World War 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
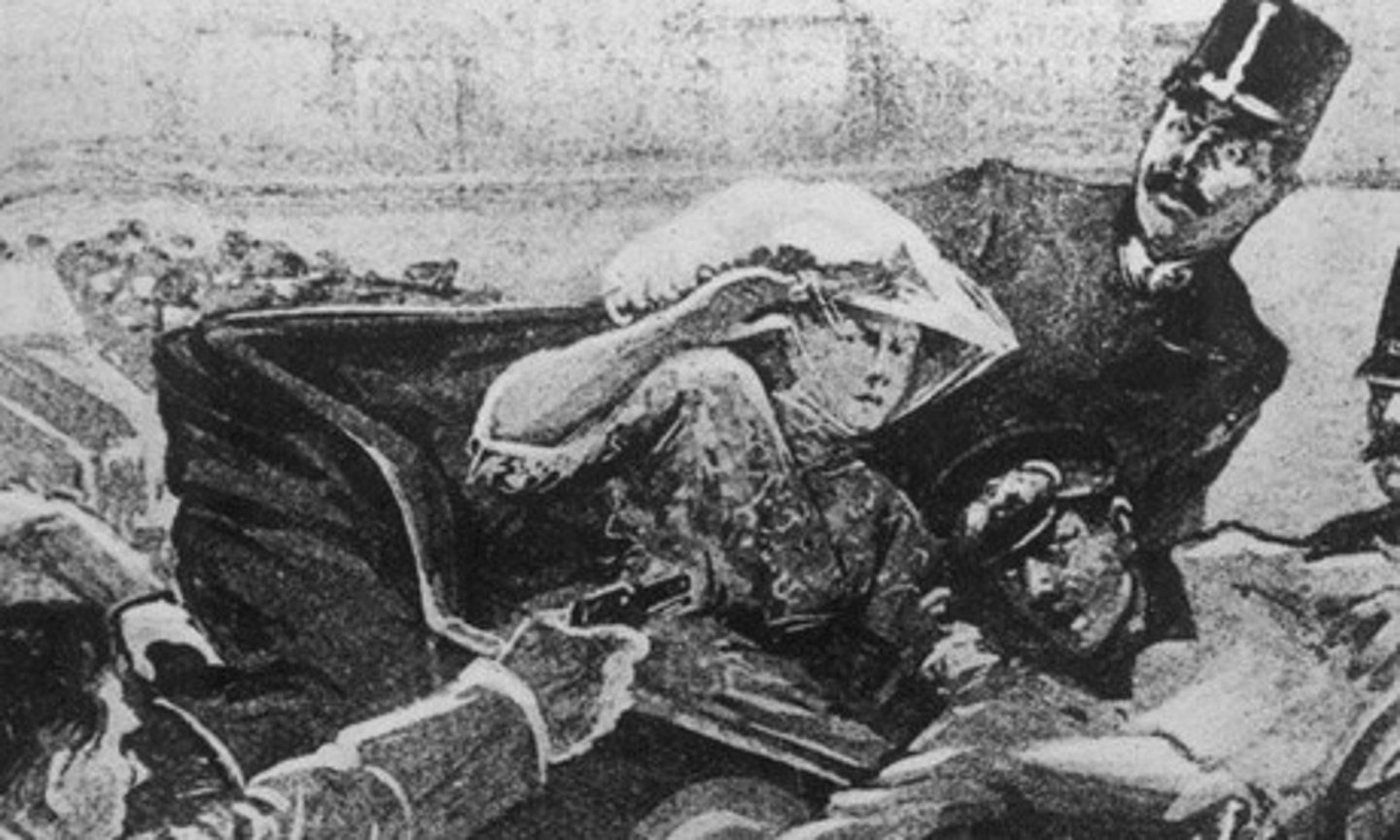
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
(crown prince) heir to Austrian throne from 1896: assassinated on June 28, 1914 during good-will mission in Sarajevo, Bosnia by Serbians, sparking WWI
Militarism
A political orientation of a people or a government to maintain a strong military force and to be prepared to use it aggresively to defend or promote national interests
Nationalism
Pride for your country
Imperialism
A stronger nation taking over a weaker nation
total war
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort

propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion

armistice
A temporary peace agreement to end fighting.

unrestricted submarine warfare
A policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters. President Wilson believed that this action by Germany violated the laws of neutrality, and when Germany went back on their promise to stop, Wilson asked Congress to declare war.

Treaty of Versailles
Treaty that ended WW I. It blamed Germany for WW I and handed down harsh punishment.

Fourteen Points
A series of proposals in which U.S. president Woodrow Wilson outlined a plan for achieving a lasting peace after World War I.

League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations. President Wilson's ultimate goal at the Paris Peace Conference.

reparations
As part of the Treaty of Versailles, Germany was ordered to pay fines to the Allies to repay the costs of the war. Opposed by the U.S., it quickly lead to a severe depression in Germany.

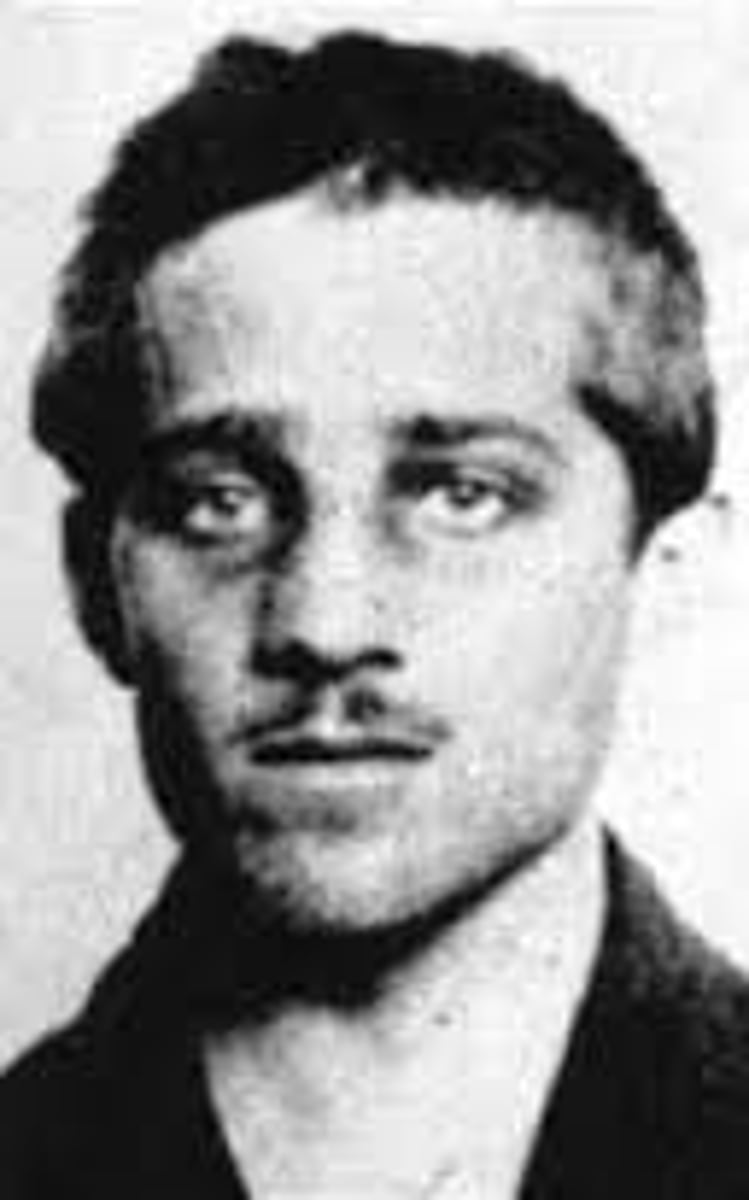
Gavrilo Princip
The assassin of Archduke Francis Ferdinand of Austria, a member of the Black Hand

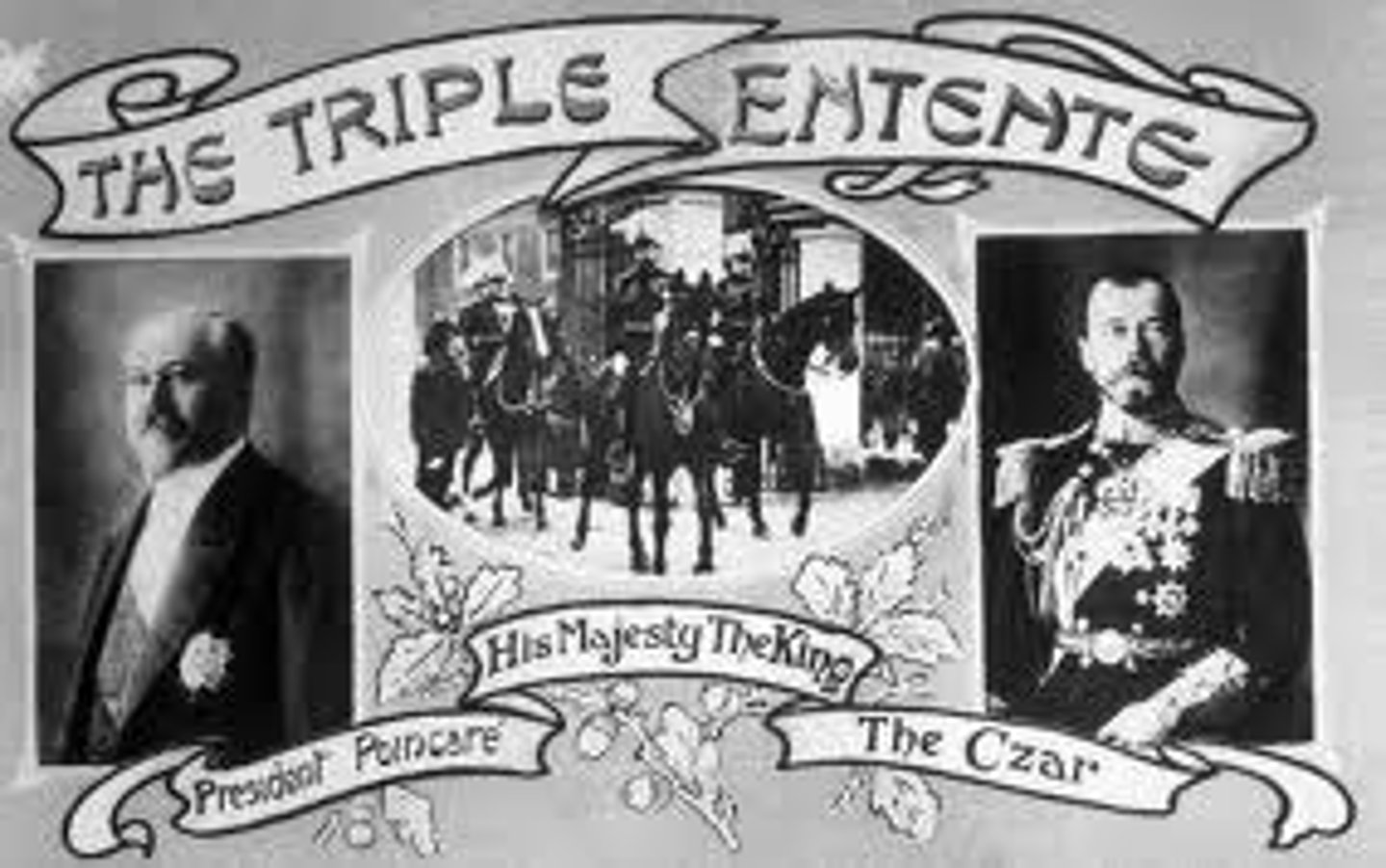
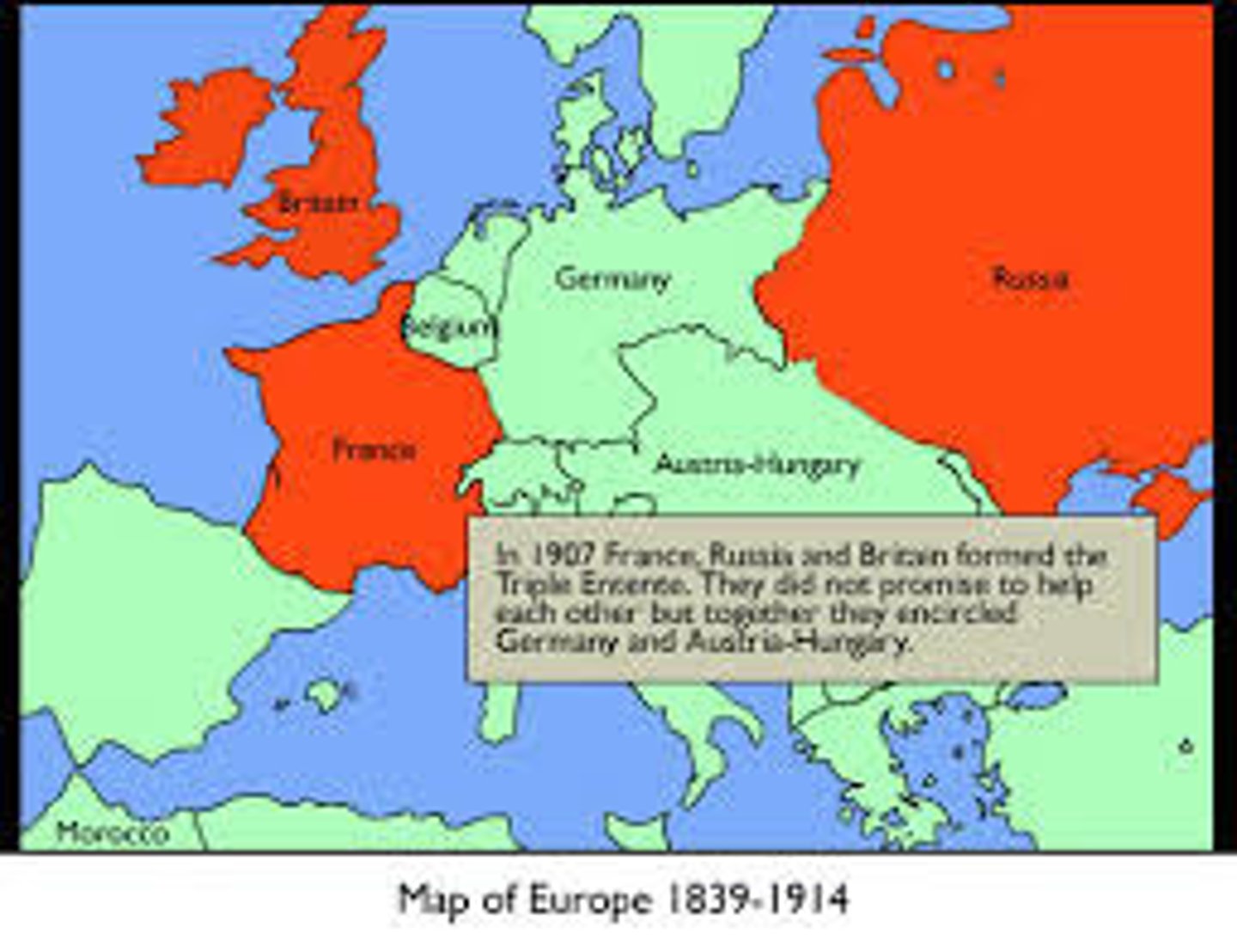
Triple Entente
A military alliance between Great Britain, France, and Russia in the years preceding World War I.
Triple Alliance
A military alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy in the years preceding World War I
Allies of World War I
Composed of France, Britain, and Russia, and later Japan and Italy, the Allies fought the Central Powers in World War I. The United States joined the Allies in 1917.

Central Powers
A military alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire.

alliance system
The alliance system in Europe was a major cause of World War 1.

Woodrow Wilson
Winner of 1912 and 1916 elections. World War I leadership, Treaty of Versailles, sought 14 points post-war plan, League of Nations (but failed to win U.S. ratification)

Zimmerman Telegram
A coded message sent by Germany to try to get Mexico to attack the US

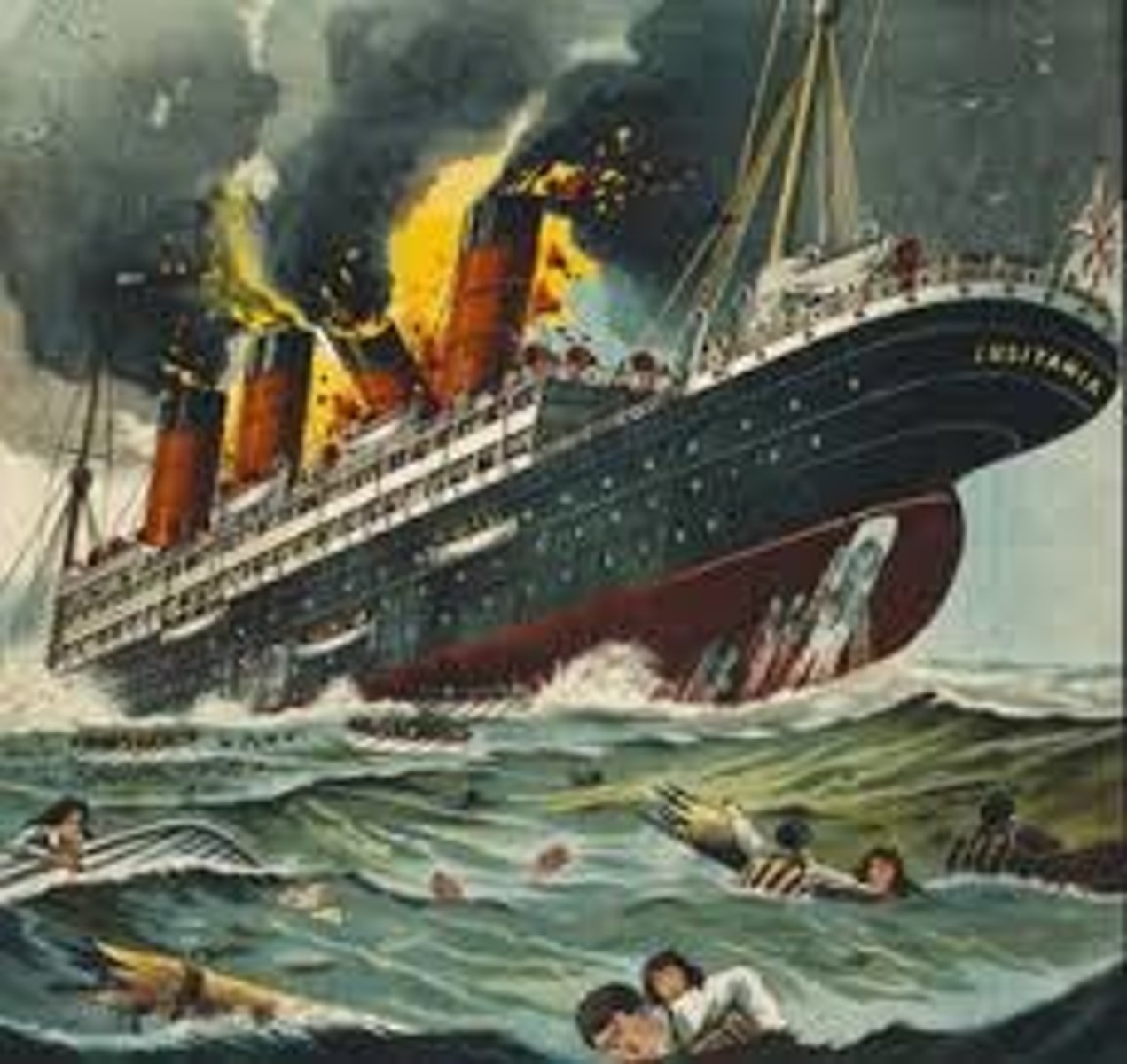
Lusitania
British passenger boat sunk by a German submarine that claimed 1,000 lives. One of main reasons US decided to join the war.

stalemate
A deadlock in which neither side is able to defeat the other.

Versailles Peace Treaty
The Treaty of Versailles (French: Traité de Versailles) was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
U-boat
German submarine - u boat is short of the German word, Unterseeboot (Under Sea Boat)
Belguim
Germany invaded France through this country, which effectively brought Great Britain into the war.
isolationists
People who wanted the United States to stay out of world affairs
The Big Four
US, Britain, France, Italy
Self-determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government
War Guilt Clause (Treaty of Versailles)
An article in the Treaty of Versailles that declared that Germany (with Austria) was solely responsible for the war and had to pay reparations equal to all civilians damages caused by the fighting.
War Industries Board
Agency that increased industrial production; set priorities for goods to be made, fixed prices, & standardized products
Committee on Public Information
government organization that produced propaganda to build support for the war
Eugene V. Debs
Debs repeatedly ran for president as a socialist, he was imprisoned after he gave a speech urging resistance to the draft. Arrested for 10 counts of sedition.
Charles Schenck
Convicted by the U.S. government of distributing anti-draft pamphlets
Sedition Act
1918 law that made it illegal to criticize the government
Espionage Act
This law, passed after the United States entered WWI, imposed sentences of up to twenty years on anyone found guilty of aiding the enemy, obstructing recruitment of soldiers, or encouraging disloyalty.
19th Amendment
Gave women the right to vote
16th Amendment
Allows the federal government to collect income tax & helped fund WWI
Liberty Bonds
sold to American people to raise money for the war efforts
Rationing
Restricting the amount of food and other goods people may buy during wartime to assure adequate supplies for the military
Victory Gardens
Backyard gardens; Americans were encouraged to grow their own vegetables to support the war effort
Convoy System
the protection of merchant ships from U-boat-German submarine-attacks by having the ships travel in large groups escorted by warships
influenza
nearly 600,000 Americans lost their lives to this between 1918 and 1919
United States
Nation that emerged as the overriding economic world power at the end of WWI
"Make the world safe for democracy"
President Wilson persuaded the American people to enter WWI by declaring this
Senate
Legislative body in Congress that has the power to ratify treaties
League of Nations
The most controversial aspect of the Treaty of Versailles. The Senate believed it robbed Congress of it's power to declare war because it would force us to get involved in world conflicts.
Isolationism
Foreign policy that the US adopts after WWI.
neutrality
Policy that the US adopted at the beginning of the war, but became increasingly difficult as America wanted to maintain freedom of the seas to trade with Europe
Sinking of the Lusitania
May of 1915, off the coast of Ireland. 1,195 perished, including 123 Americans.
Women's suffrage
Wilson felt pressured to grant women the right to vote after all of their help and support during the war.
Selective Service Act
Gave Congress the power to enact a draft for the war
Vittorio Orlando
He was the Italian representative at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919. Sided more with the USA at the conference to NOT severely punish Germany. Angry that Italy was promised land that they never received.
Woodrow Wilson
Knew that punishing Germany was a bad idea. Pushed for self-determination.
David Lloyd George
the British prime minister, had just won reelection on the slogan "Make Germany Pay." Didn't want to destroy the German economy, but punished them because of their alliance to France
George Clemenceau
French prime minister in last years of WWI and during Versailles Conference of 1919. Pushed for heavy reparations from Germans. Wanted to get lost territory back and set up strict rules to de-arm them.