BCM - Biological membranes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Main function of biological membranes
Compartmentation - plasma membrane, organelles (e.g. ER and Golgi apparatus; not all organelles have membranes)
Regulation of transport - uptake of nutrients and excretion of waste (channels and transporters, endocytosis), vesicular transport within and out of the cells (secretory pathway)
Energy conversion - mitochondria (outer and inner membrane, H+ gradient across inner membrane), chloroplasts (outer and inner membrane, H+ gradient across thylakoid membrane)
Detection and transmission signals - cell surface receptors (e.g. hormones and neurotransmitters), nerve impulses (depend upon asymmetric ion distribution across the membrane)
Mitochondral ATP synthase
energy derived from breakdown of food is used to pump protons from the matrix into the inter membrane space, generating an electrochemical gradient
protons flowing from the inter membrane space back into the matrix drive rotation of the C-ring and axle of the ATP synthase
the stator holds the 3 catalytic subunits in place - the rotating axle changes the structure of the catalytic subunits, leading to the ATP formation
Plasma membrane of an animal cell
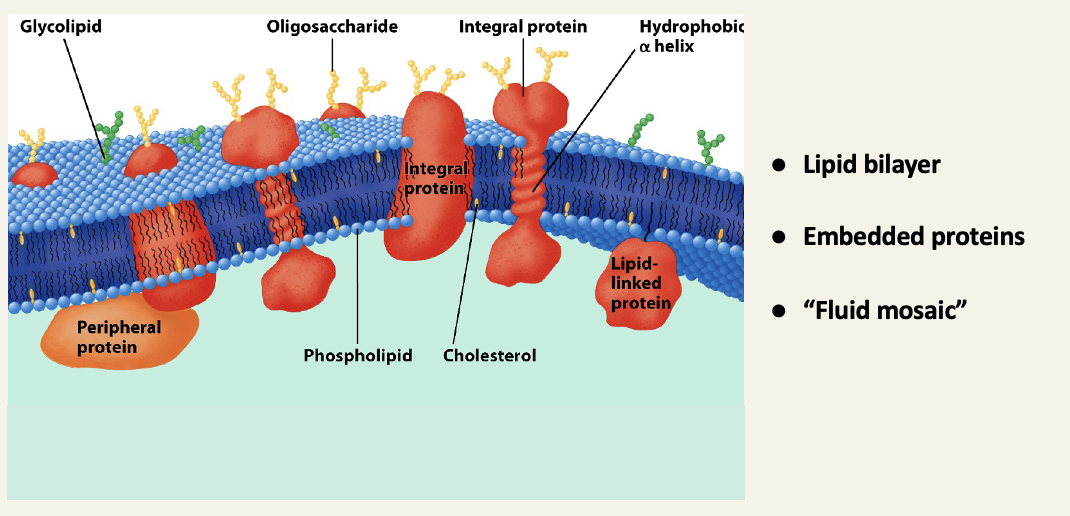
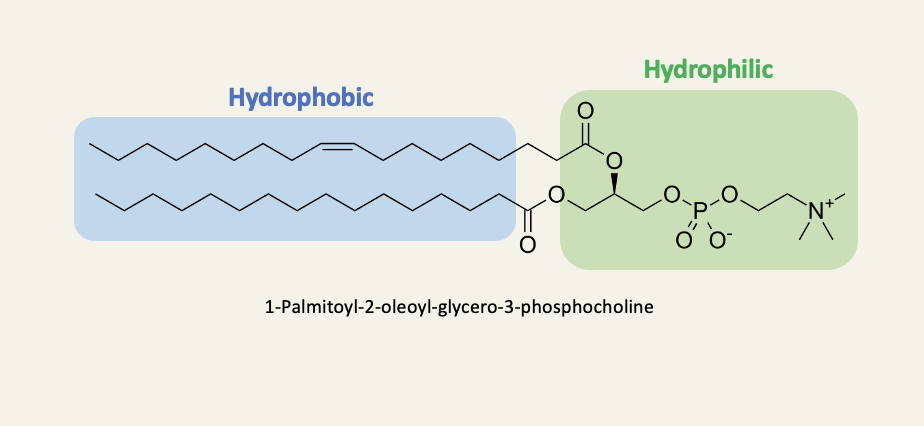
Lipids that form biological membranes are amphipathic molecules
Amphiphilic moelcules are also referred to as amphipathic molecules - the two terms are synonymous depending on -philic or -pathic
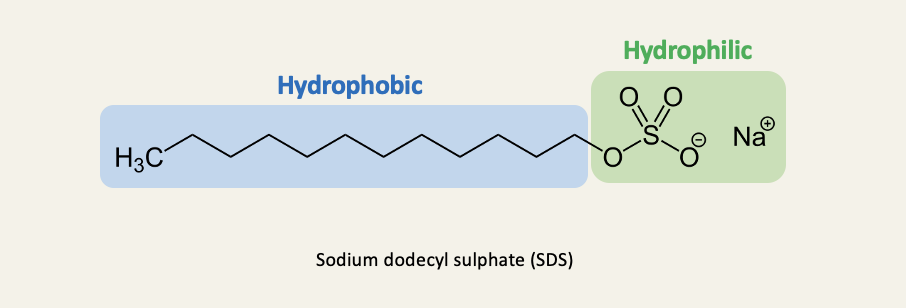
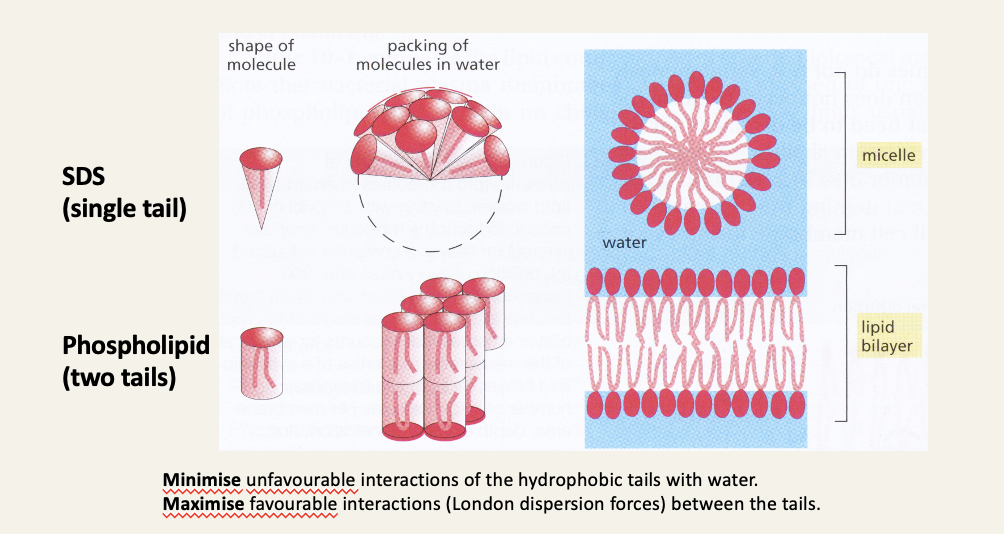
A typical detergent (only one tail)
Sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) is a common ingredient of shower gels and shampoos (often labelled sodium lauryl sulphate)
in biochemical research, SDS is used to denature proteins for gel electrophoresis
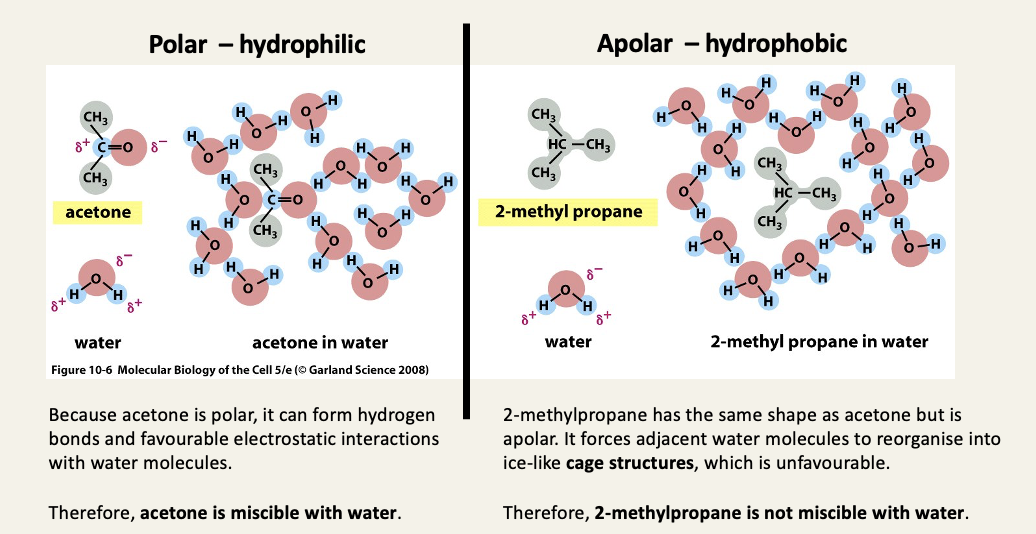
Hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules interact differently with water
Amphipathic molecules in water form micelles and bilayers
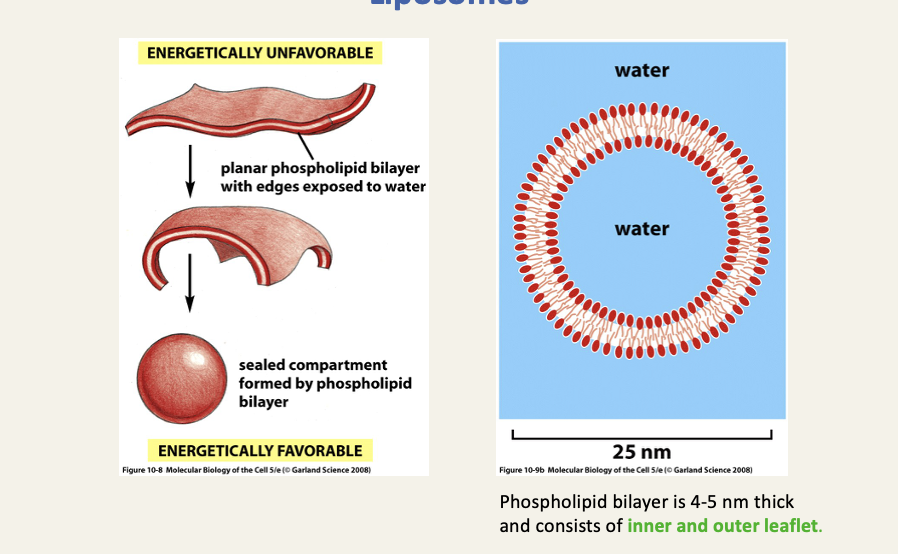
Liposomes
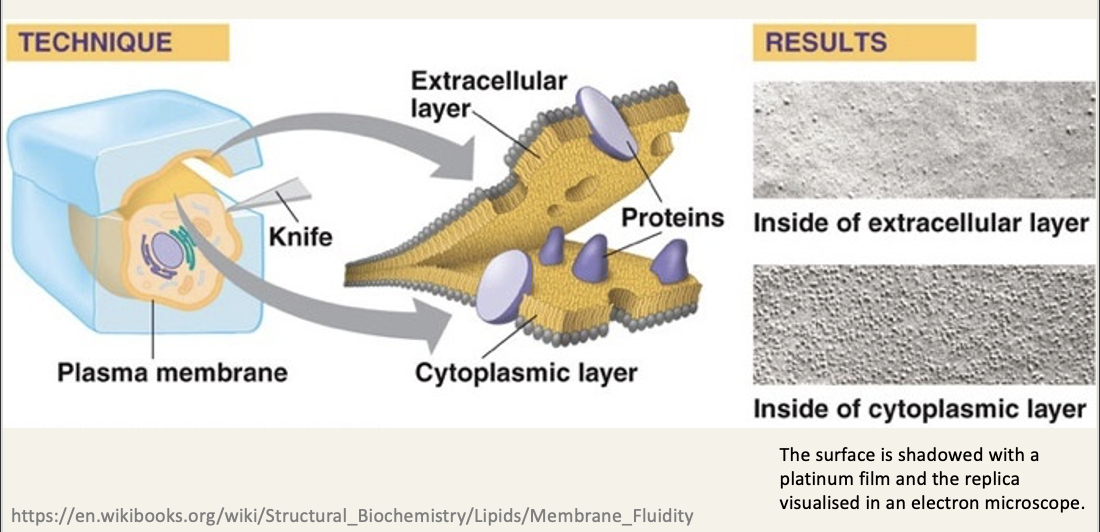
Electron microscopy - freeze fracture reveals embedded proteins
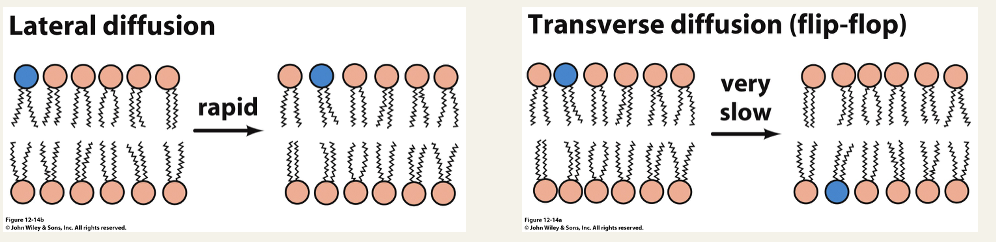
Bilayer dynamics
Lateral diffusion:
2D fluid - diffusion speed ~2 micrometers/s
Transverse diffusion:
large energy barrier because the head group must cross the hydrophobic interior of the bilayer
catalysed by 2 classes of enzymes - lipid scramblases (bidirectional and ATP-independent), lipid flippases (unidirectional and ATP-dependent)
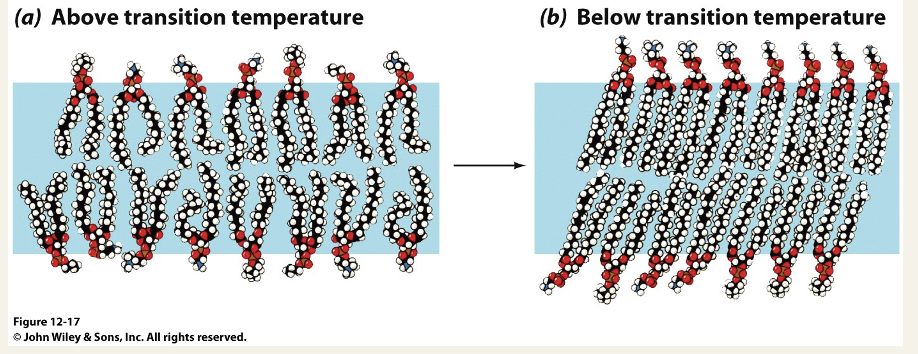
Loss of fluidity below the transition temperature
below the transition the bilayer is no longer liquid but adopt a more ordered gel phase - a type of solid state
the transition temperature depends on the chemical structure of the lipids
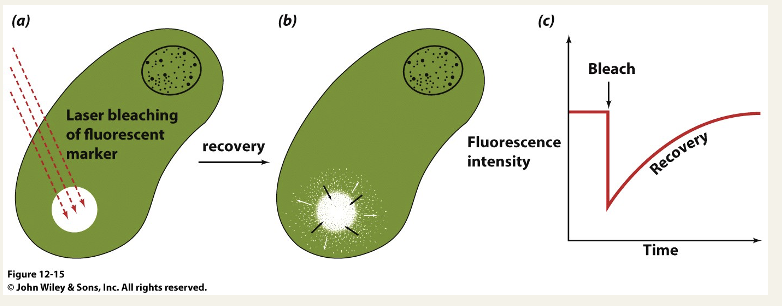
Experimental evidence for lipid bilayer fluidity
a fluorescent molecule is added to the plasma membrane
an intense laser beam is used to ‘bleach’ a membrane spot - destroys the fluorphore
the recovery of fluorescence in the bleached spot is due to diffusion of intact fluorescent molecules into the area - Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP)
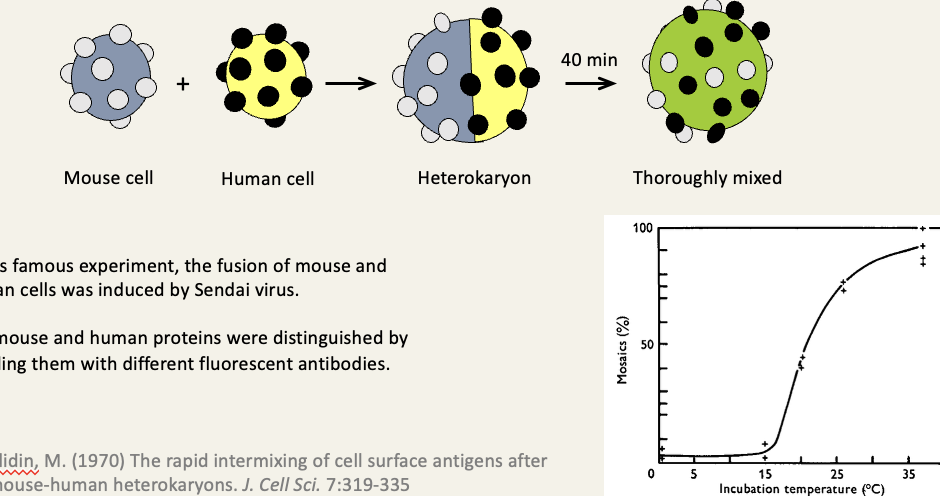
Experimental evidence for rapid lateral diffusion of proteins
in this famous experiment, the fusion of mouse and human cells was induced by Sendai virus
the mouse and human proteins were distinguished by labelling them with different fluorescent antibodies
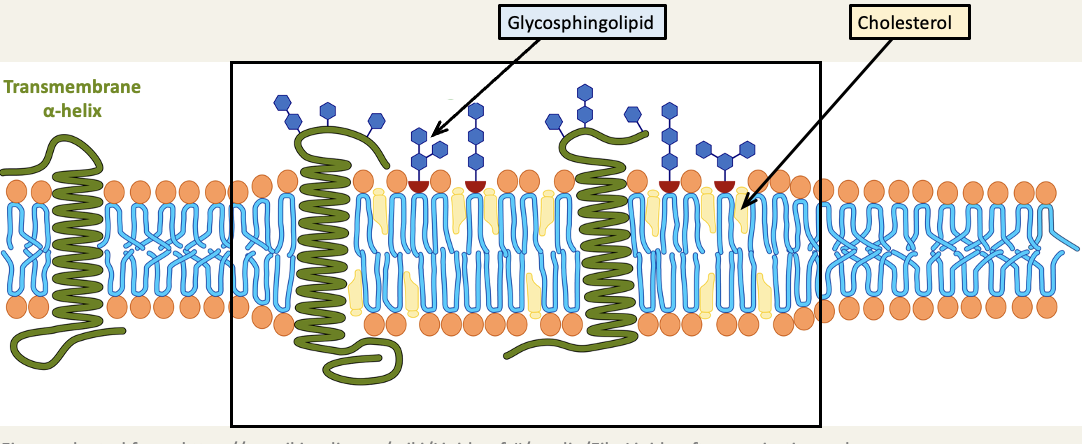
Lipid rafts
lipid rafts are micro domains within the lipid bilayer that have a characteristic glycolipid and protein composition, they are believed to float freely in the bilayer, like a raft on water
subject of lipid rafts is still hotly debated - everyone agrees the plasma membrane is not uniform though
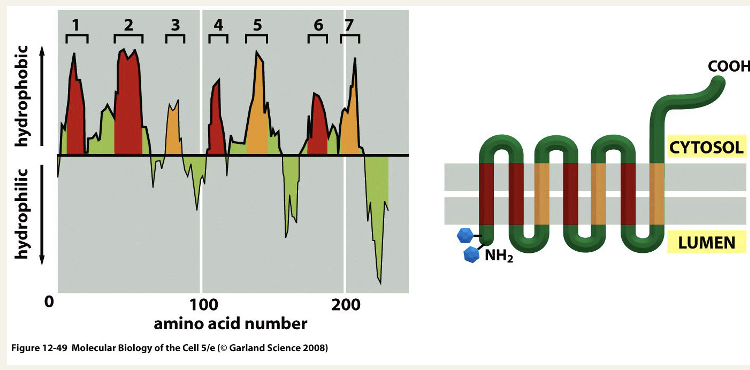
Hydropathy plot helps identify transmembrane helices
because transmembrane helices typically contain only apolar amino acid residues, they can be predicted from the proteins sequence
a hydropathy plot of the rhodopsin amino acid sequence identifies the 7 membrane helices
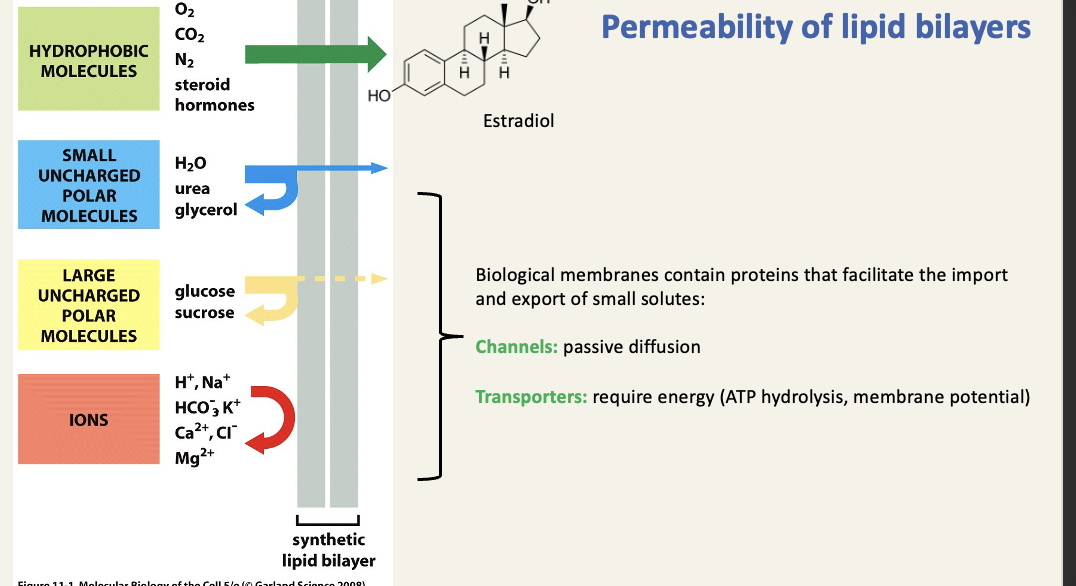
Permeability of lipid bilayer