of organisms is most directly affected by human activities that accelerate the Carbon Cycle and cause acidification?
sea grass
corals
sponges
fishes
marine mammals
corals
In the 1990s, the first strong clues to indicate a link between Carbon Dioxide levels and the effects of acidification on marine life came from
a sea life aquarium in Texas.
a coral reef in the Florida Keys.
the Great Salt Lake in Utah.
an indoor biosphere experiment in Arizona.
the lobster industry in Maine.
an indoor biosphere experiment in Arizona.
Which of the following groups would be most likely to exhibit uniform dispersion?
cattails, which grow primarily at edges of lakes and streams
red squirrels, which actively defend territories
lake trout, which seek out deep water
dwarf mistletoes, which parasitize particular species of forest tree
moths in a city at night, which are attracted to light sources
red squirrels, which actively defend territories
You initially trap and mark 100 sunfish in a lake. You return one week later and capture 200 fish. But only 50 were marked. The estimated population size is:
400
100
5
200
400
Where in the world would you find a place called "One Tree Island" with an isolated research station accessible only by boat?
Iceland
Australia
Italy
Fiji
Mexico
Australia
All species are equally important to the overall function of an ecosystem.
True
False
False
For most groups, species diversity most often
increases from the poles to the tropics.
is high at the equator and the poles, and lowest at temperate latitudes.
increases from the tropics to the poles.
is low at the equator and the poles, and peaks at temperate latitudes.
increases from the poles to the tropics.
What kind of organism might a biologist study using the “ring and fling” sampling method?
frogs
fungi
insects
large trees
birds
birds
Chapter 10 of The Sixth Extinction is called "The New Pangaea," which is a reference to the supercontinent that existed from about 335 million years ago until about 175 million years ago. This metaphor of a modern supercontinent applies to which modern ecological crisis?
Human activities are accelerating the Carbon Cycle, causing an average increase in global temperatures.
Deforestation is resulting in unprecedented rates of soil erosion.
Invasive species are causing unprecedented change in terrestrial ecosystems.
Agricultural pollution is resulting in nutrient run-off and eutrophication.
Invasive species are causing unprecedented change in terrestrial ecosystems.
This chapter features a captive animal at a facility run by the San Diego Zoo. “Kinohi” is a rare species of Hawaiian
fruit fly.
happy face spider.
rodent.
crow.
hummingbird.
crow
A long-term ecological study in Brazil resulted from collaboration between the government, scientists, conservationists, and landowners engaged in...
shade grown coffee farms
Christmas tree farms
cattle ranching
development of residential housing
mining operations
cattle ranching
“Suci” was a star creature at the Cincinnati Zoo, with a “prodigious backside.” Suci was a(n)…
gelada baboon
hippopotamous
Asian elephant
Sumatran rhinocerous
Florida manatee
Sumatran rhinocerous
A Kentucky State Park called “Big Bone Lick” is famous for its fossils from the…
Jurassic period
Pleistocene ice age
Devonian period
Anthropocene epoch
Cretaceous period
Pleistocene ice age
South America has one surviving species of bear.
True
False
True
Which factor has probably contributed most toward the loss of biodiversity known as the Holocene Extinction?
overharvesting
habitat destruction
population growth of humans
invasive species
habitat destruction
What did scientists at the San Diego Zoo need from an endangered Hawaiian animal named Kinohi?
DNA
blood samples
semen
sound recordings
tissue samples
semen
"In Ecology, rules are hard to come by. One of the few that's universally accepted is..."
catastrophism
the species area relationship (SAR)
uniformitarianism
game theory
the "ghost of competition past"
the species area relationship (SAR)
“Stop Aquatic Hitchikers! … Clean all recreational equipment.” This sign “shows a picture of a boat entirely coated in: _____."
mud dauber nests
barnacles
snail eggs
an invasive species of algae
zebra mussels
zebra mussels
Which of the following is a correct statement about MacArthur and Wilson's island biogeography equilibrium model?
As the number of species on an island increases, the emigration rate decreases.
Competitive exclusion is less likely on an island that has large numbers of species.
Islands closer to the mainland have higher extinction rates.
Small islands receive and/or maintain few new immigrant species.
Small islands receive and/or maintain few new immigrant species.
The premise of Kolbert's entire book (that we are currently experiencing a sixth mass extinction event precipitated by the actions of our own species) is best encapsulated by which term?
The Pleistocene Epoch
The Neolithic (or Agricultural) Revolution
The Anthropocene Epoch
The Industrial Revolution
The Holocene Epoch
The Anthropocene Epoch
Canada's boreal forest has been identified by the scientific community as a "hot spot" of biological diversity.
True
False
False
“A particularly famous—and ghastly—instance” of a biological invasion involves the Island of Guam, and…
zebra mussels
hairy tarantulas
killer fruit flies
brown tree snakes
little brown bats
brown tree snakes
The equilibrium model of island biogeography predicts that, once equilibrium is reached, an island will be occupied
by an unchanging number of species, but extinctions and immigrations will continue.
by an unchanging set of species as extinctions and immigrations stop.
by a steadily increasing number of species.
only by species that evolved on that island.
by an unchanging number of species, but extinctions and immigrations will continue.
The Sixth Mass Extinction featured in the title of Elizabeth Kolbert's book corresponds with which event mentioned in Openstax Biology 2e chapter 47?
The End-Cretaceous Extinction
The End-Permian Extinction
The Holocene Extinction
The End-Ordovician Extinction
The Holocene Extinction
The equilibrium model of island biogeography predicts
both the rate of extinction is greater for small islands and the rate of immigration is greater for near islands.
the rate of extinction is greater for small islands.
the rate of immigration is greater for near islands.
the rate of immigration is greater for far islands.
both the rate of extinction is greater for small islands and the rate of immigration is greater for near islands.
How does inefficient transfer of energy among trophic levels result in the typically high endangerment status of many top predators?
Predators are more disease-prone than animals at lower trophic levels.
Predators exhibit clumped dispersion patterns.
Predators have relatively large population sizes.
Predators have short life spans and short reproductive periods.
Top-level predators are destined to have small populations that are sparsely distributed.
Top-level predators are destined to have small populations that are sparsely distributed.
In 2007 New York state biologist received a frantic phone call from his staff, “Holy shit, there’s dead bats everywhere[!]” Which one of the following statements accurately represents what we now understand about this event?
climate change had altered the temperature in the cave and killed the bats
human vandals had entered the cave and sprayed the bats with insecticide
these bats were early victims in the spread of a mysterious fungus called “white nose syndrome”
the bats had starved to death as a result of competition with an invasive South American bat
the bats had been shocked by sound waves from military airplanes passing overhead
these bats were early victims in the spread of a mysterious fungus called “white nose syndrome”
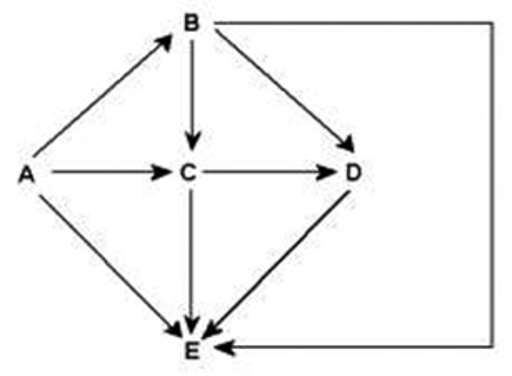
Arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species. Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem. Species C is toxic to predators. Which species is most likely to benefit from being a mimic of C?
D
E
A
B
B
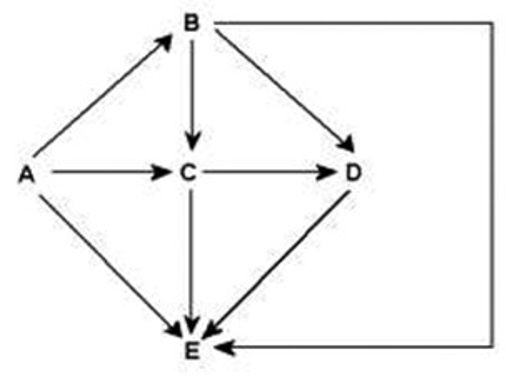
Arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species. Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem. Which organism is a primary producer?
C
B
D
A
A
What would happen to a temperate grassland biome without droughts and/or fires?
eutrophication
habitat fragmentation
biomagnification
ecological succession
ecological succession
In chapter 9 of The Sixth Extinction, Elizabeth Kolbert compares patches of the Amazon rainforest to "islands on dry land". She proceeds to describe a long term research project called the Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project, which is the result of a collaboration between
local farmers and a Hollywood producer
several South American nations
local indigenous tribes and the Brazilian government
cattlemen and conservationists
cattlemen and conservationist
In Chapter 11 of The Sixth Extinction, Elizabeth Kolbert tells the story of a Sumatran rhino named Suci, and in Chapter 13, she tells the story of a Hawaiian crow called Kinohi. Suci and Kinohi are both examples of:
species so rare, their future depends on the success of captive breeding programs
species that represent conservation success stories
species acutely affected by global climate change
generalist species that have broad ecological niches
species so rare, their future depends on the success of captive breeding programs
An estimate of one per million species per year (E/MSY) is best described as
the current extinction rate
background extinction rate
a mass extinction
a biological invasion
background extinction rate
defining and describing where in space and time different organisms live on earth is best described as a subdiscipline of:
ecosystem ecology
biogeography
community ecology
behavioral ecology
biogeography
In Chapter 10 of The Sixth Extinction, ("The New Pangaea"), Elizabeth Kolbert discusses a population of North American species called the little brown bat. This chapter is a cautionary tale about
a) habitat destruction
b) invasive species
c) overharvesting
d) global warming
invasive species