1.2 how markets work
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
law of demand
states ceteris paribus( all other things being the same)
if price increases then quantity demanded falls
law of dimishing marginal utility
as you use or consume more of something you will get less satisfaction from that thing
the demand curve
downwards sloping curve because the law of dimishing marginal utility,shows the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
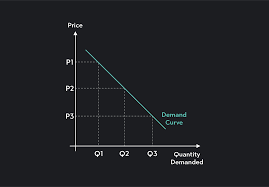
what does a shift in price do to the demand curve
movement - either a contraction(moves up the curve) or a extension(moves down the curve)
factors the cause a shift in demand curve
Population
Advertising
Substitutes
Interest rates
Fashion trends
Income
Compliments

increase in population affect on demand curve
shift to right
increase in advertisment affect on demand curve
shift to right
increase in price of a substitute affect on demand curve
shift to right, as consumers switch to the relatively cheaper alternative.
increase in interest rates affect on demand curve
shift to left, as borrowing costs increase and consumer spending decreases.
product in fashion trends affect on demand curve
shift to right, as consumers desire more trendy products.
increase in income affect on demand curve
shift to right, as consumers have more purchasing power and can buy more goods.
increase in price of compliment affect on demand curve
shift to left, as higher prices for complementary goods decrease the quantity demanded.
demand
the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices over a given period.
rational decision making
the process of making choices that result in the optimal level of benefit or utility for the individual. It involves weighing the costs and benefits of different options.
AD - aggregate demand
sum of all individuals demand
PED
price elasticity of demand - the responsiveness of demand to a change in price
elastic
percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than percentage change in price
inelastic
percentage change in quantity demanded is less than percentage change in price.
formula for PED
Percentage change in quantity demanded /percentage change in price.
what happens if PED is negative
usually the coefficient of PED is negative but economists ignore that sign
price elastic goods
very responsive to price changes
many substitutes
unnecessary
price inelastic goods
less responsiveness to demand changes
tend to be:
highly branded
innovative
necessity
few substitutes
habit forming
inelastic demand curve

elastic demand curve

if PED is 0
perfectly inelastic - price has no affect on demand at all
if PED is 0-1
relatively inelastic - price has a small effect on demand
if PED is 1
unitary - changes are the same
if PED is 1 - infinity
relatively elastic - price has large effect on demand
if PED is infinity
perfectly elastic - any increase in price kills demand
factors affecting PED
S - substitutes
P-proportion of income
L - luxury
A - addiction
T - Time
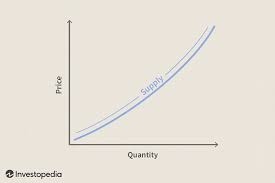
supply
the quantity of a good or service that suppliers are willing and able to supply to the market at a given price at given period of time
supply curve
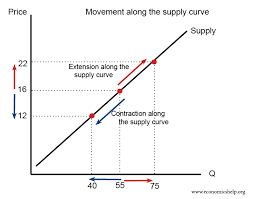
movements along the supply curve
expansions and contraction, happen when there is a change in price of the product
factors causing the supply curve to shift
P - productivity
I - indirect taxes
N - no of firms
T - technology
S - subsidies
W - weather
C - costs of production
increase in productivity affect on supply
shift to right
increase in indirect taxes affect on supply
shift left
increase in no of firms affect on supply
shift to right
increase in technology affect on supply
shift right
increase in subsidies affect on supply
shift right
increase in weather affect on supply
shift left
increase in costs of production affect on supply
shift left
YED
income elasticity of demand - responsiveness of demand to a change in income
formula for YED
percentage change in demand/percentage change in income
normal good
demand rises with average income rate e.g heinz beans
positive YED (0-1)
inferior good
demand rises as income falls
negative YED
luxury goods
demand rises more than proportionate to a change in income
positive YED > 1
XED
cross price elasticity of demand - the responsivess of demand for good A to a change in price of good B
formula for XED
percentage change in demand of good A/percentage change in price of good B
what does it mean when XED is negative
the goods are compliments
a fall in price of good B would lead to a rise in demand of good A
what does it mean when XED is positive
goods are substitutes
a fall in price of good B would mean a fall in demand of good A
if XED 0>1
weak relationship
if XED = 0
no relationship
if XED is >1
strong relationship
PES
price elasticity of supply - the responsiveness of quantity supplied of a good given a change in price
formula for PES
percentage change in quantity supplied/percentage change in price
if PES is >1
relatively elastic
if PES is 0-1
relatively inelastic
if PES =1
unitary
if PES = infinity
perfectly elastic
if PES = 0
perfectly inelastic
factors that affect PES
Barriers to entry
Resources
Inventory
Time
Spare capacity
equilibrium
a situation in which price has reached a level where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
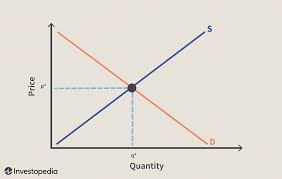
equilibrium price
the price that balances quantity demanded and quantity supplied
equilibrium quantity
the quantity demanded and quantity supplied at equilibrium price
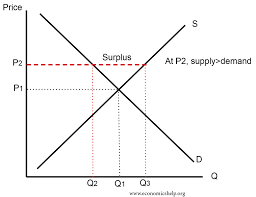
surplus
when the price is set above equilibrium price causing the quantity supplied to exceed the quantity demanded causing a surplus of products
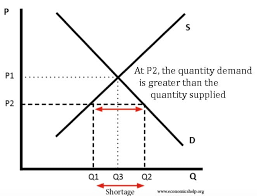
shortage
when the price is set below equilibrium price and the quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied causing a shortage of products
consumer surplus
difference between what they are willing to pay and what they do pay
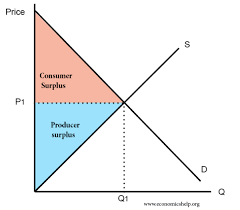
producer surplus
difference between the price a firm receives and the price they would be willing to sell at
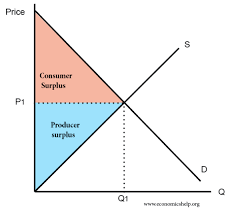
what happens to consumer and producer surplus if demand shifts right
they increase
functions of price
rationing
signalling
incentive
allocative
rationing
to control the distribution of scarce goods
increasing price- reduce demand for those who arent willing or able to buy it
signalling
prices provide important information to market participants
incentive
create incentives for market participants to change their actions
allocative
acts to divert resources to where returns can be maximised
indirect taxes
taxes on expenditure
e.g. VAT, excise duties
2 types of indirect taxes
specific
ad valorem
ad valorem
puts a tax on a good depending on its value
usually expressed as a percentage
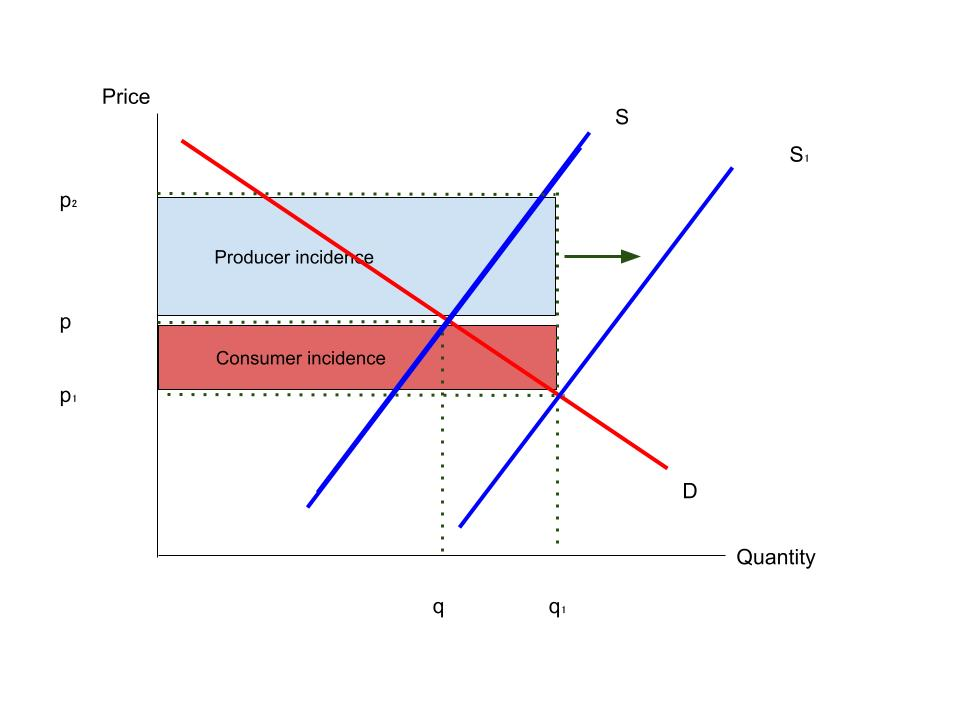
consumer incidence
burden on consumer
producer incidence
burden on producer
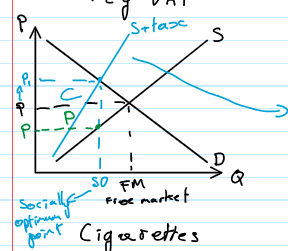
specific tax
fixed amount of tax placed on a particular good
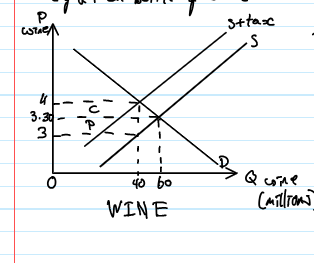
subsidy
the government pays part of the costs of production to firms
homo economics
rational man
why dont we act like the rational man
influence of others
habitual behaviour
consumer weakness in computation
inertia
influence of others
conformity
unwilling to change the bias
herding behaviour
habitual behaviour
easier
limits consumers considering alternatives
addictions
buying products at eye level
consumer weakness at computation
arent willing or able to look at alternatives
poor at self control
inertia
tendency to do nothing/remain unchanged