Muscles of the Body with pictures
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
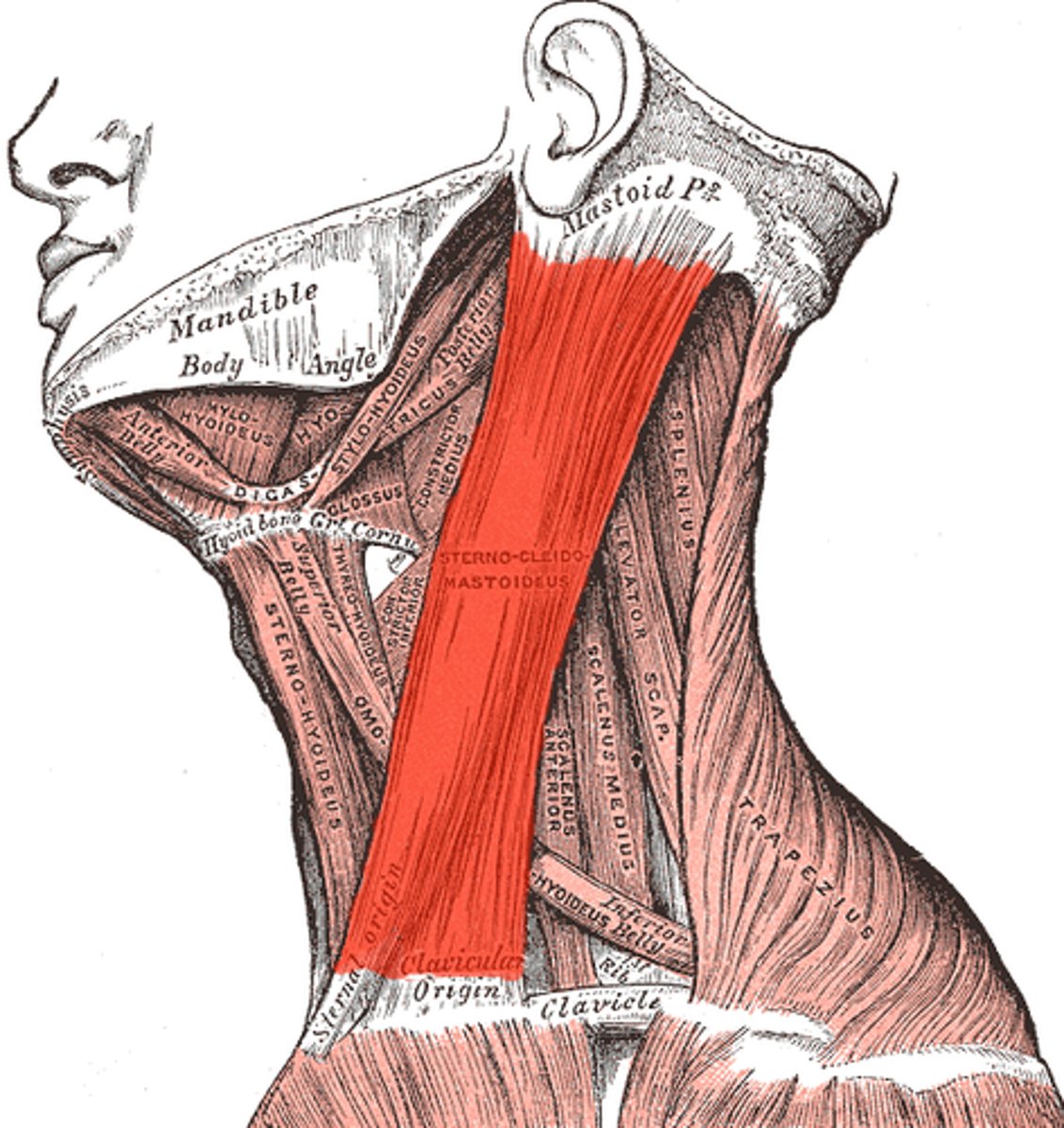
Sternocleidomastoid*
Action: together they flex the neck; alone they rotate the head
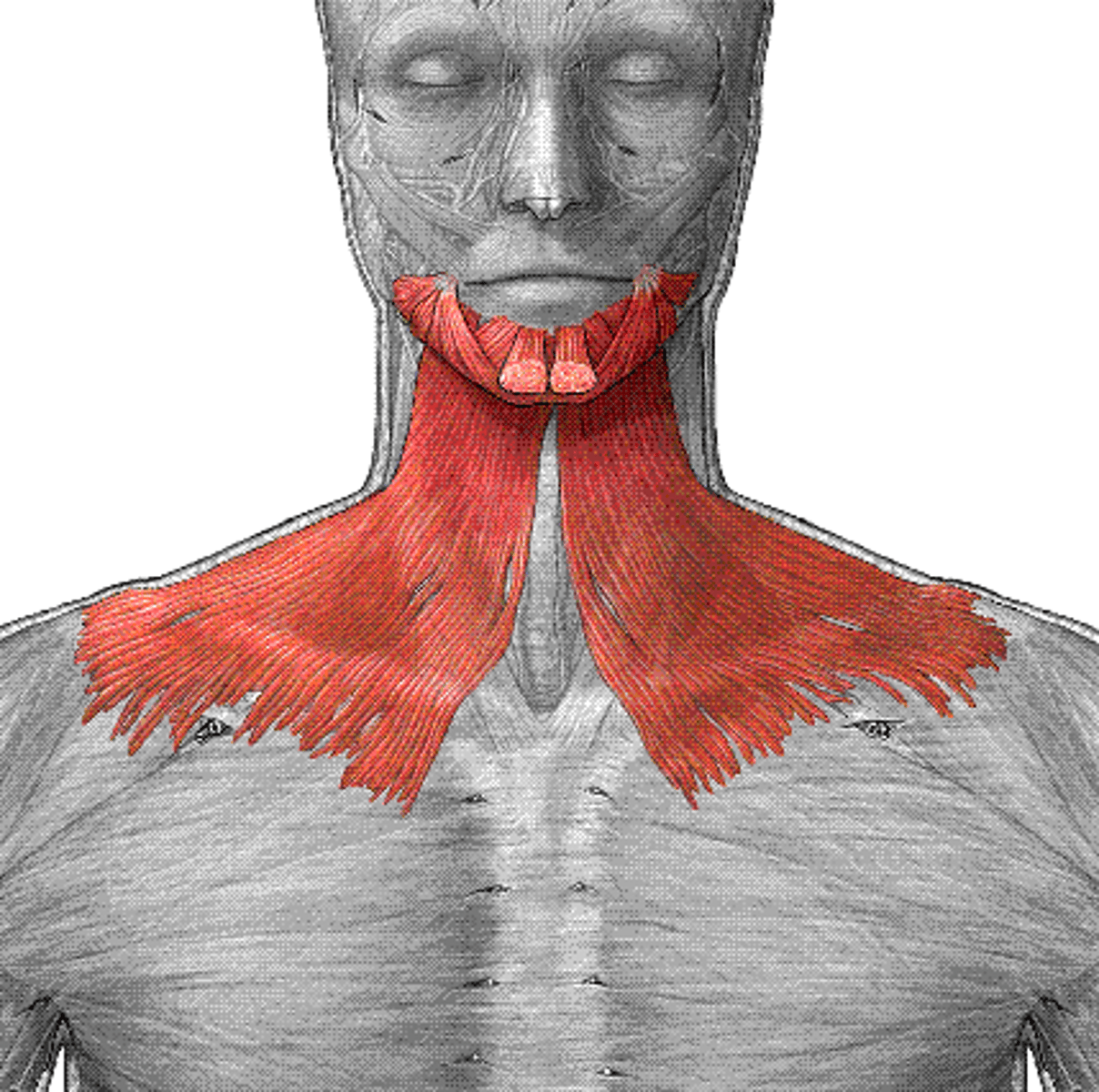
Platysma
Action: tense skin of neck; depress mandible
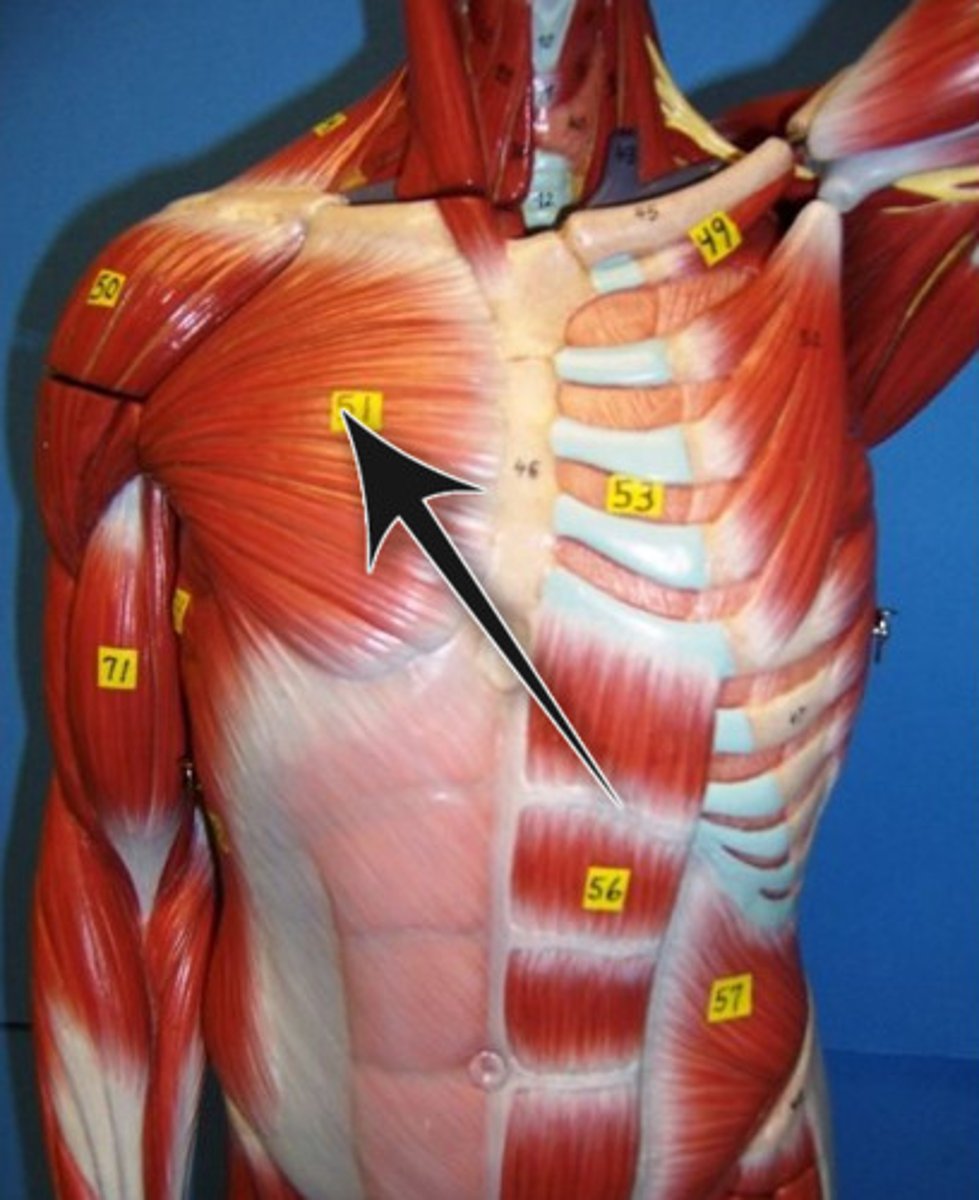
Pectorals Major*
Action: flexion, adduction, and medial rotation of shoulder
Pectoralis Minor
Action: depress and protract shoulder, rotate glenoid cavity inferiorly or elevate ribs(scapula fixed)
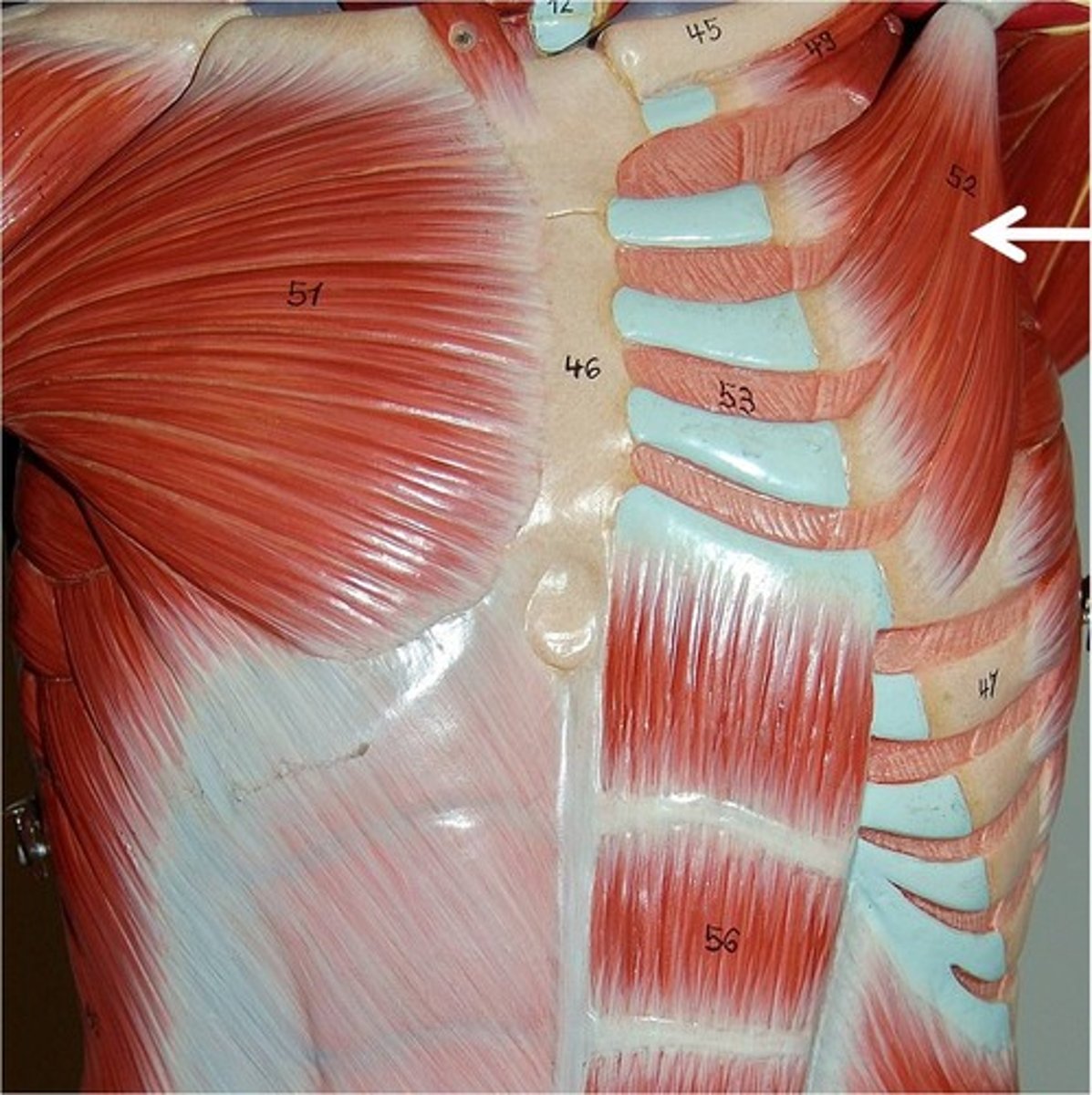
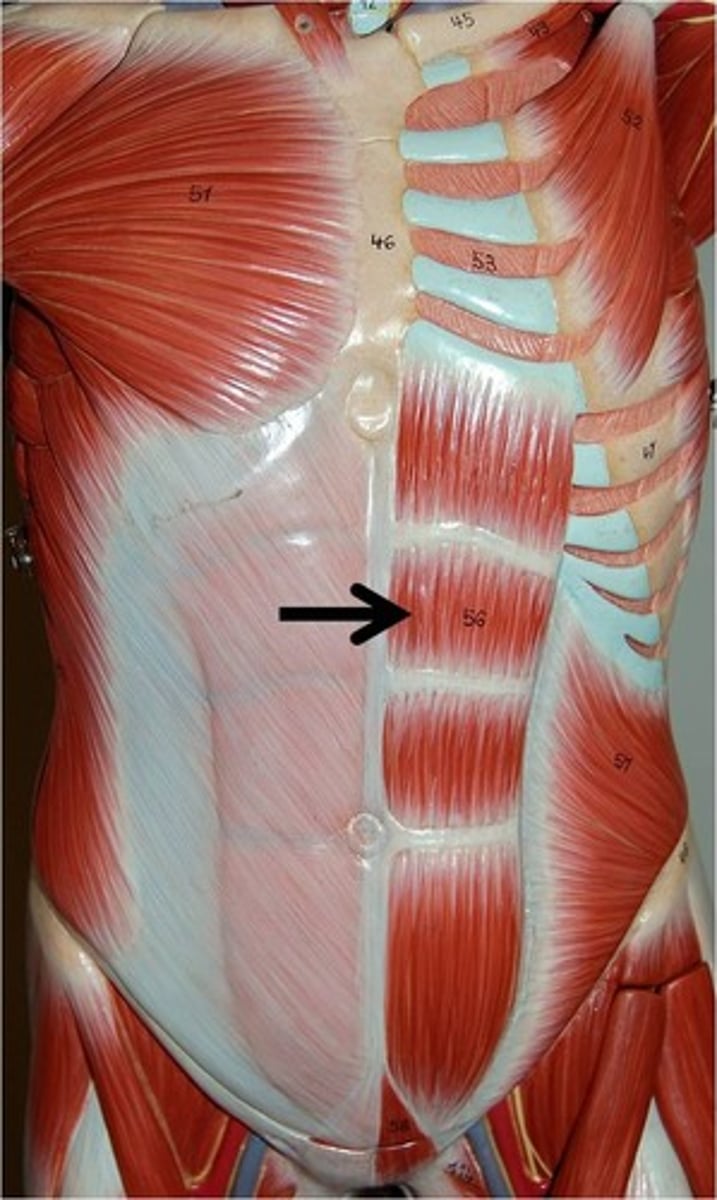
Rectus Abdominus*
Action: flex spinal column
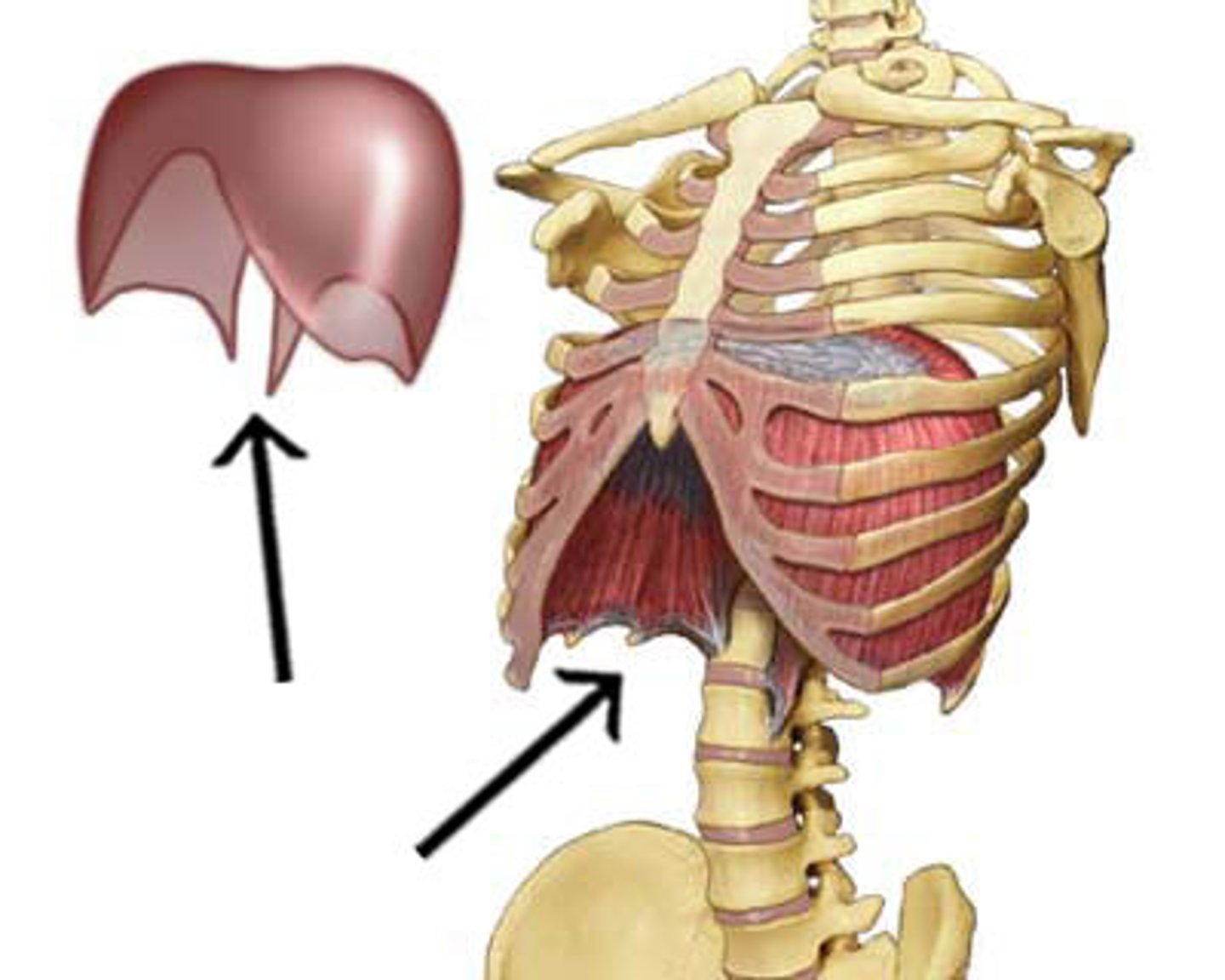
Diaphragm
Action: expand thorax, compress abdomen(respiration)
External Oblique
Action: compress abdomen, depress ribs, flex or rotate spine
Internal Oblique
Action: compress abdomen, depress ribs, flex or rotate spine
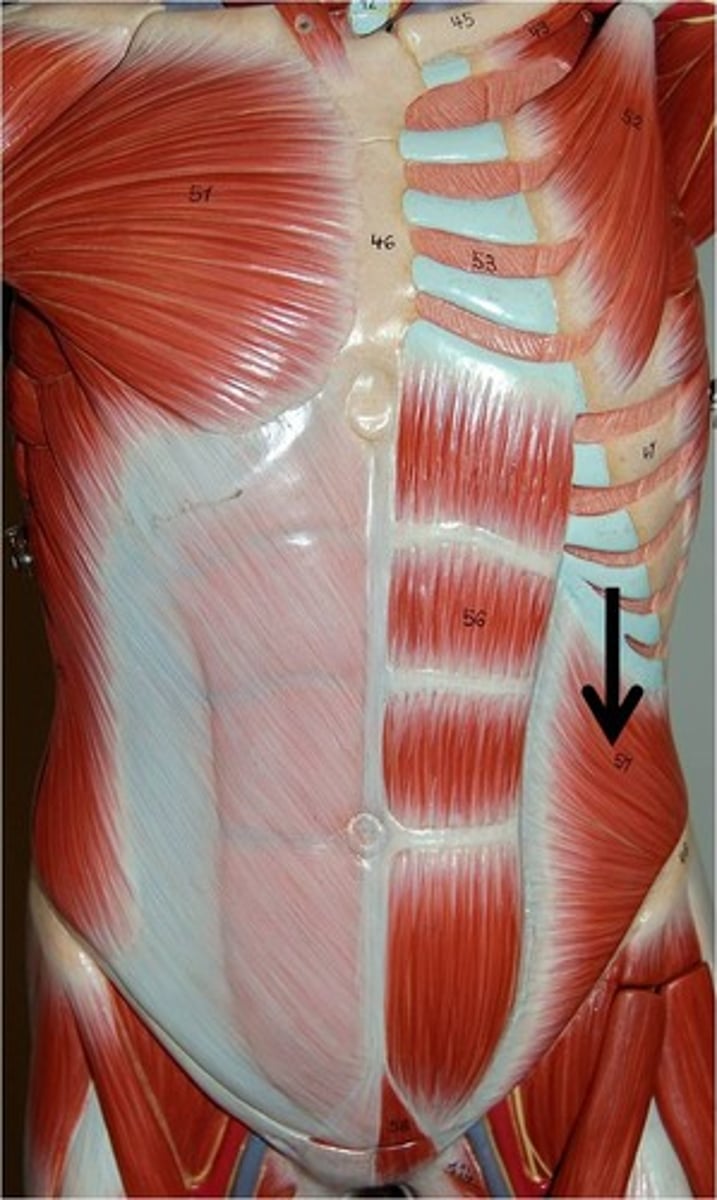
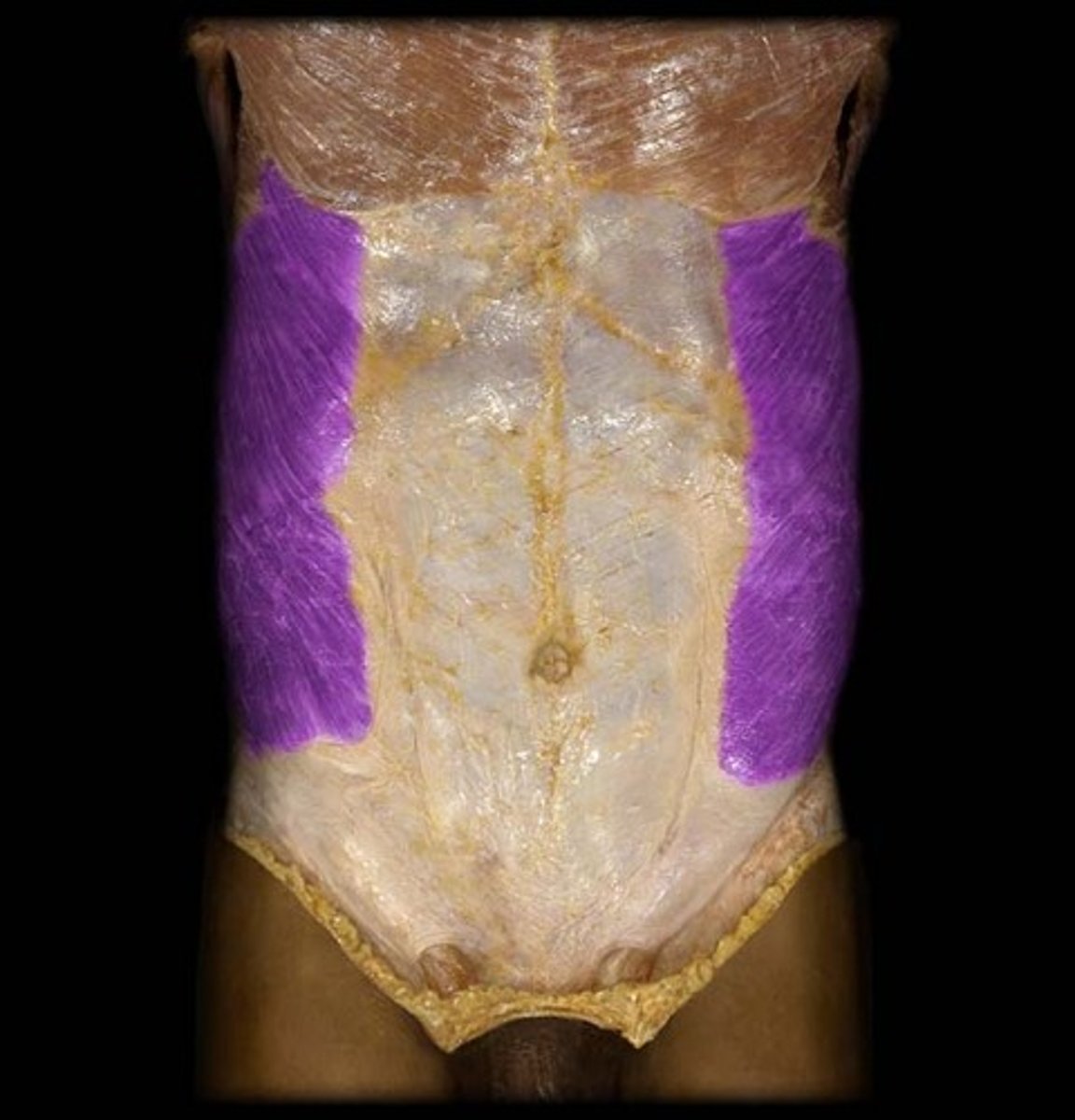
Transversus Abdominus
Action: compress abdomen
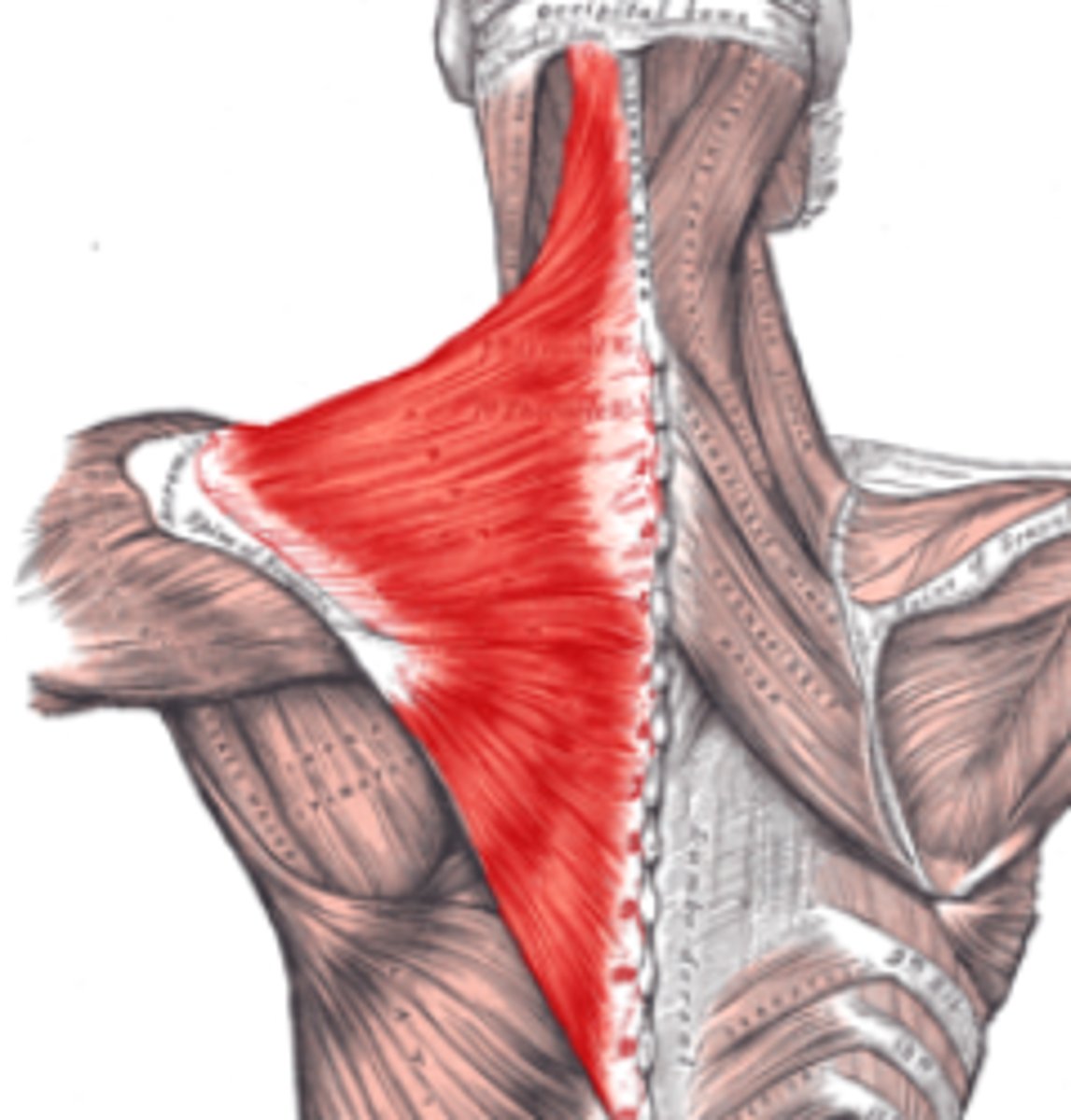
Trapezius*
Action: extend neck; elevate, retract, depress, or rotate scapula upward; elevate clavicle
Teres Major
Action: extension, medial rotation, adduction of shoulder
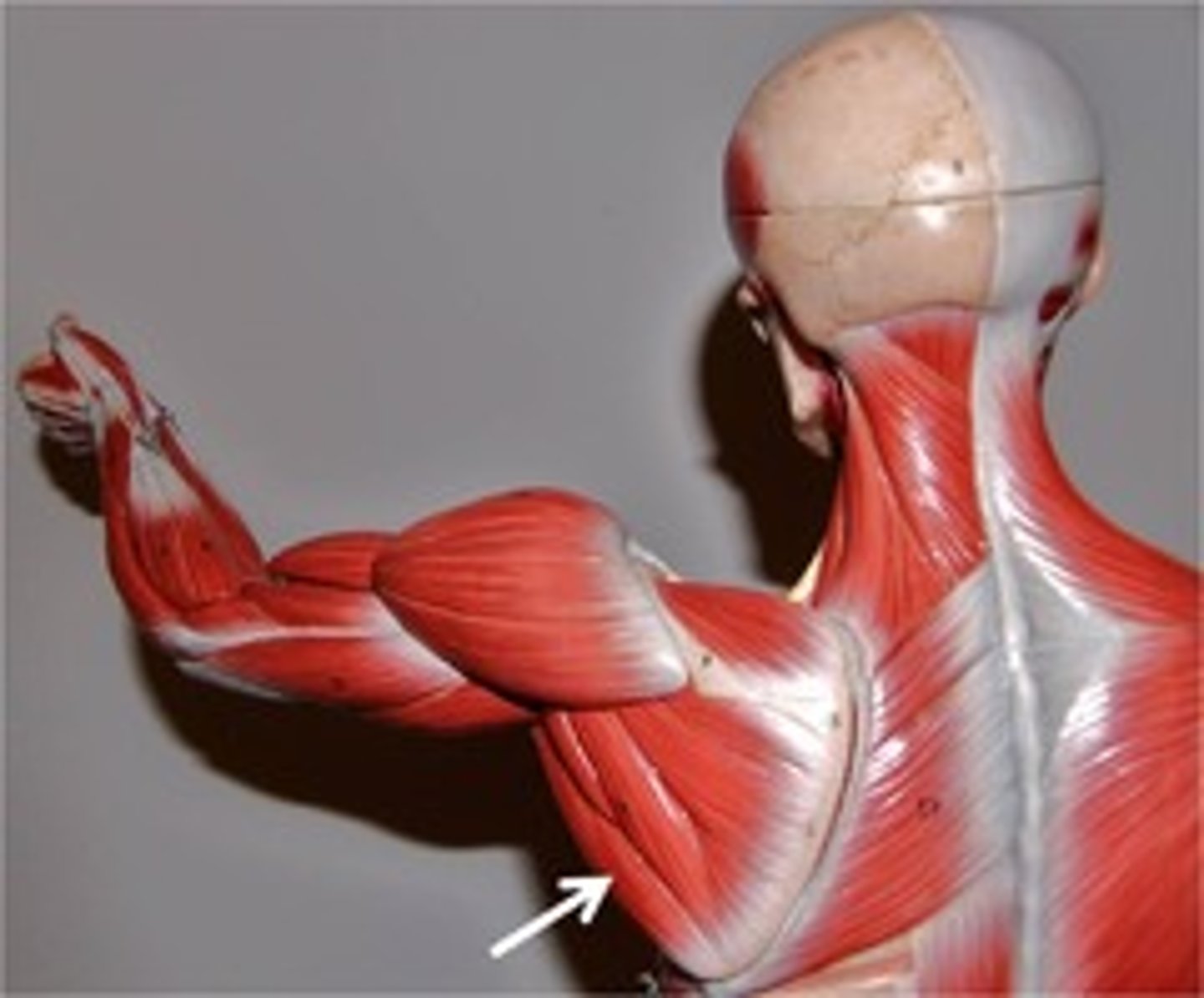
Teres Minor
Action: lateral rotation of shoulder
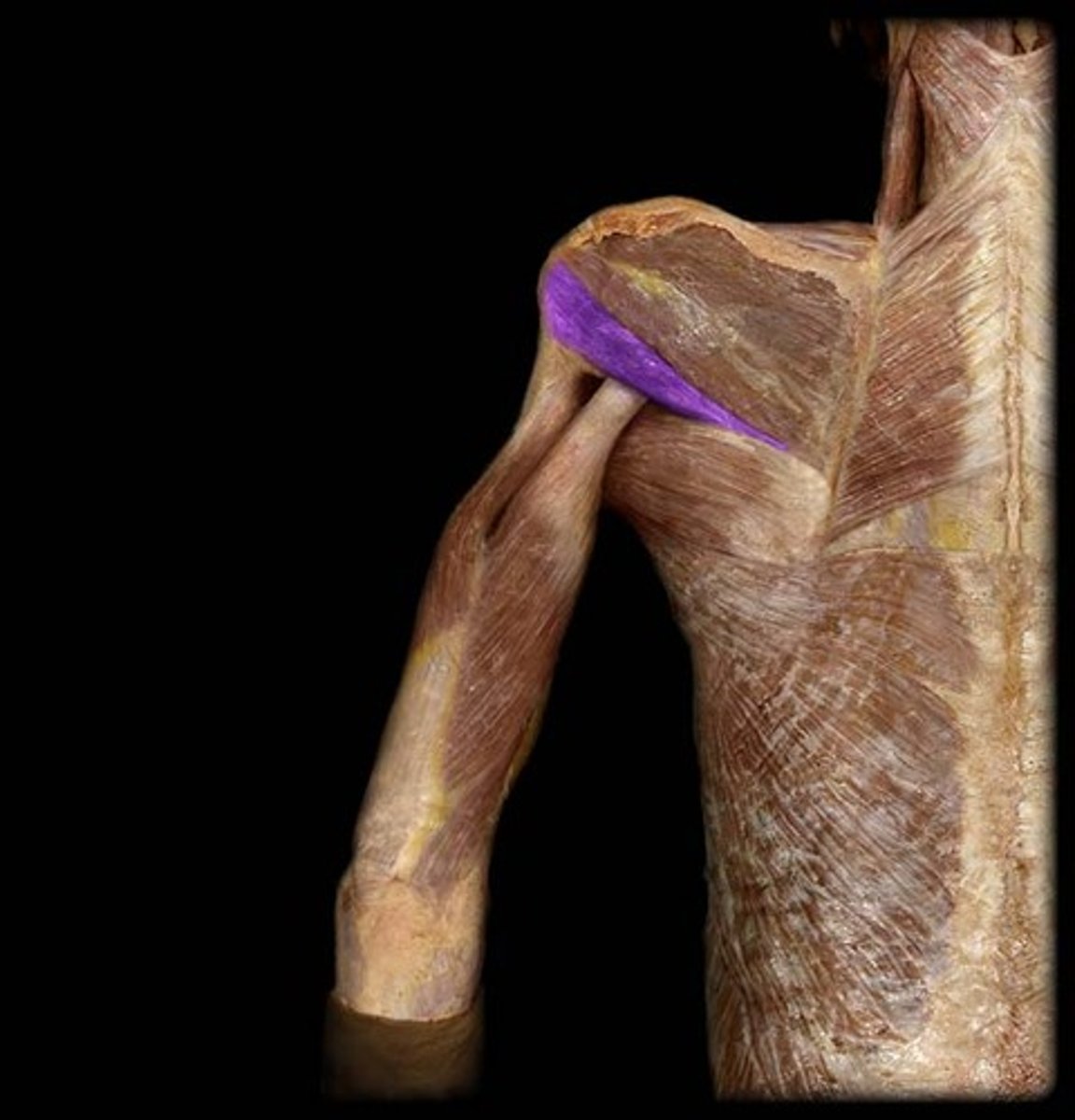
Latissimus Dorsi*
*Action: extension, medial rotation, adduction of shoulder
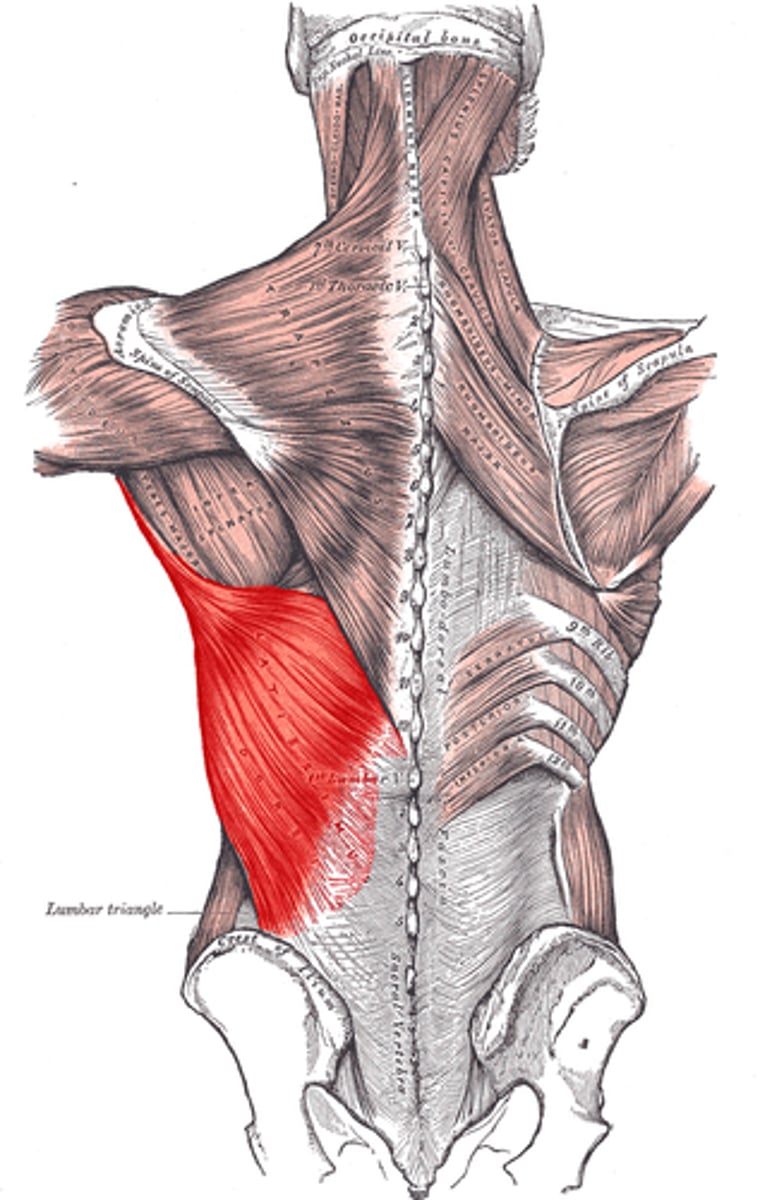
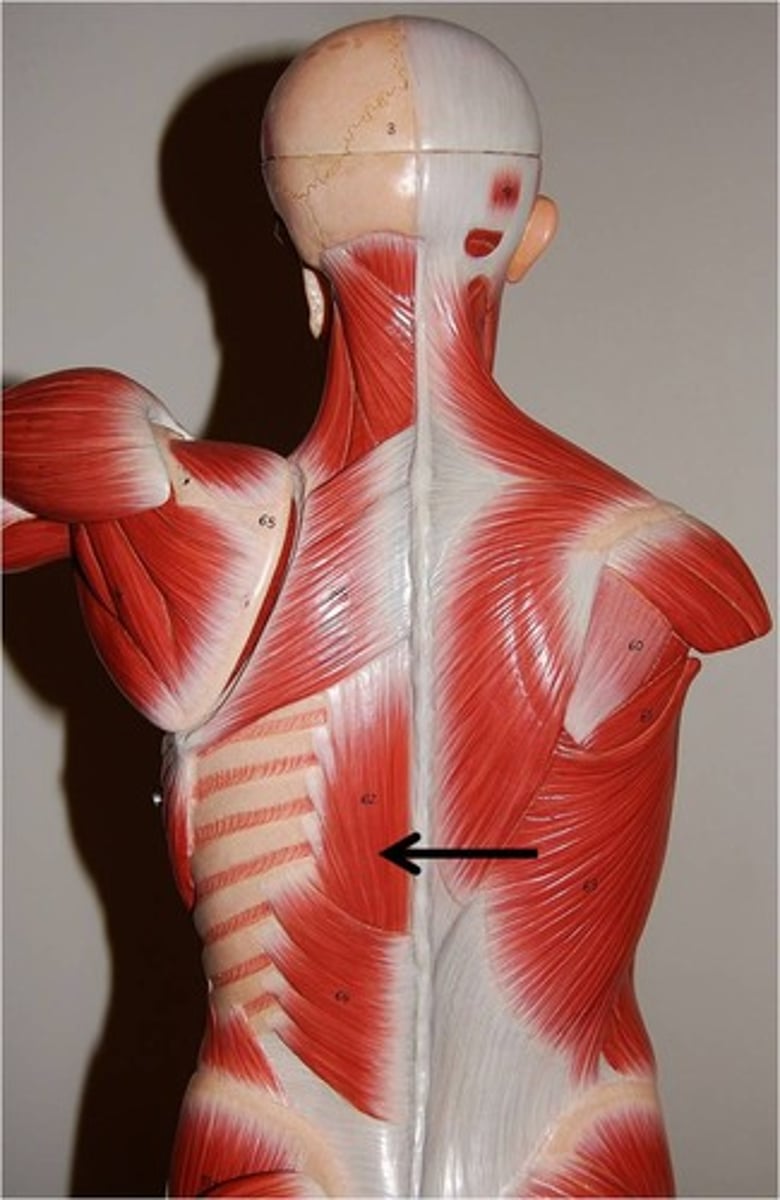
Erector Spinae Group*
Action: extend spine, flex spine, extend neck
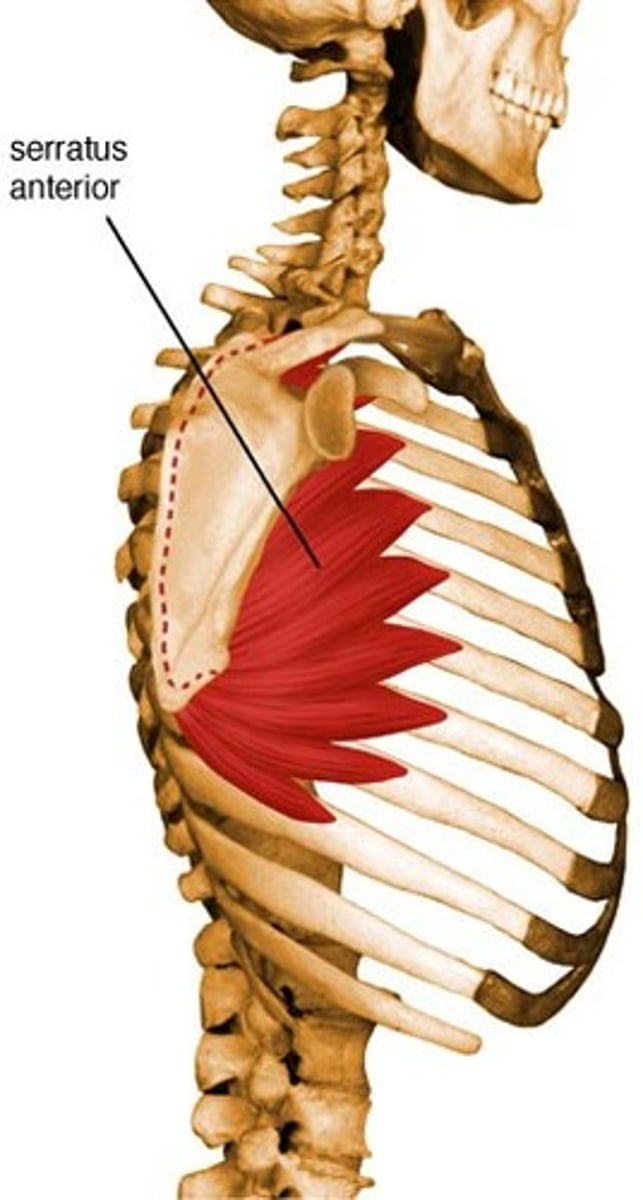
Serratus Anterior
Action: protract shoulder, rotate glenoid cav superiorly or elevate ribs (scap fixed)
Subscapularis
Action: medial rotation of shoulder
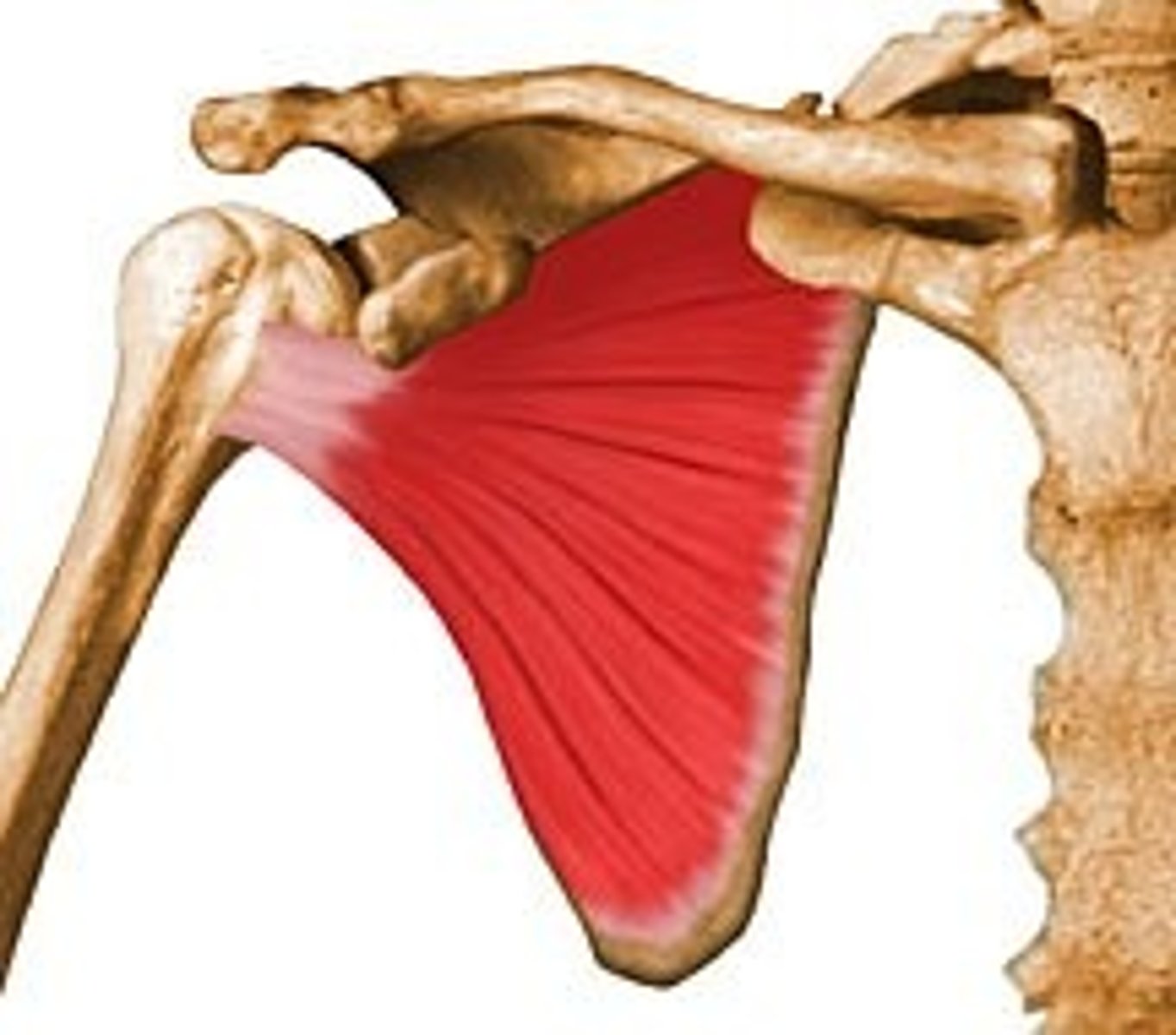
Infraspinatus
Action: lateral rotation of shoulder
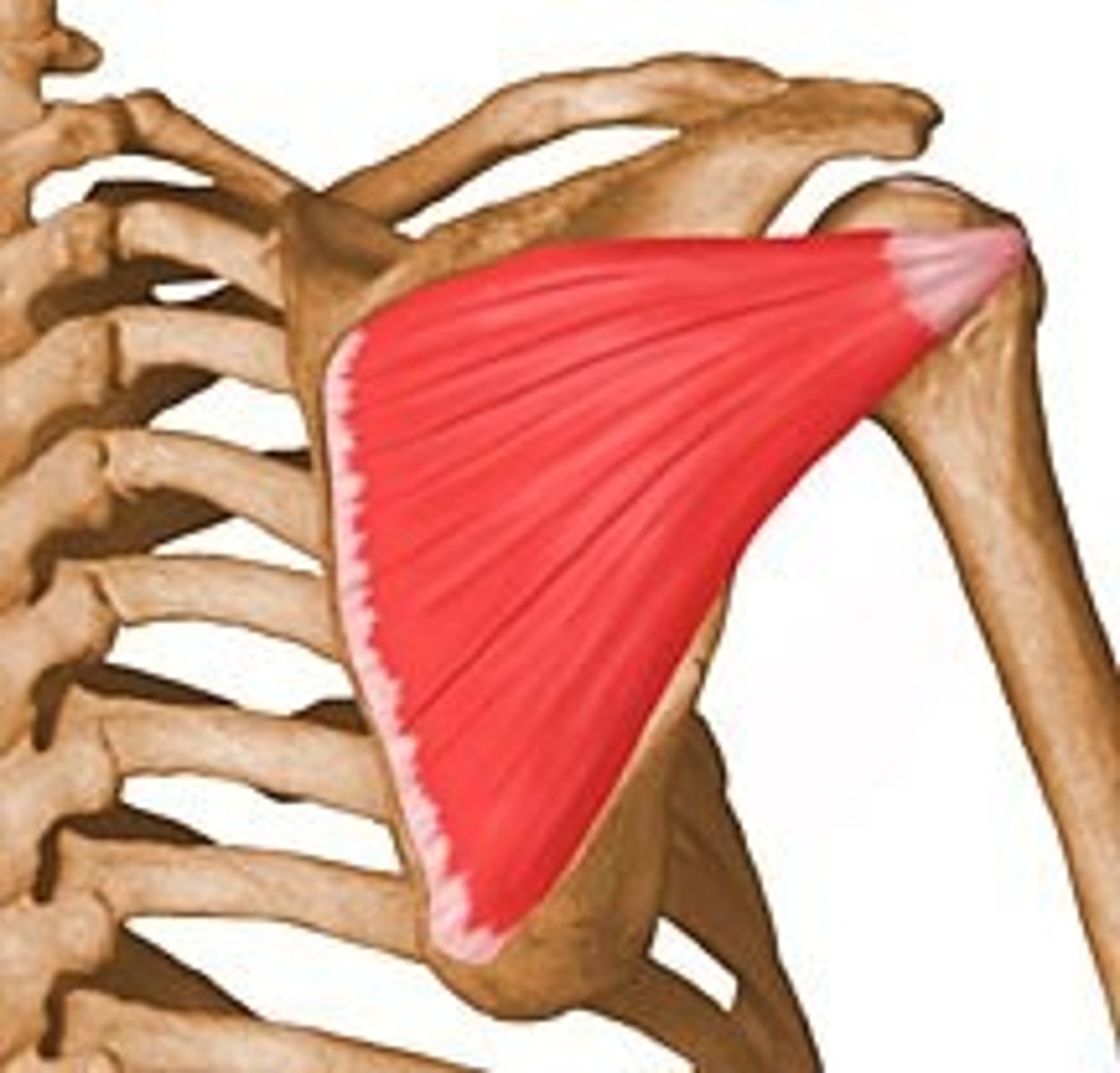
Supraspinatus
Action: abduction of shoulder
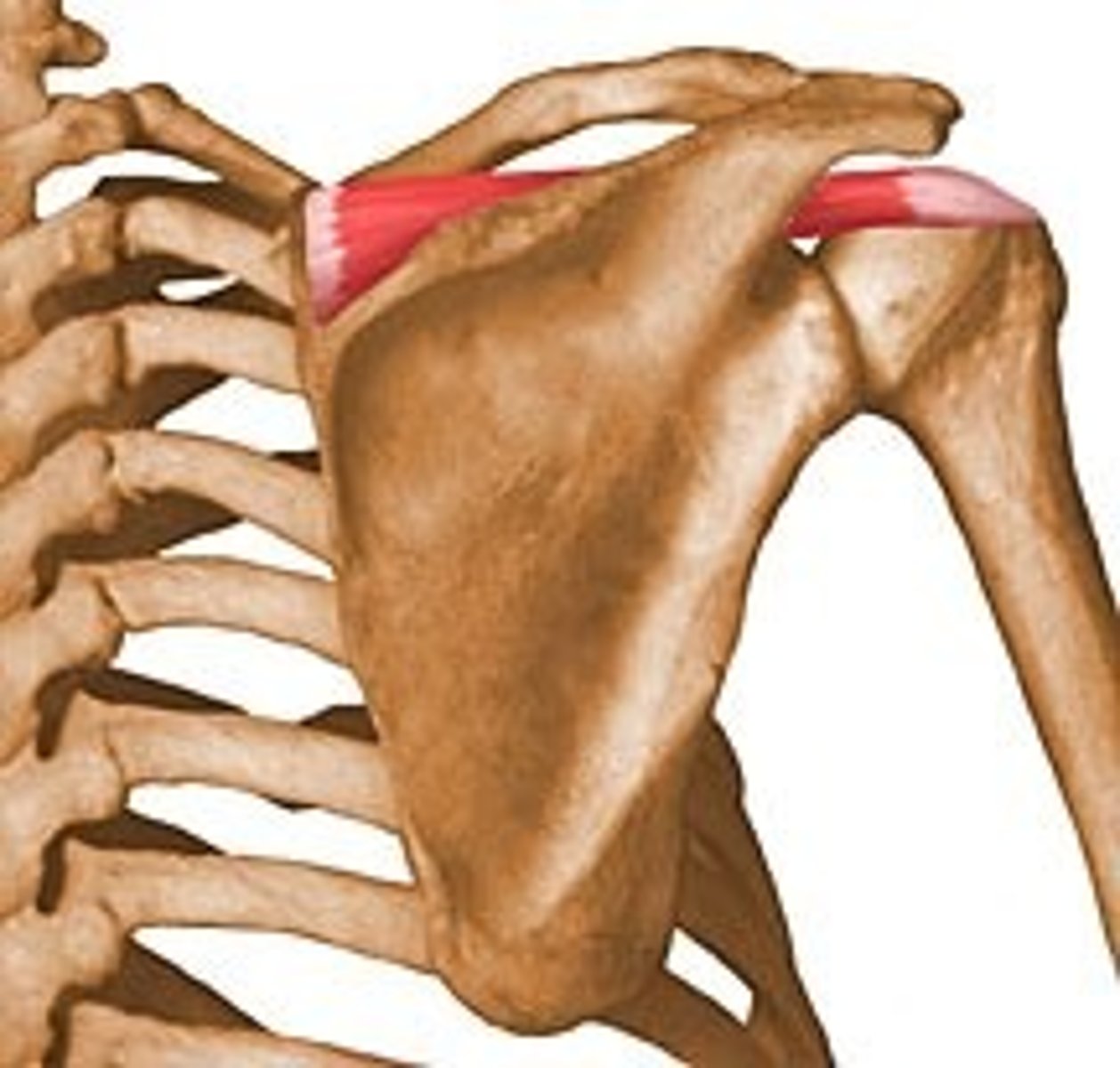
Rhomboid Major
Action: adduct scapula, downward rotation of scapula
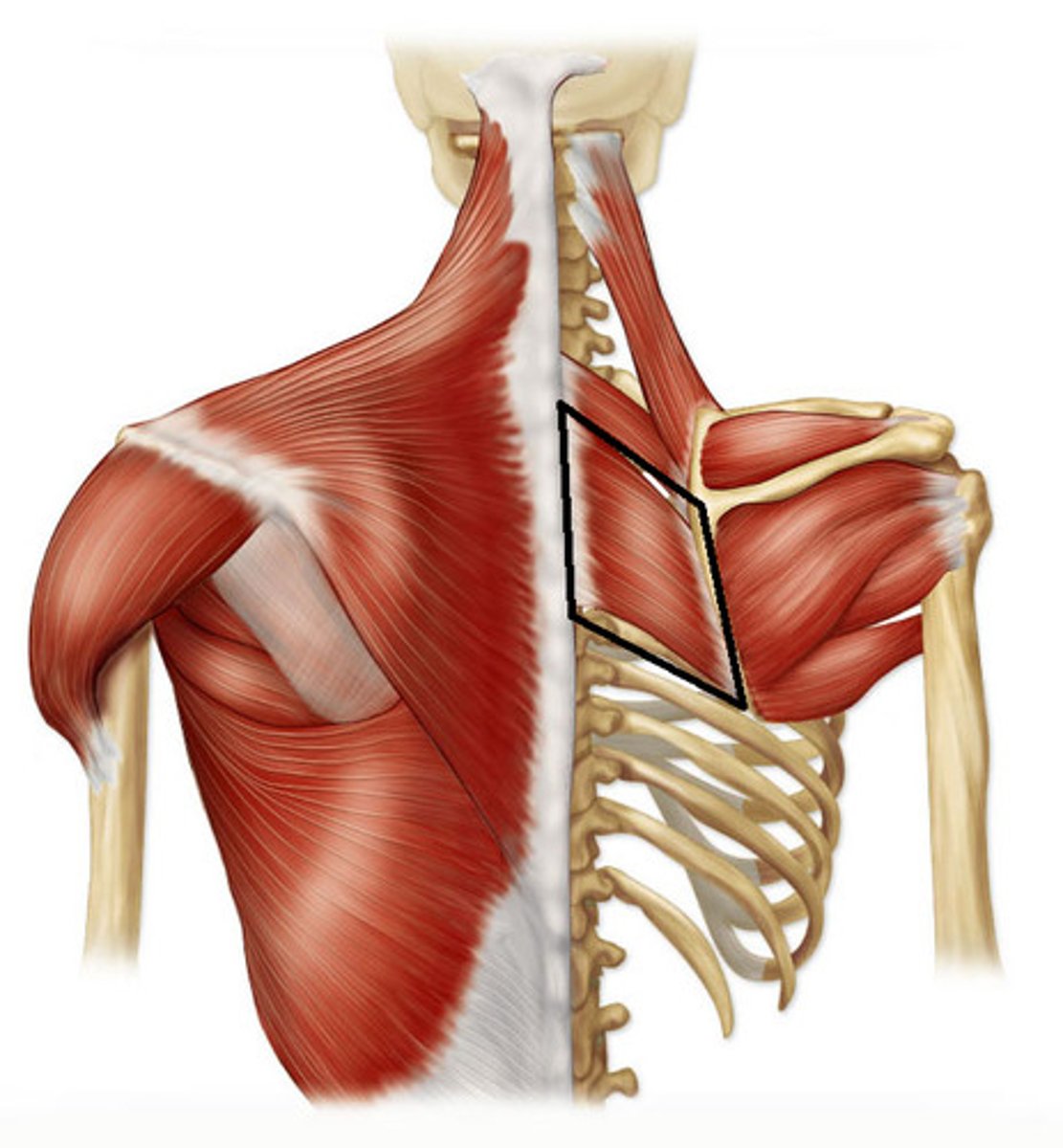
Rhomboid Minor
Action: adduct scapula, downward rotation of scapula
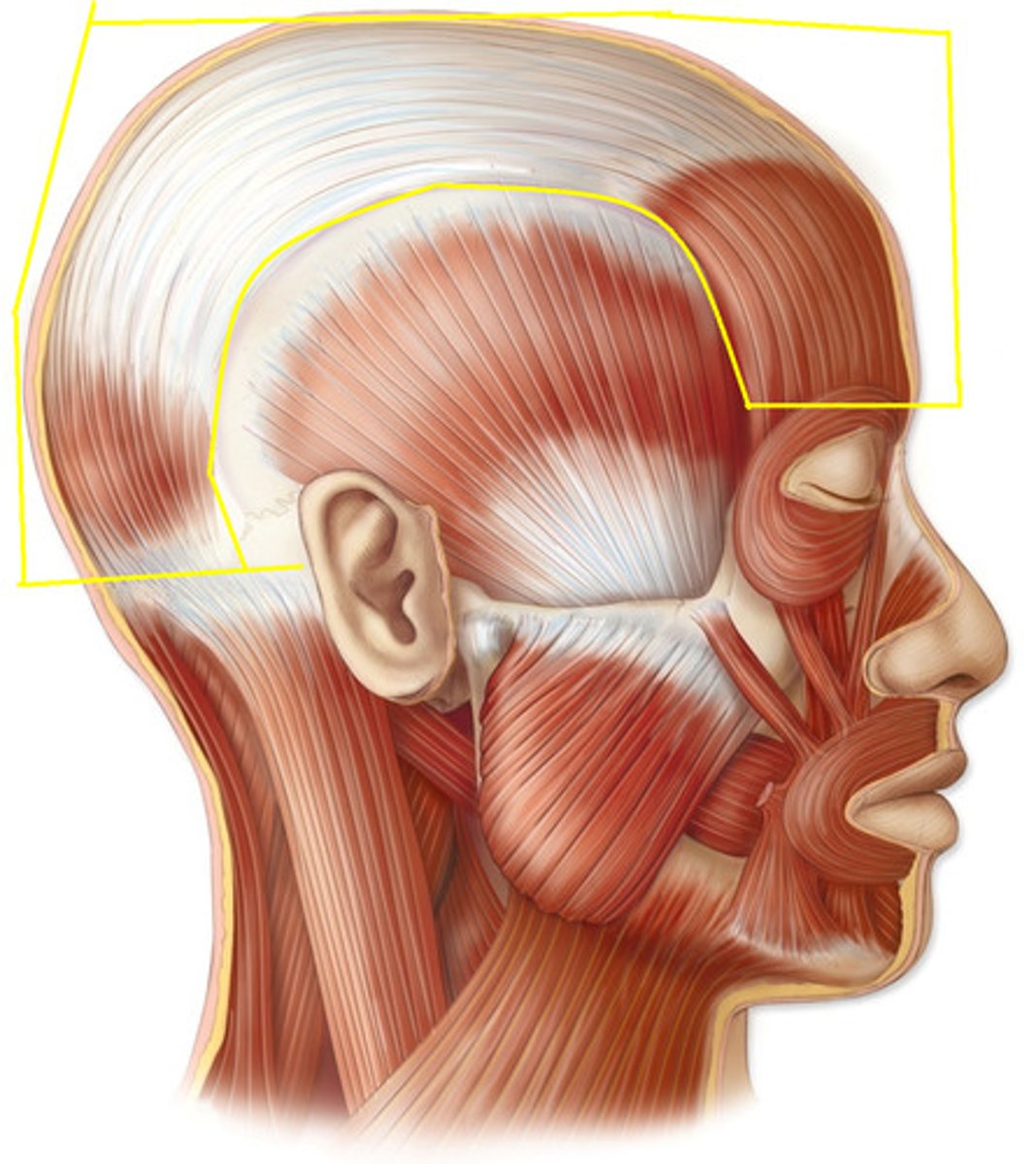
Occipitofrontalis (epicranius)
Action: raise eyebrows, wrinkle forehead
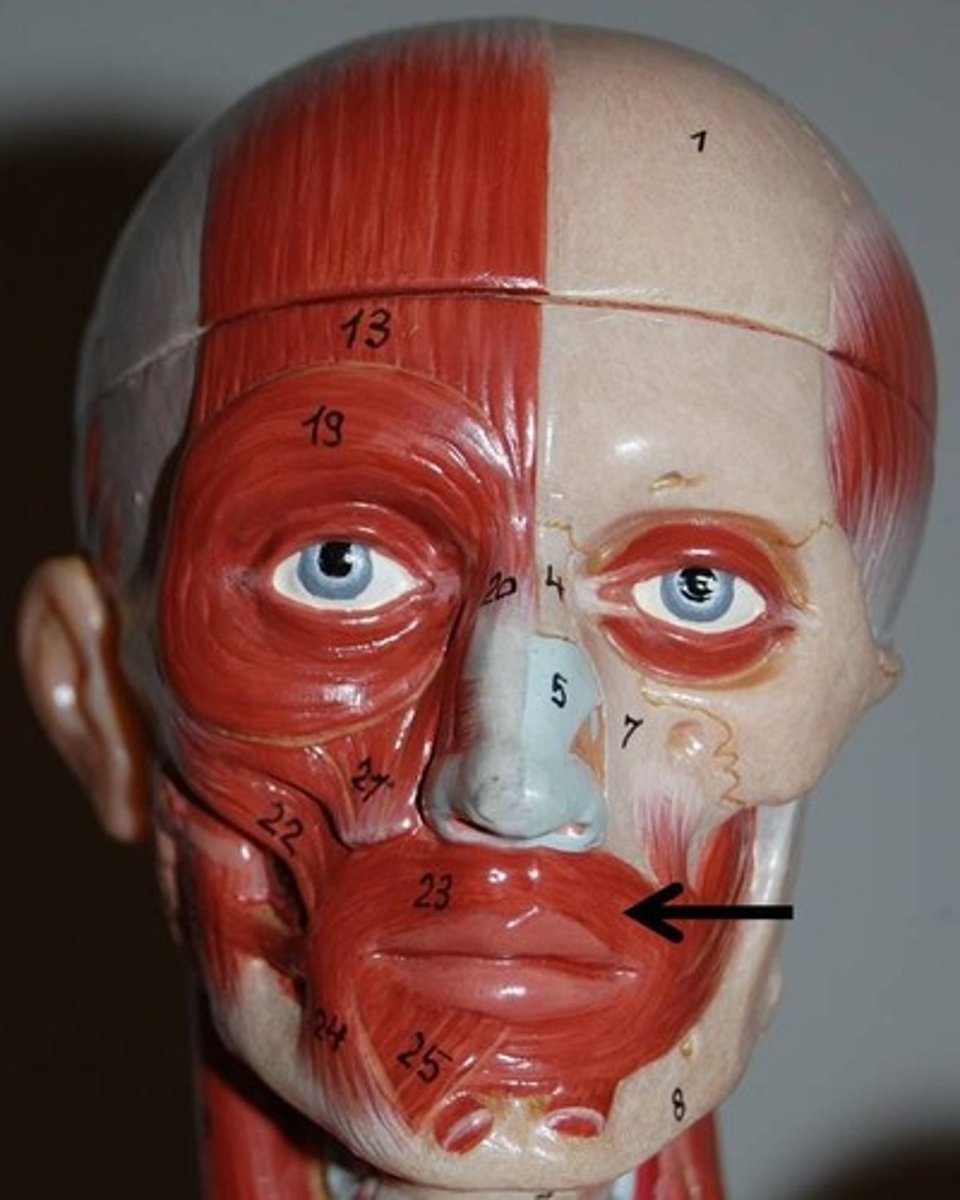
Orbicularis Oris
Action: compress lips, pucker lips(kissing muscle)
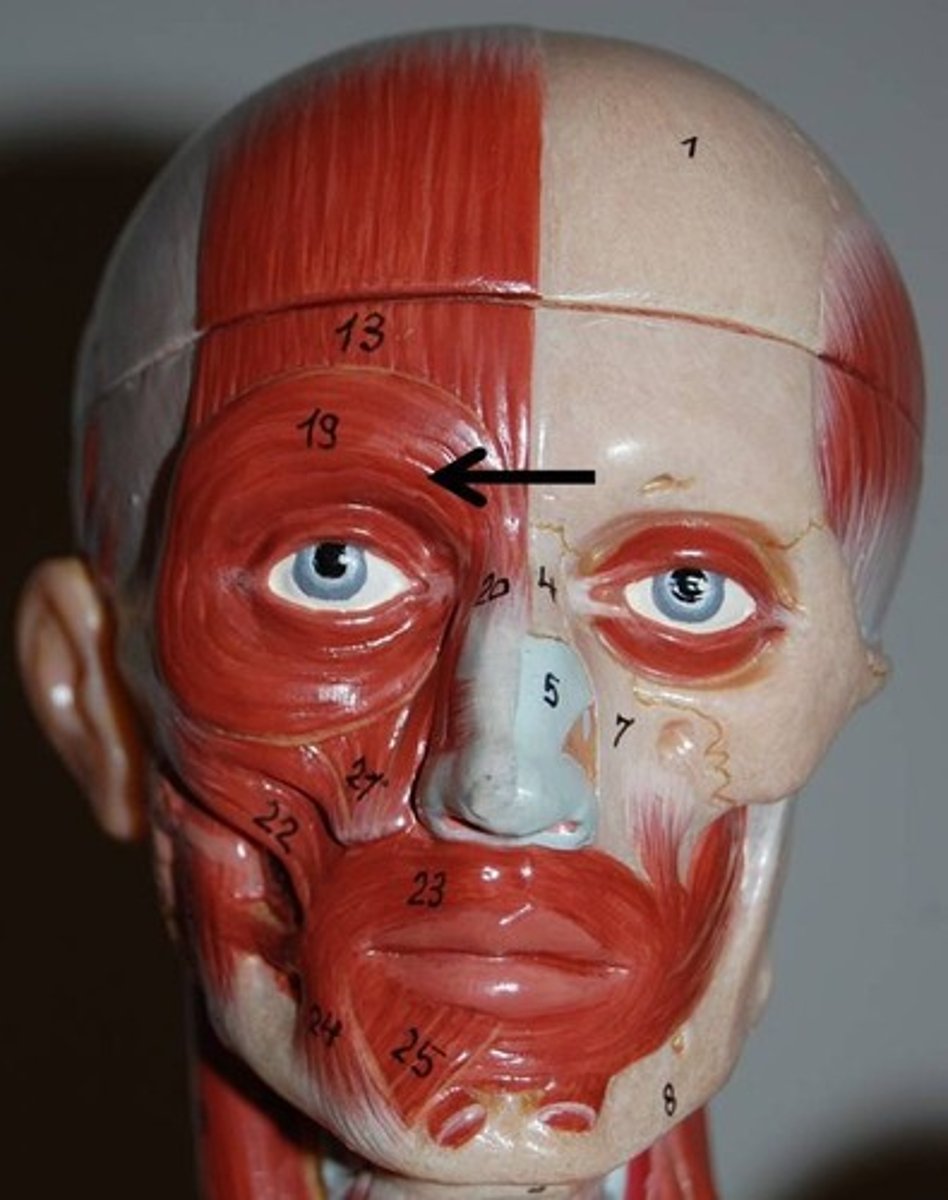
Orbicularis Oculi
Action: close eyelids(blink)
Zygomaticus Major
Action: retract and elevate corner of mouth
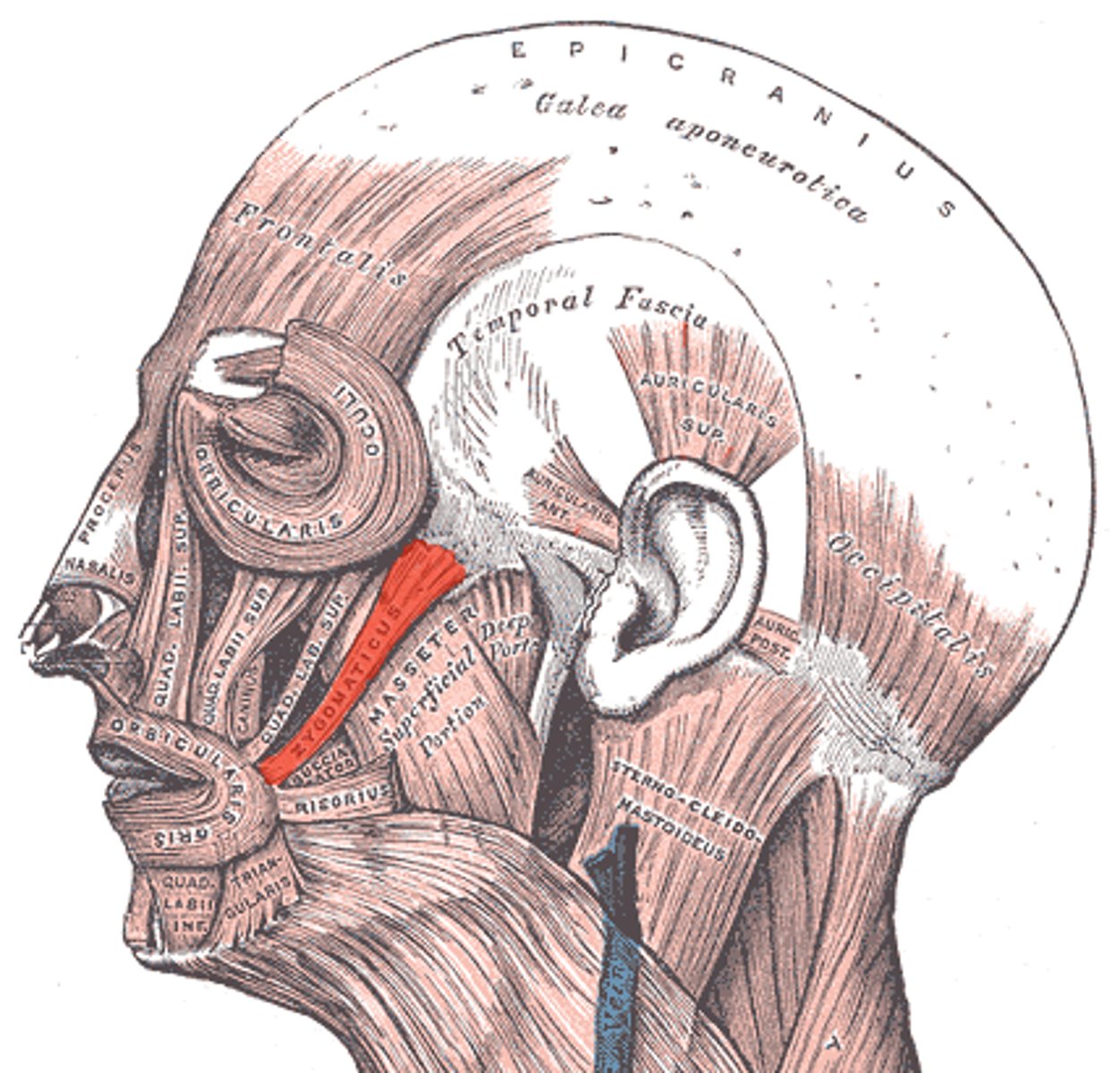
Zygomaticus Minor
Action: retract and elevate upper teeth
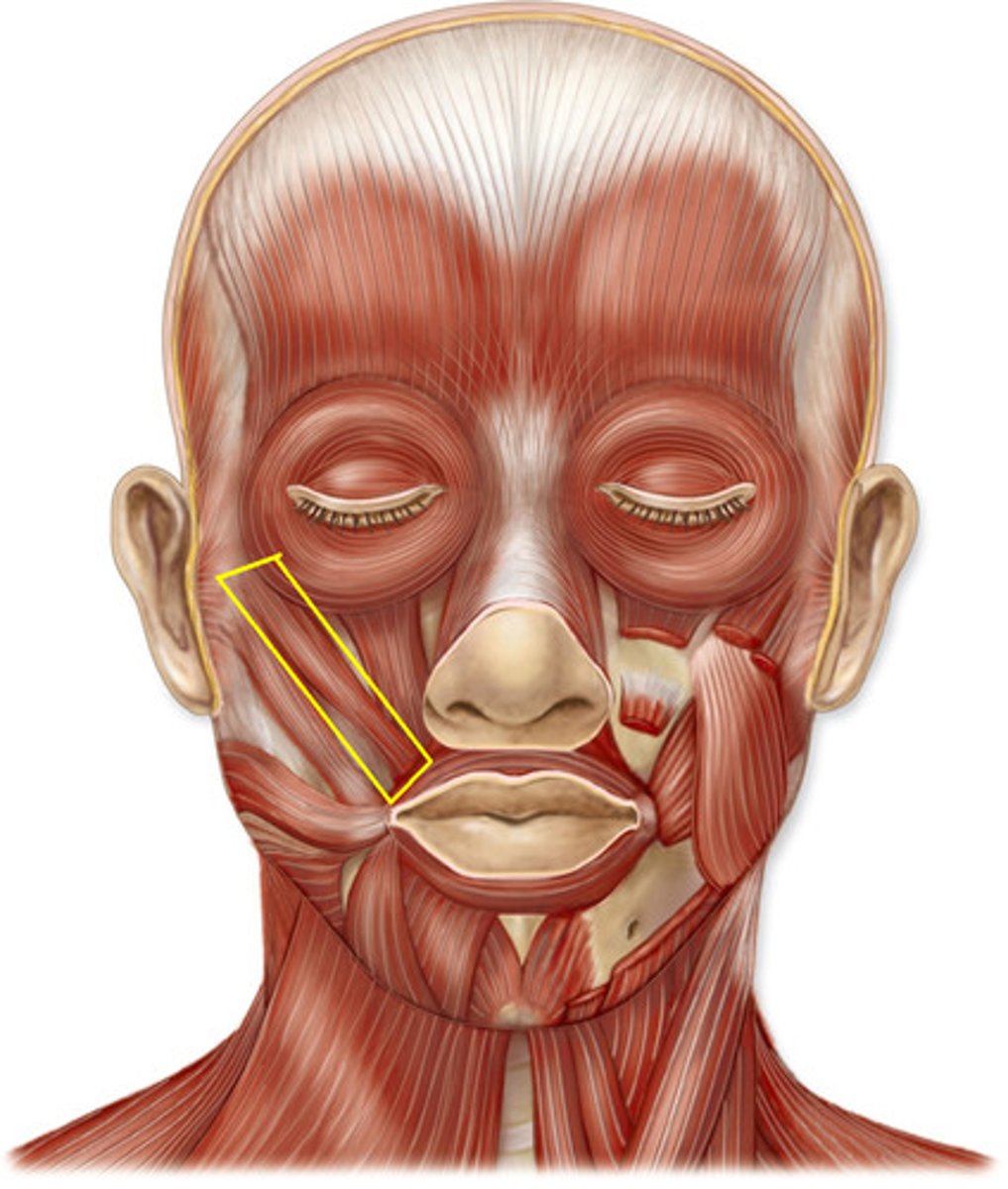
Masseter*
Action: elevate mandible
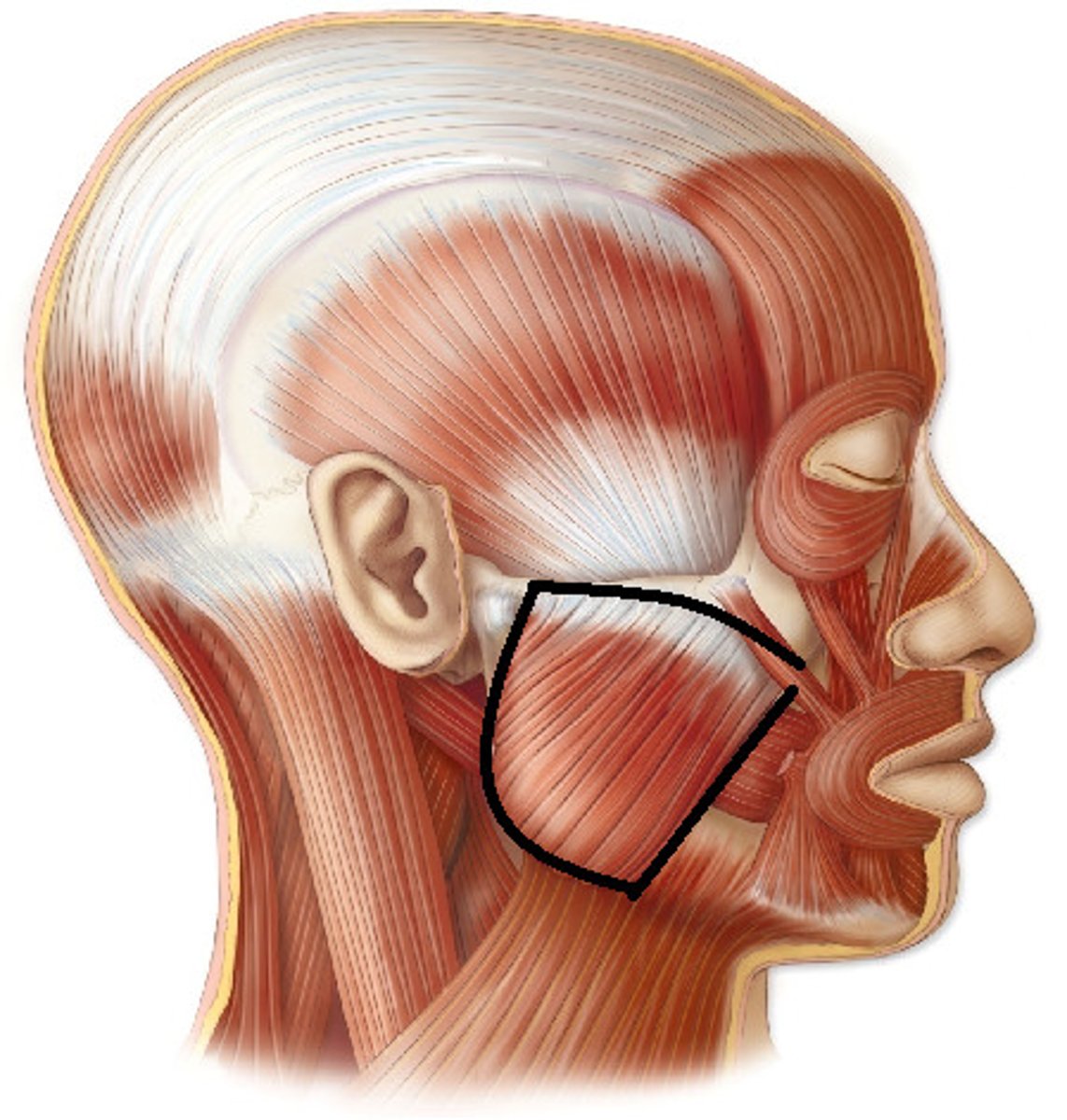
Buccinator
Action: pull back corners of lips
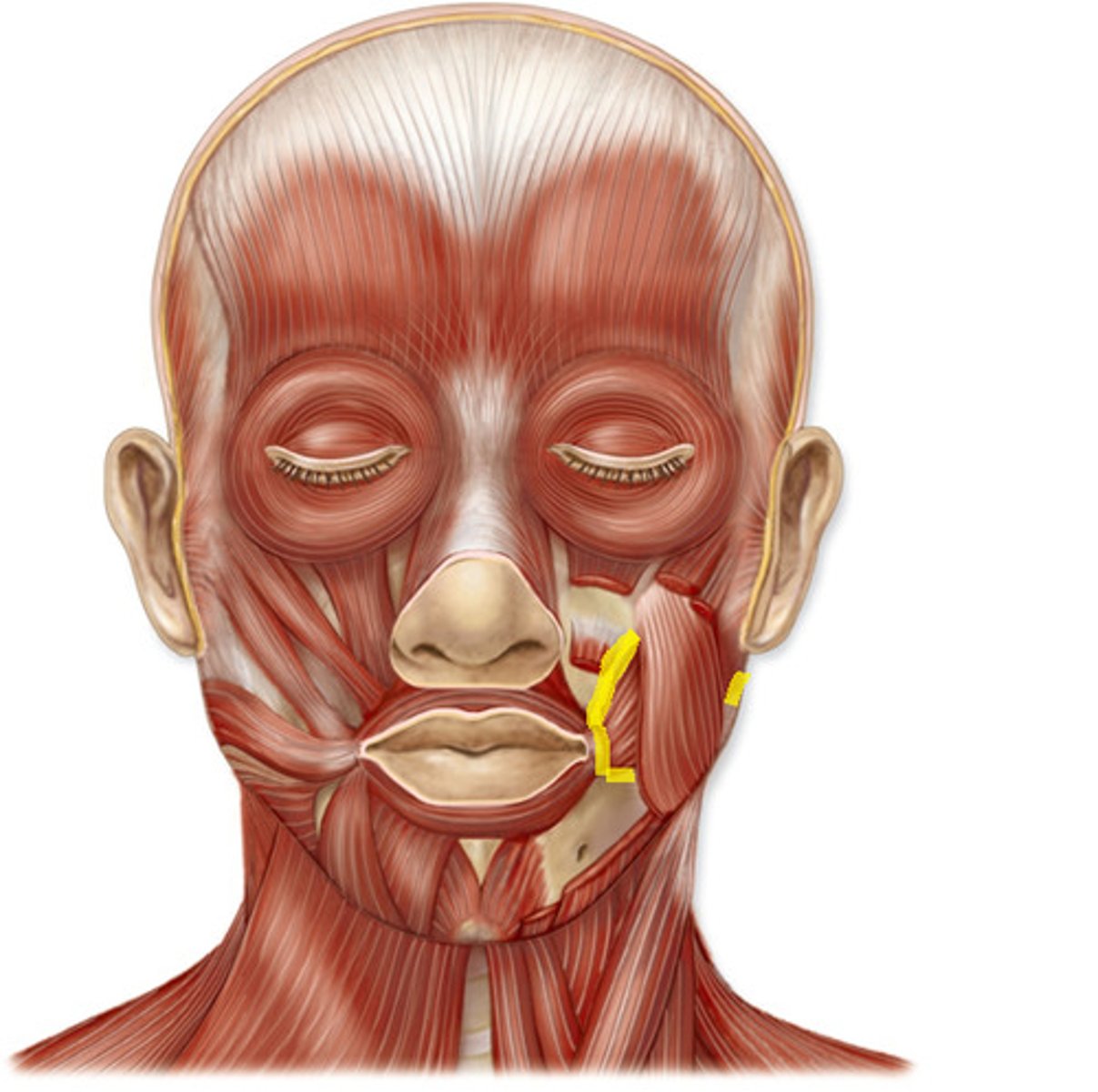
Temporalis*
Action: elevate mandible
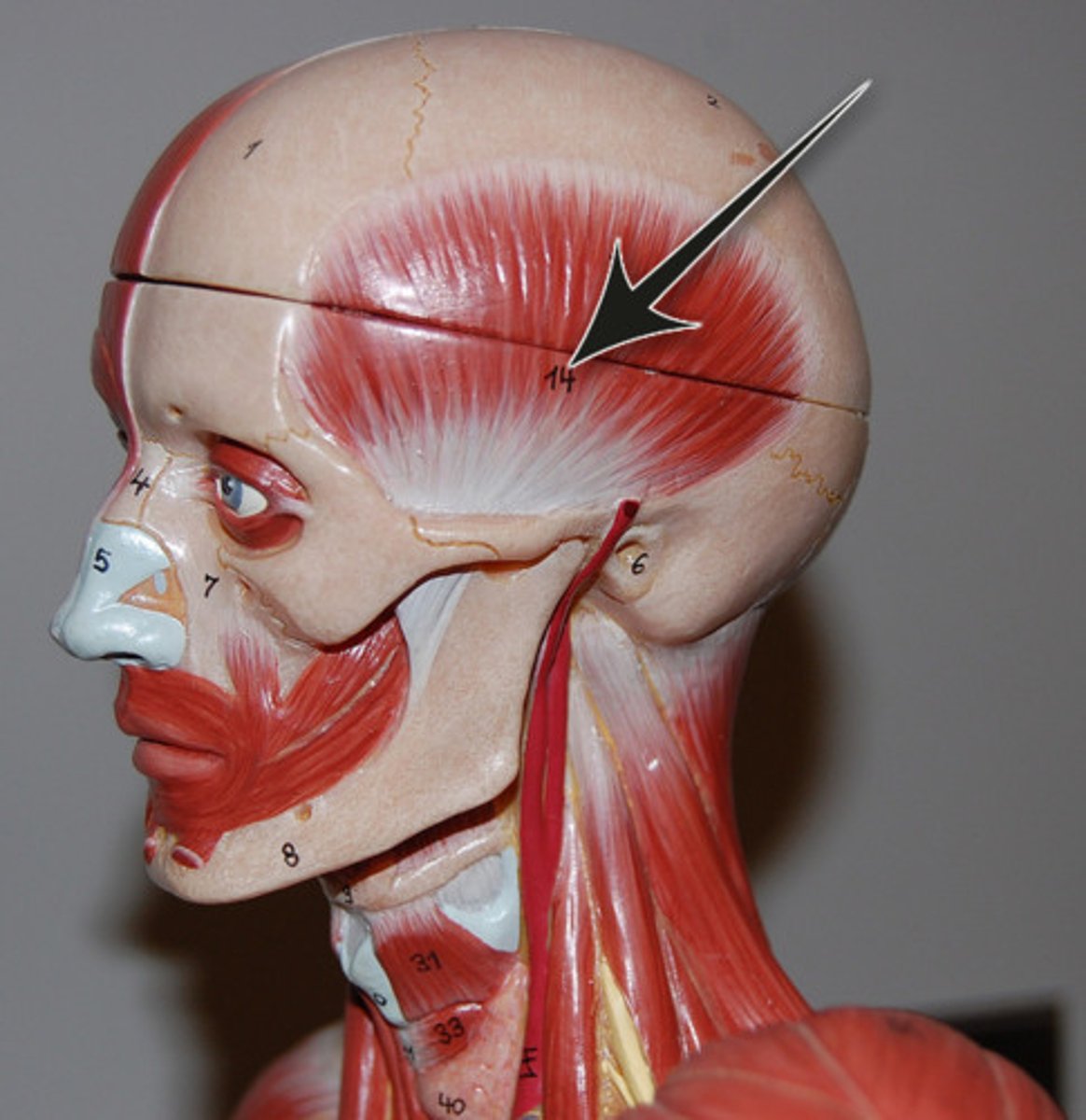
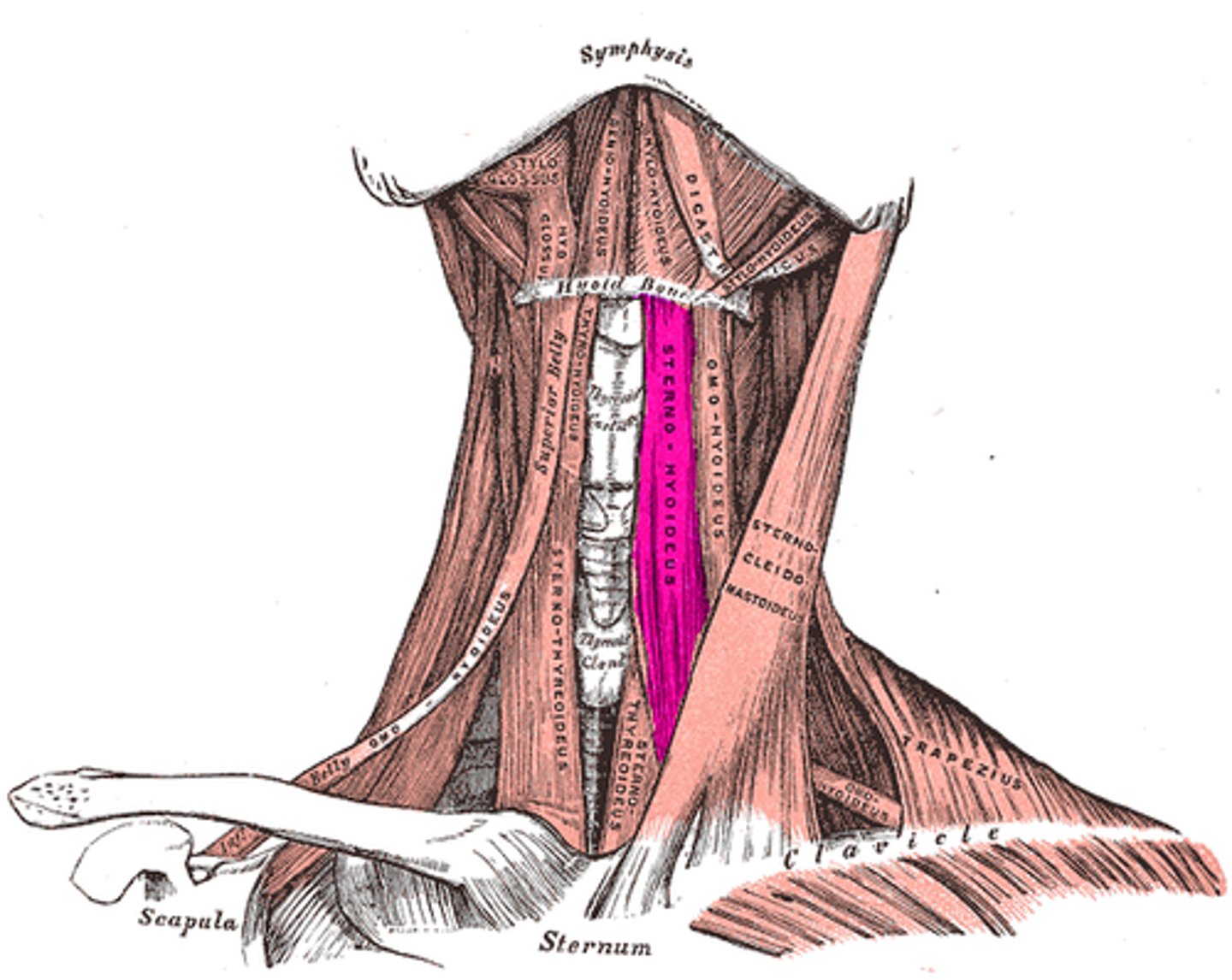
Sternohyoid
Action: depress hyoid bone and larynx
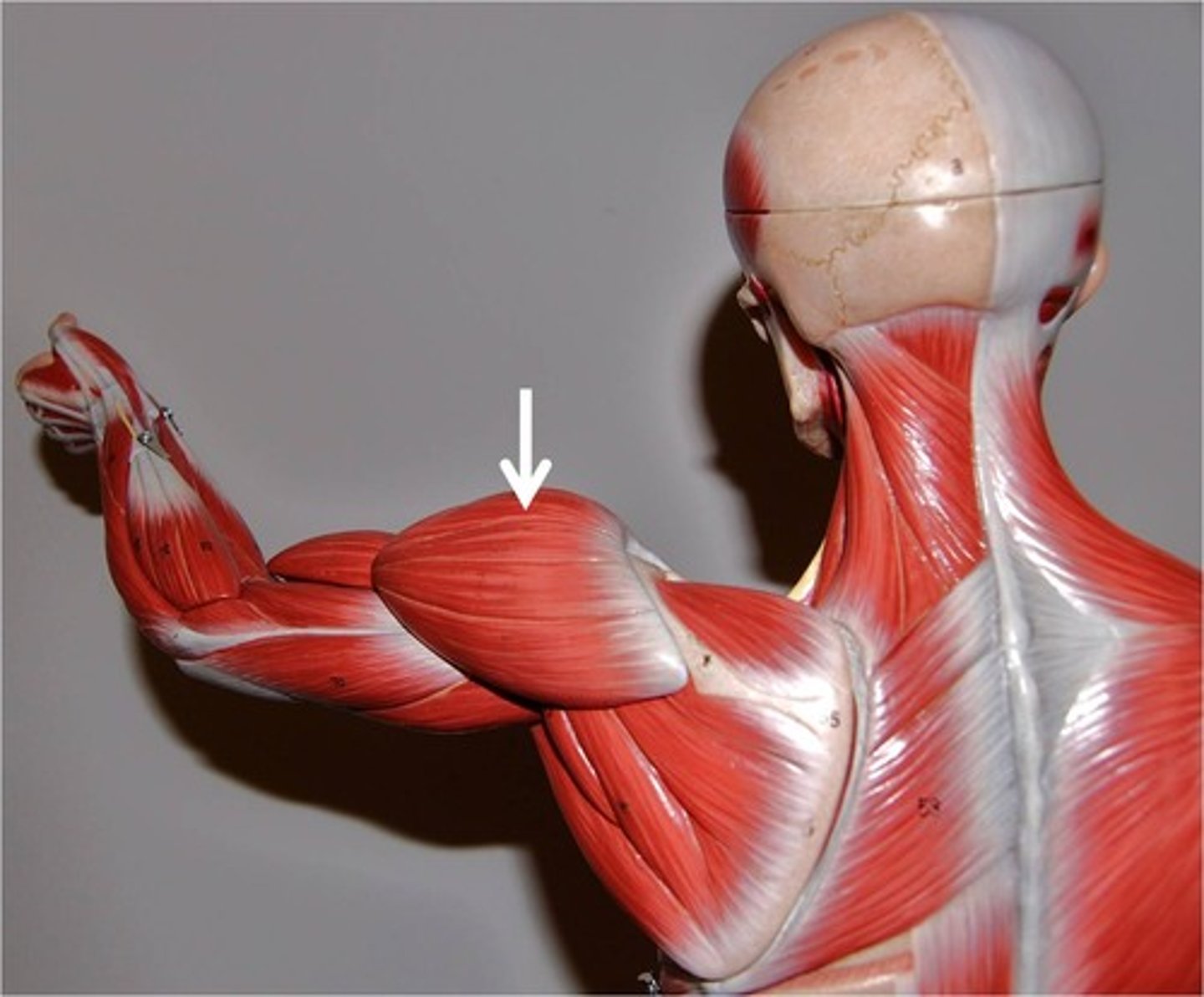
Deltoid*
Action: together:abduction of shoulder; anterior part: flexion and medial rotation of shoulder; posterior part: extension and lateral rotation of shoulder
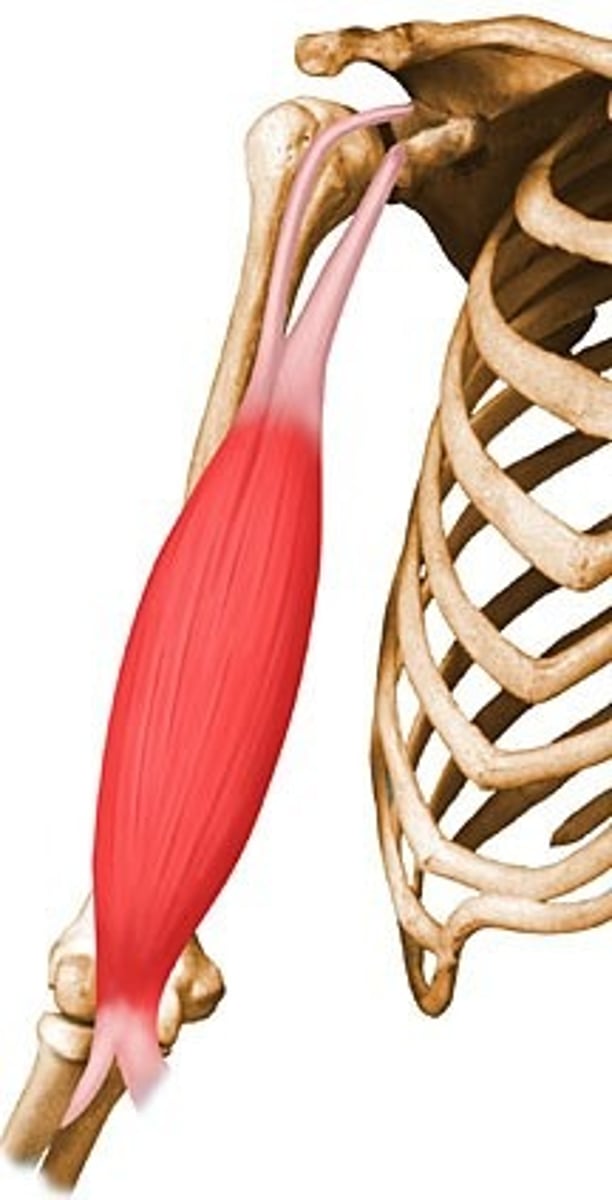
Biceps Brachii
Action: flexion of elbow, flexion of shoulder, assist supination
Triceps Brachii
Action: extension of elbow(long head also contributes to extension and adduction of shoulder)
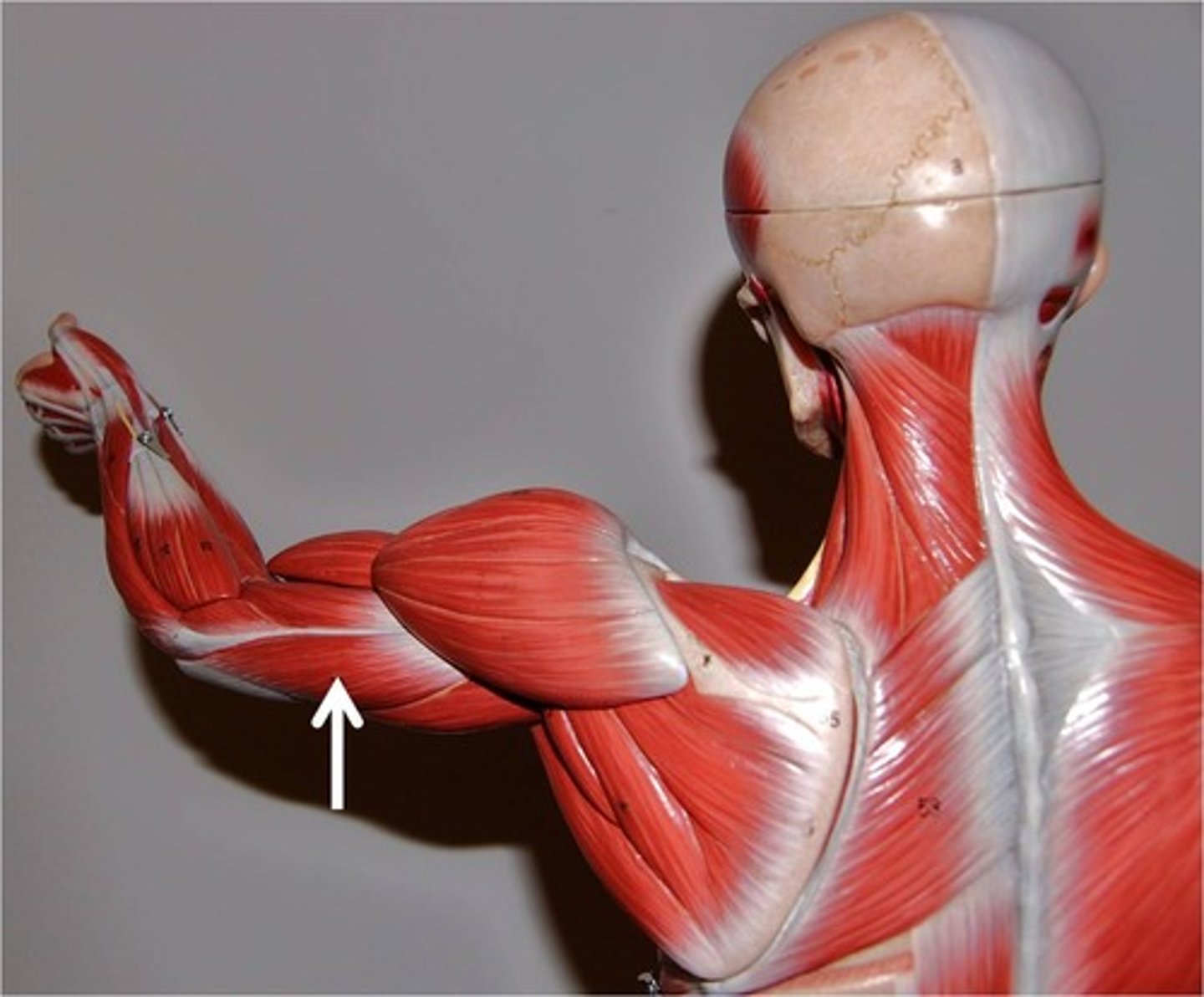
Brachialis
Action: flexion of elbow
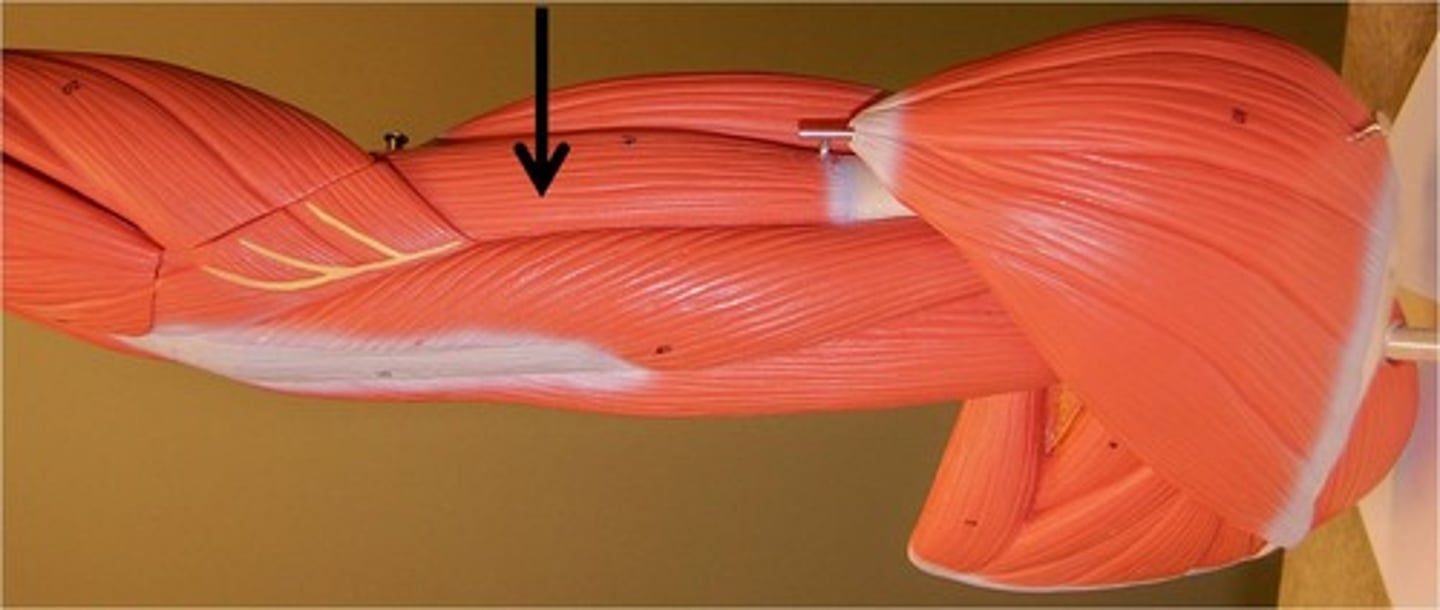
Brachioradialis
Action: flexion of elbow
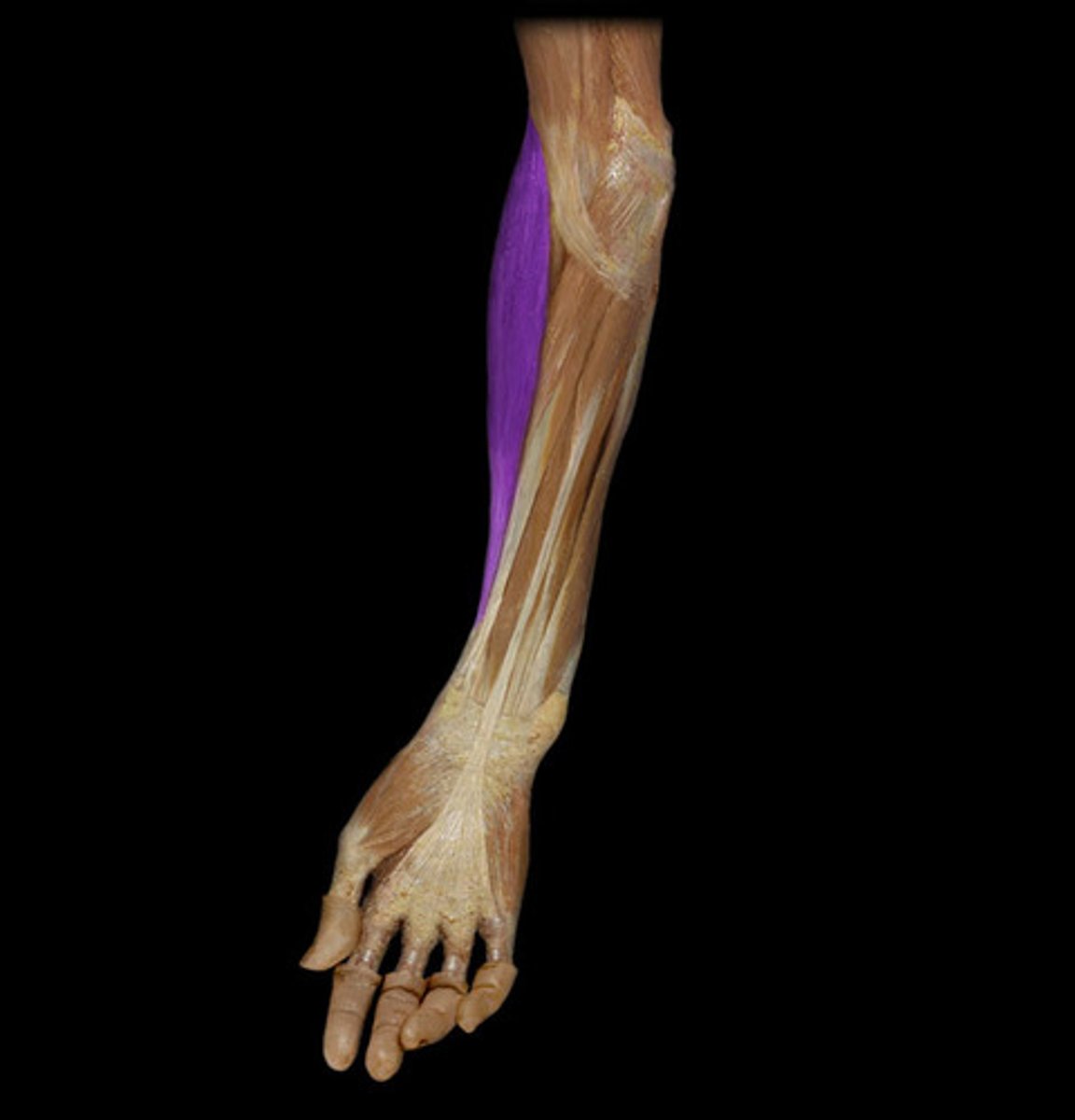
Pronator Teres
Action: pronation of forearm
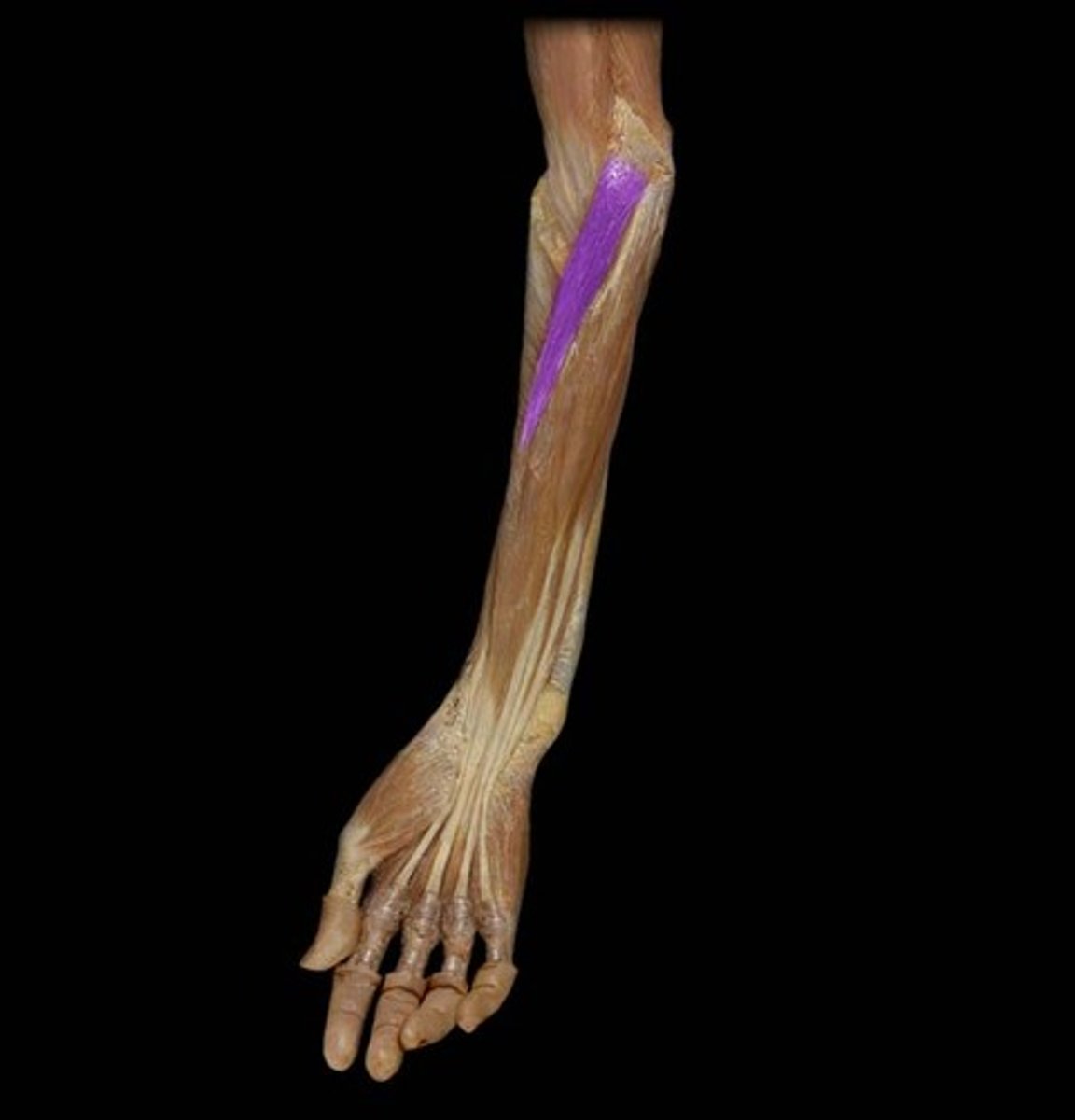
Extensor Digitorum
Action: extension of fingers and wrist
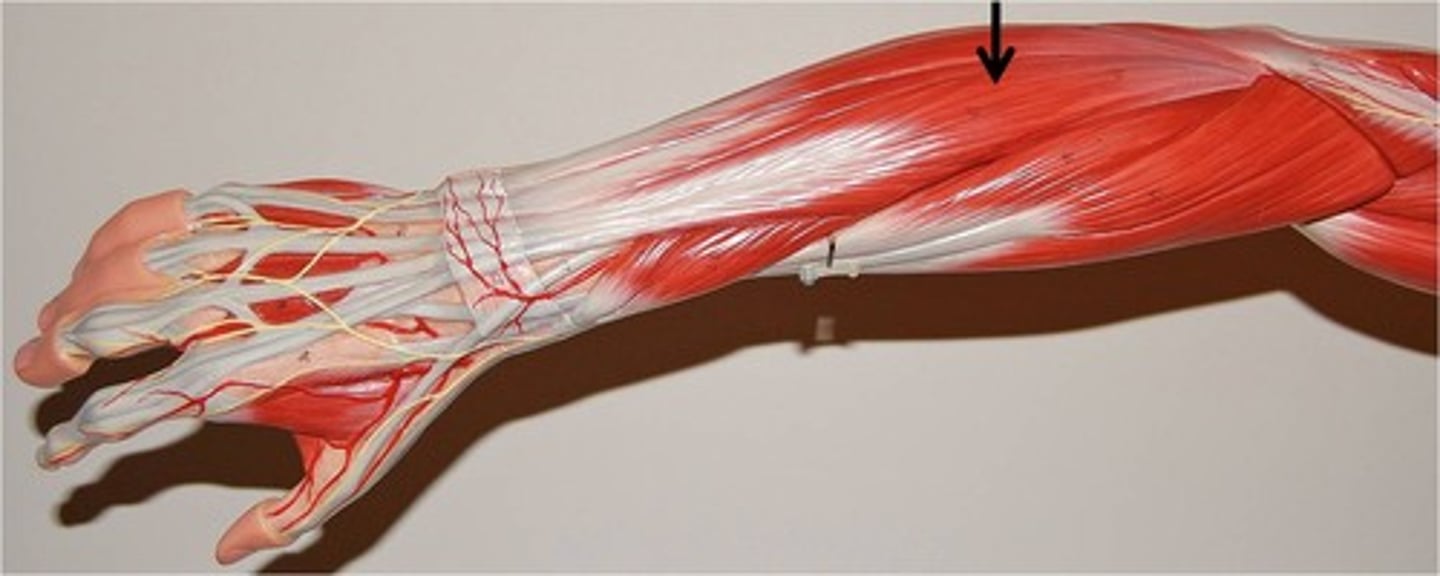
Palmaris Longus
Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: palmar aponeurosis and flexor retinaculum
Action: flexion of wrist
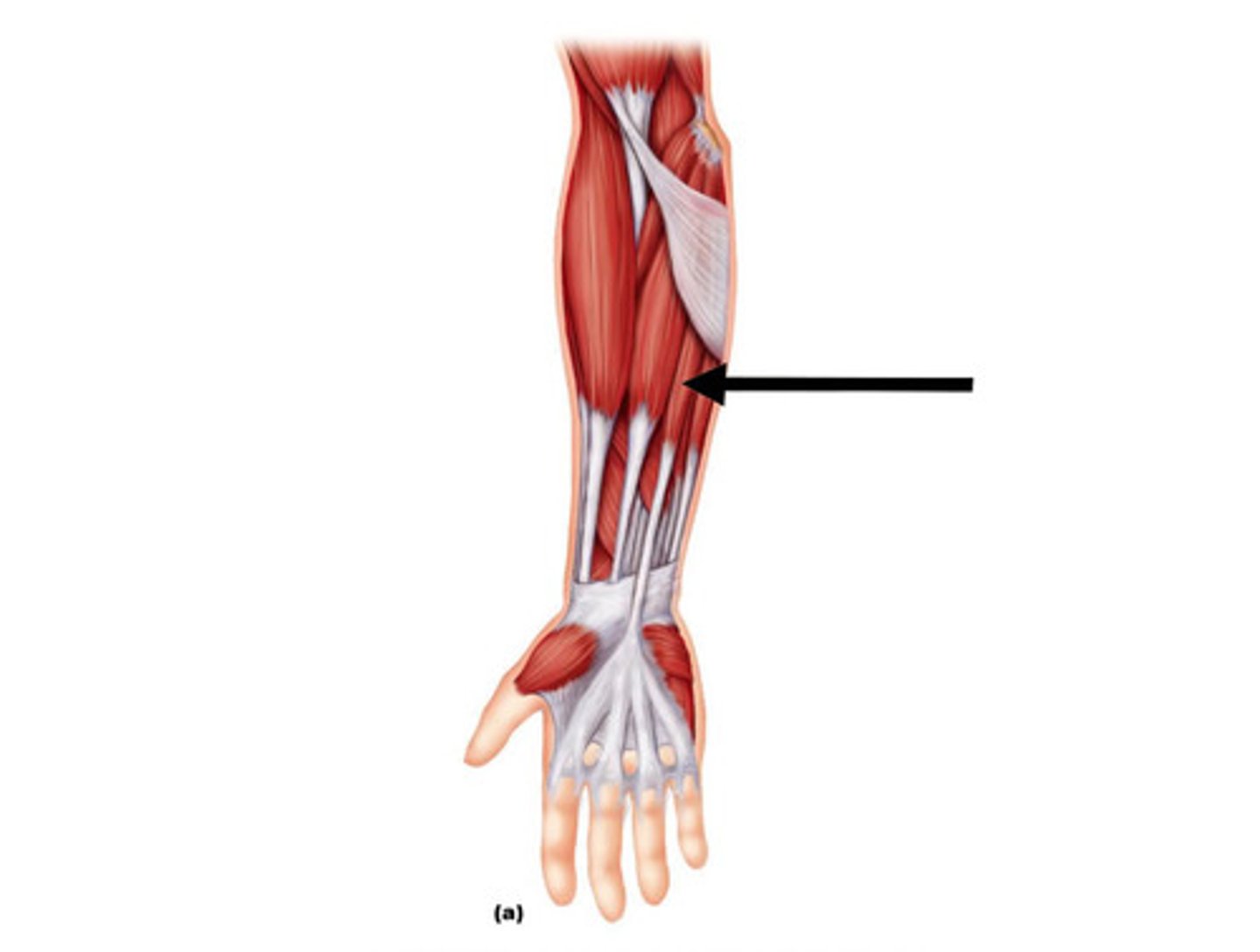
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Action: flexion and abduction of wrist
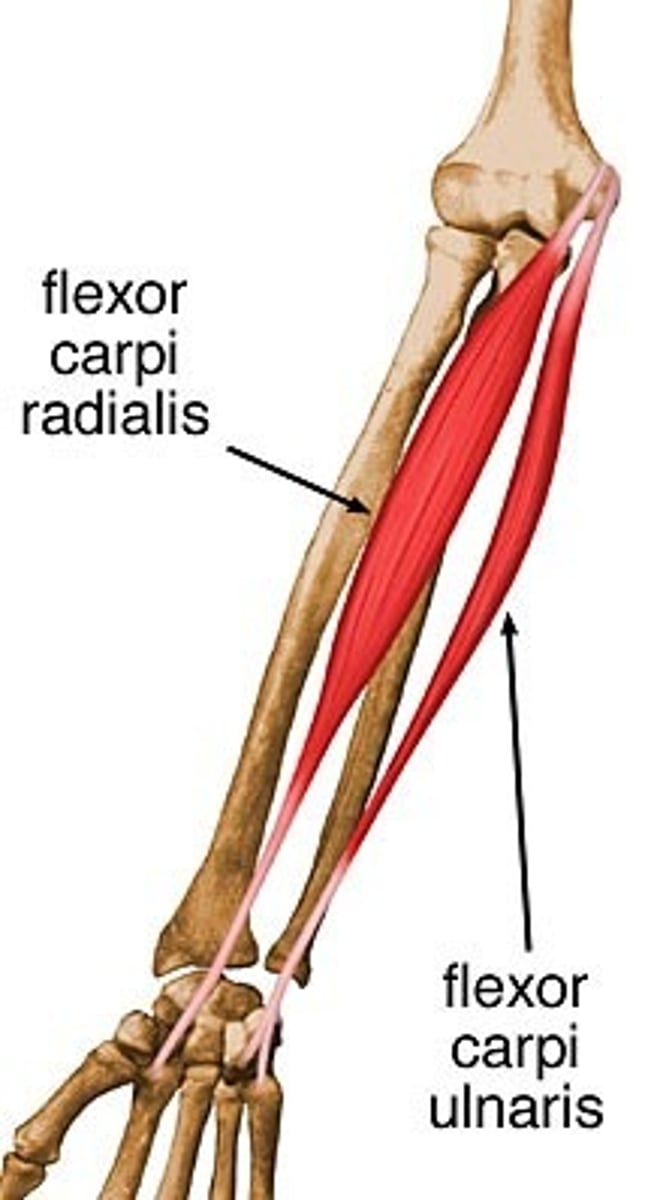
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Action: flexion and adduction of wrist
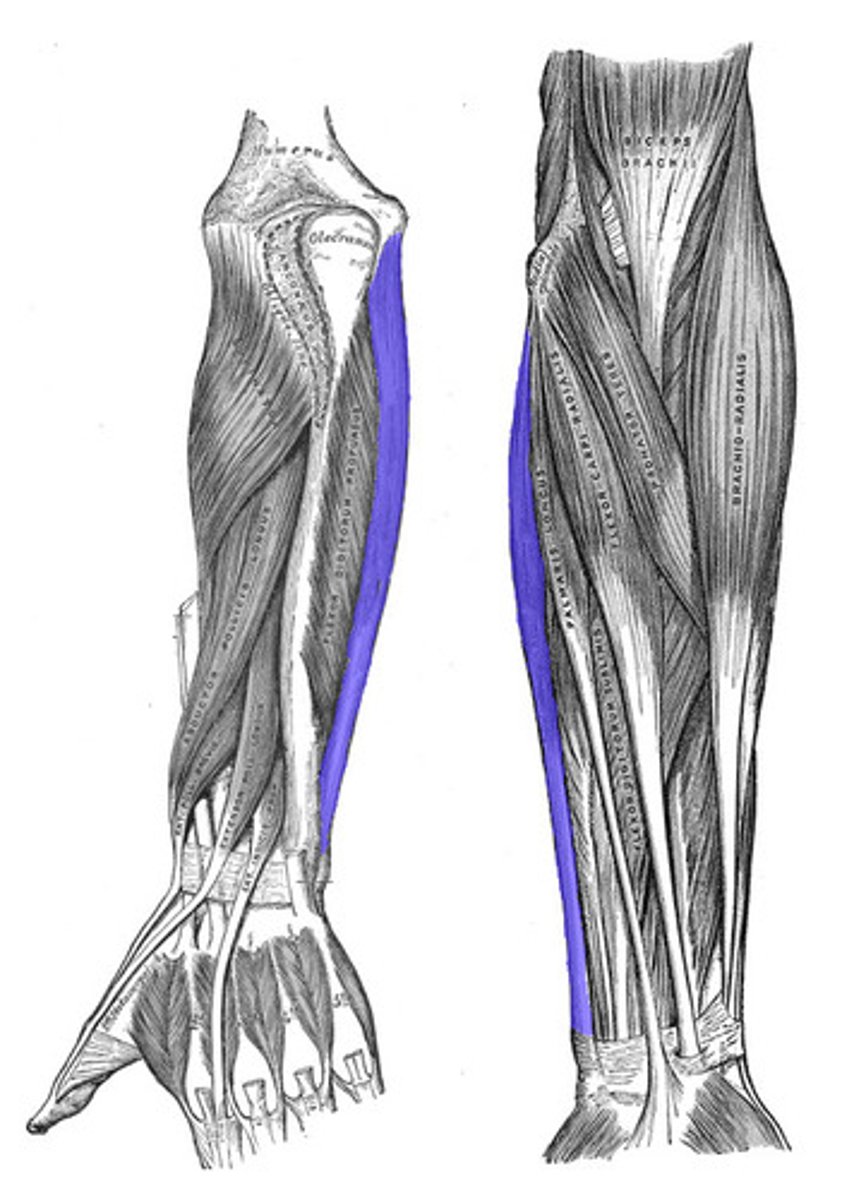
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Action: extension and adduction of wrist
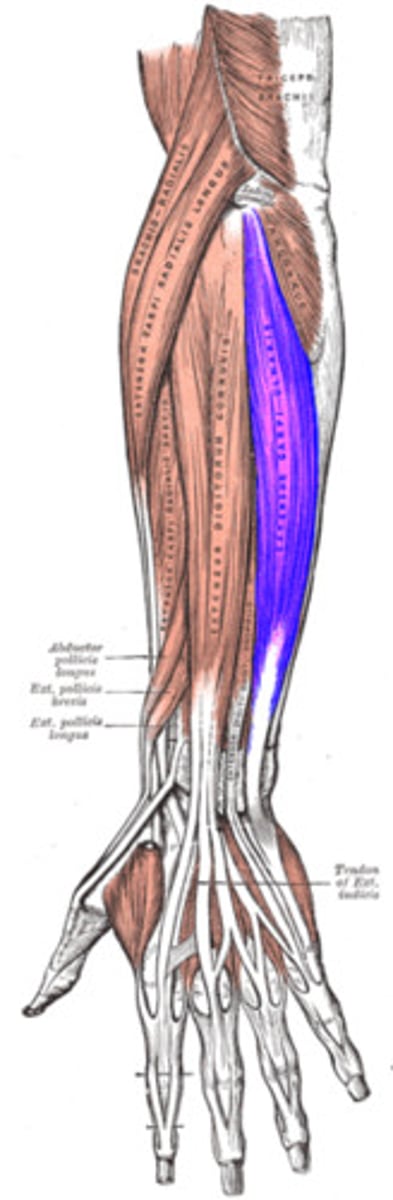
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
l
Action: extension and abduction of wrist
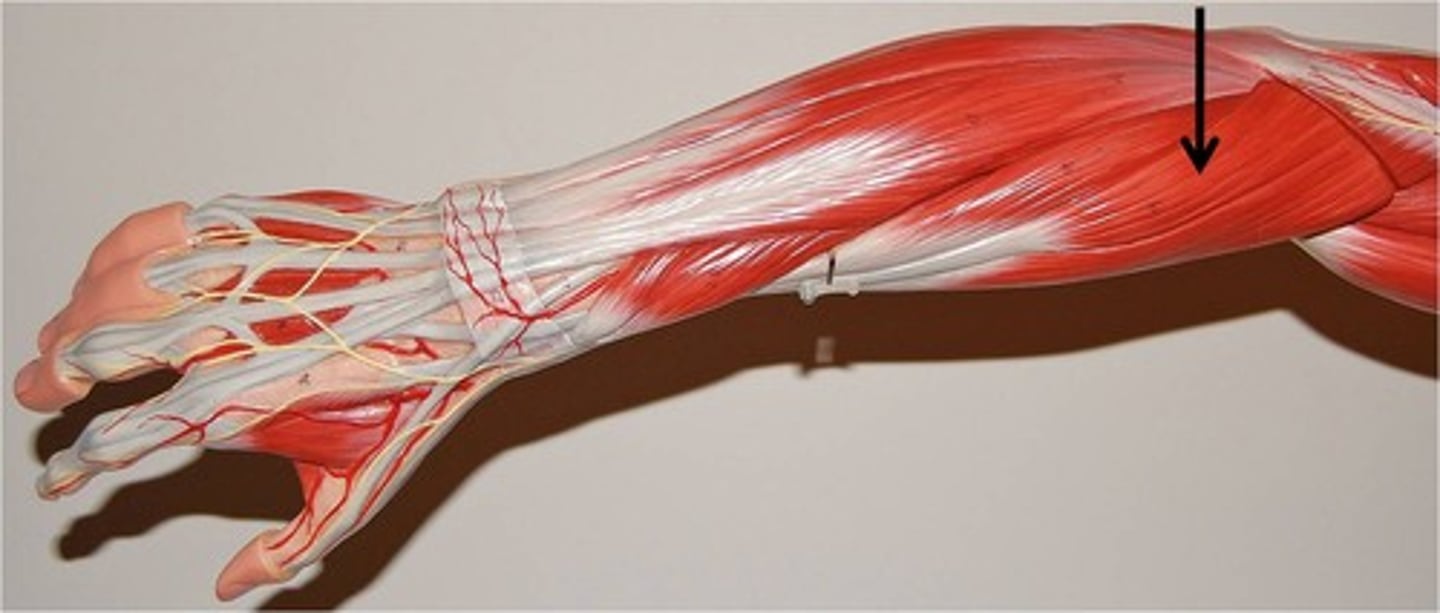
Abductor Pollicis Longus
Action:abduction of thumb and wrist
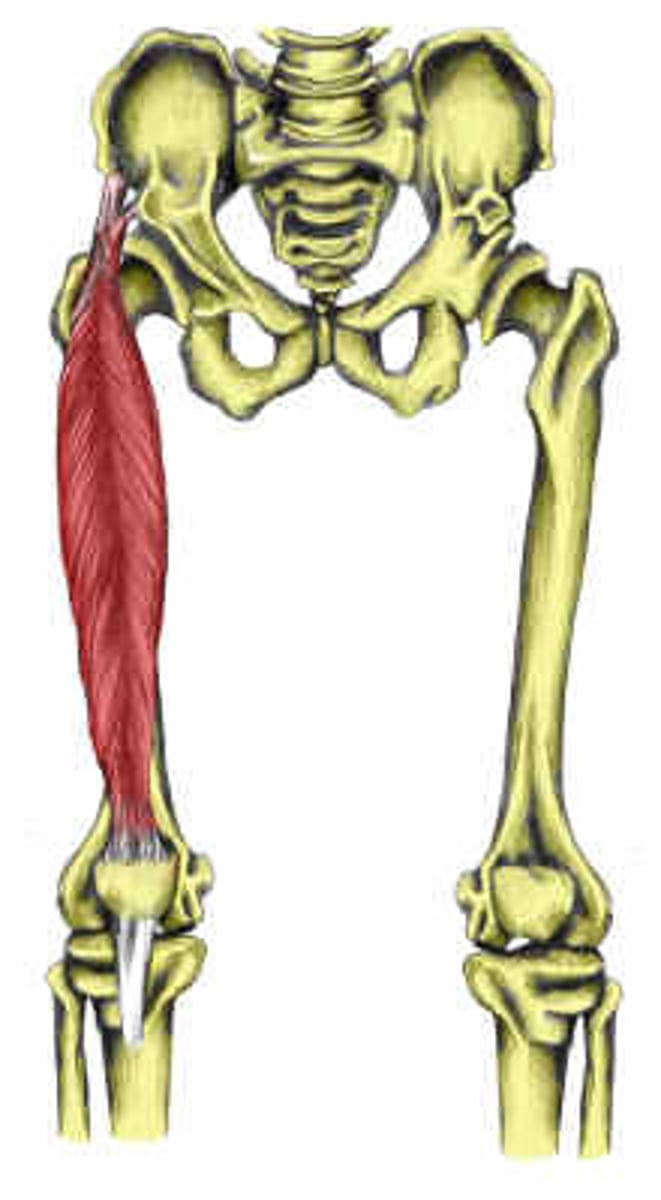
Rectus Femoris*
Action: extension of knee, flexion of hip
Vastus Lateralis
Action: extension of knee
Vastus Medialis
Action: extension of knee
Vastus Intermedius
Action:extension of knee
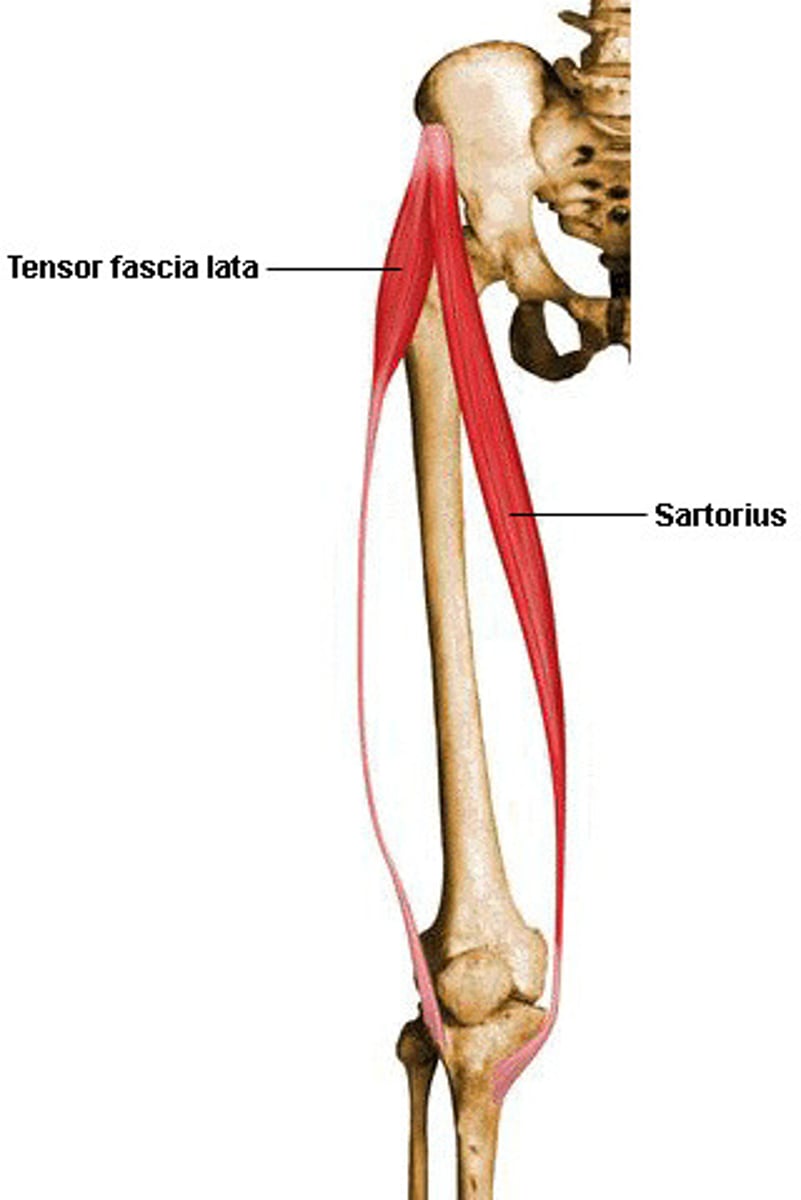
Sartorius*
Action: flexion of knee, flexion and lateral rotation of hip
Biceps Femoris
Action: flexion of knee, extension and lateral rotation of hip
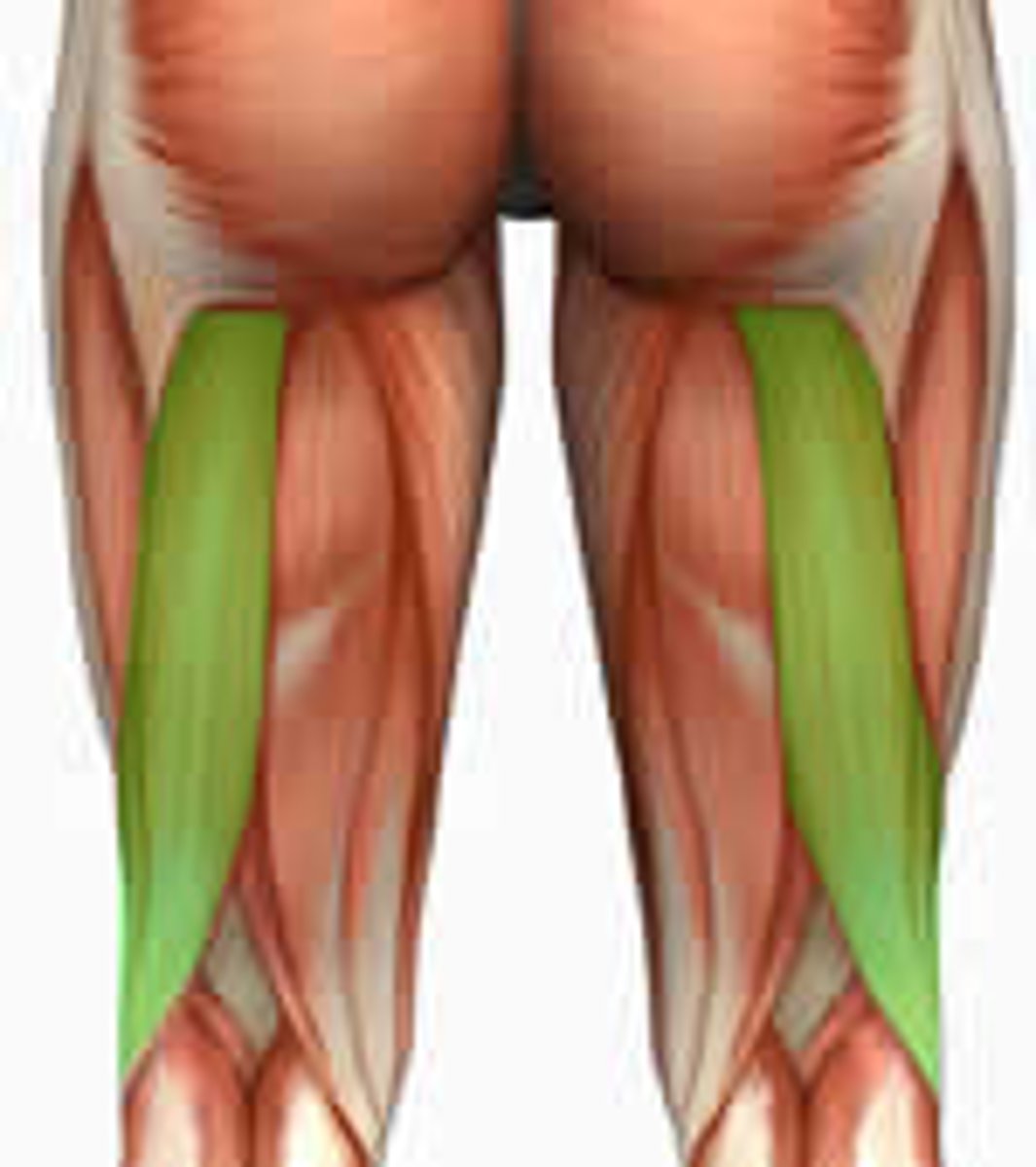
Semitendinosus
Action: flexion of knee, extension and medial rotation of hip
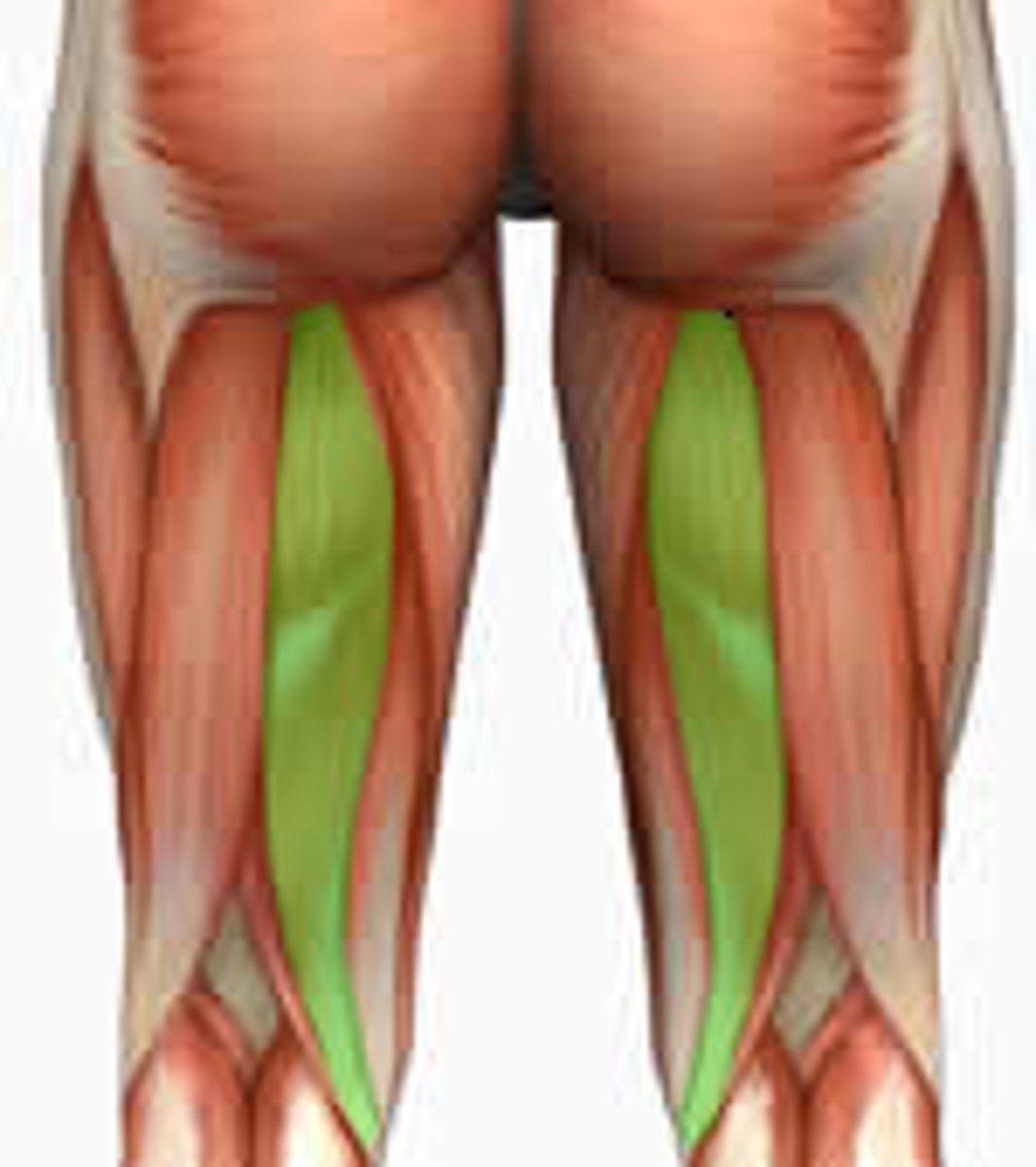
Semimembranosus
Action: flexion of knee, extension and medial rotation of hip
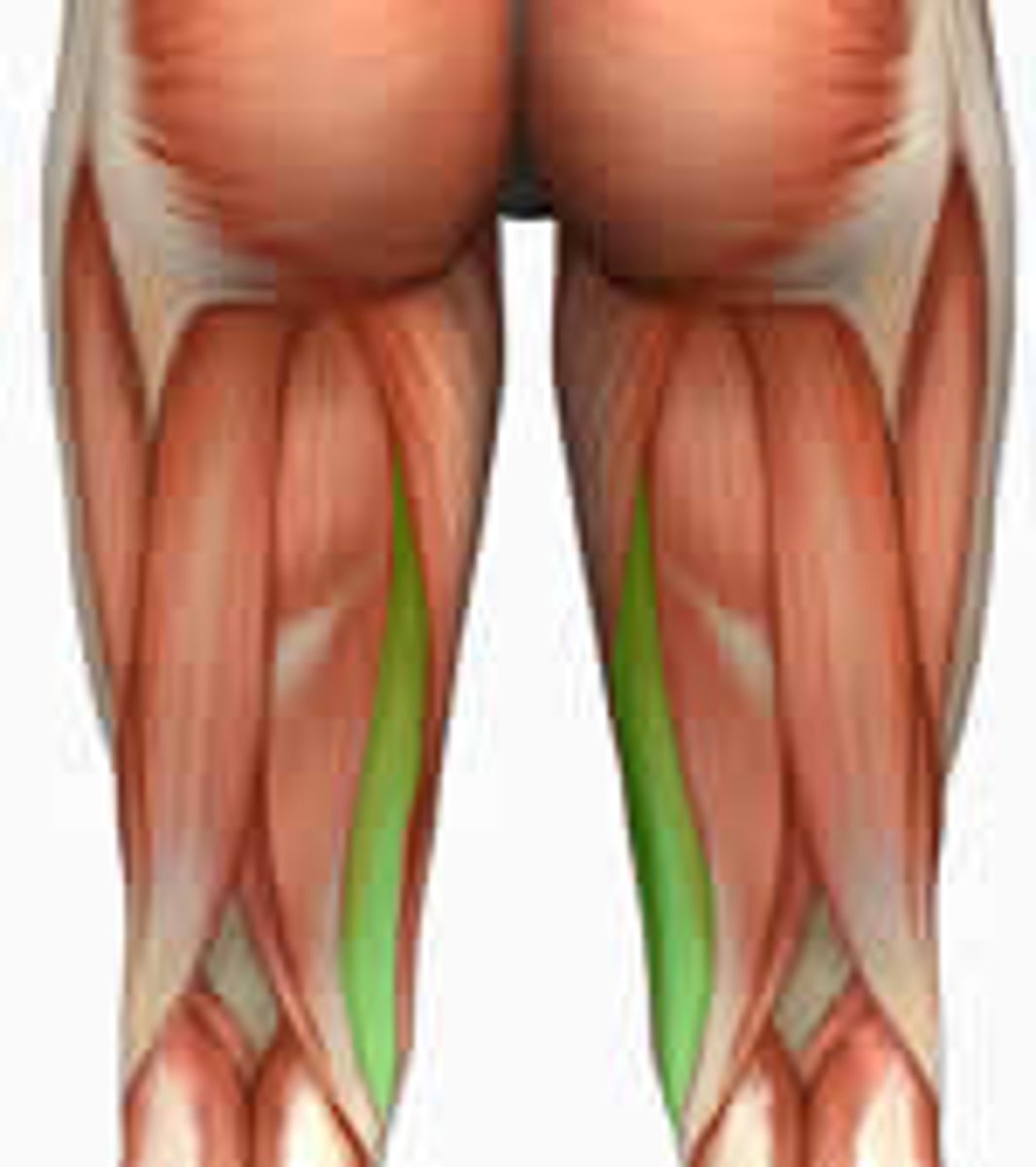
Adductor Magnus
Action: adduction and medial rotation of hip
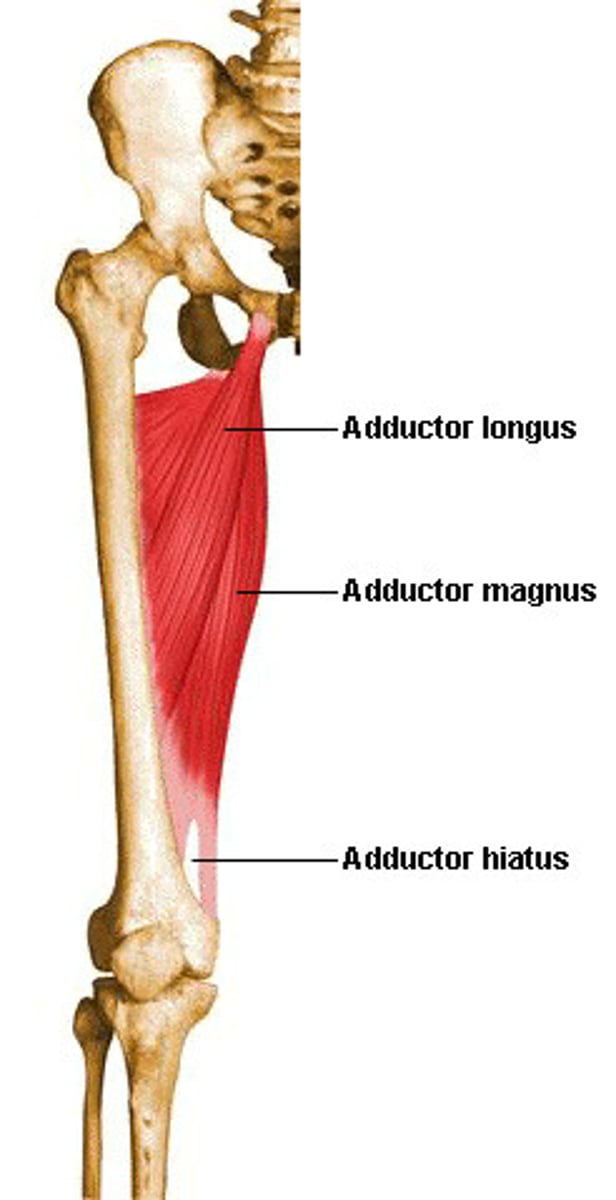
Adductor Longus
Action: adduction, flexion, and medial rotation of hip
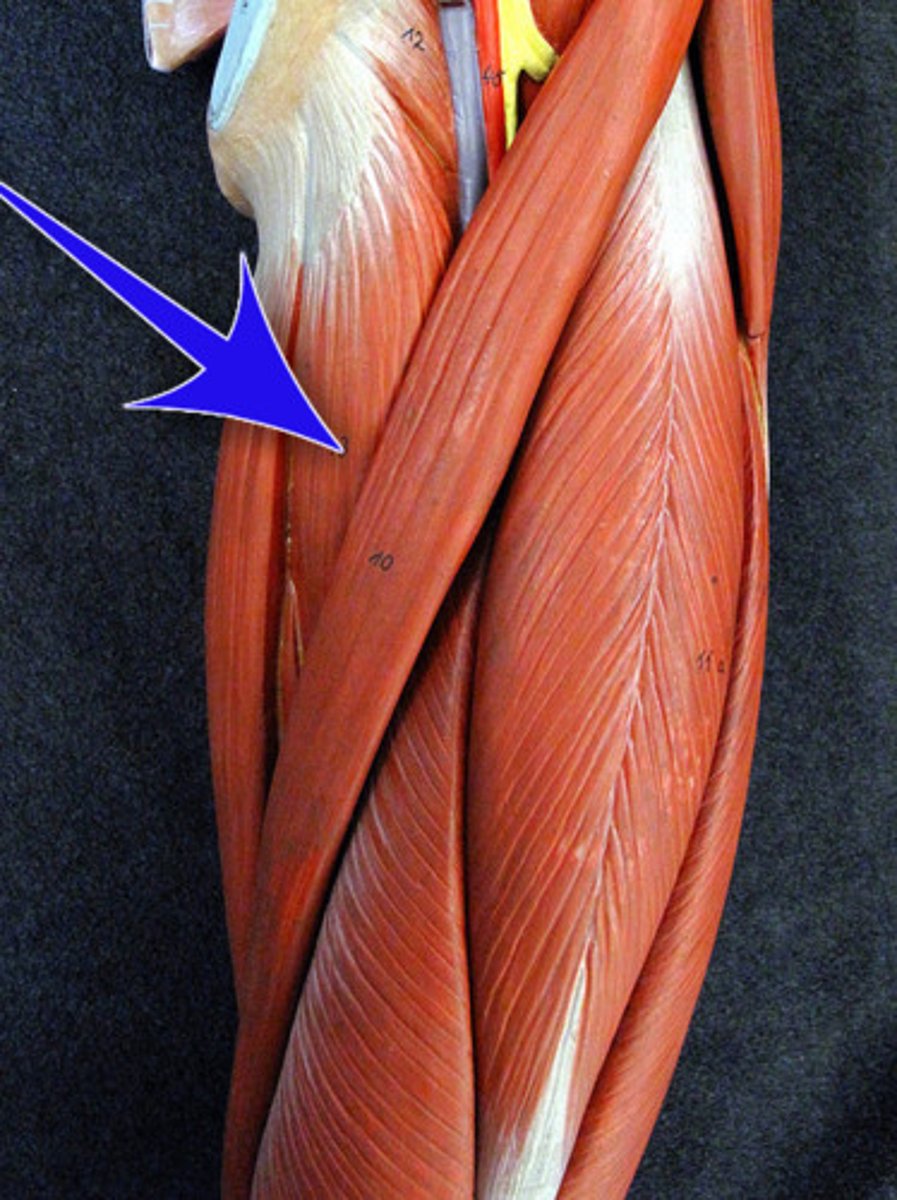
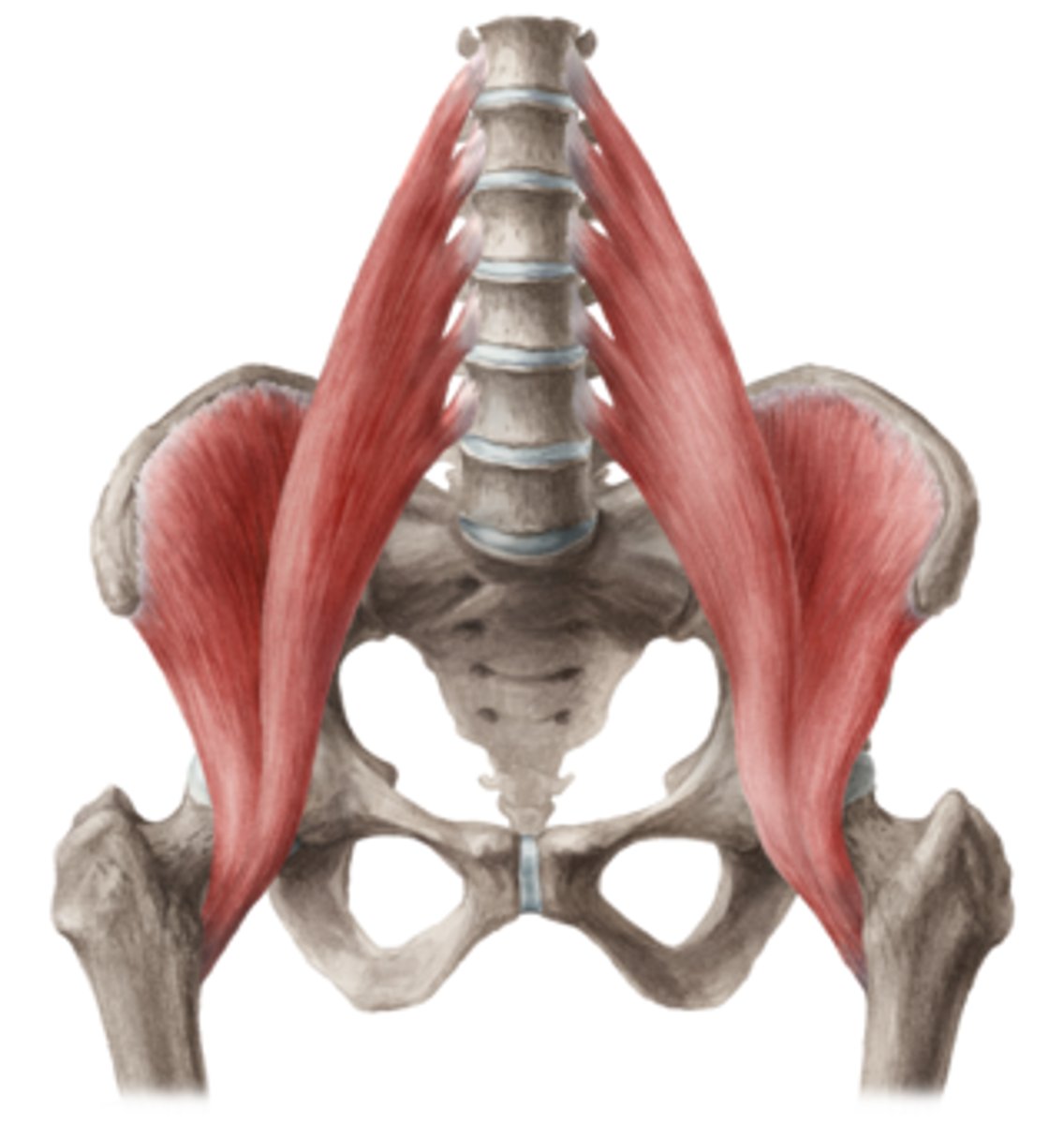
Gluteus Maximus*
Action: extension and lateral rotation of hip
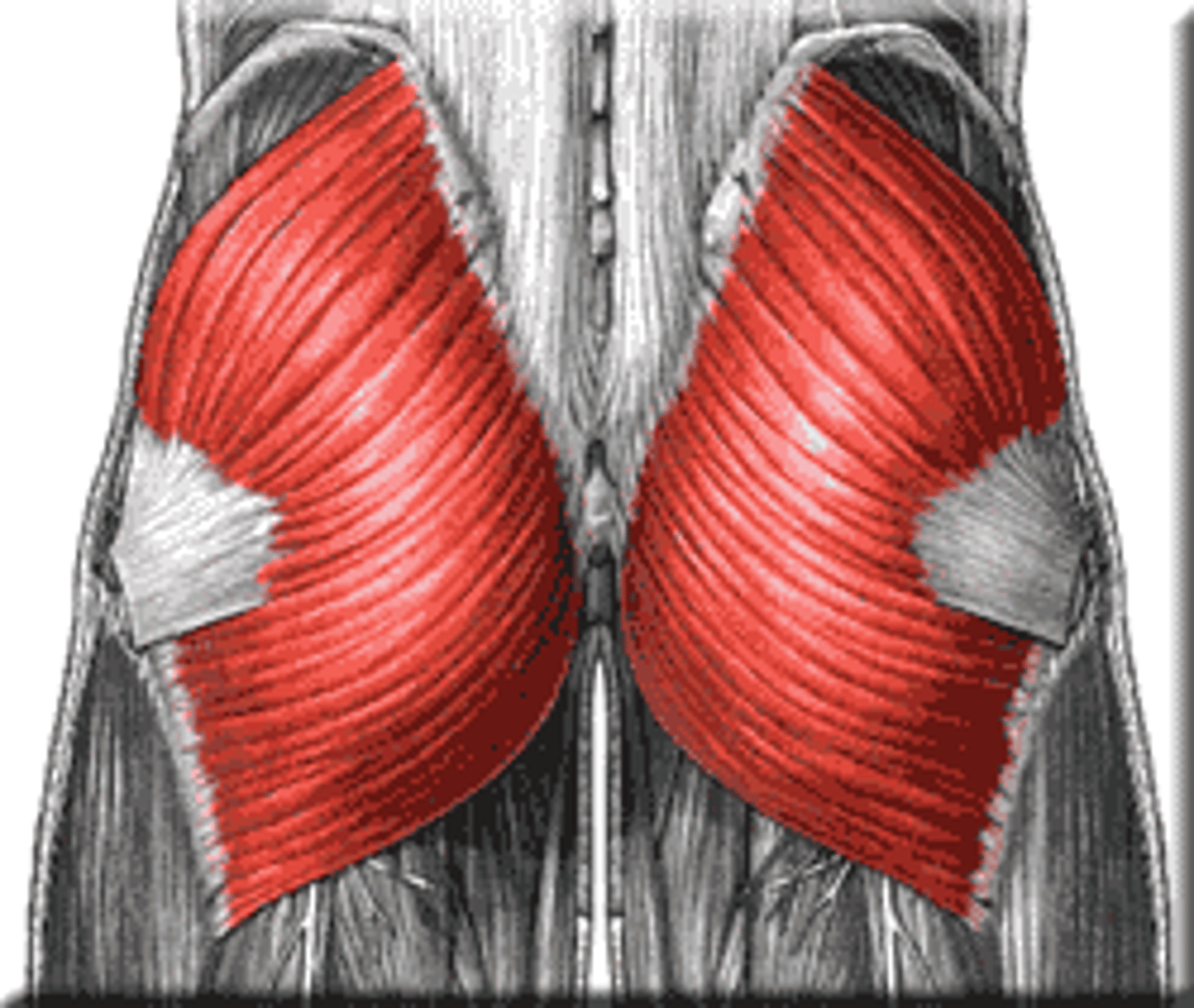
Gluteus Medius
Action: abduction and medial rotation of hip
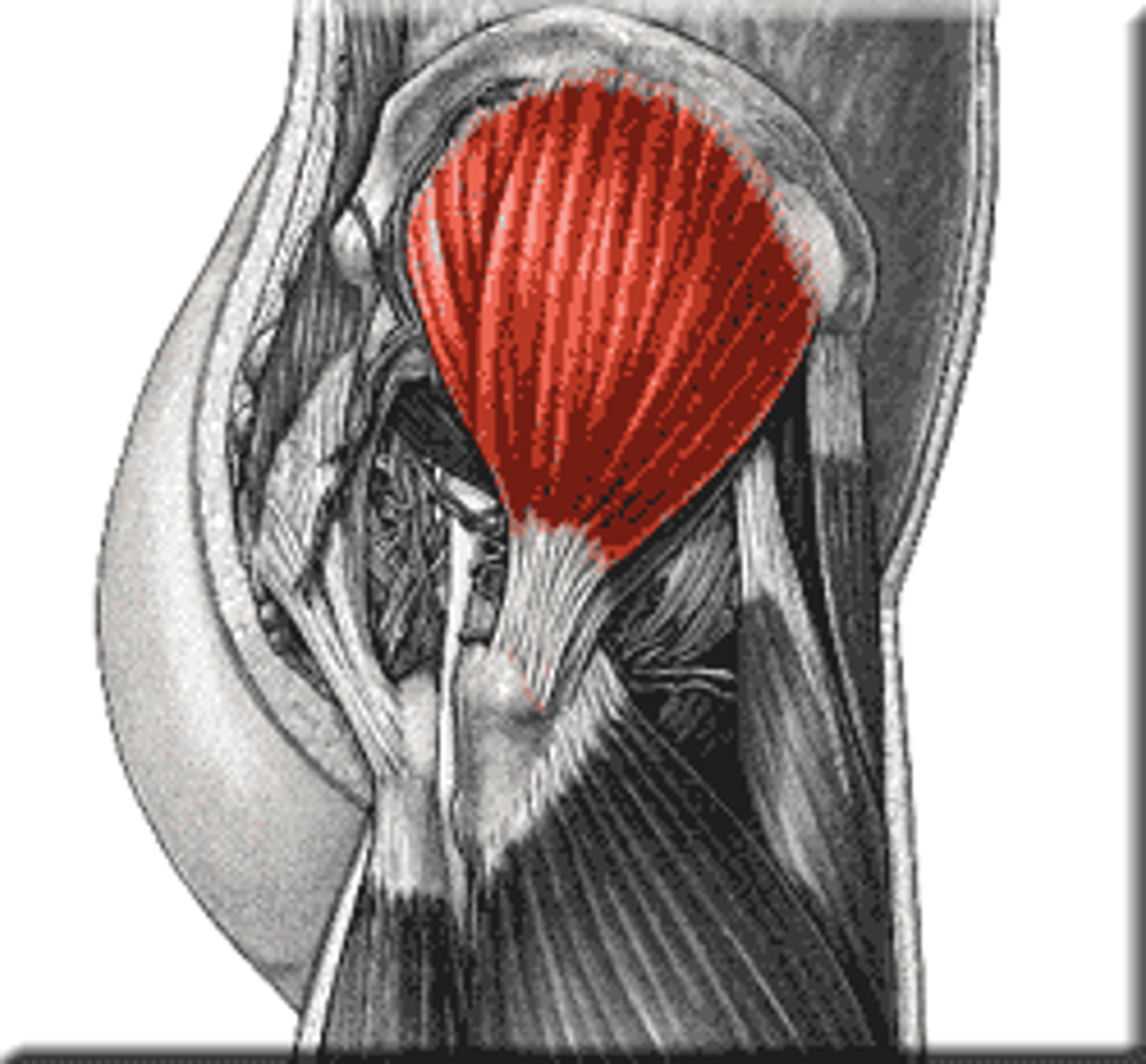
Gluteus Minimus
Action: abduction and medial rotation of hip
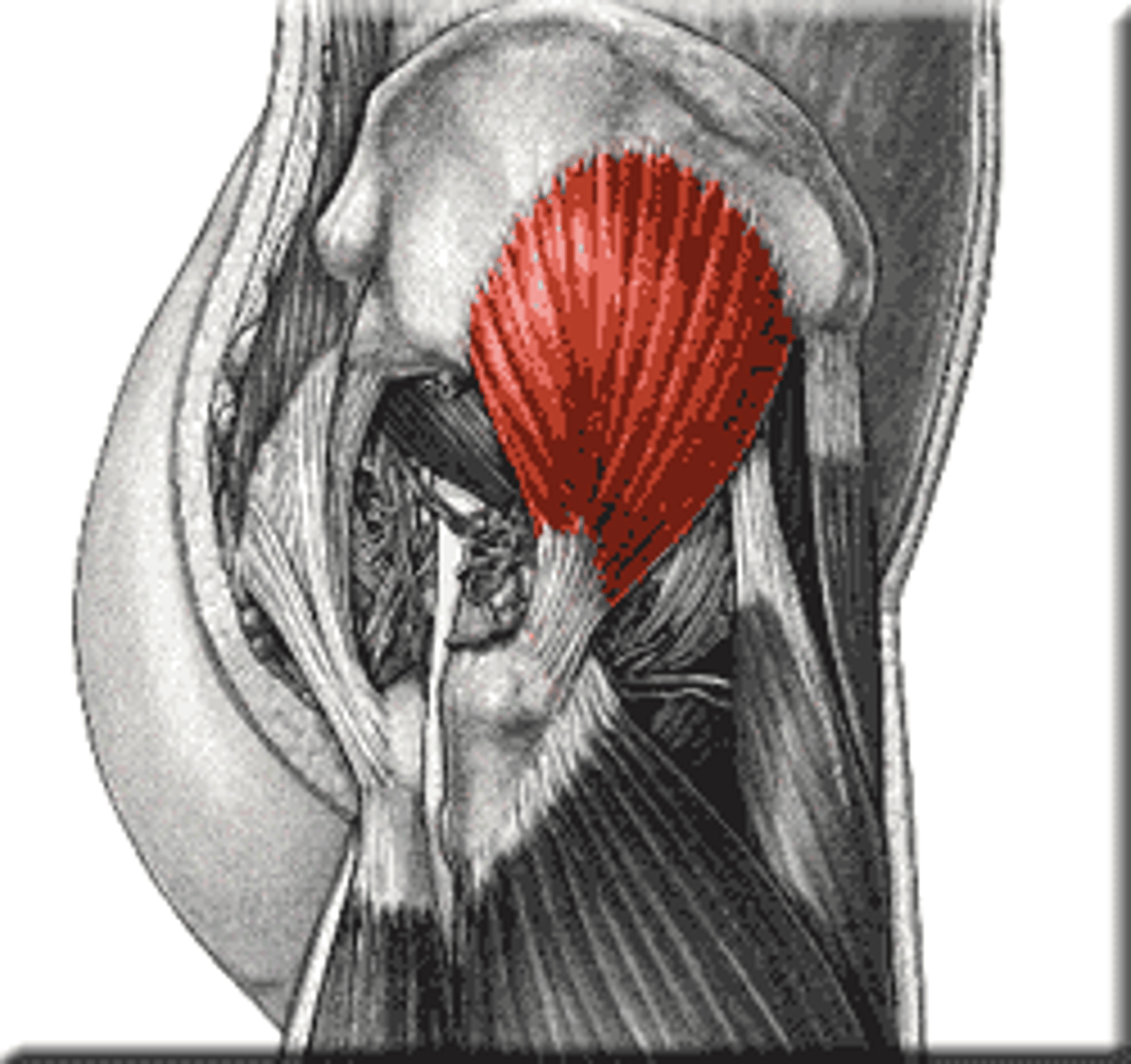
Tensor Fasciae Latae
Action: flexion and medial rotation of hip, support and knee joint
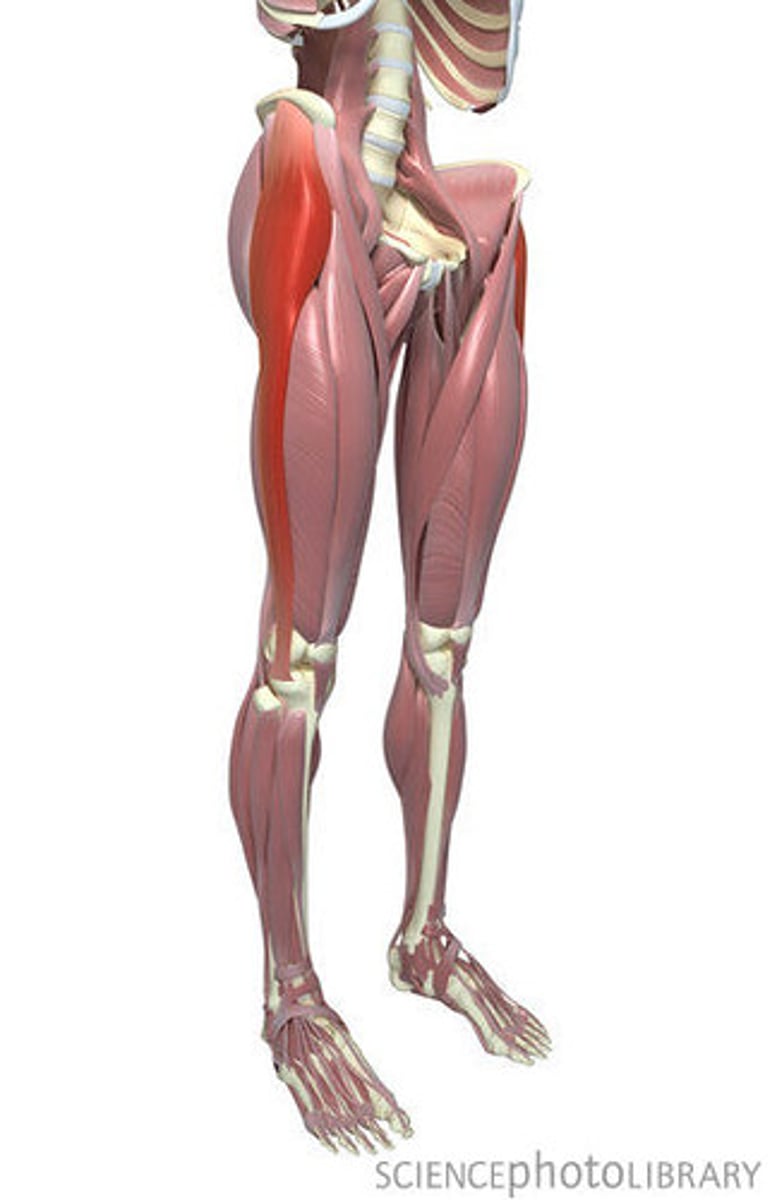
Iliopsoas
Action: flexion of hip
Iliotibial Tract
Band of longitudinal fibers on lateral side of fascia lata, connects distally to the lateral condyle of tibia
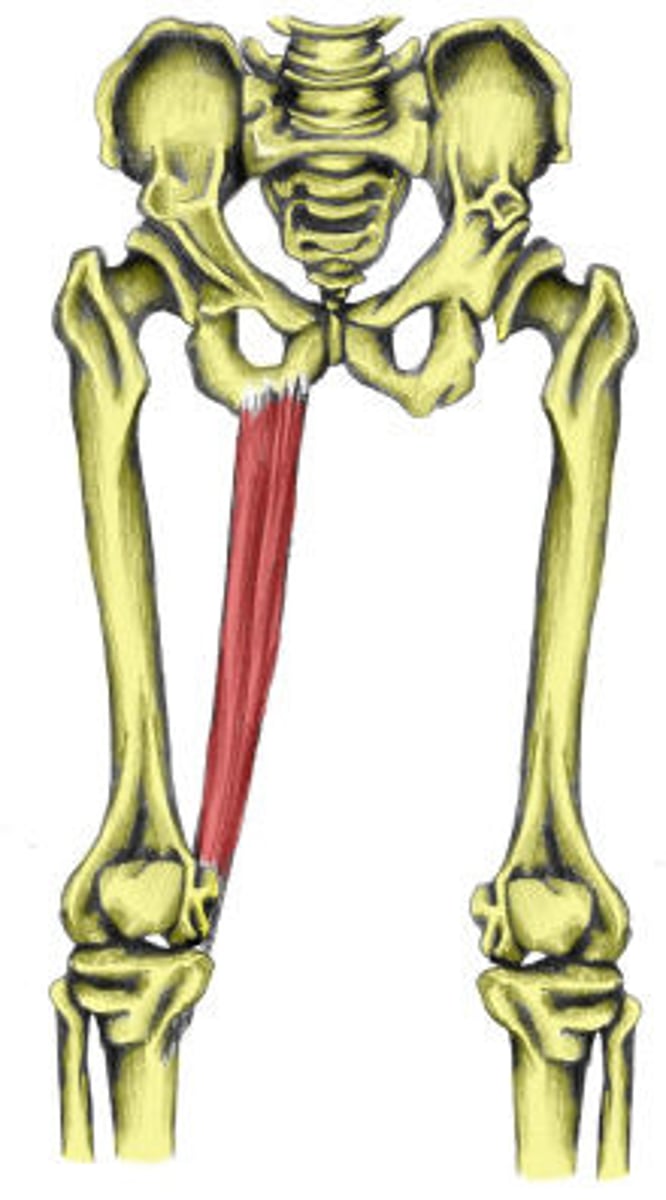
Gracilis
Action: flexion of knee, adduction and medial rotation of hip
Gastrocnemius*
Action: ankle extension, foot inversion, and knee flexion
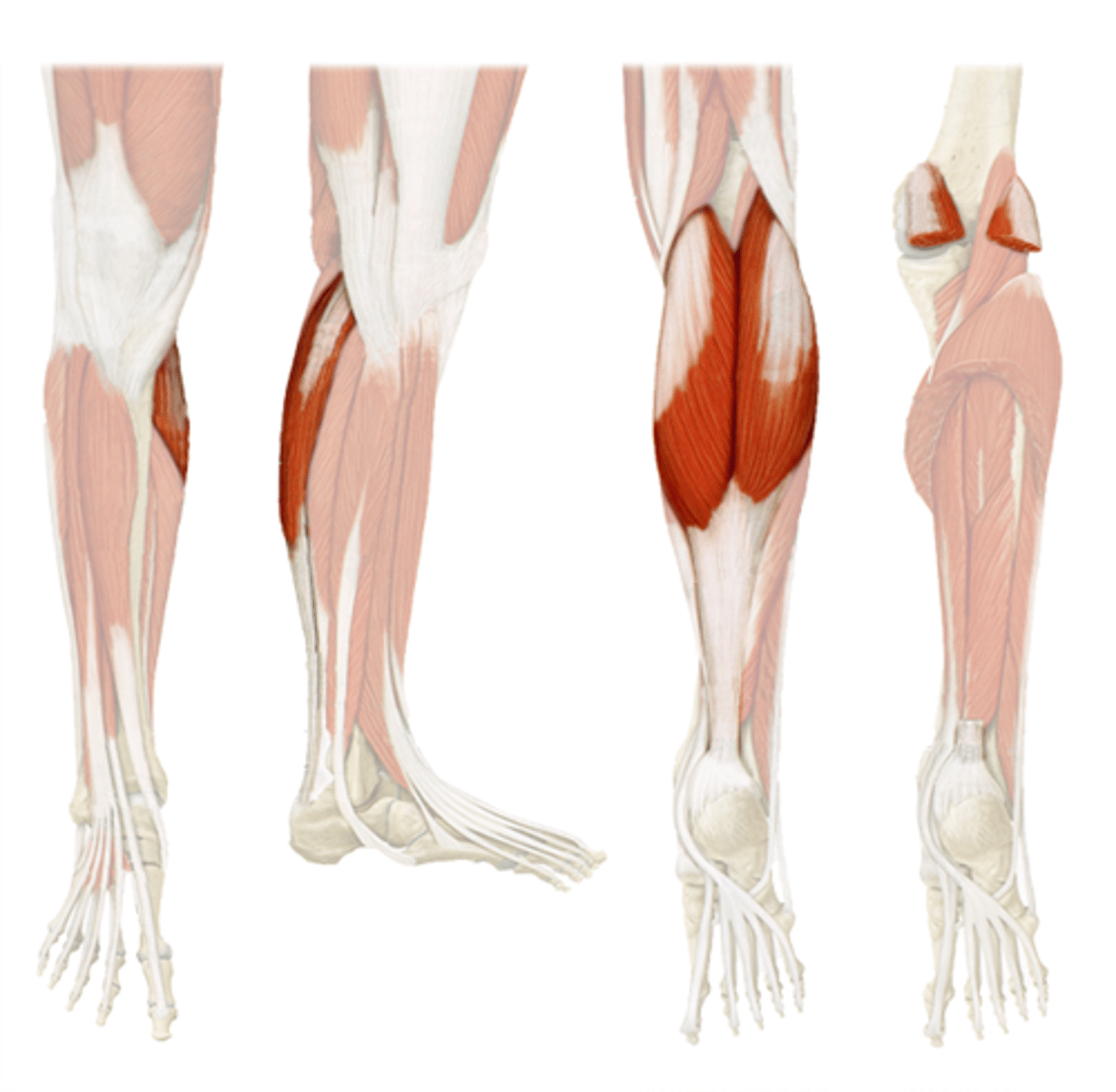
Soleus*
Action: ankle extension
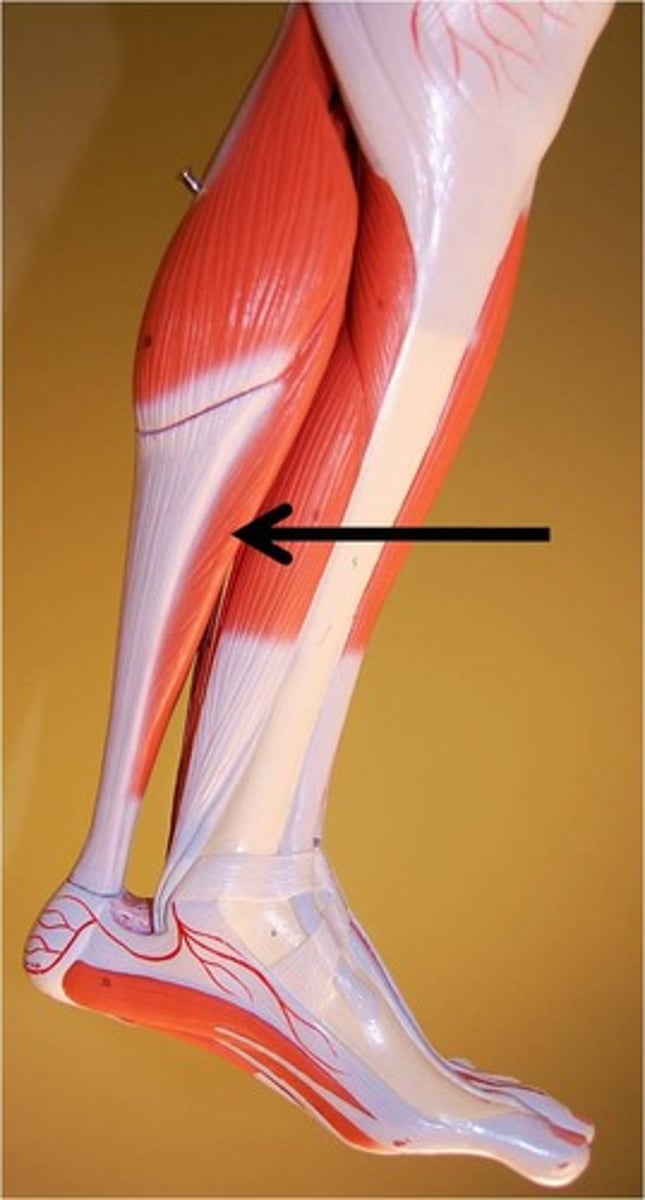
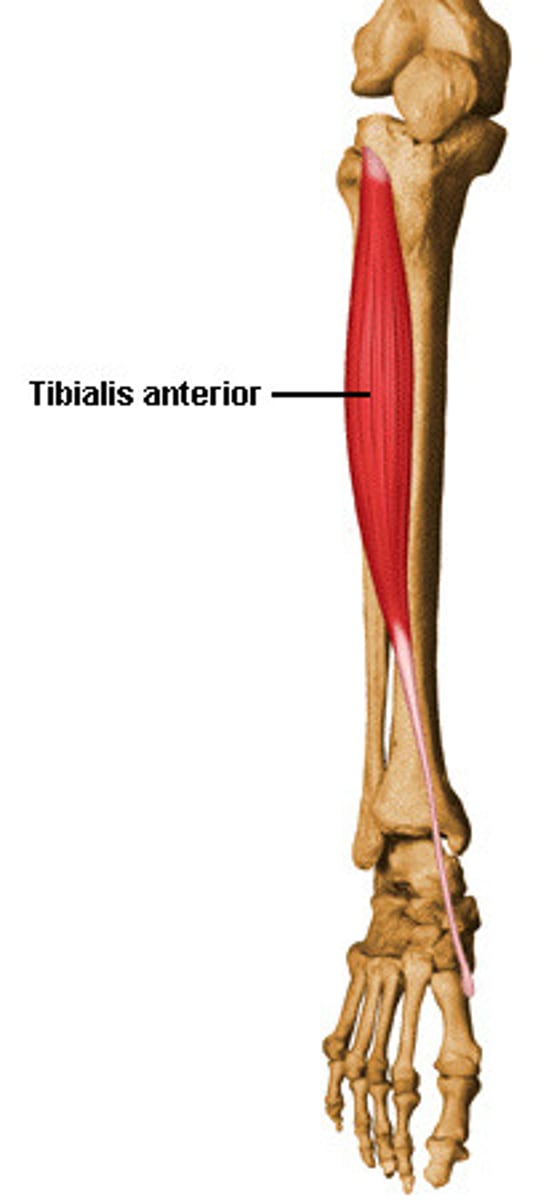
Tibialis Anterior
Action: ankle flexion, inversion of foot
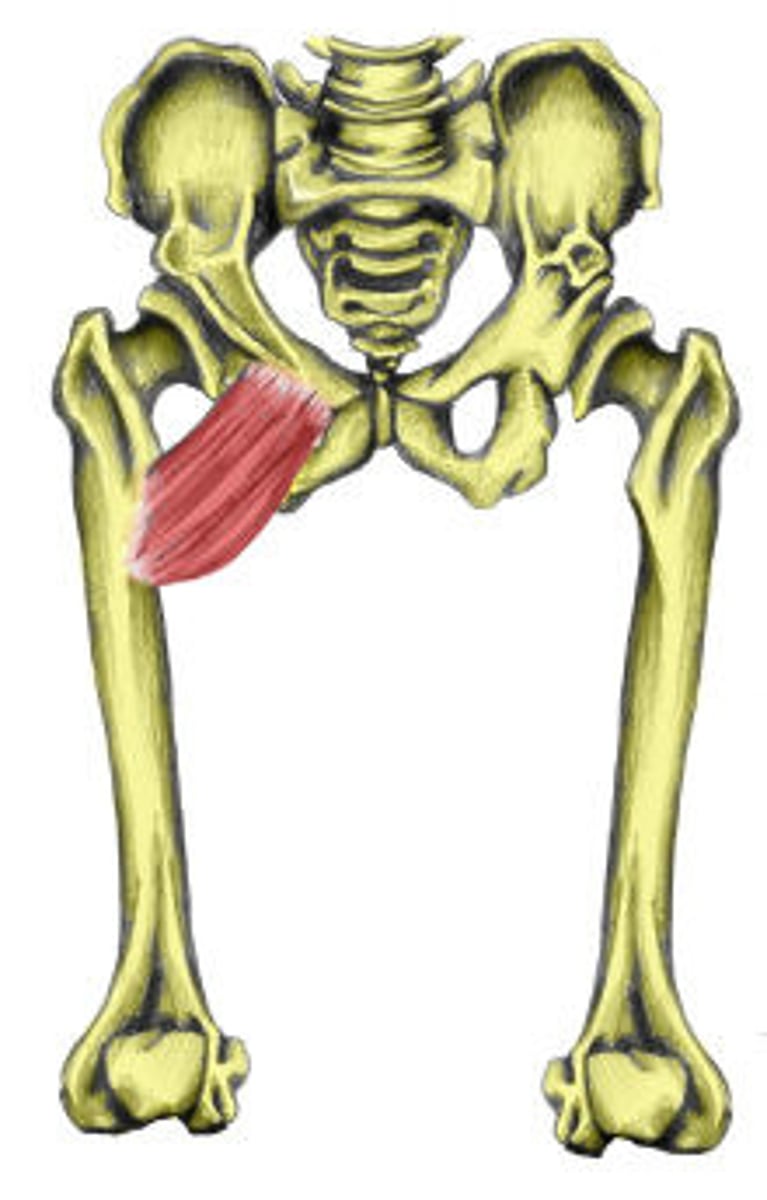
Pectineus
Action: flexion, medial rotation and adduction of hip
Plantaris
Action: ankle extension, knee flexion
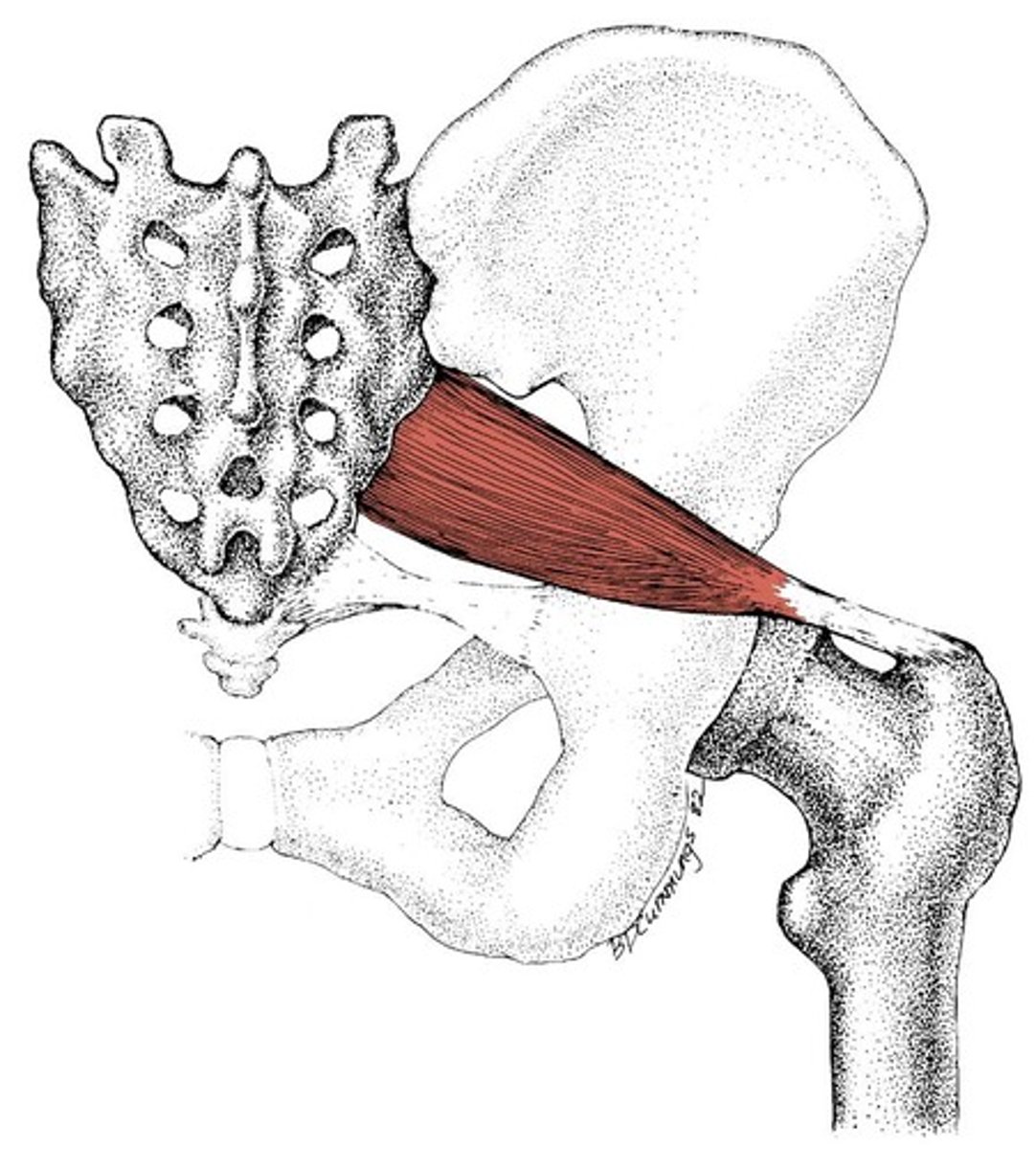
Piriformis
Action: abduction of hip
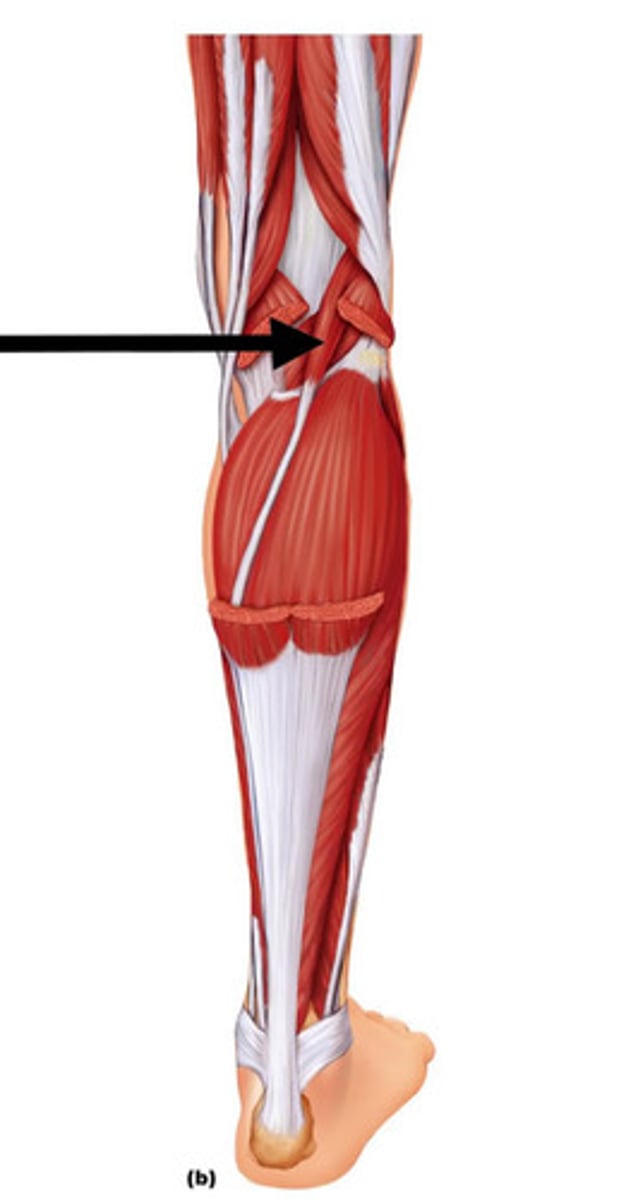
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Action: extension of toes 2-5
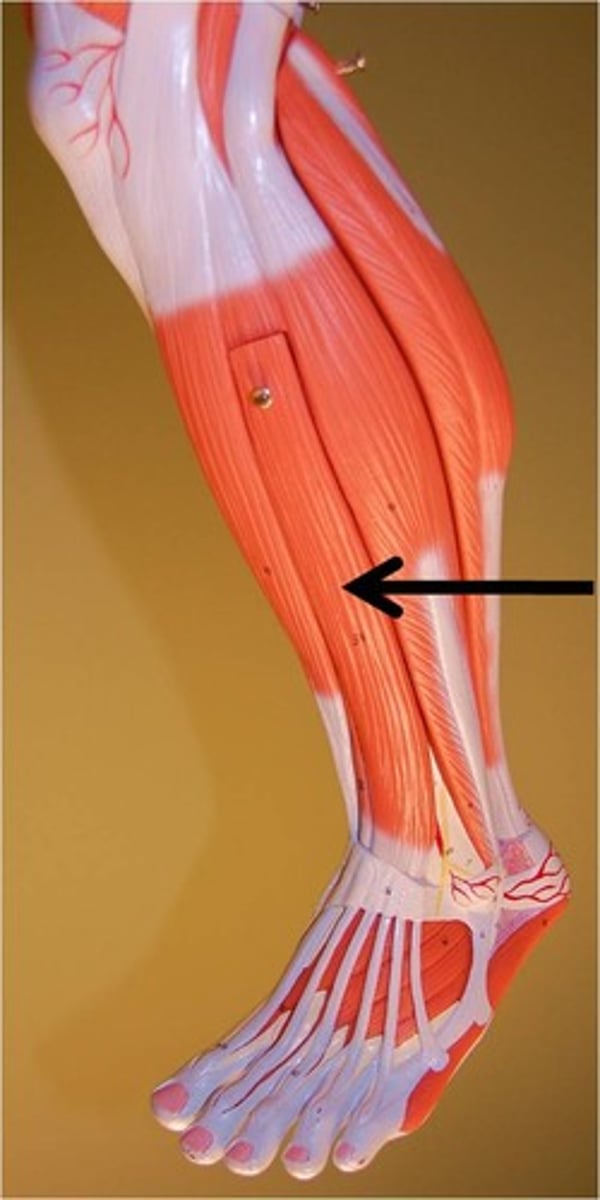
Fibularis (peroneus) Longus*
Action: foot eversion, ankle extension
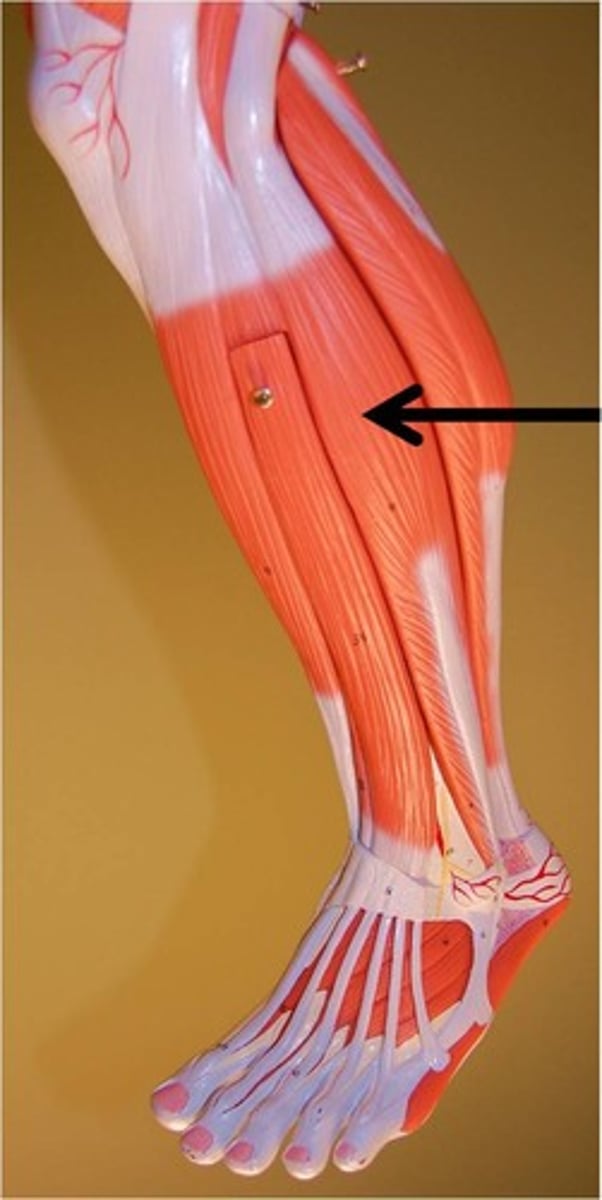
Fibularis (peroneus) Brevis*
Action:foot eversion, ankle extension
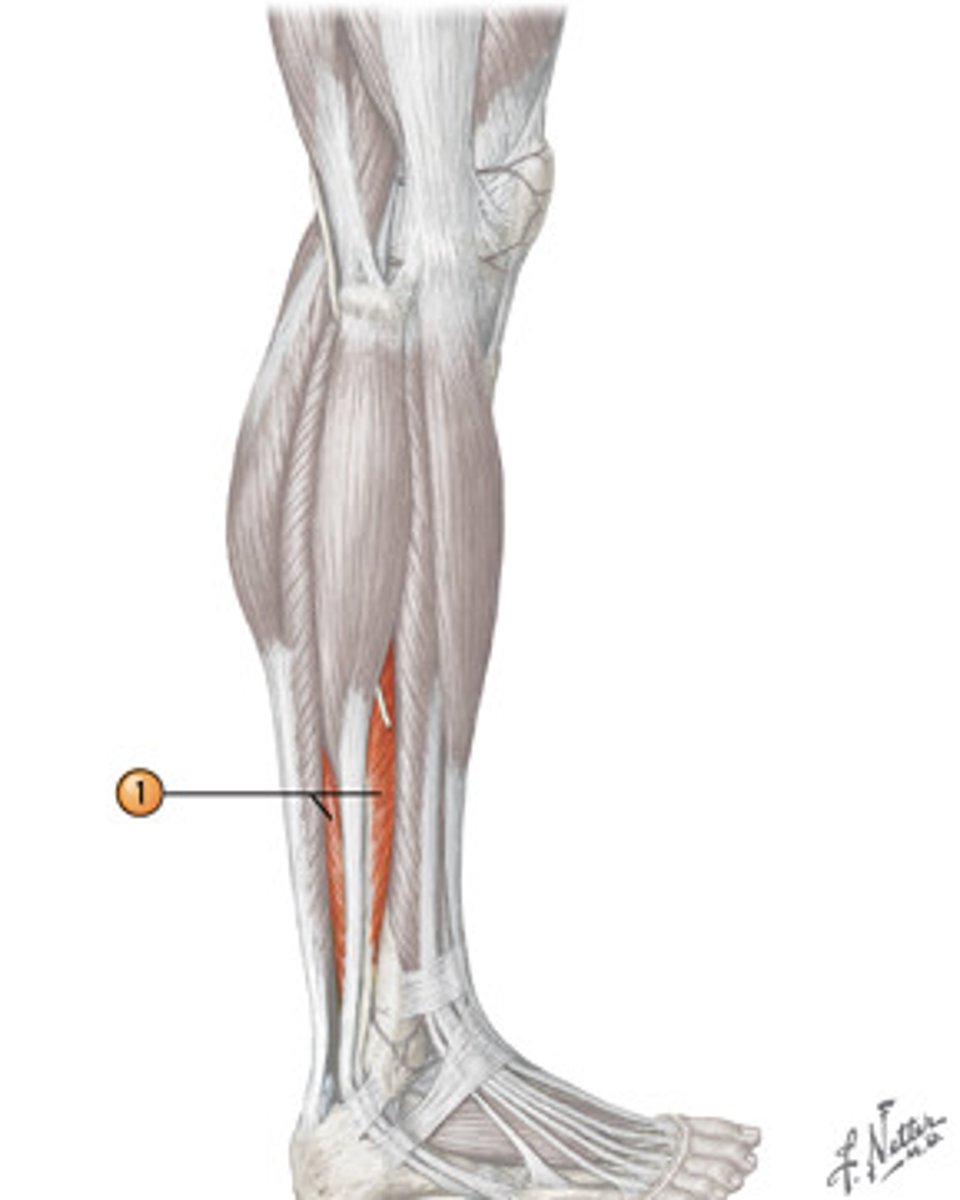
Flexor Hallucis Longus*
Action: flexion of great toe
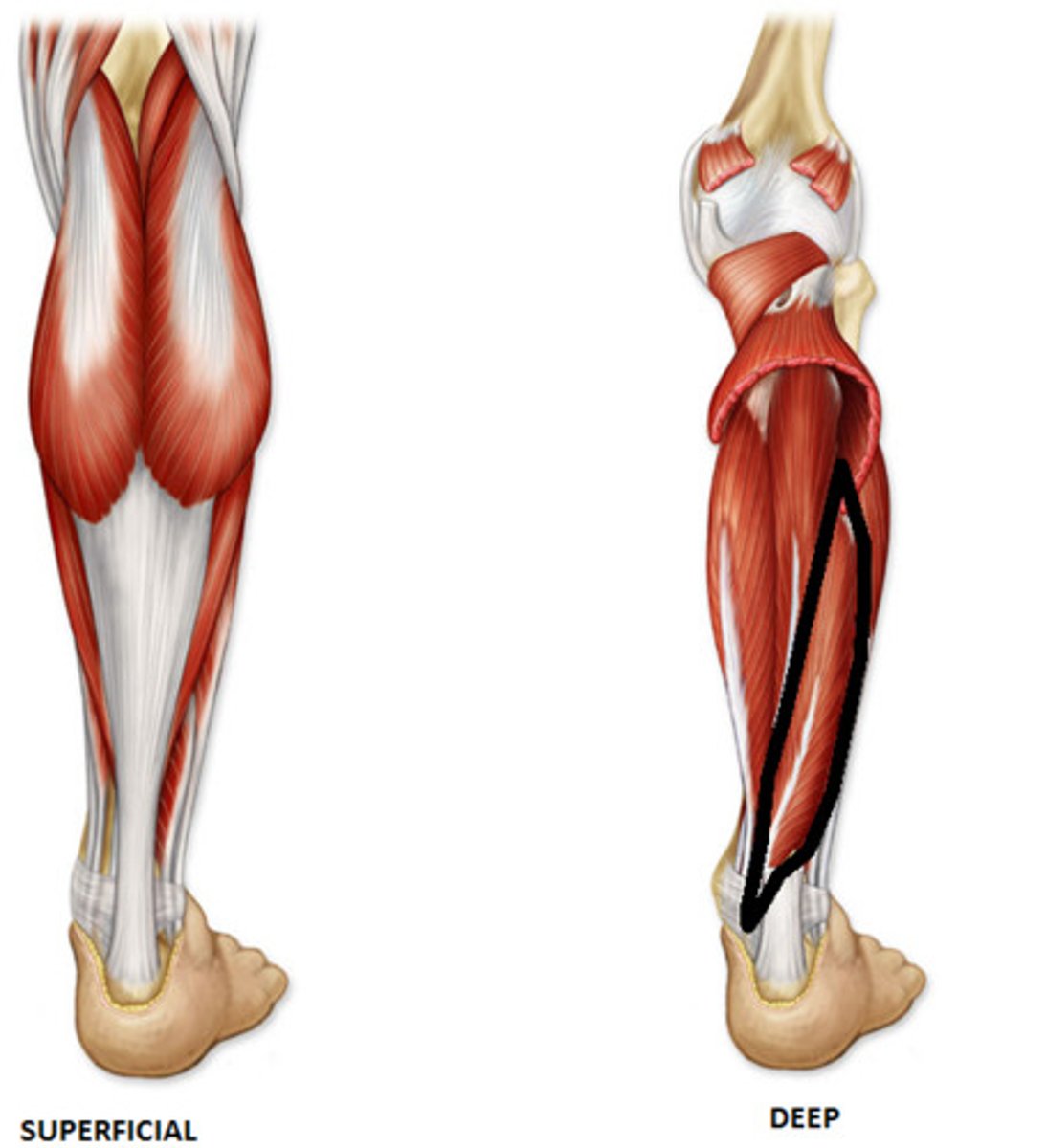
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
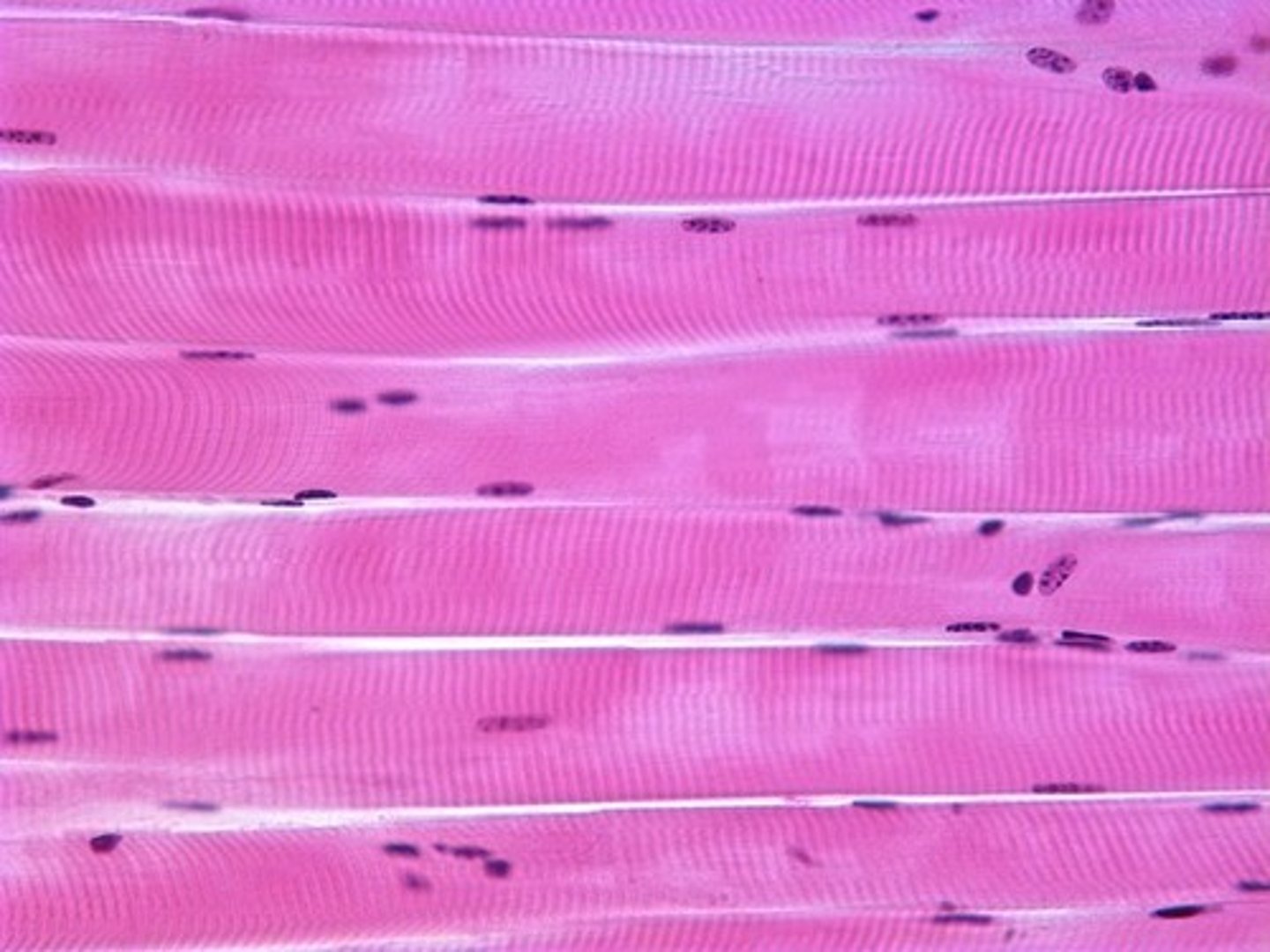
cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
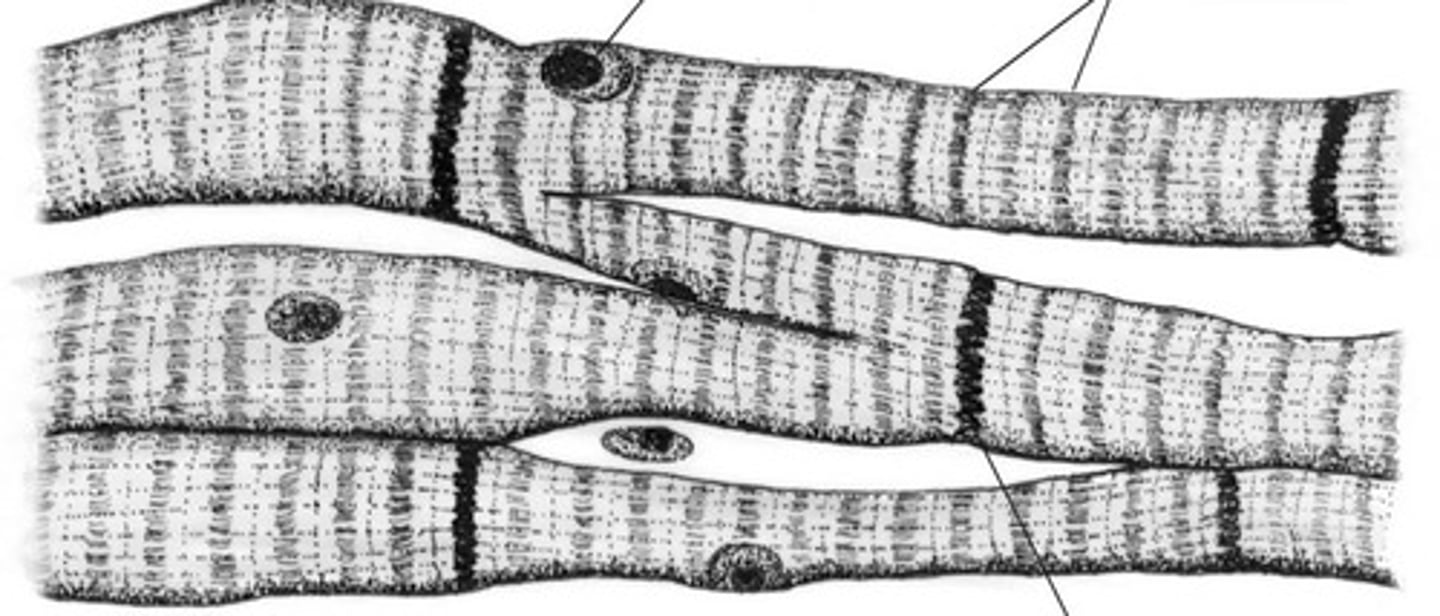
smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body
function of muscle tissue
-movement
–maintain posture
–stabilize joints
–generate heat
–regulate flow of materials through hollow organs
Properties of muscle tissue
excitability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity, conductivity
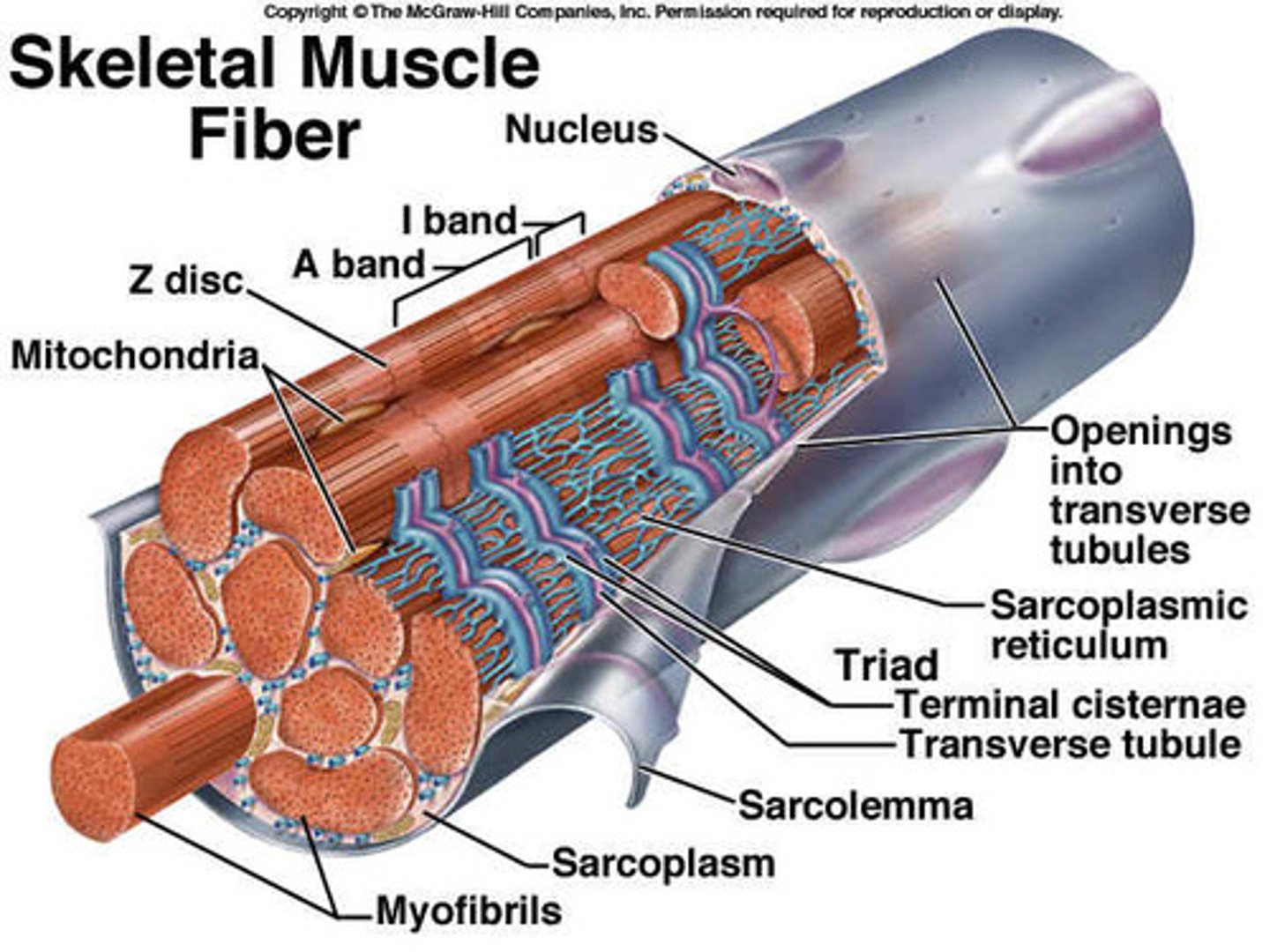
structure of muscle fiber
each fiber cell is packed with myofibrils which is packed with myofilaments.
myocyte/muscle fiber
individual muscle cell inside fascicle
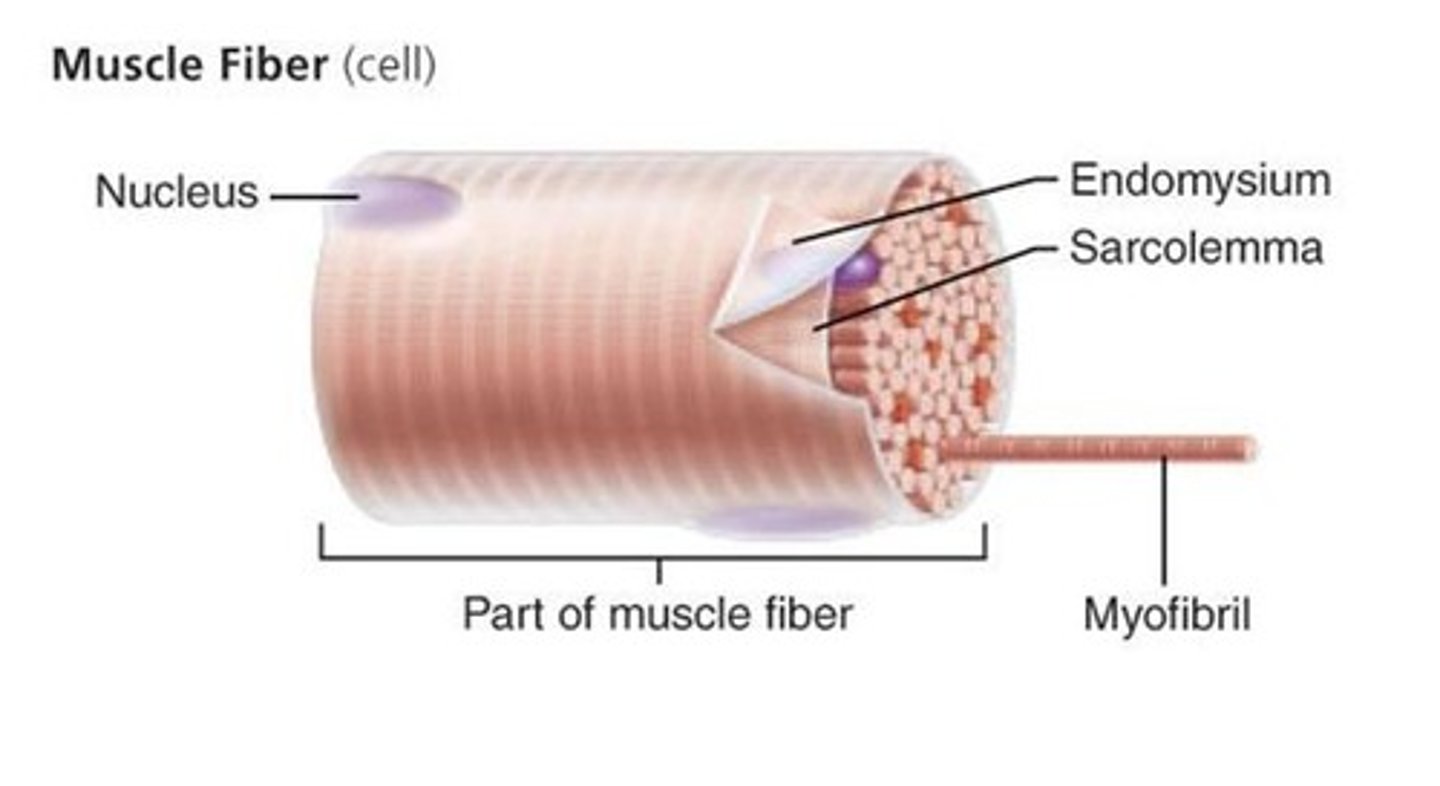
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
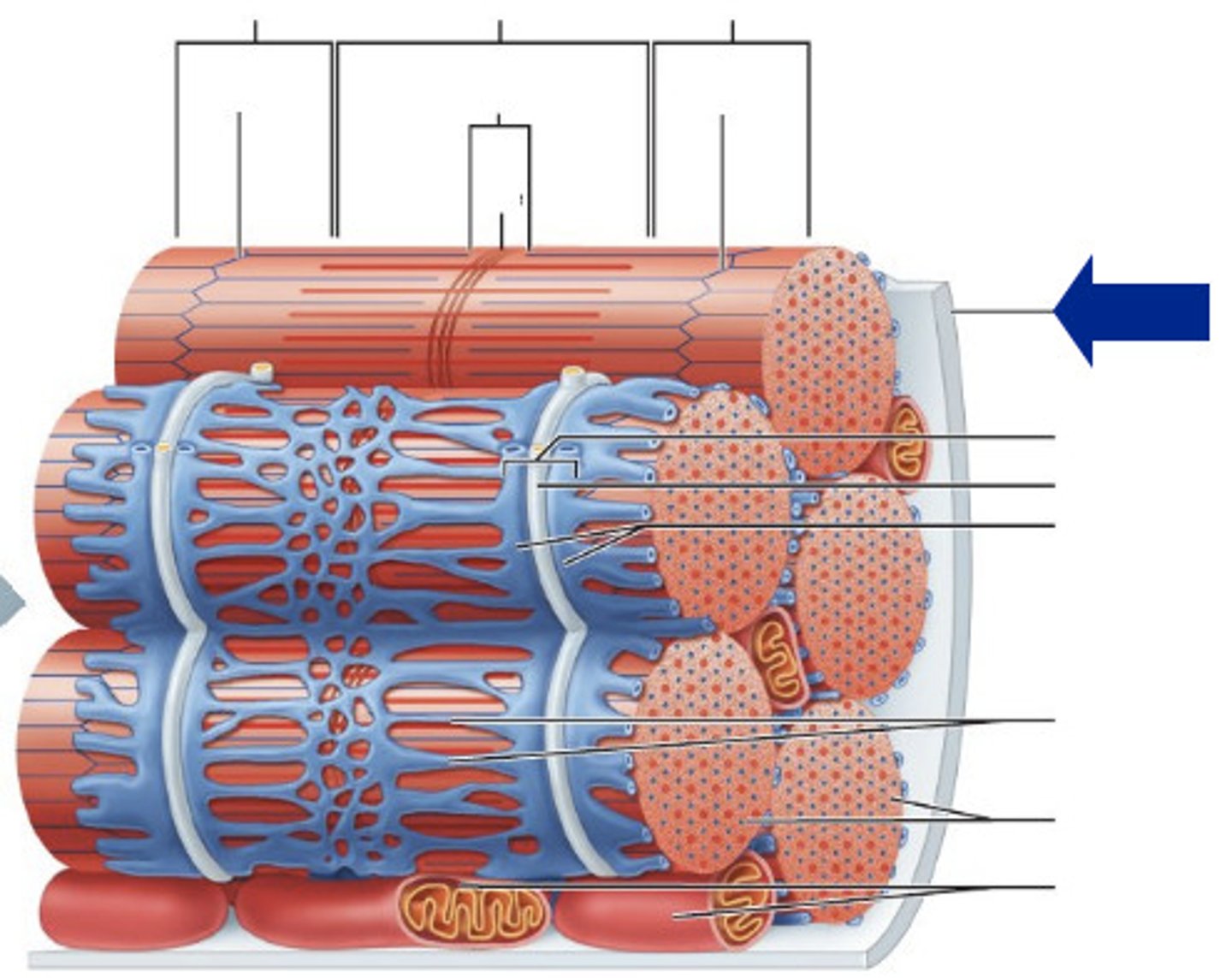
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium.
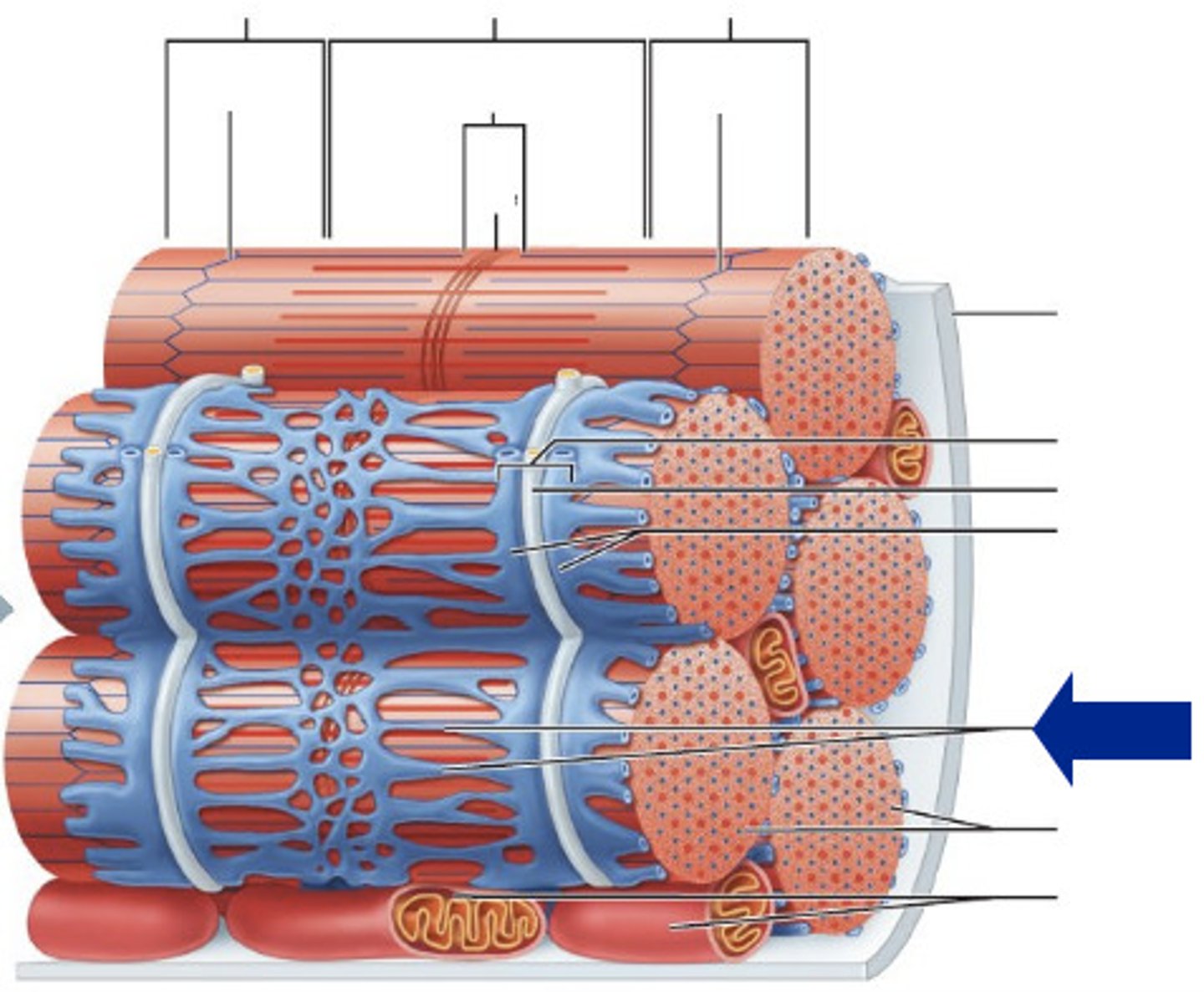
Myofibrils
Microscopic protein filaments that make up muscle cells.
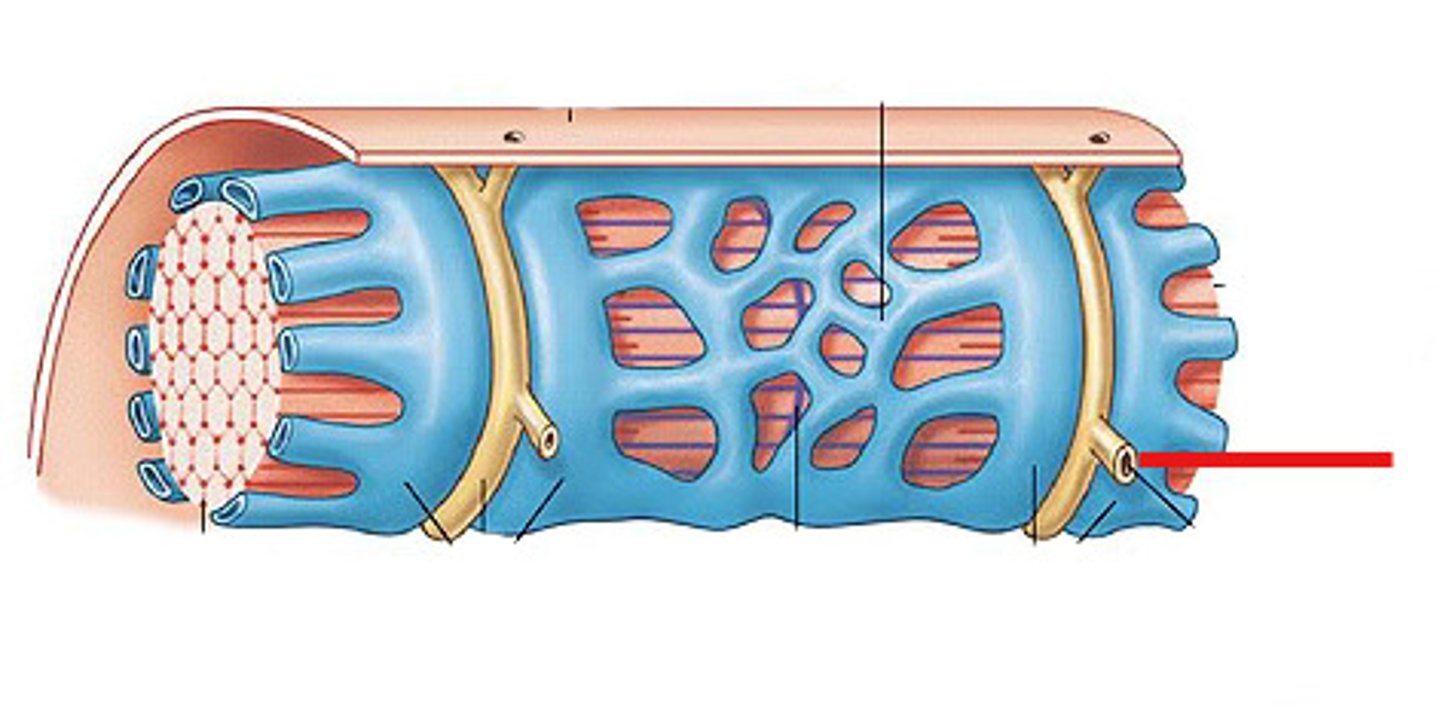
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
transverse tubules
System of tubules that provides channels for ion flow throughout the muscle fibers to facilitate the propagation of an action potential.
Myofilaments
filaments of myofibrils, constructed from proteins, principally myosin or actin

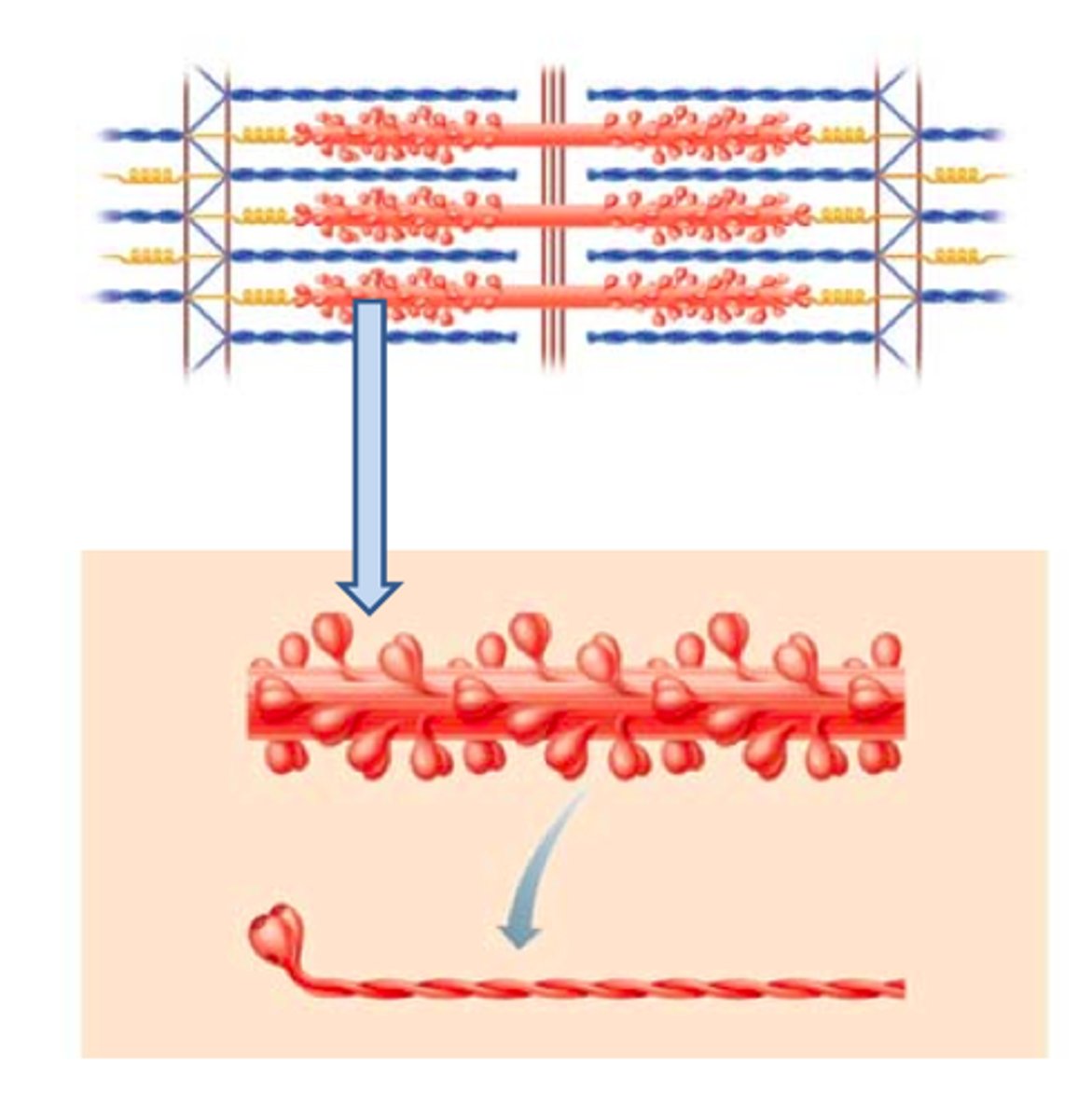
thick filaments
composed of myosin
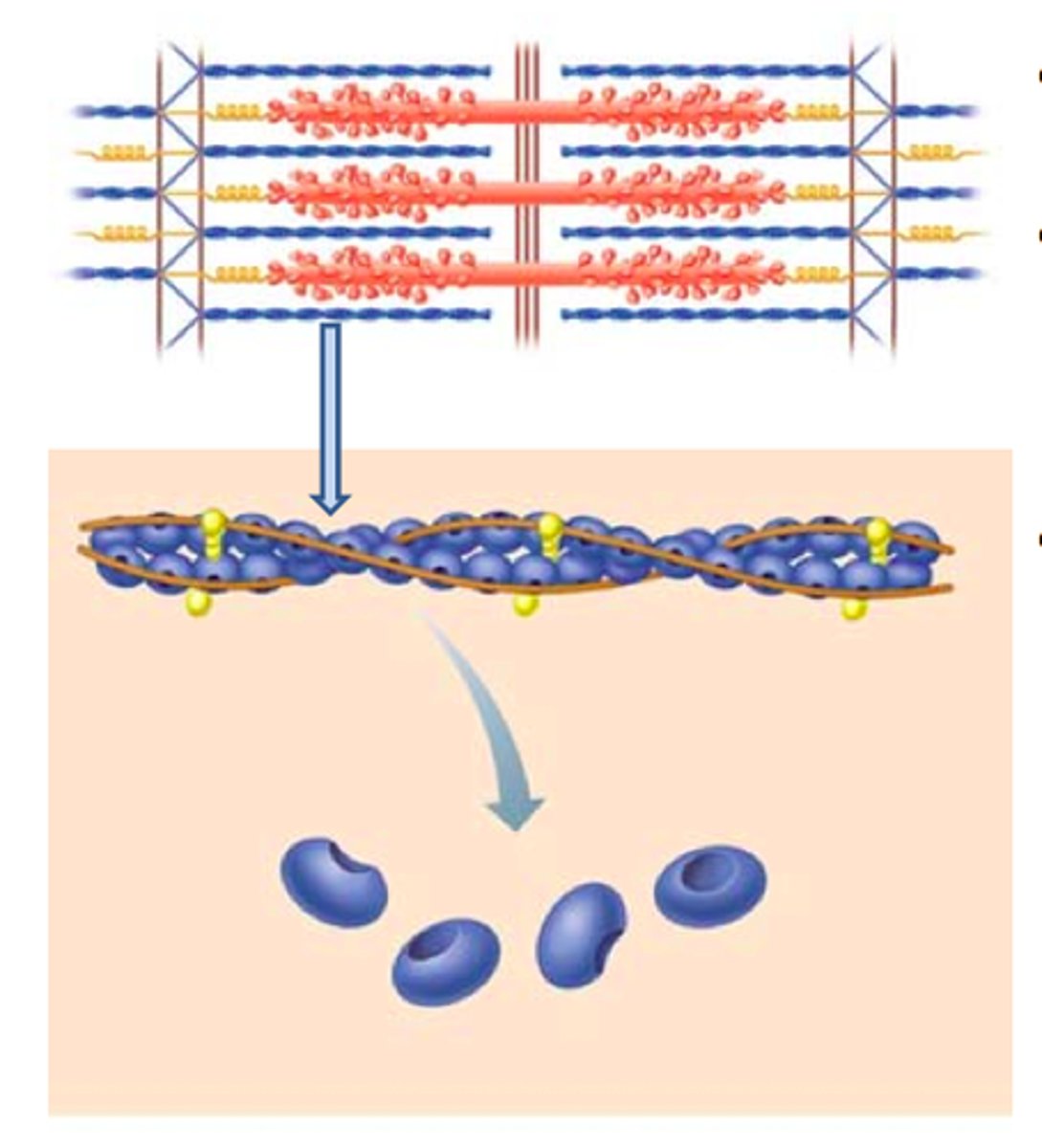
thin filaments
composed of actin
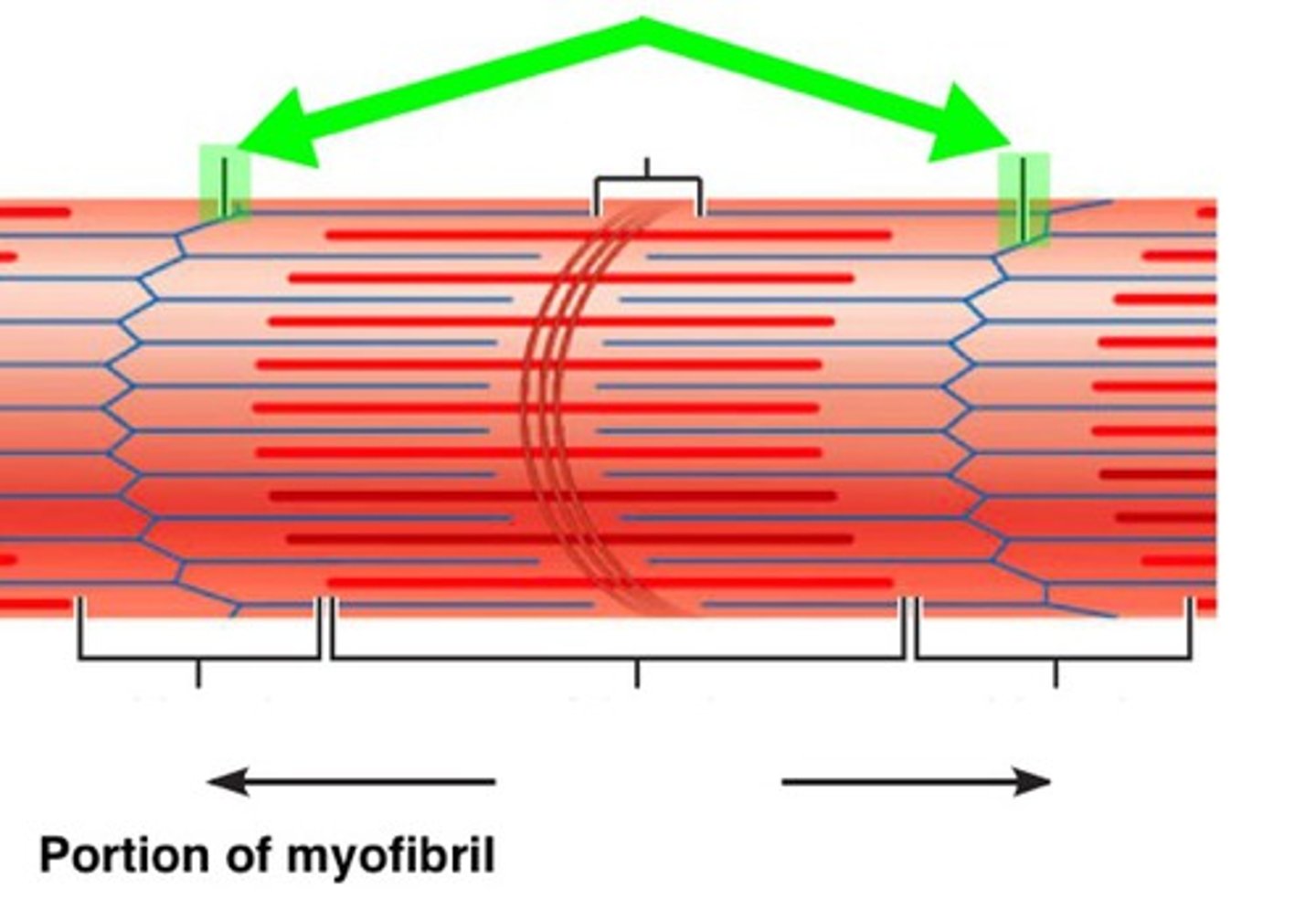
Sarcomere
Contractile unit of muscle
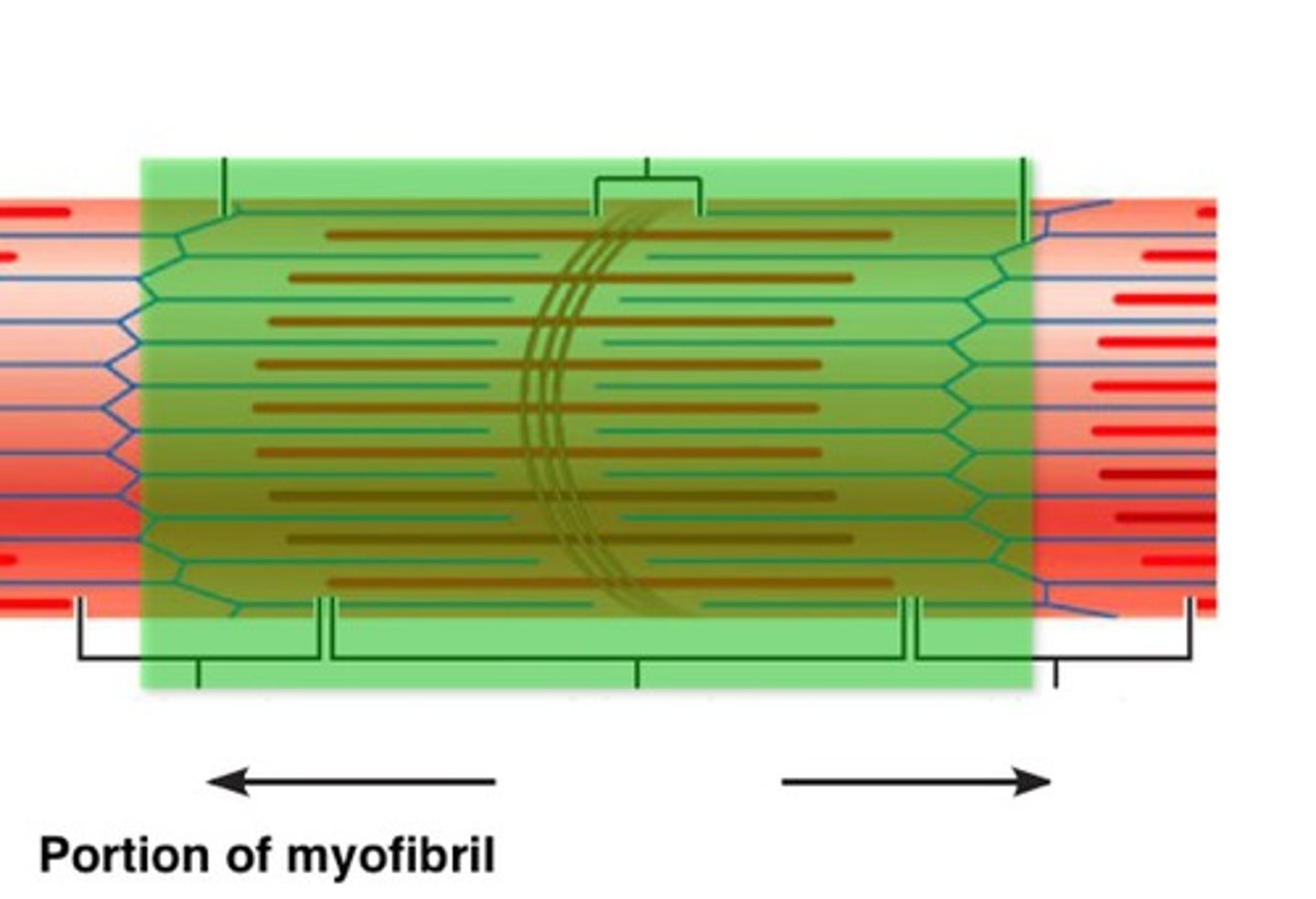
I bands (light)
-Composed of thin actin filaments
-attach to Z disks or Z lines (A Z line is the point at which the actin filaments from adjacent sarcomeres interweave to create lines.)
Z disc
coin-shaped sheet of proteins that anchors the thin filaments and connects myofibrils to one another
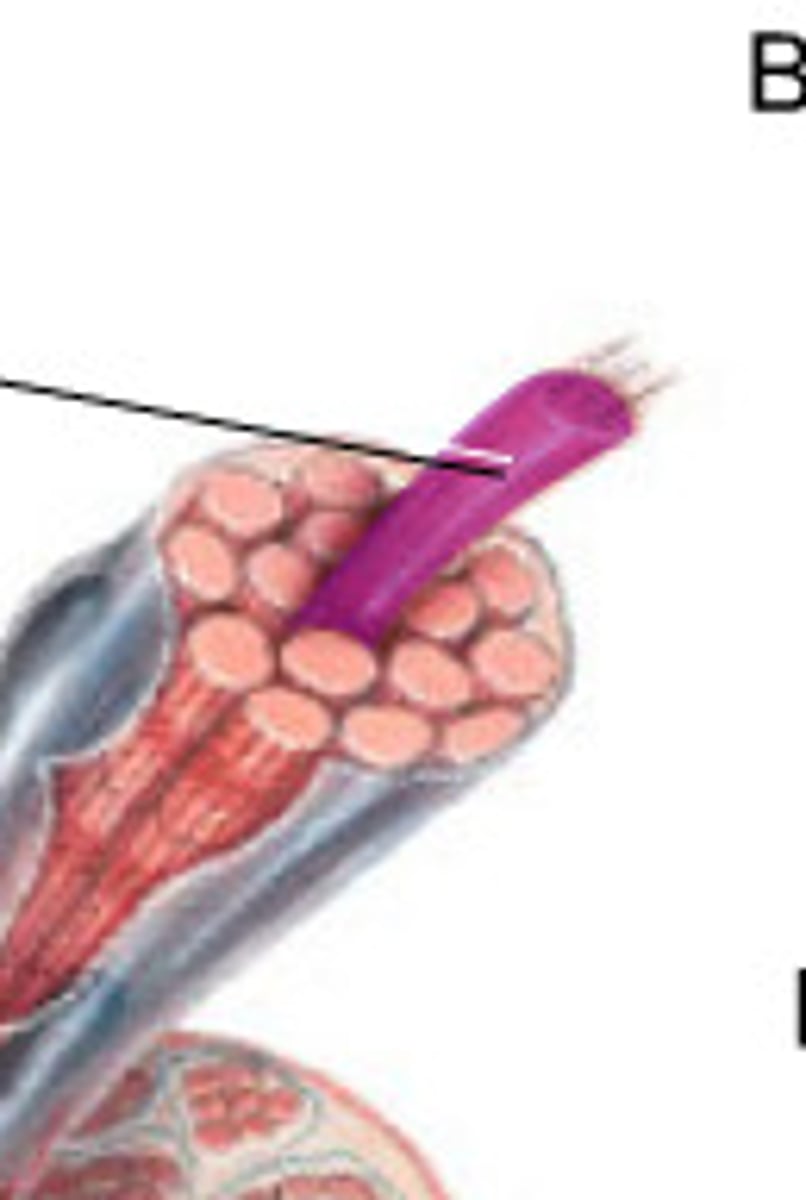
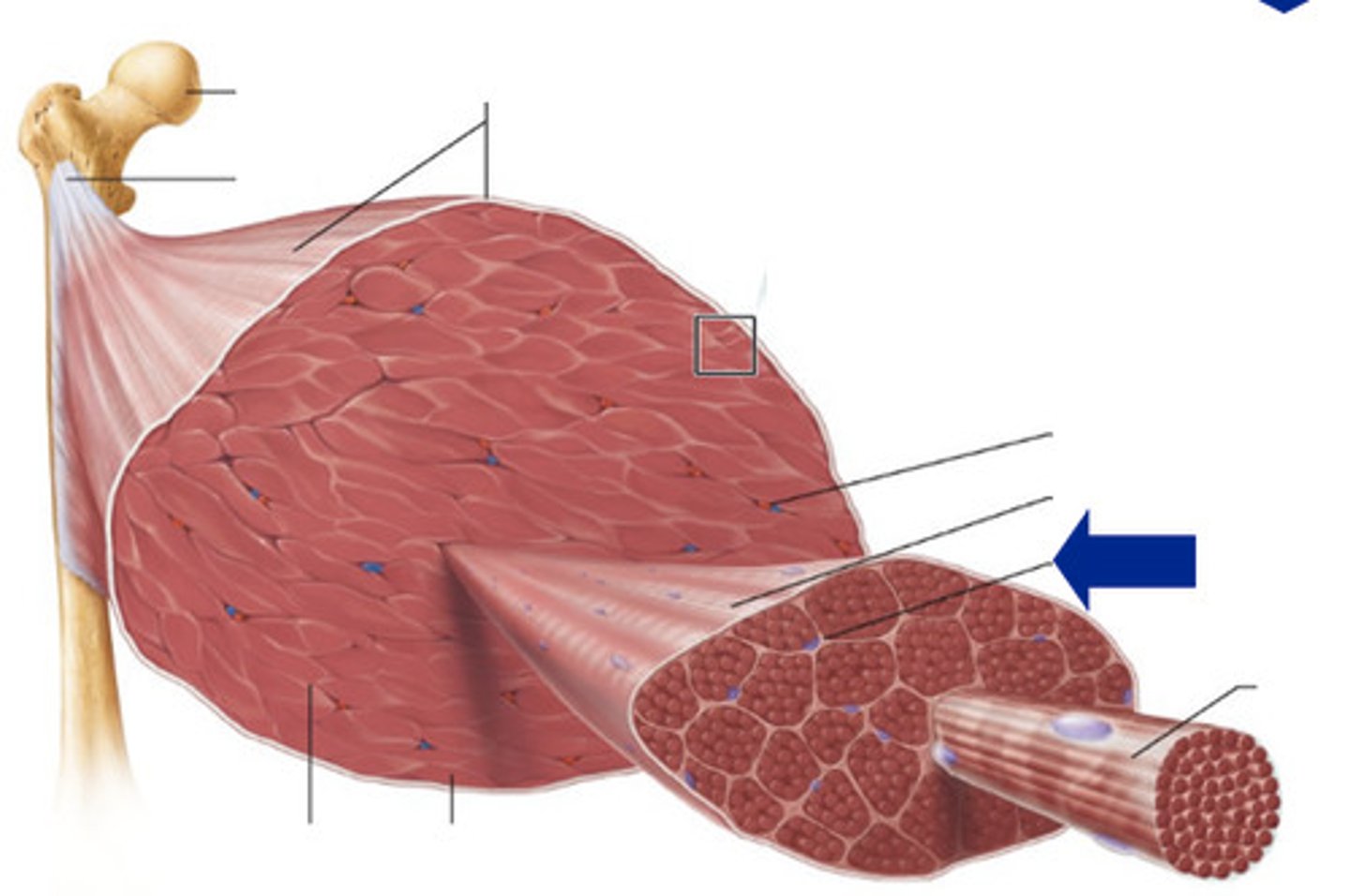
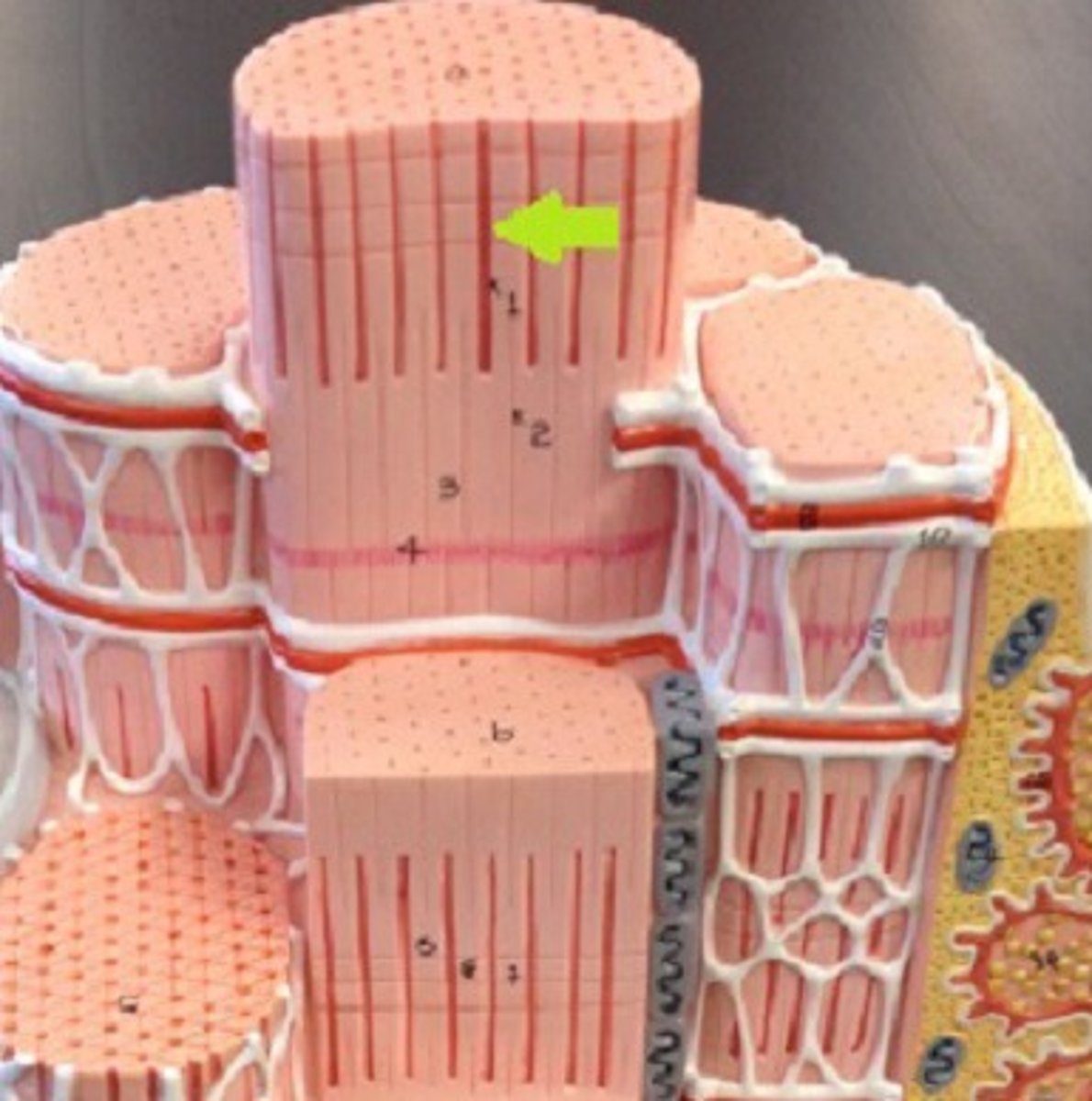
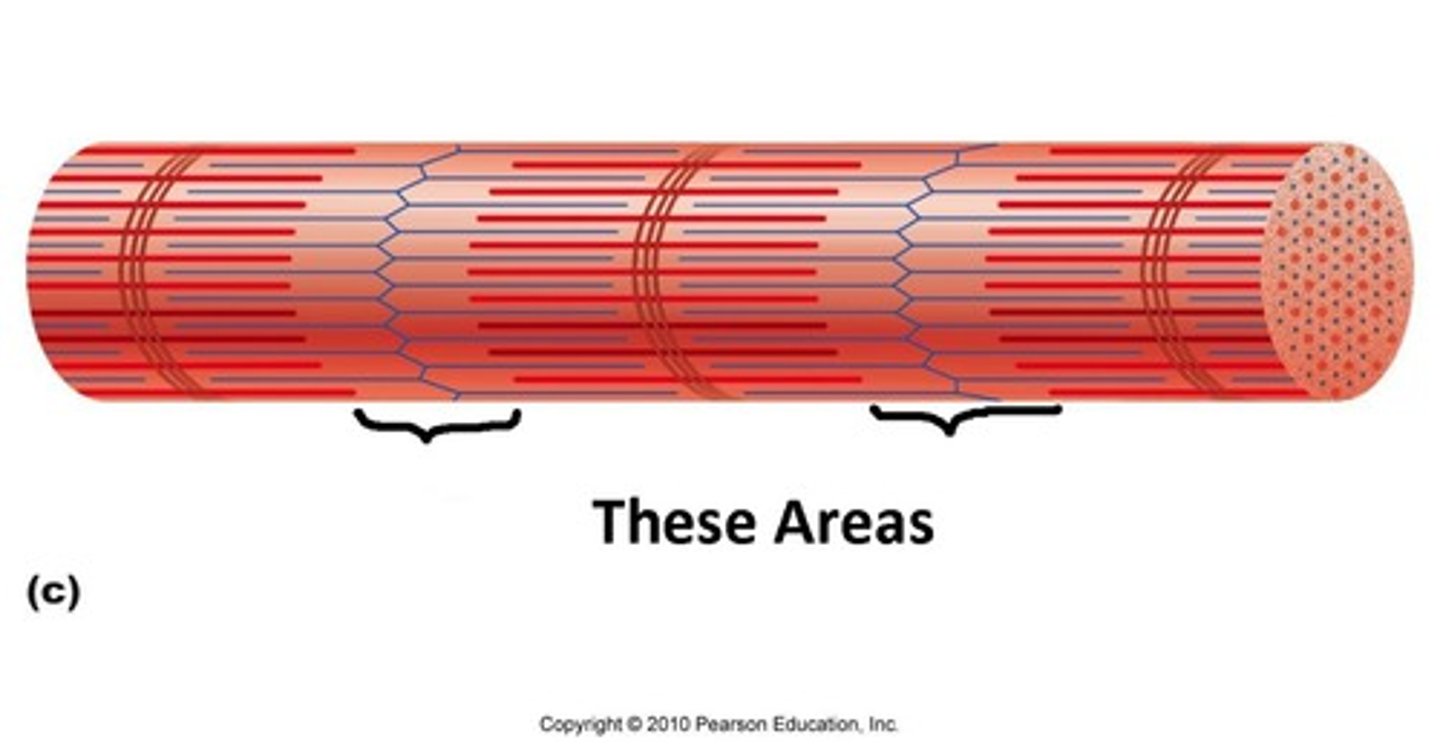
Fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
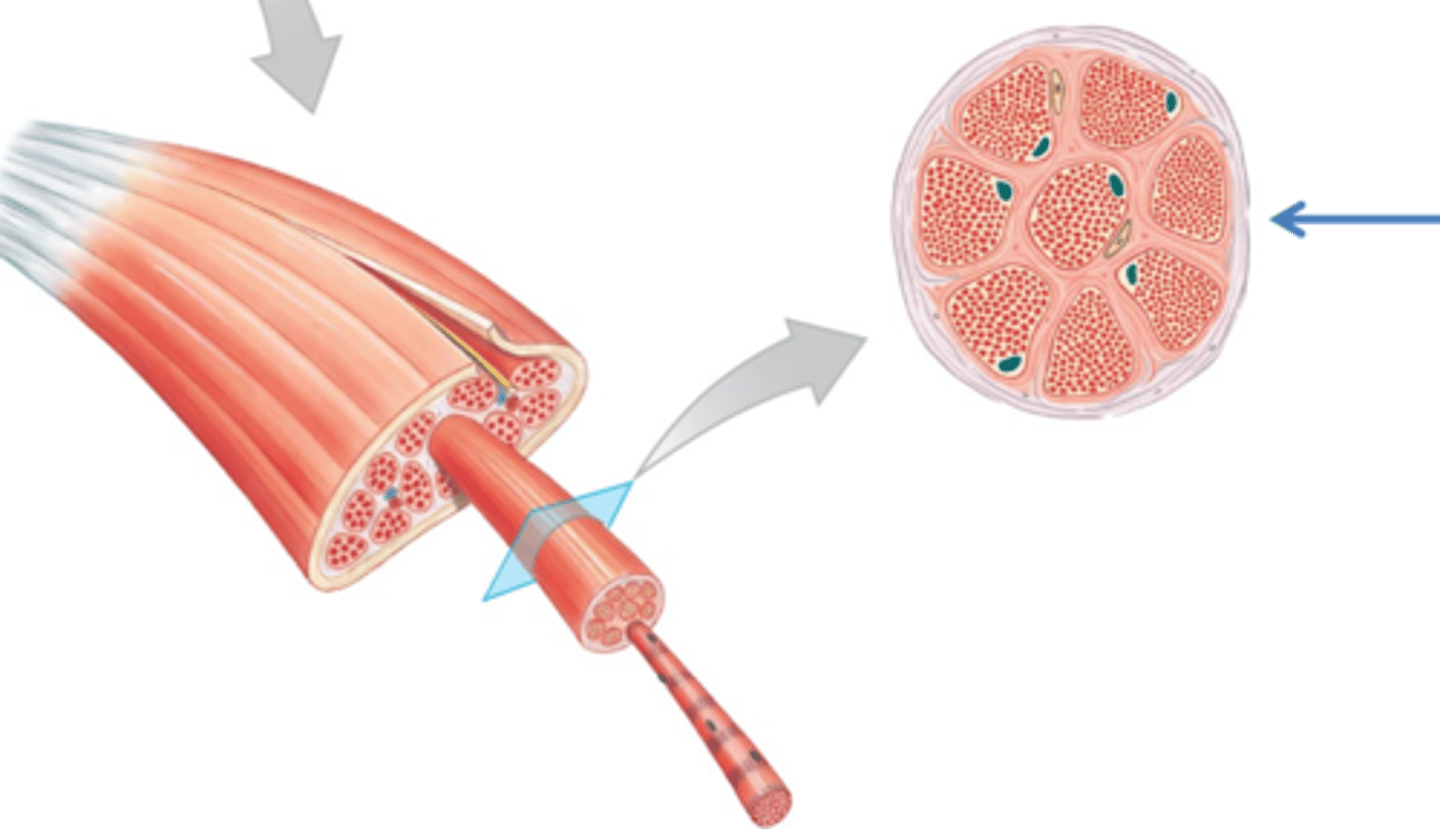
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
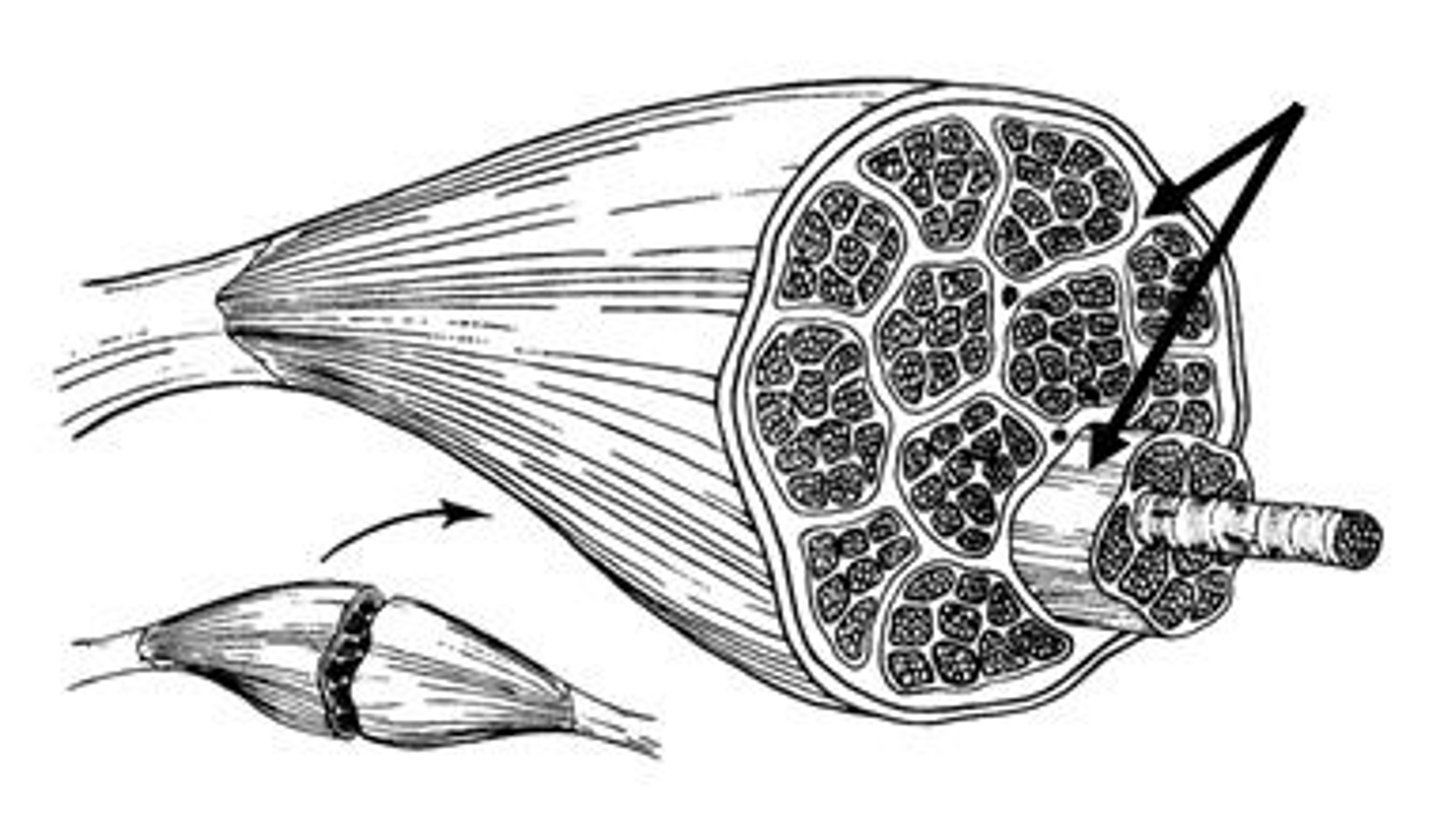
Epimysium
surrounds entire muscle
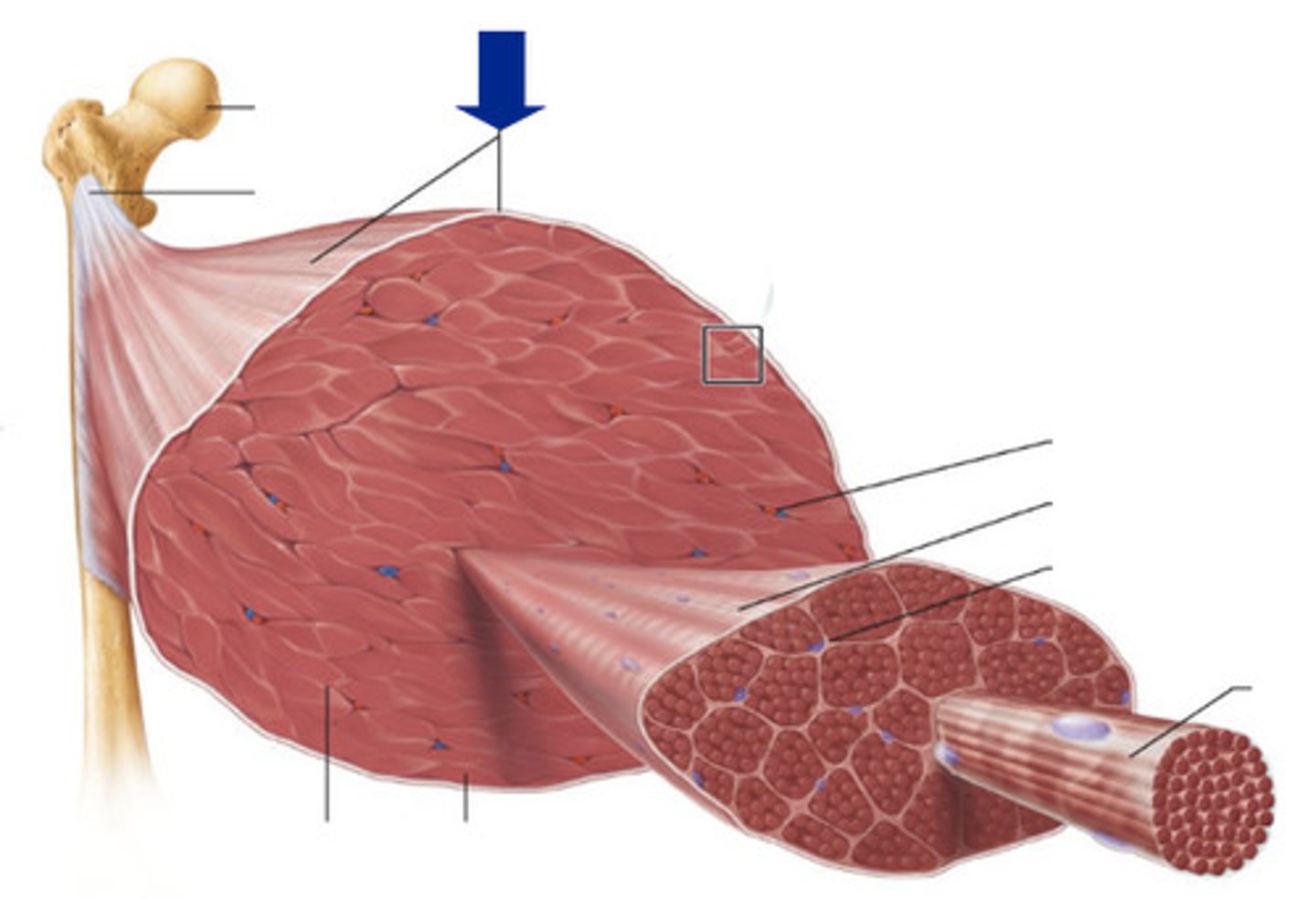
fascia
a band or sheet of fibrous connective tissue that covers, supports, and separates muscle
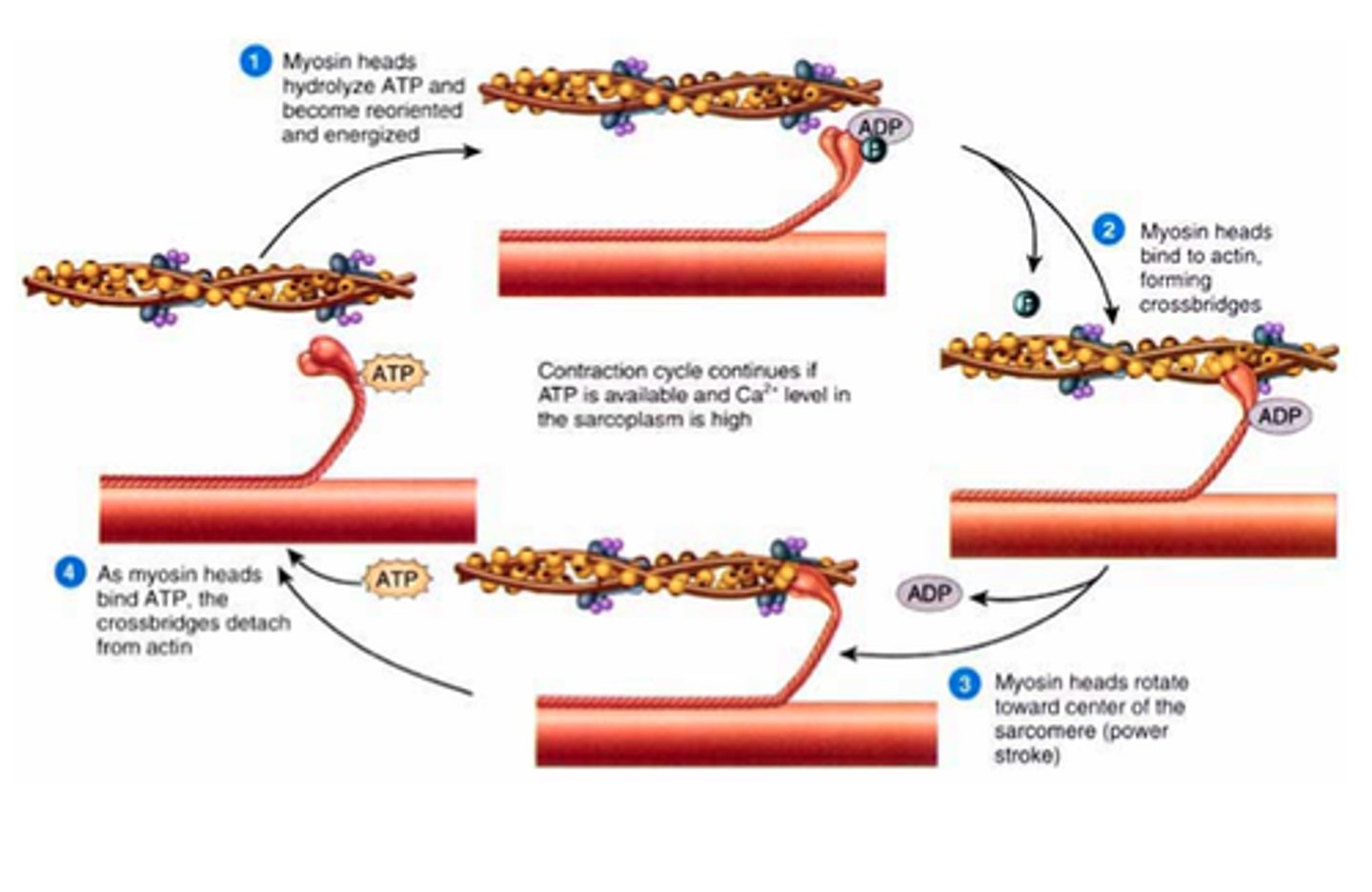
sliding filament mechanism
The explanation of how thick and thin filaments slide relative to one another during striated muscle contraction to decrease sarcomere length
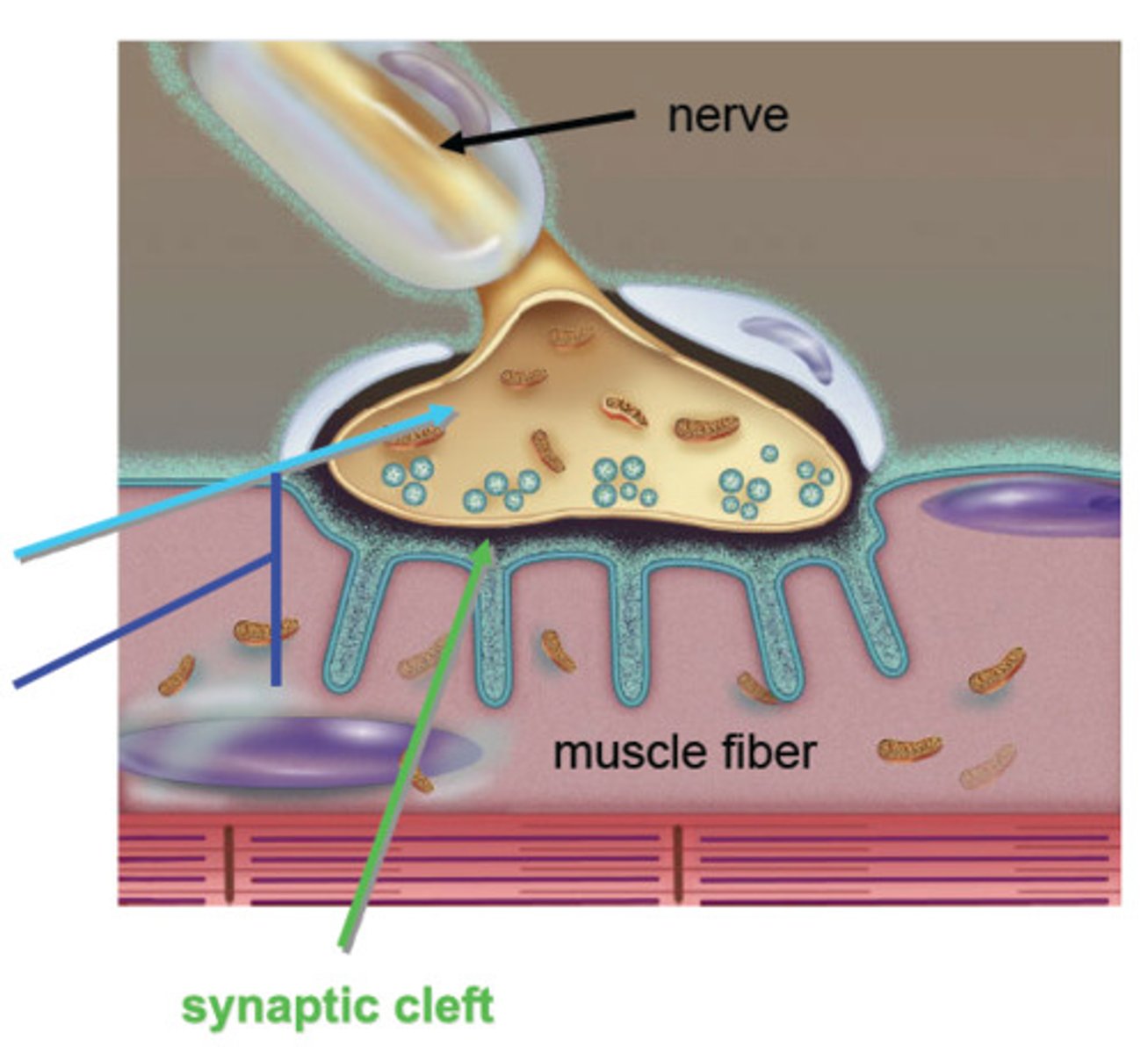
membrane potential
The voltage across a cell's plasma membrane.
neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
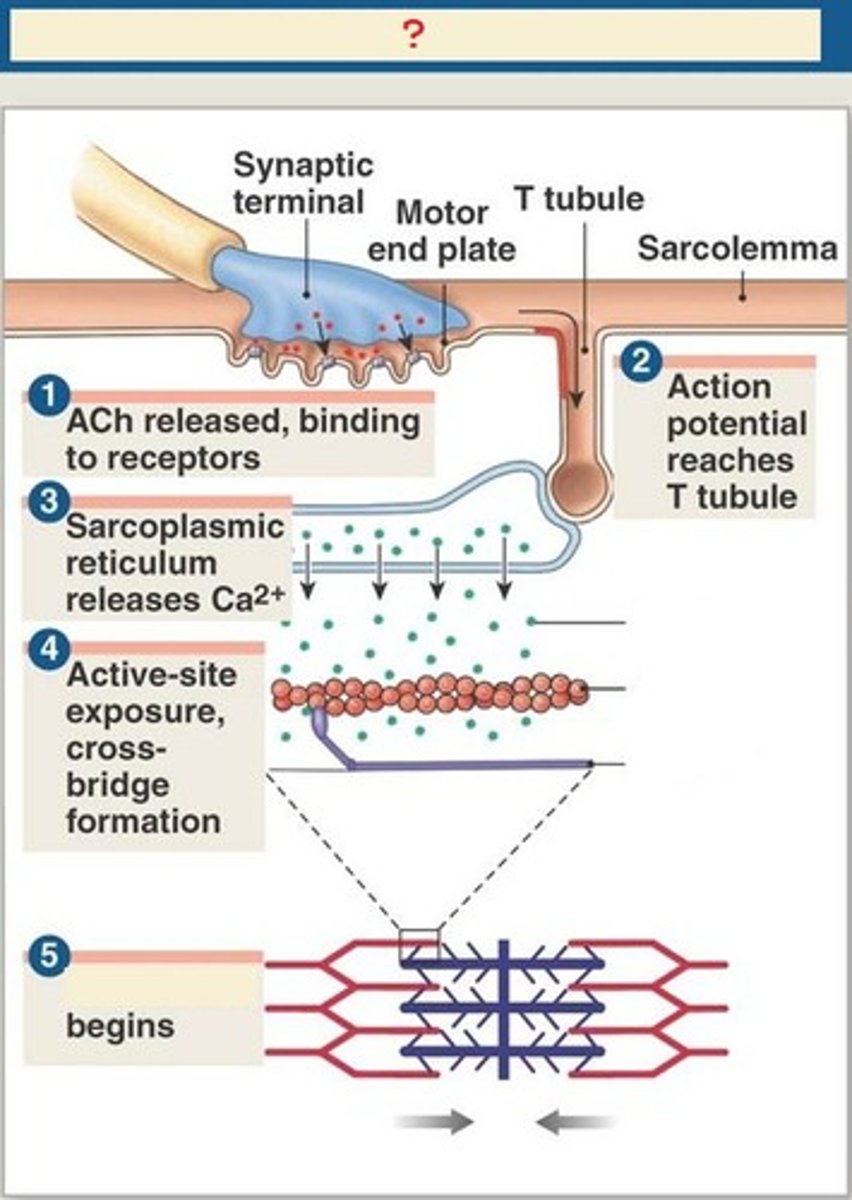
muscle contraction steps
1) Motor neuron releases acetylcholine into the neuromuscular junction and causes the depolarization of the sarcolemma.
2) Depolarization spreads down the sarcolemma to the T-tubules, triggering the release of Ca2+ ions.
3) Ca2+ binds to troponin, causing a shift in tropomyosin and exposure of the myosin-binding site on the actin filament.
4) Shortening of the sarcomere occurs as the myosin head binds to the exposed sites of actin, forming a cross-bridge and pulling the actin filament along the thick filament, resulting in contraction.
5) Muscle relaxes when acetylcholine is degraded by acetylcholine esterase and the allowing Ca2+ is brought back into the SR. ATP binds to myosin head, allowing it to relax from actin.
How does muscle contraction occur?
The cross bridges 'grab hold' of the actin filaments and pull them in order to cause contraction - ATP supplies energy for this
Troponin
regulatory protein that binds to actin, tropomyosin, and calcium
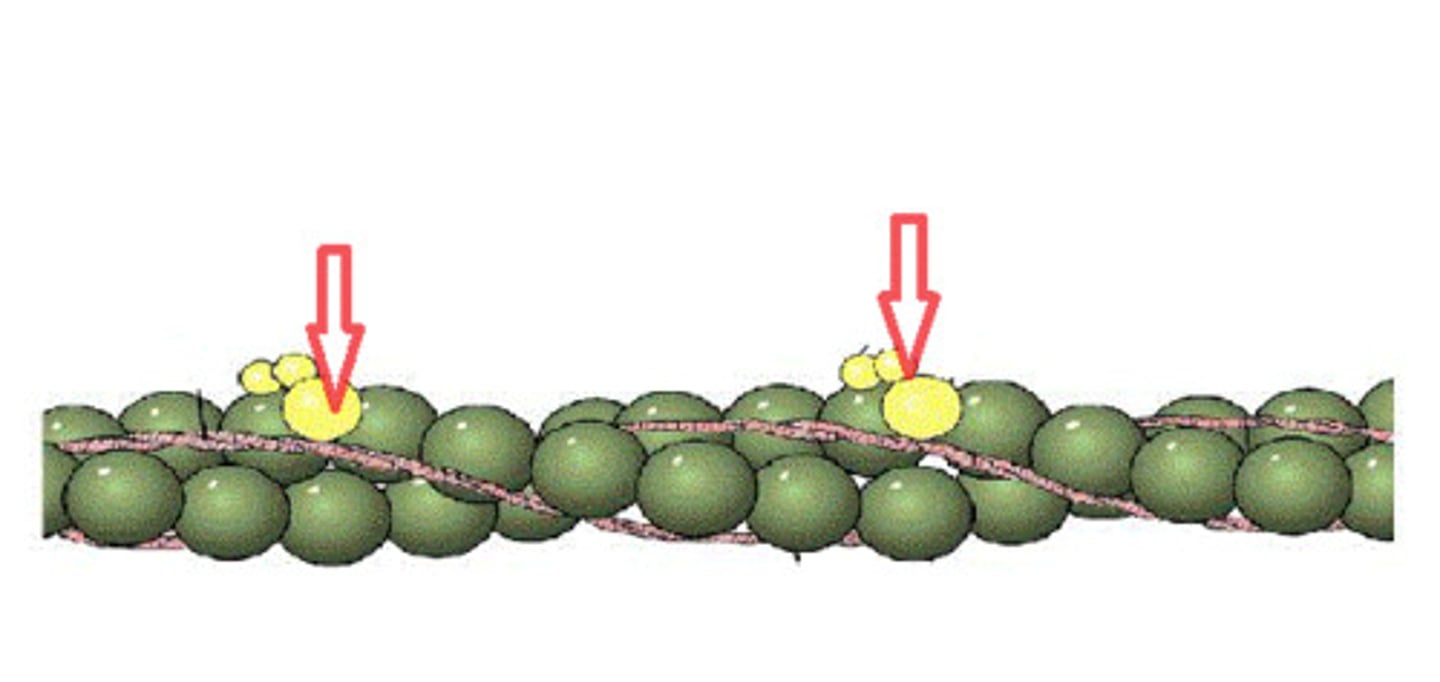
Tropomyosin
covers myosin binding sites on the actin molecules
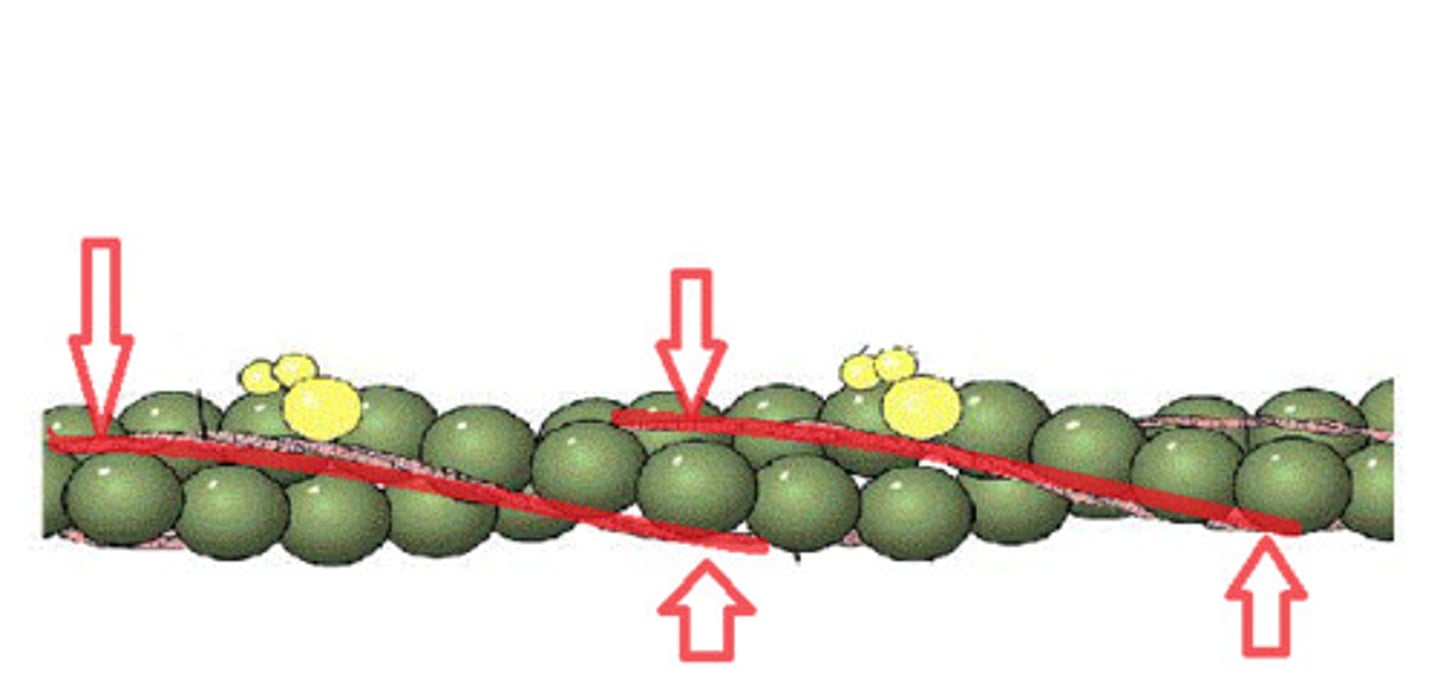
Actin
A globular protein that links into chains, two of which twist helically about each other, forming microfilaments in muscle and other contractile elements in cells.