Basic Laboratory Equipment - Binocular Microscope
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
compound microscope
a light microscope that uses more than one lens to magnify an object

oculars / eyepieces of a microscope
(magnification of the image formed by the objective lens)
(one fixed, one adjustable)
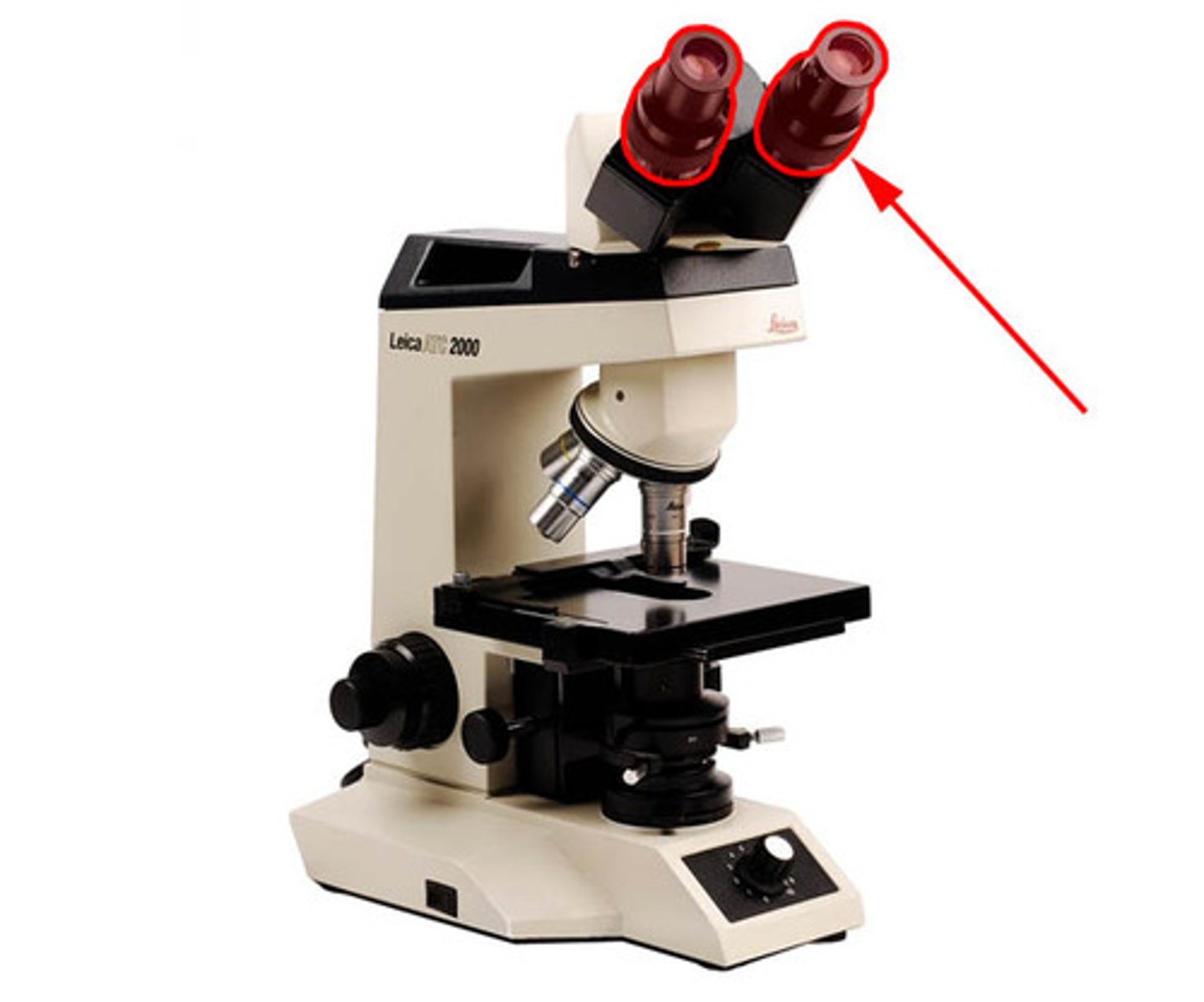
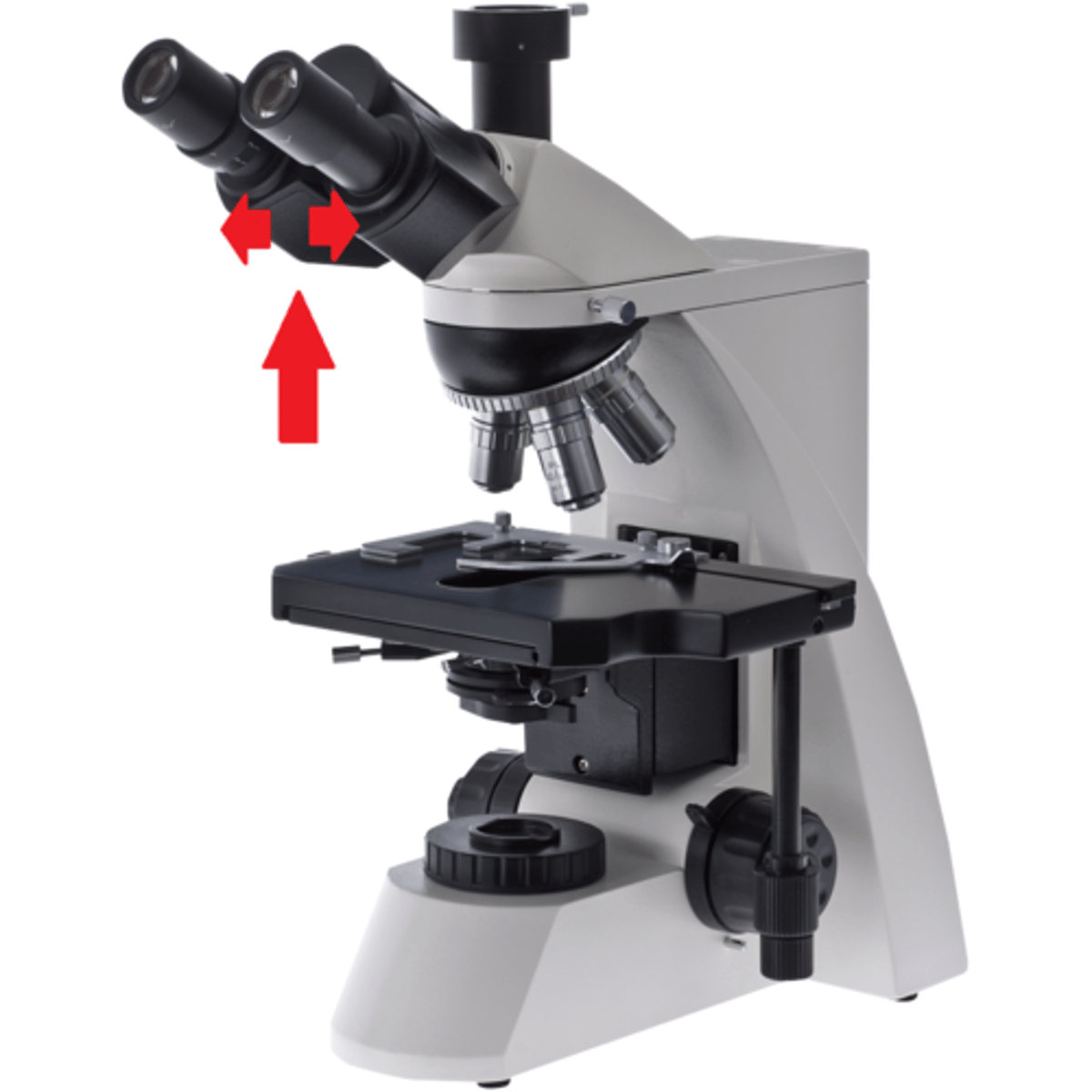
interpupillary control of a microscope
(located between the two ocular lenses)
(adjusts the width of the eyepieces)

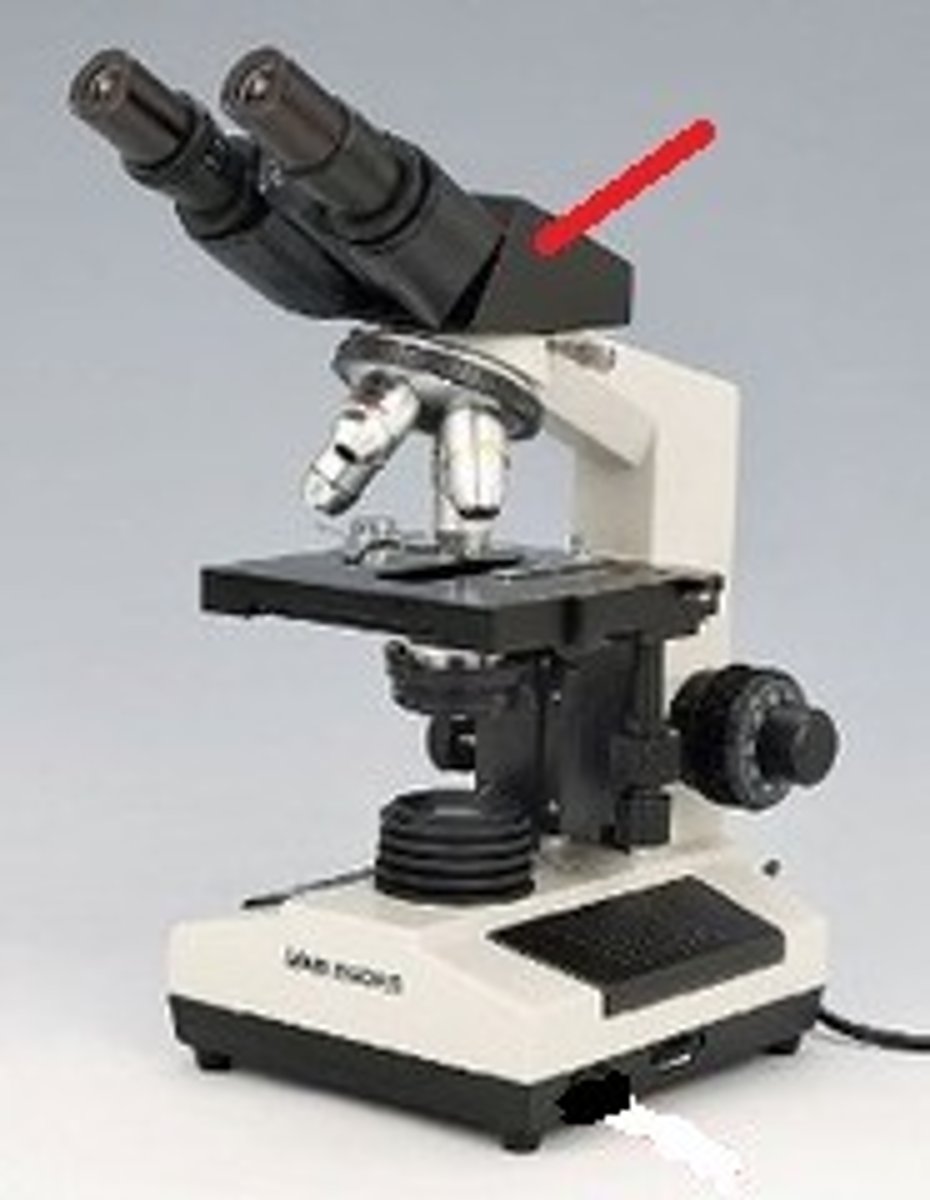
optical tube of a microscope
(connects eyepieces with objective lens)
(forms intermediate image)

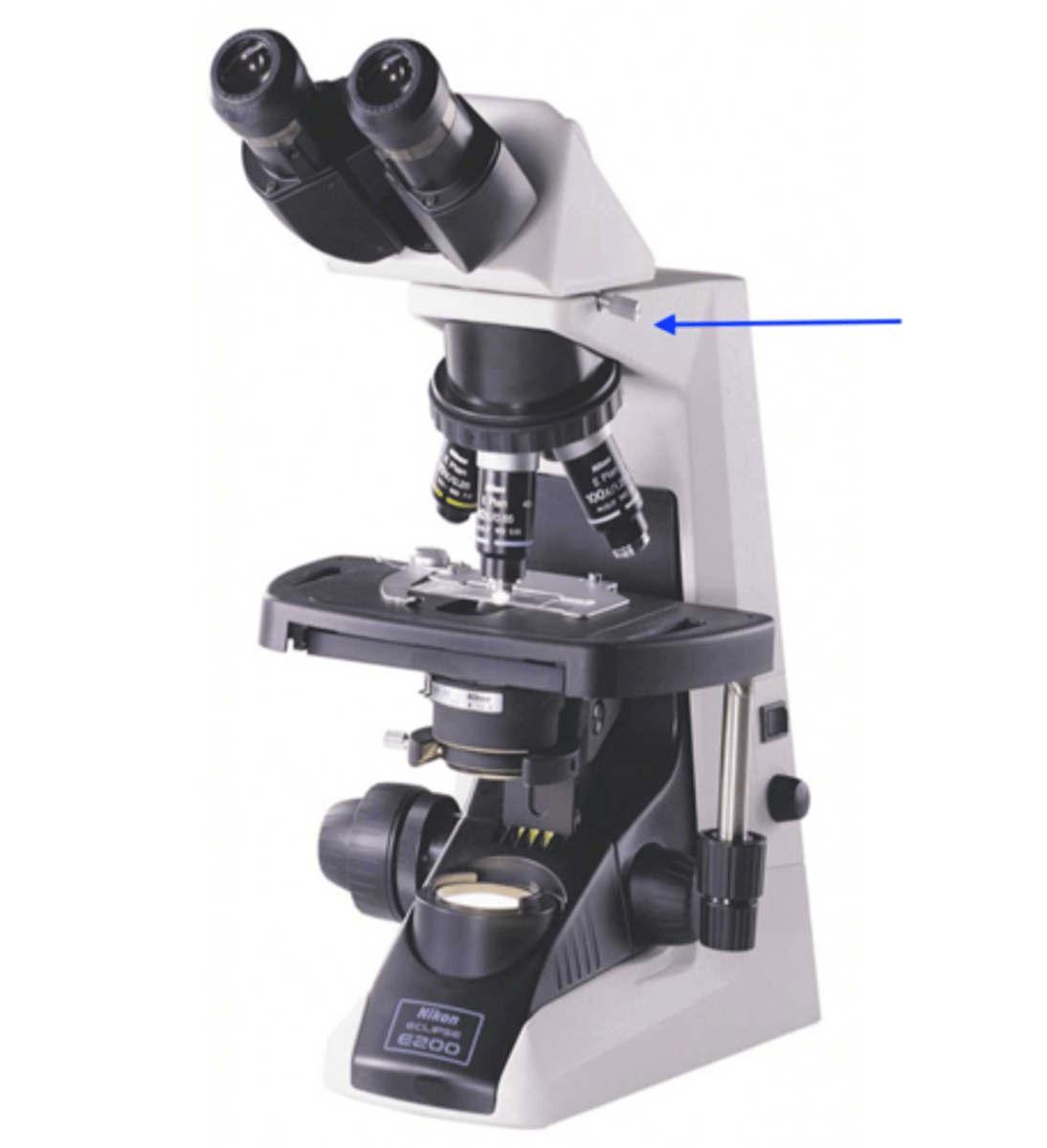
neck / arm of a microscope
(attachment site for revolving nosepiece)
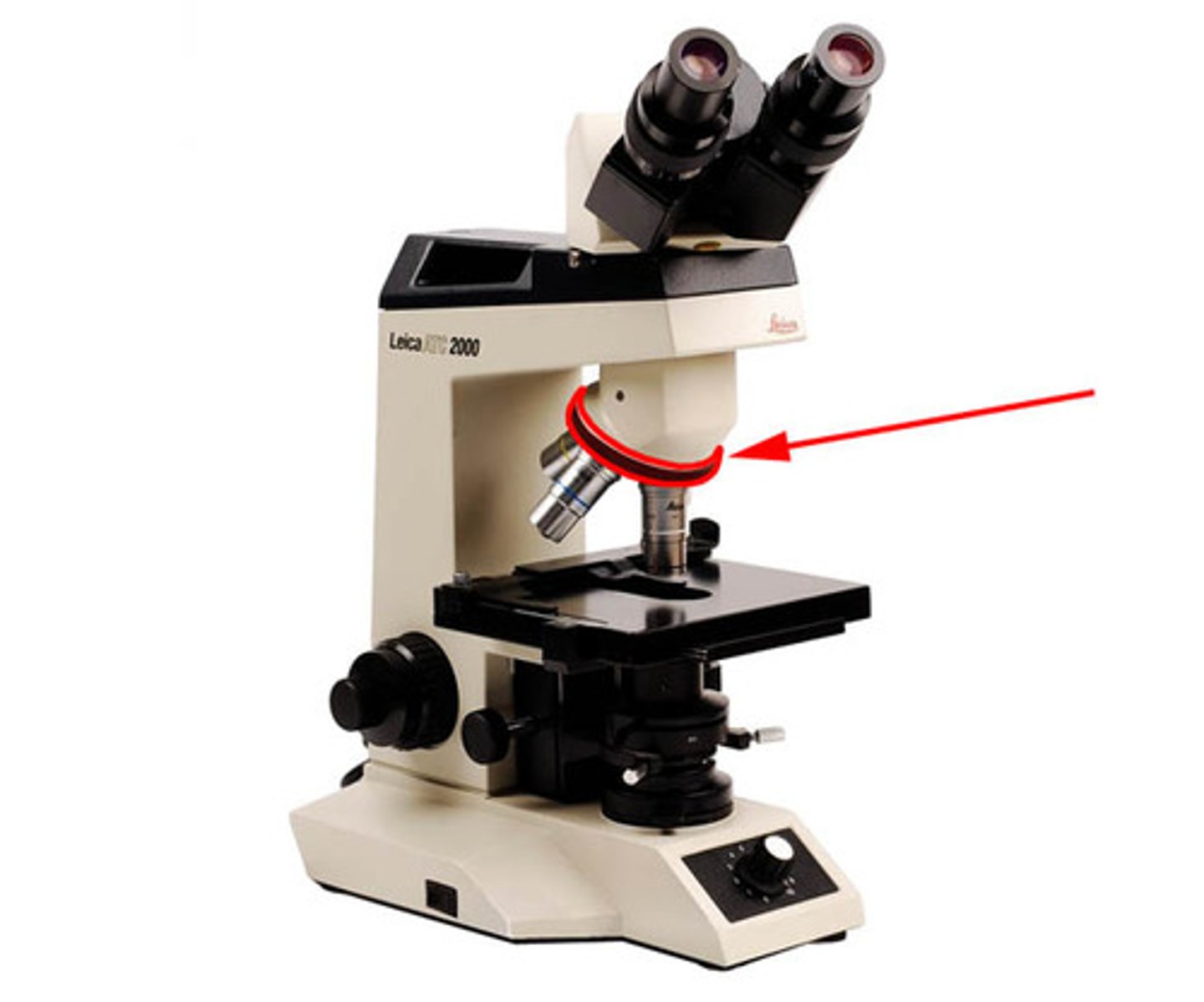
revolving nosepiece of a microscope
(holds the objective lenses)
(can choose an objective lens by rotating)
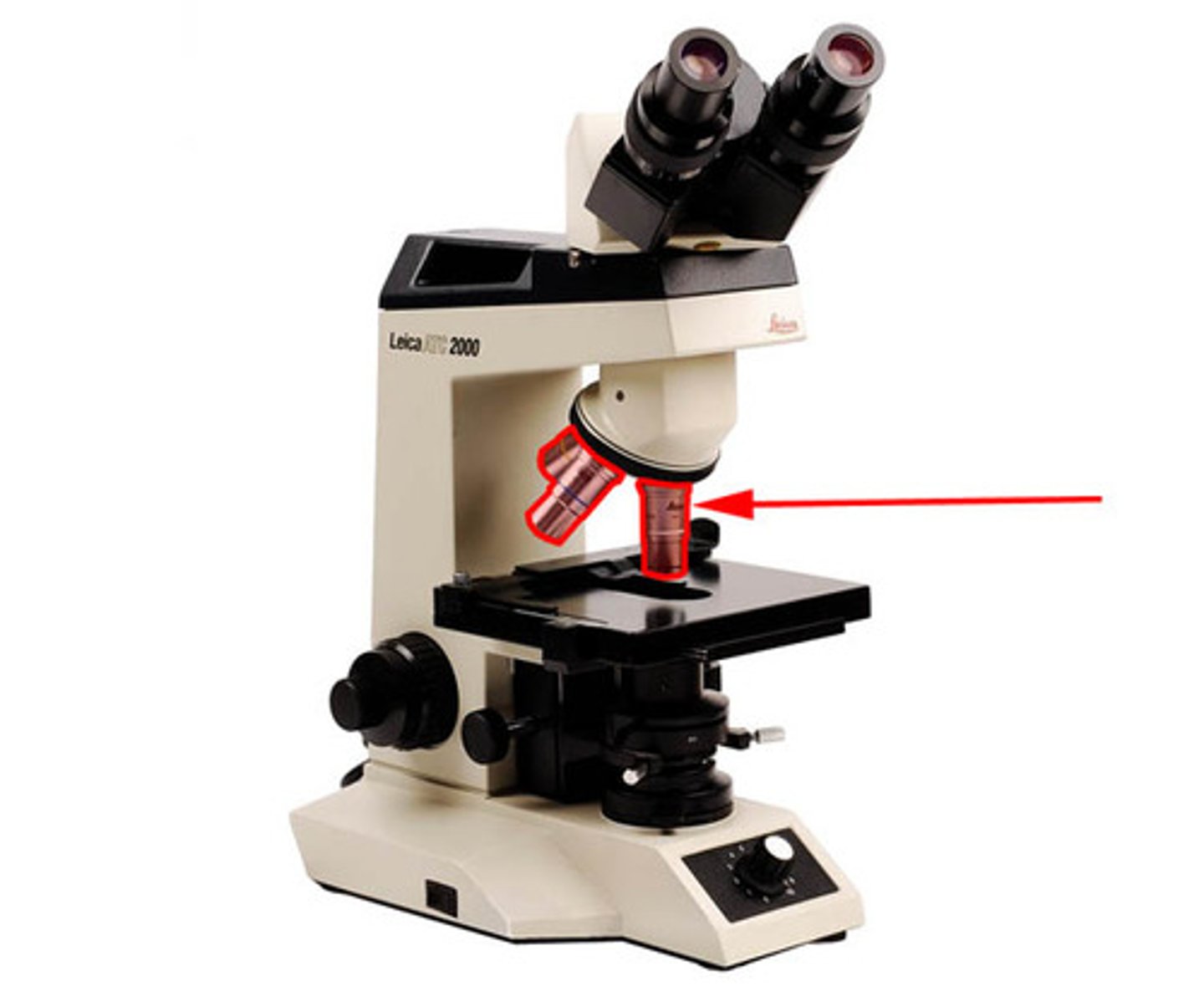
objective lenses of a microscope
(3-4 objective lenses attached to a nosepiece)
(magnification)
purpose of 4x objective
for scanning
purpose of 10x objective
low power, for scanning
purpose of 40x objective
high power, for dry or wet preps
purpose of 100x objective
immersion oil, for fixed and stained preps
how to calculate total magnification
ocular lens x objective lens
(ocular is usually 10x)
parfocal lenses
a set of objective lenses with corresponding focal points all in the same plane
(specimen remains in focus when switching between objective lenses - should only need to slightly adjust fine focus)
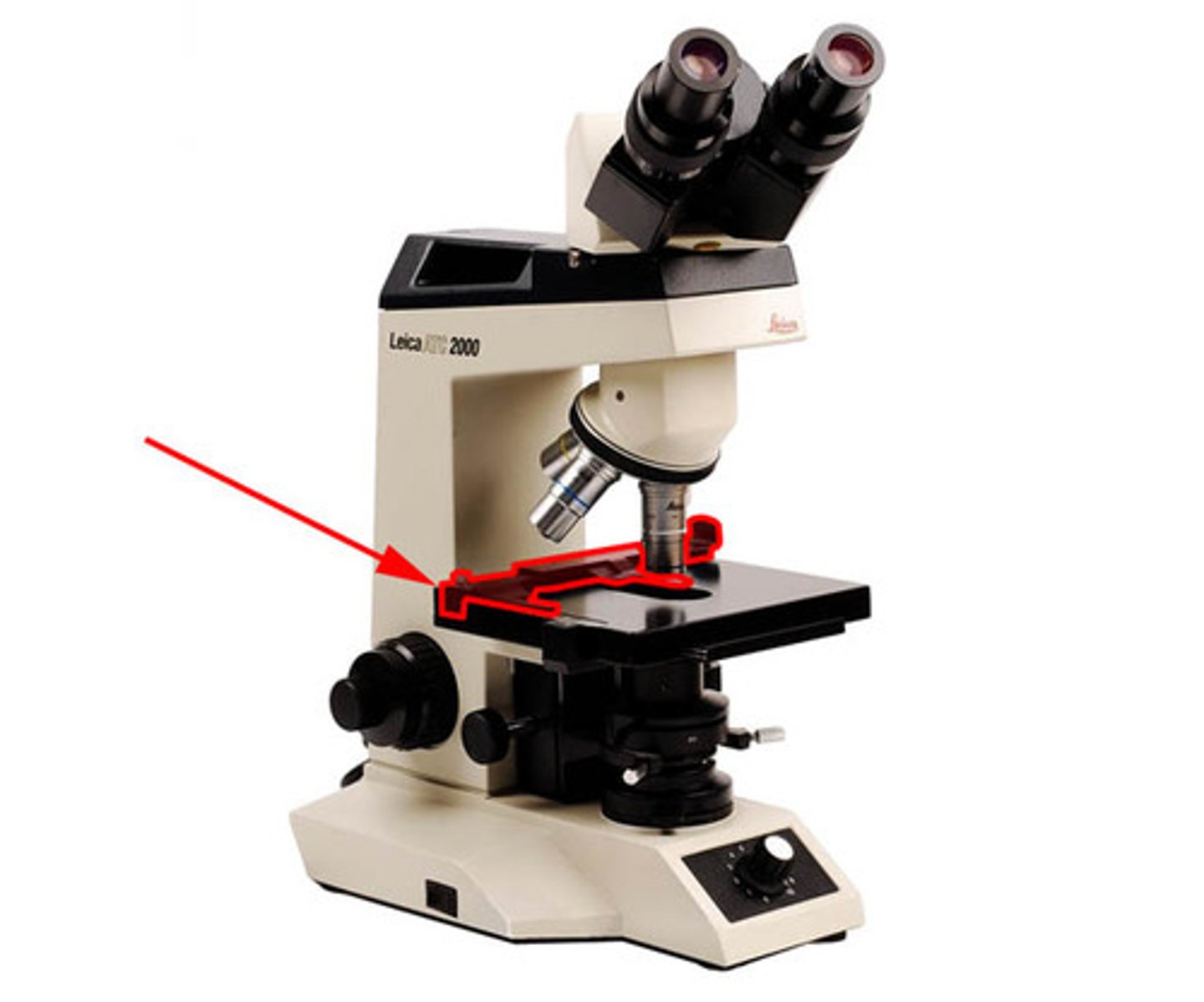
stage of a microscope
(holds the prepared microscope slide to be viewed)
(slide is held in place by a spring mechanism)
condenser of a microscope
(lens located below the stage)
(gathers and directs light from the light source through the specimen)
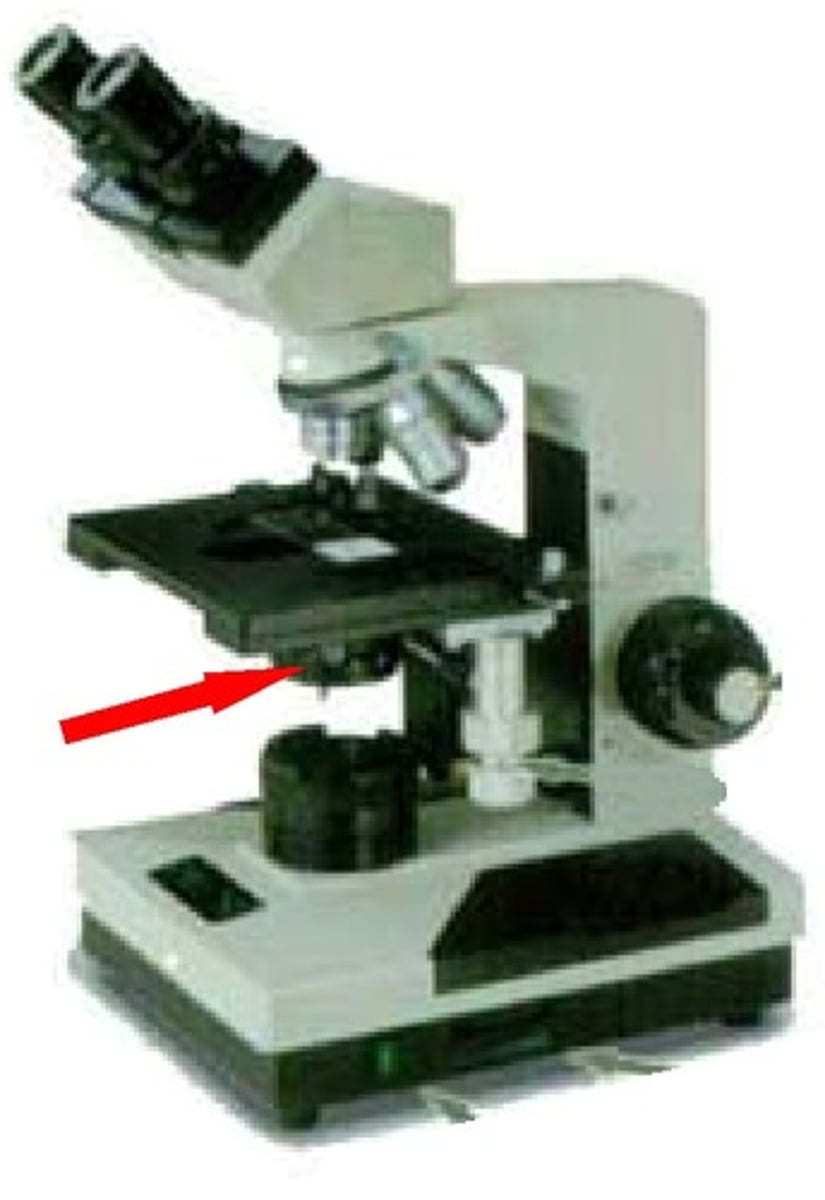
aperture diaphragm of a microscope
(adjustable iris controlling angle and amount of light sent though specimen)
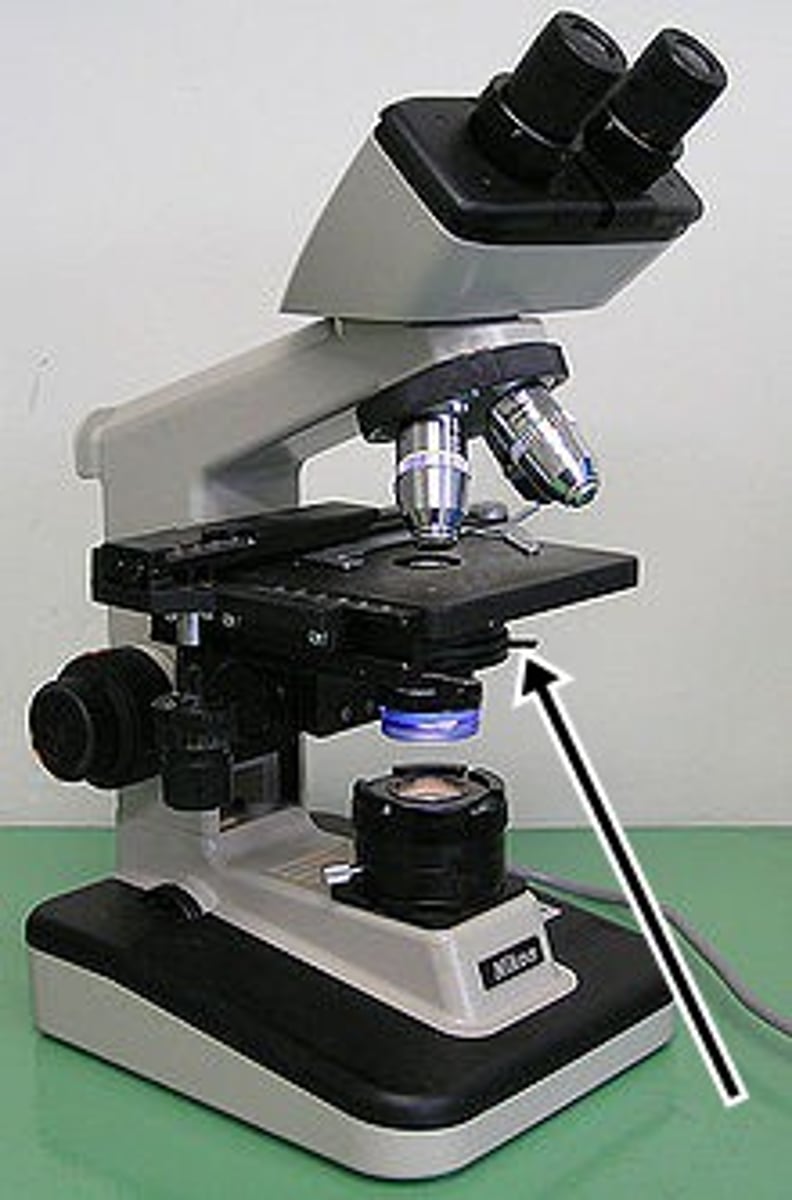

condenser position for wet preps
lower the condenser
use with 4x, 10x and 40x objectives
condenser position for fixed and stained preps
raise the condenser
use with 100x oil immersion objective
stage controls of a microscope
(control knobs which move the specimen/slide on the stage vertically and horizontally)
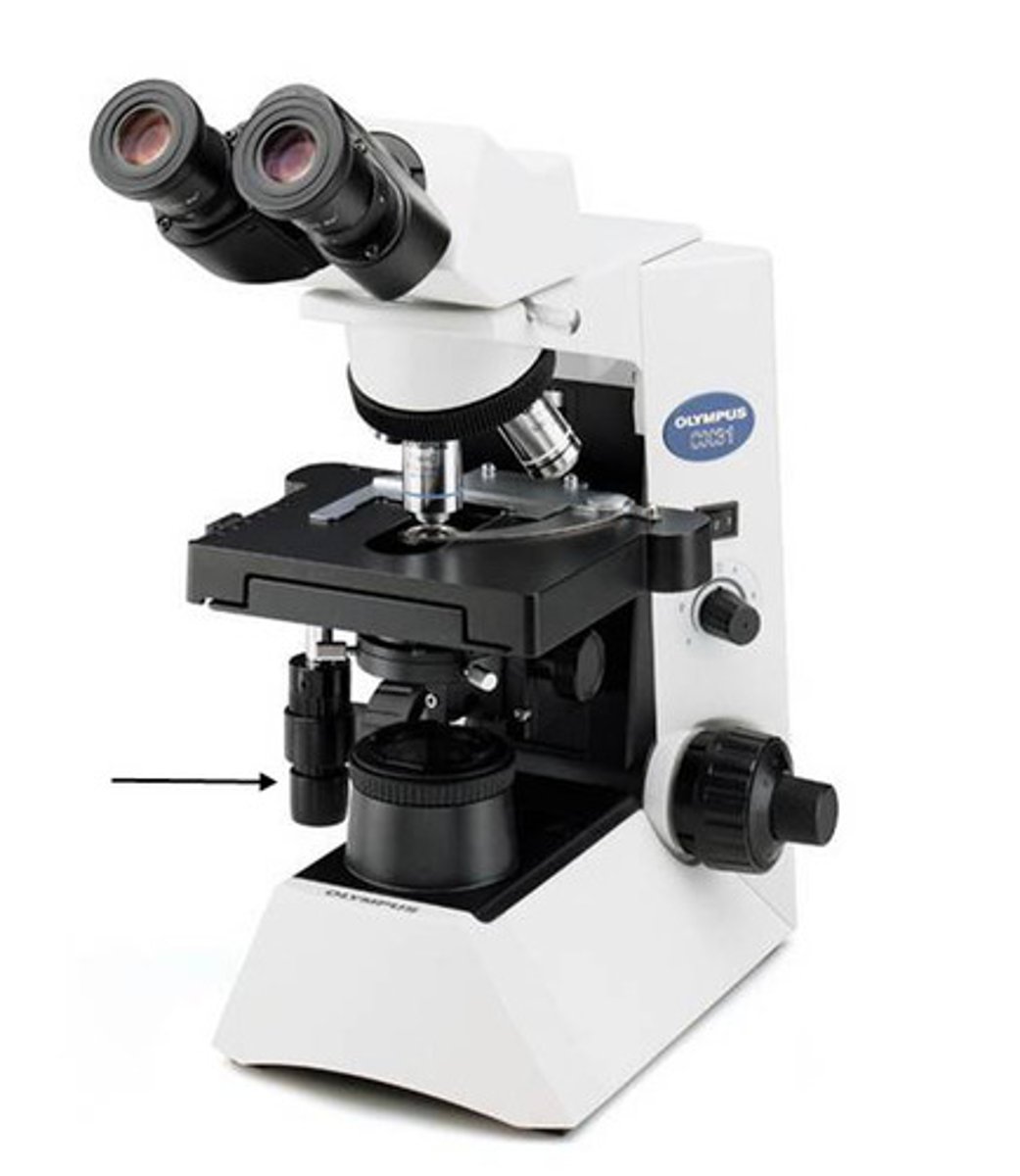

focus controls of a microscope
(control knobs on either side of the microscope which move the stage up and down)
(use coarse adjustment with 4x and 10x)
(use fine adjustment with 40x and 100x)
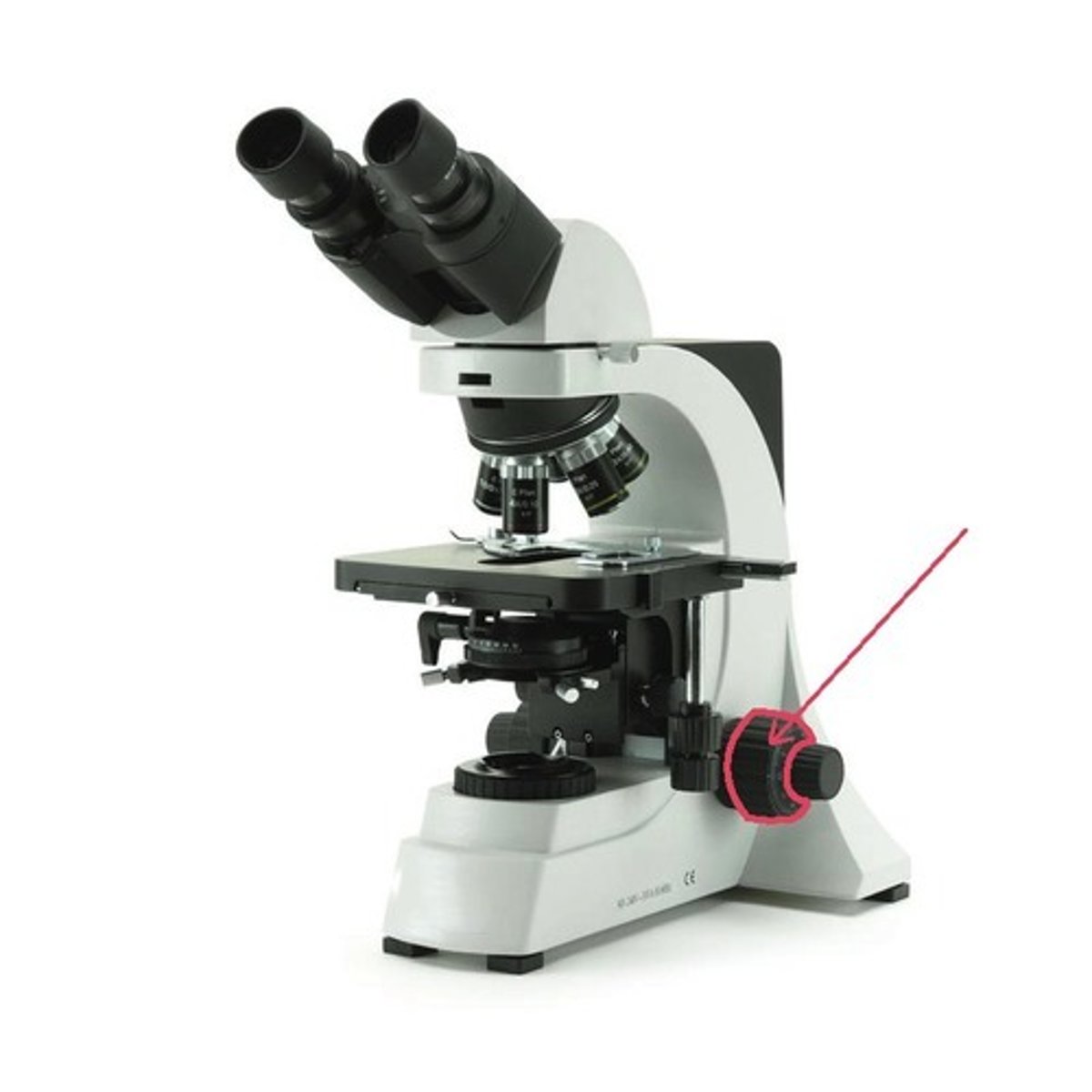

light source of a microscope
(brightfield microscopy uses tungsten-halogen bulbs)
(brightfield microscopy is what is used with the compound scopes at LCCC)
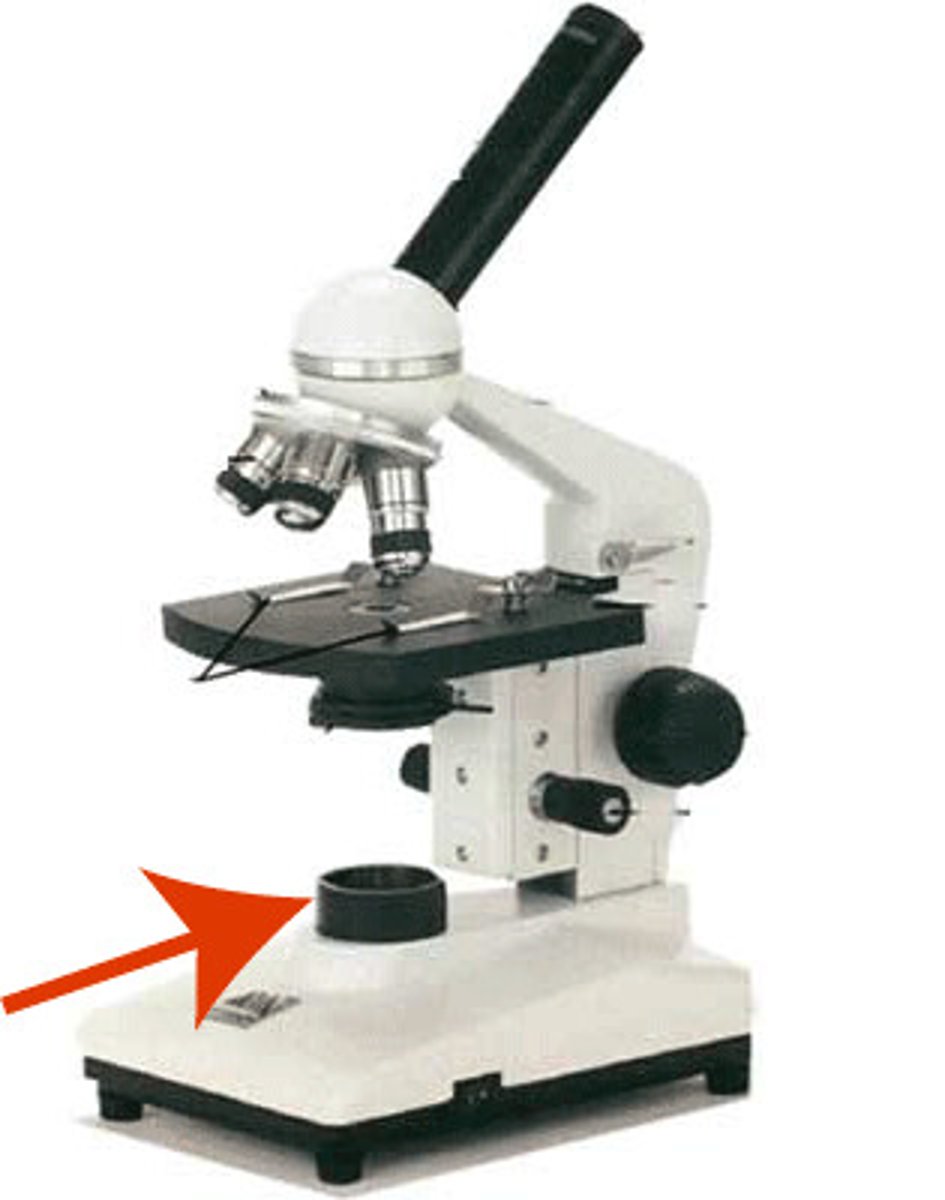

other types of microscopy (5)
1. phase contrast
2. polarized
3. fluorescence
4. dark field
5. electron
microscope use (5)
1. focus image with 4x or 10x using coarse adjustment knob
2. rotate to higher objective - do not drag lenses through oil
3. focus image with 40x or 100x using fine adjustment knob
4. 100x is used with immersion oil, high intensity light and condenser raised
(for wet preps, condenser is lowered)
5. adjust oculars