ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN BODY
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Anatomy
is the study of body structures and their relationships
Physiology
is the science of how body parts function.
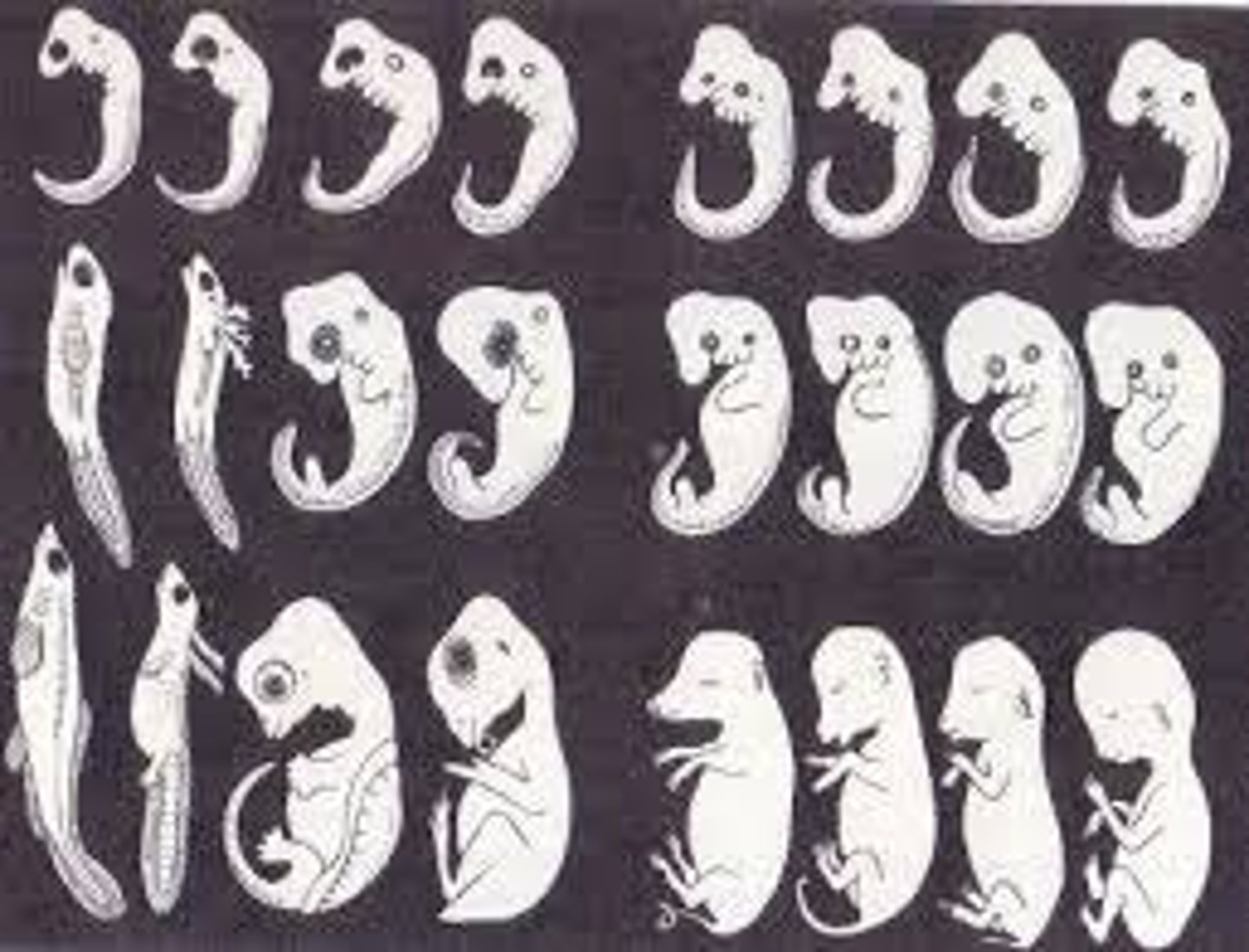
Embryology
the study of structures that emerge from the time of the fertilized egg through the eight week in utero.
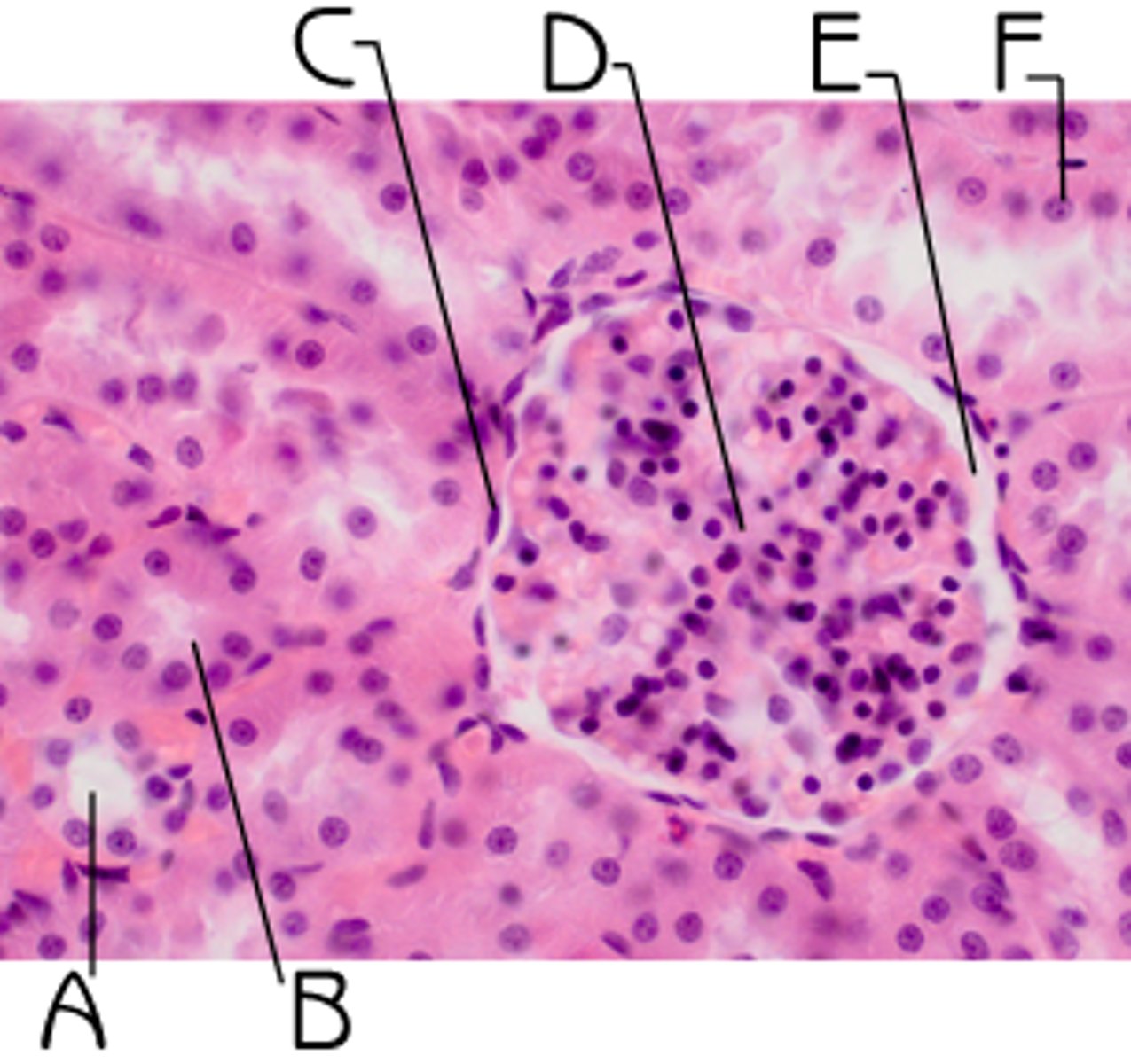
Histology
is the study of the microscopic structures of tissues.
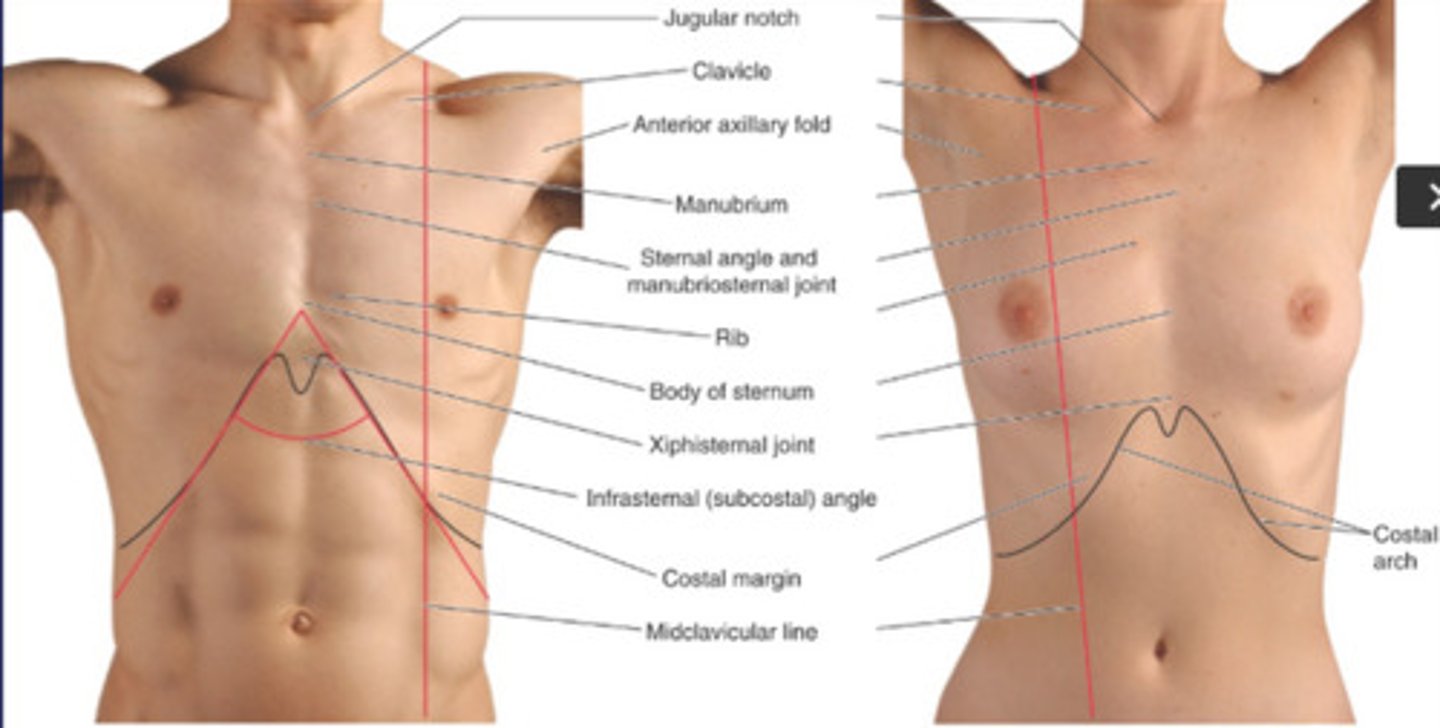
Surface anatomy
is the study of anatomical landmarks on the surface of the body through visualization and palpation.
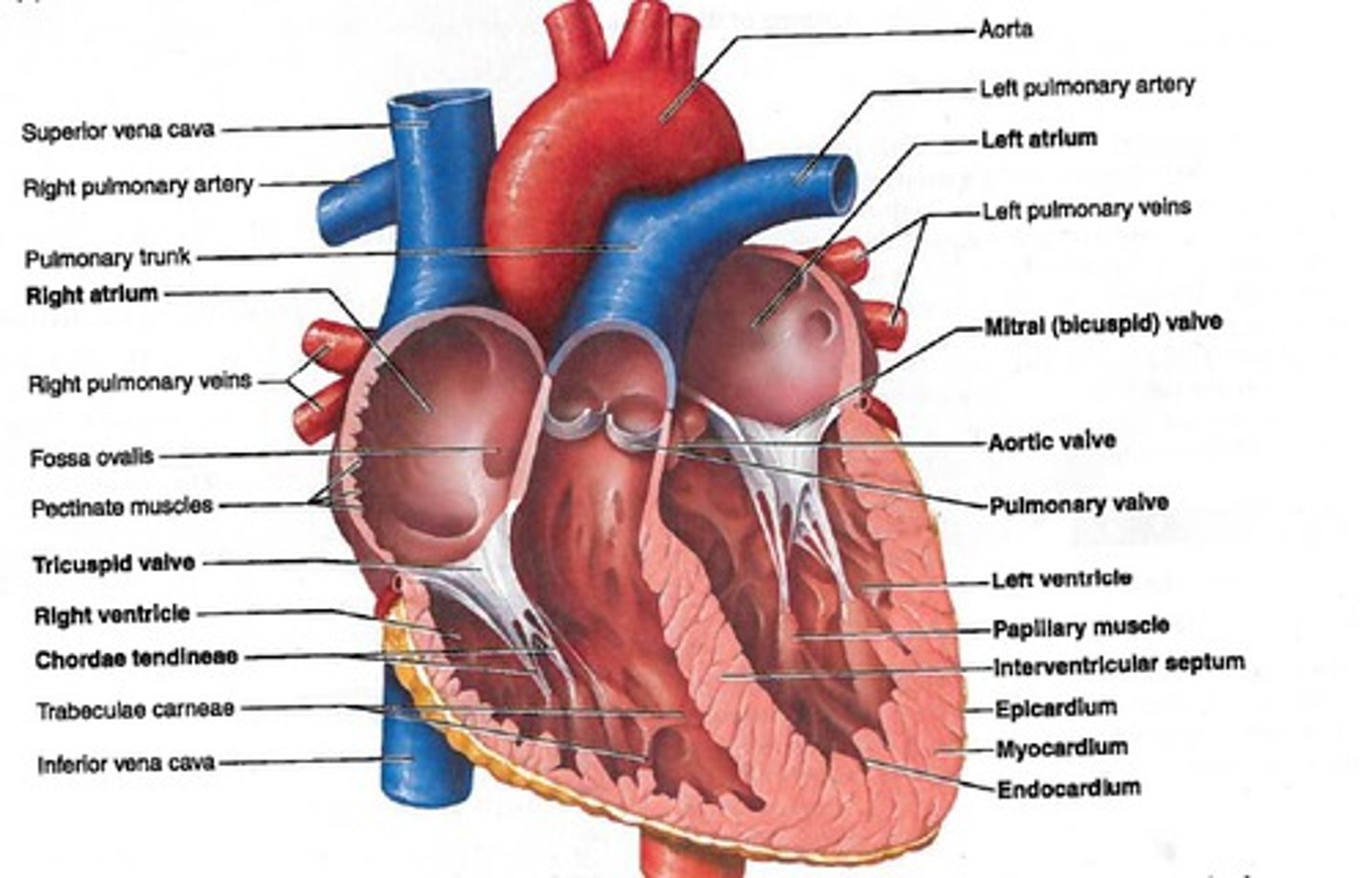
Gross anatomy
is the study of structures that can be examined without using a microscope.
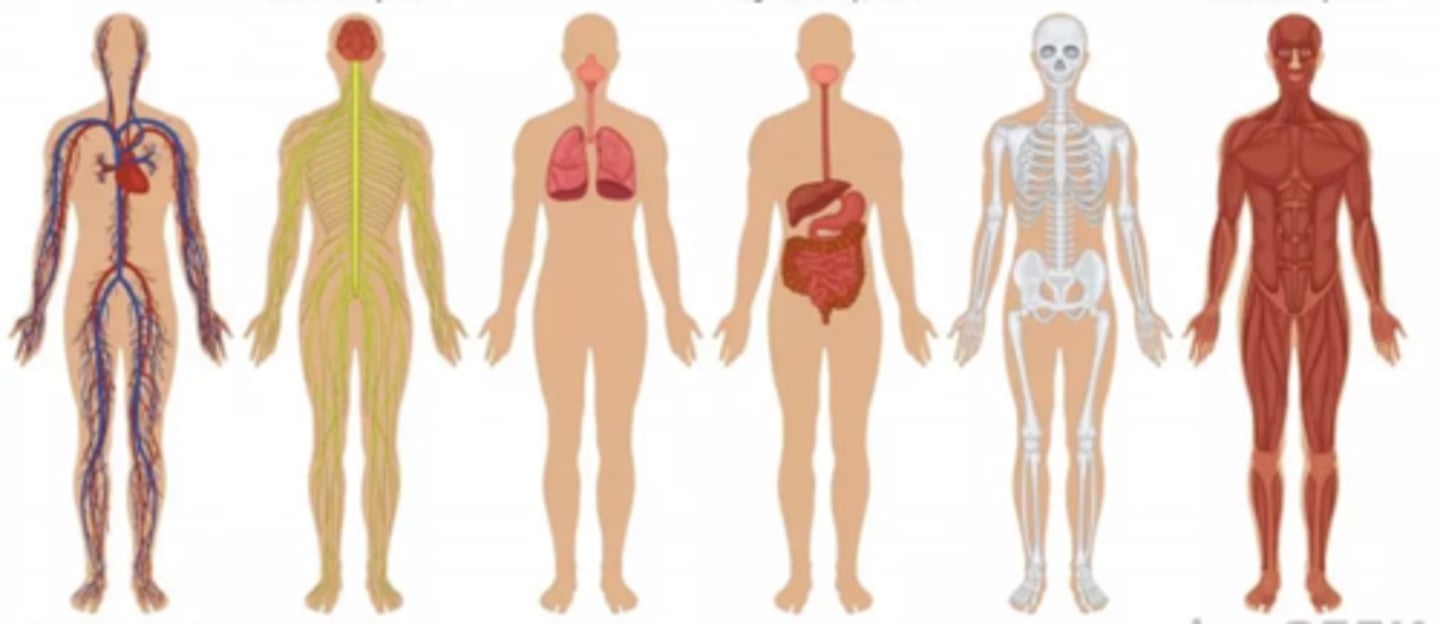
Systemic anatomy
is the study of structures of specific systems of the body.
Regional anatomy
is the study of structures in specific regions of the body such as head or chest.

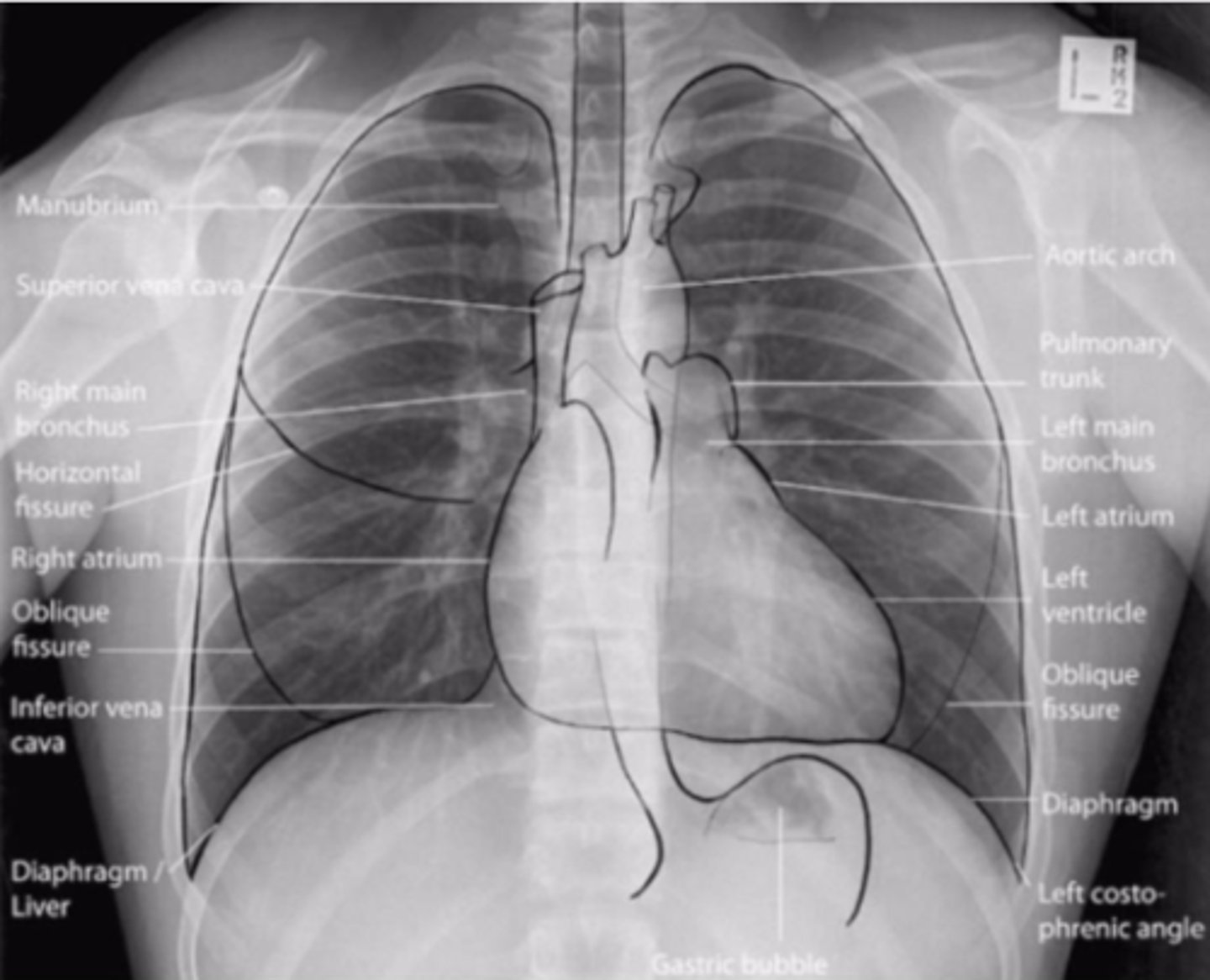
Radiographic anatomy
is the study of body structures that can be visualized with x-rays.
Pathological anatomy
is the study of structural changes associated with disease
embryology
histology
surface anatomy
gross anatomy
systemic anatomy
regional anatomy
radiographic anatomy
pathological anatomy
(8) sub-disciplines of ANATOMY
Neurophysiology
It is the study of the properties of nerve cells.
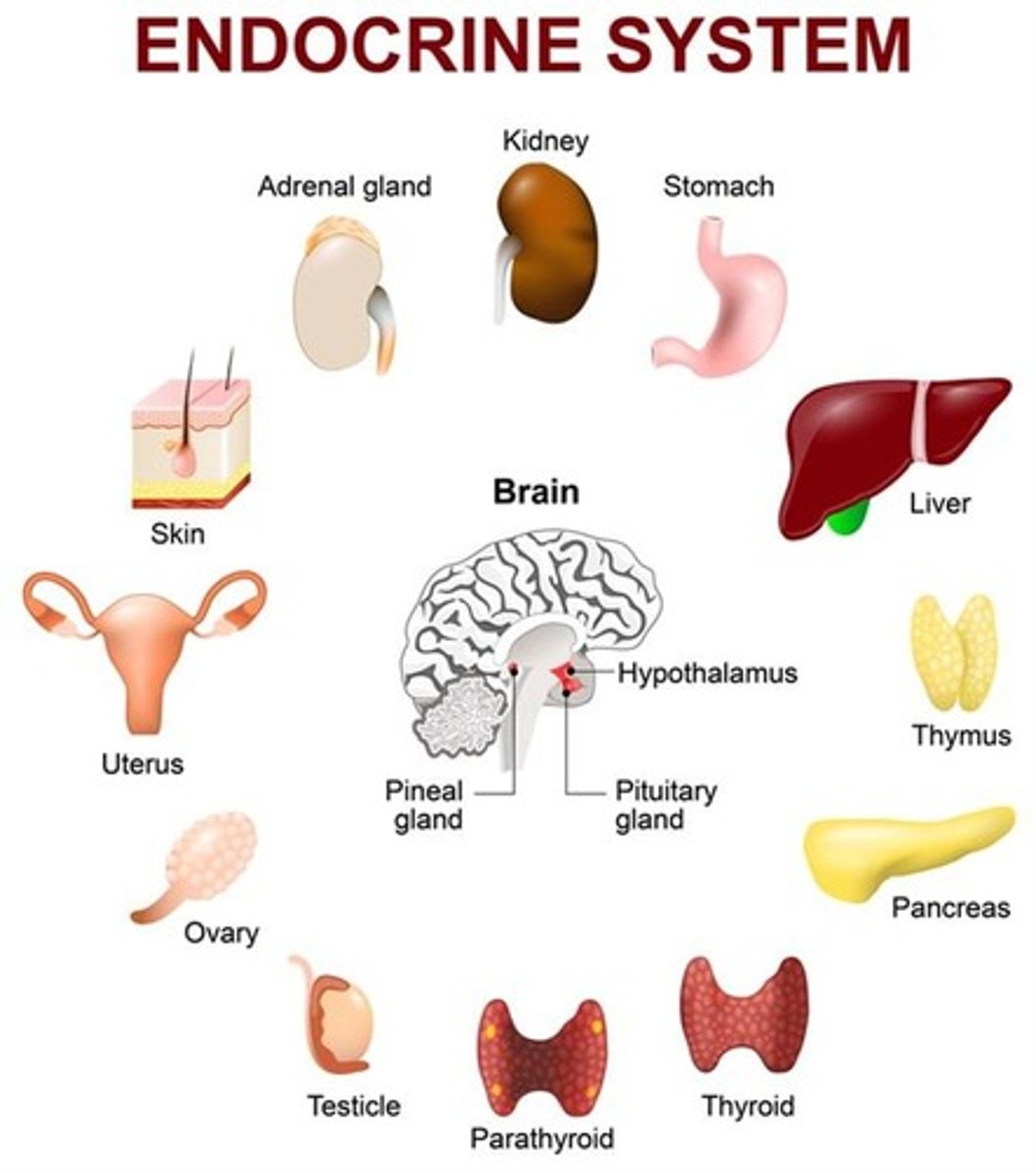
Endocrinology
It is the study of hormones and how they control body functions.
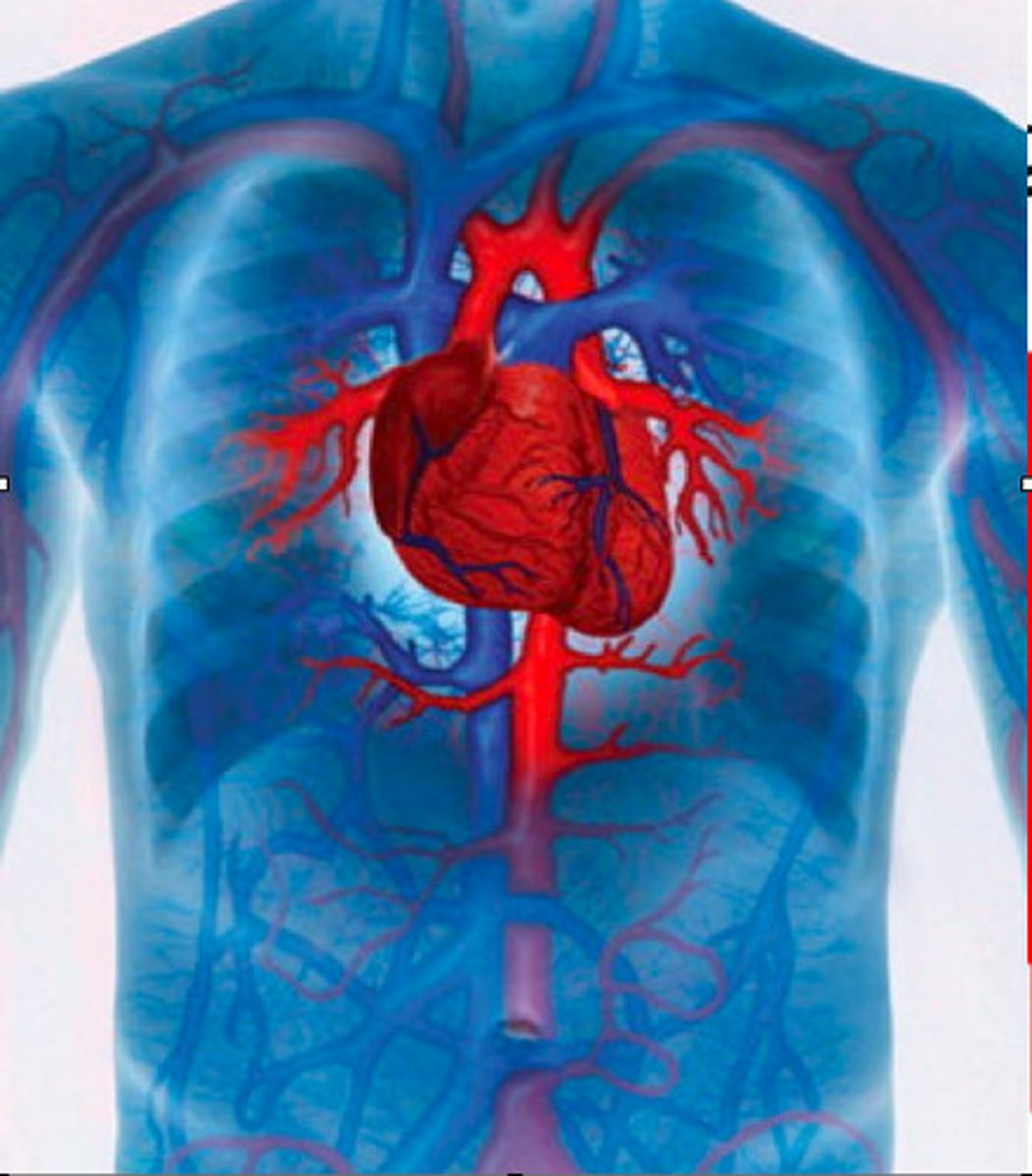
Cardiovascular physiology
It is the study of the heart and blood vessels.
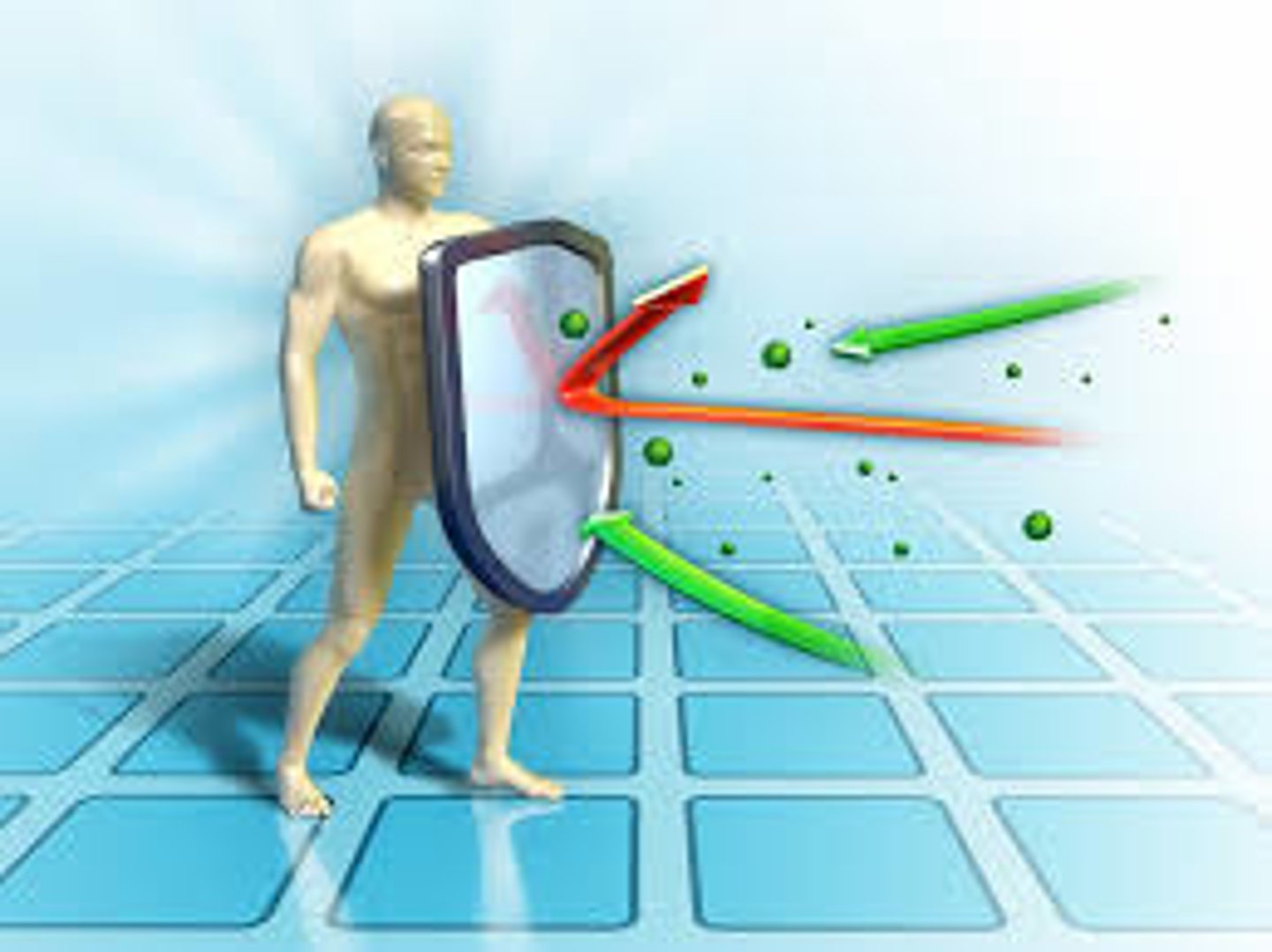
Immunology
The study is about how the body defends itself against disease-causing agents.
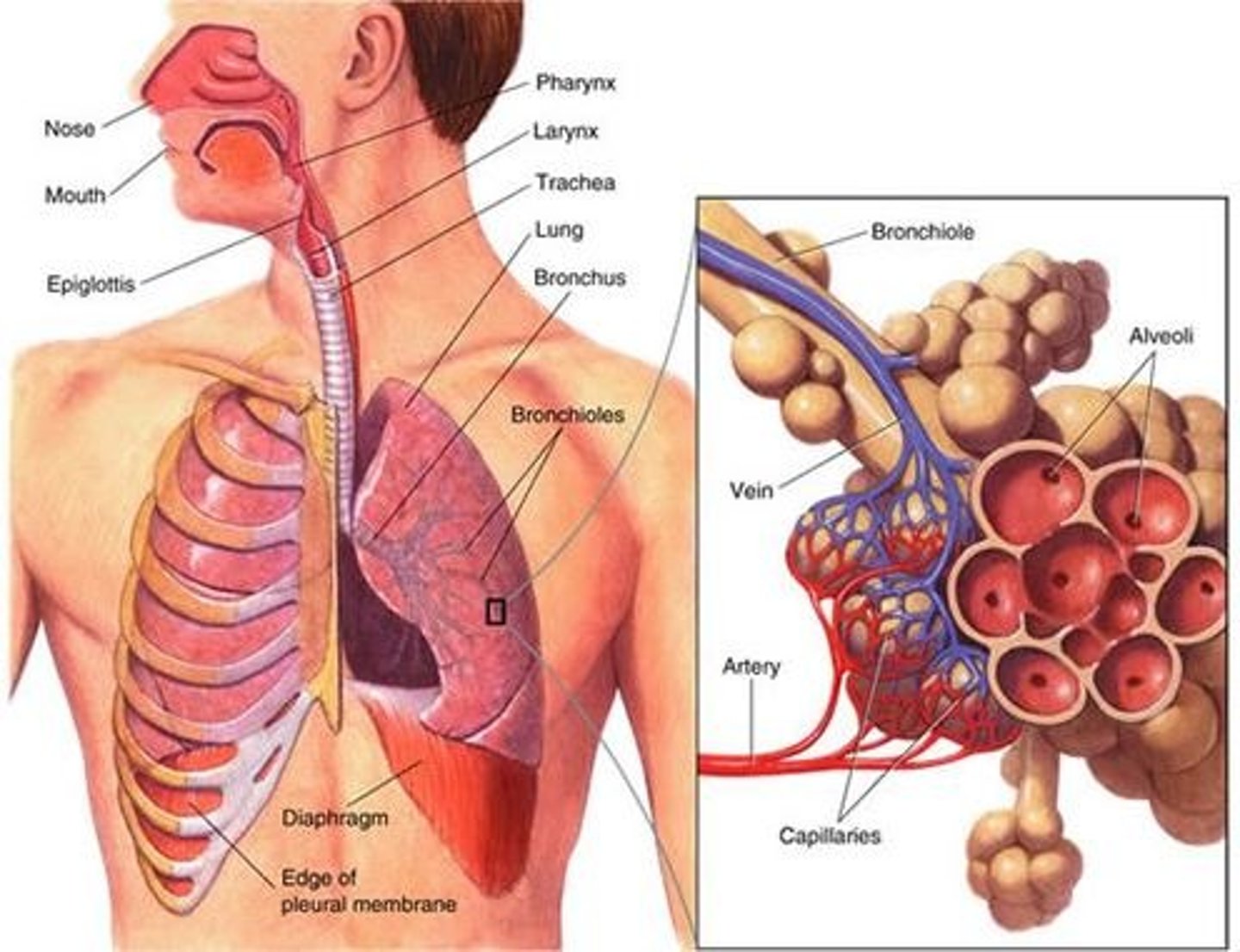
Respiratory physiology
is the study on the functions of the air passageways and lungs.
Renal physiology
is the study of the function of the kidneys
Pathophysiology
is the study of functional changes associated with disease and aging

neurophysiology
cardiovascular physiology
immunology
respiratory physiology
renal physiology
pathophysiology
(6) sub-disciplines of PHYSIOLOGY
chemical
cellular
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
(6) The levels of structural organization of the body
Chemical level
includes inorganic and organic chemicals make up all matter, both living and non-living.
Cells
the basic structural and functional units of the body.
Tissues
are groups of similar cells bound by supporting matrix that performs specific functions.
Organs
are structures that are composed of two or more different types of tissue that are integrated to perform a particular function.
Systems
consist of related organs that have a function
Maintaining boundaries
states that living organisms must be able to maintain its boundaries so that its "inside" remains distinct from its "outside".

Movement
includes motion of the whole body, individual organs or single cell.
Responsiveness or irritability
is the ability to sense changes in the environment and react to them.
Digestion
is the process of breaking down ingested food into simple molecules.
Metabolism
refers to all chemical reactions that occur within body cells.
Excretion
the process of removing excreta or wastes from the body.
Reproduction
is the production of offspring.
Growth
is the increase in size, usually accomplished by an increase in the number of cells.
Homeostasis
is a state of good health maintained by the normal functioning of the organ systems. The body constantly responds to internal and external changes, yet remains stable; its many aspects of metabolism are kept within normal limits.
receptor(s)
control center
effector(s)
Control systems of the body contain at least (3) three elements
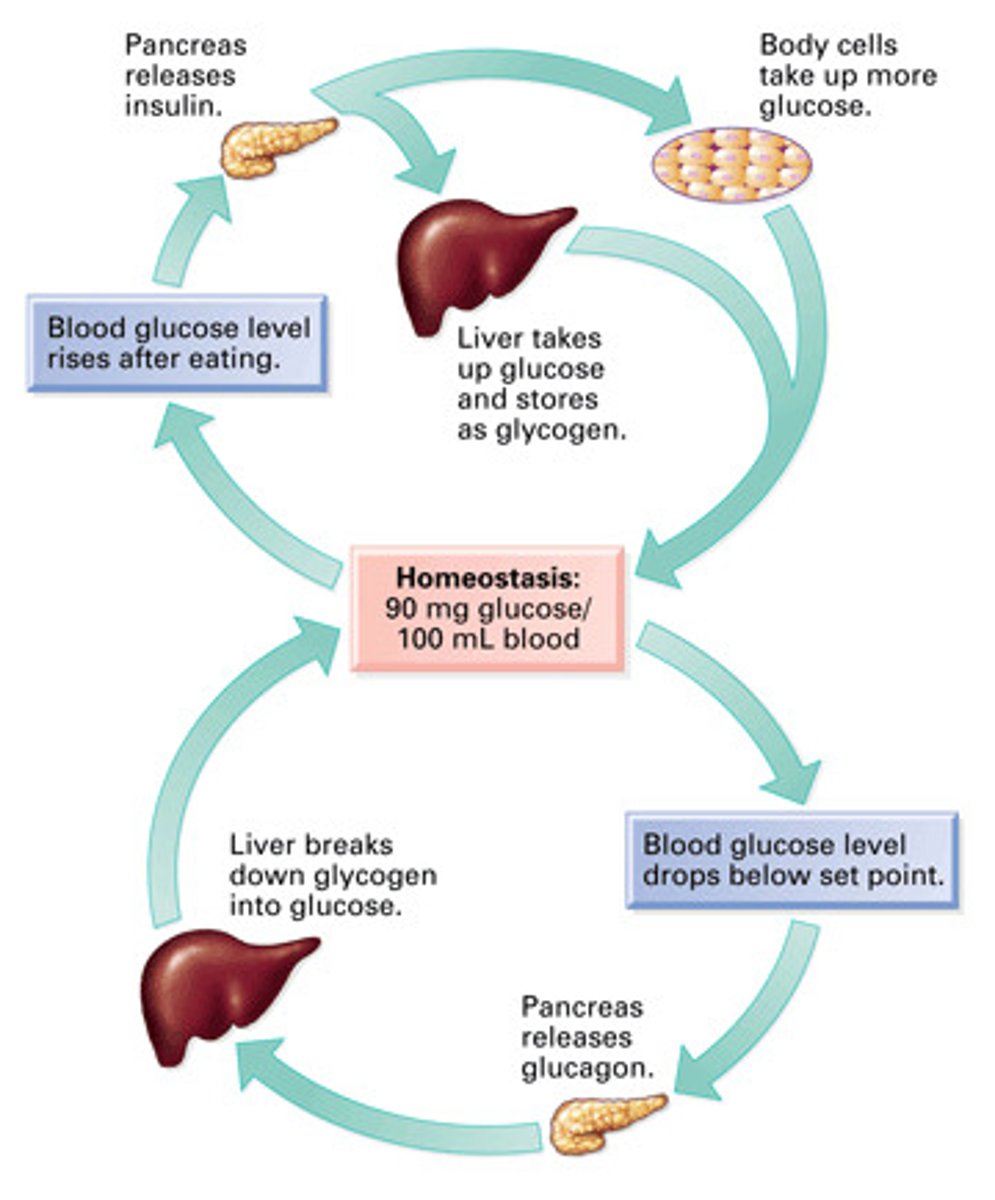
Negative feedback mechanism
- a control system in which a stimulus initiates a response that reduces the stimulus itself.
b. - Body temperature, heart rate, breathing rate and depth, and blood levels of glucose and certain ions are regulated.
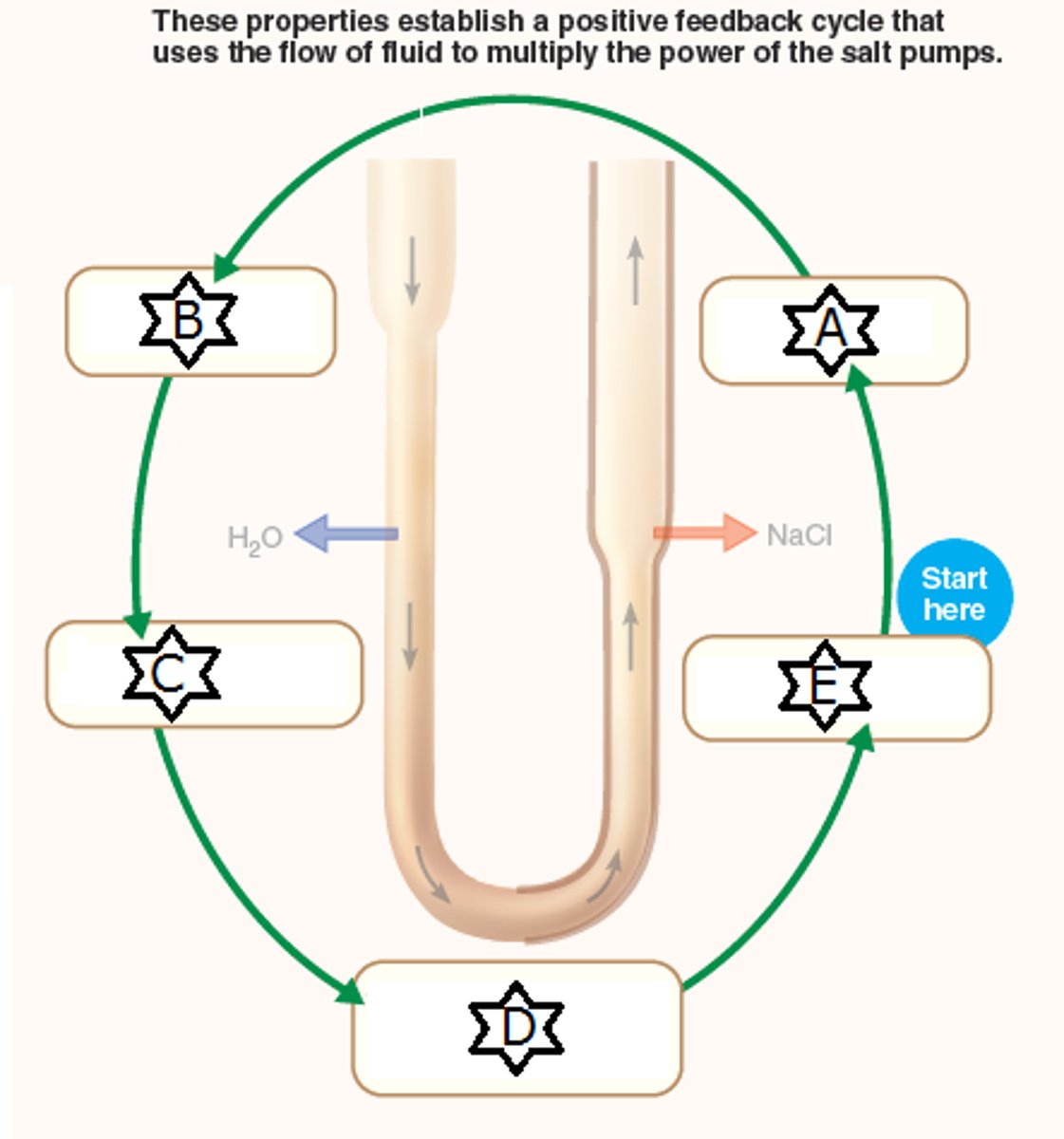
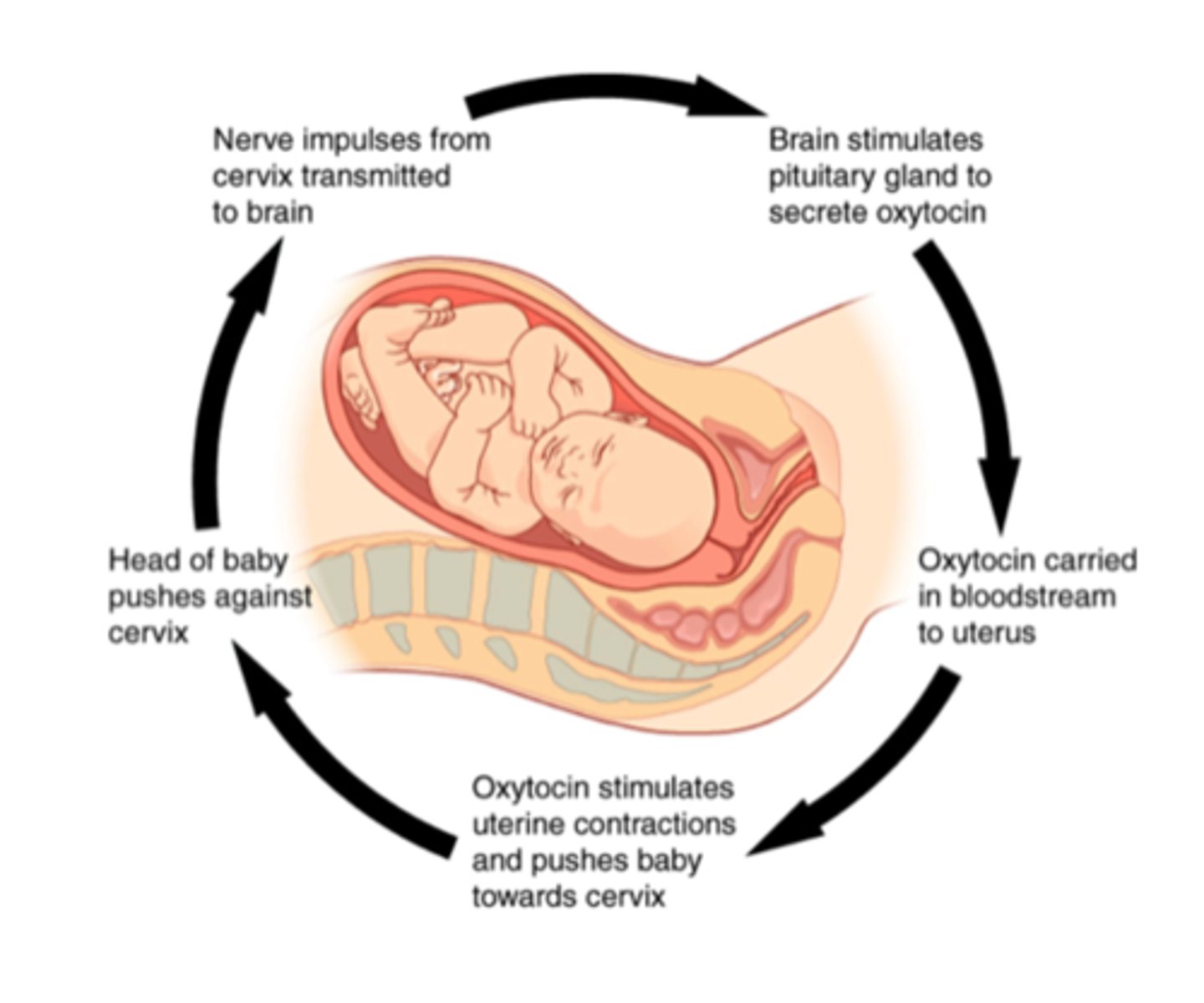
Positive feedback mechanism
intensify the initial stimulus, leading to an enhancement of the response. Blood clotting and labor contractions are regulated by such mechanisms.
Homeostatic Imbalance
Disruptions of homeostasis can lead to disorders, diseases, and even death. With age, the efficiency of negative feedback mechanisms declines, and positive feedback mechanisms occur more frequently
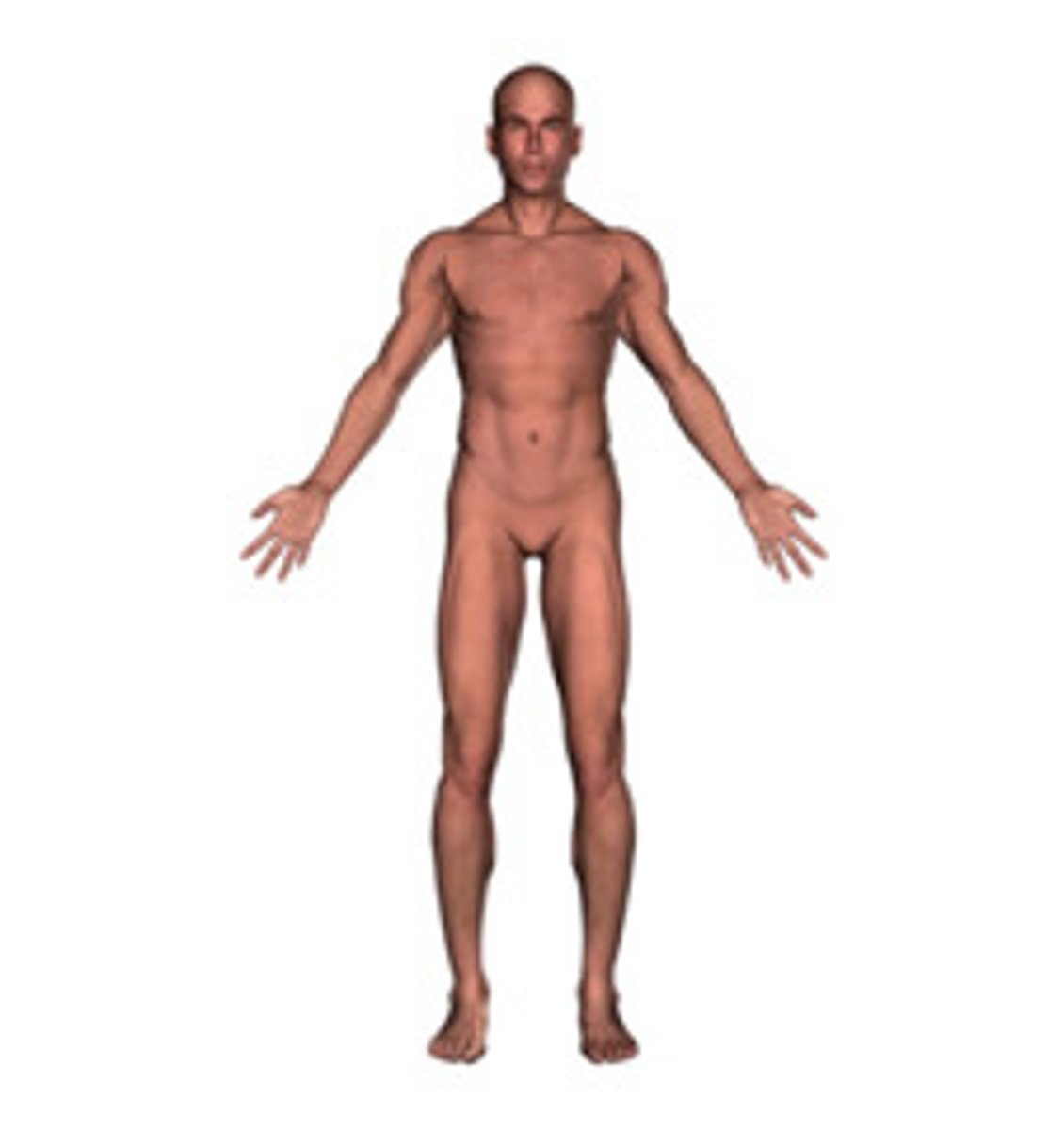
Anatomical Position
Standing erect, facing the observer, with the head level and eyes facing directly forward. The feet are flat on the floor and directed forward, and the arms are at the sides, with the palms turned forward.
Planes and sections
- cutting the body or an organ in a specific way.
Sagittal
- separates right and left parts.
Midsagittal
- exact midline, divides body/organ into equal right & left parts.
Parasagittal
- doesn't pass thru midline, divides body into unequal right and left parts
Frontal/coronal
- separates anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts
Transverse
- separates superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts.
Oblique
- passes thru the body/organ at an angle between transverse & frontal/sagittal.