Multicultural Psychology Final Chapter 8-14
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Masuda and Nisbett (2001)
Differences in attention between american and japanese. 1st task Had to identify as many objects as possible. American focused on focal points while japanese focused on background.
2nd task- recognize objects with same, different, or no background. Japanese recognition went down with no/ different background.
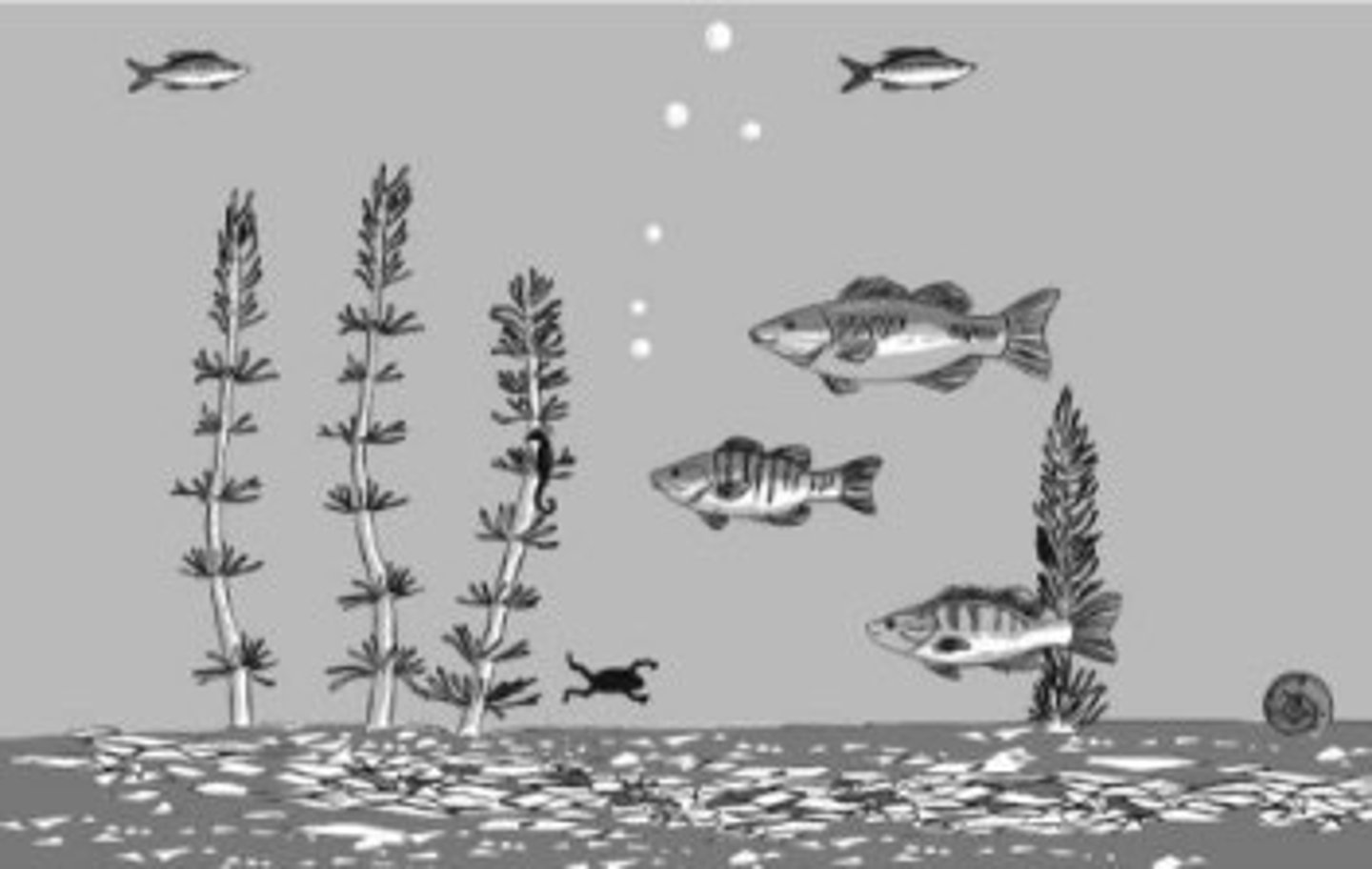

Masuda et al. (2008)
Faces version of fish study. Japanese looked at background faces more
Miyamoto et al 2006
Primed with japanese scenery. Japanese environments have more elements, so they attend to background more. After Americans were primed with jap background, they also recalled more background.
holistic perception
Context dependent, focus on relationships, collectivistic
Analytic perception
context independent, focuses on a salient object independently from the context, individualistic
Muller-Lyer Illusion
Carpentered world theory. Urbanized places used to seeing rectangles. industrialized communities "fooled" by ML illusion
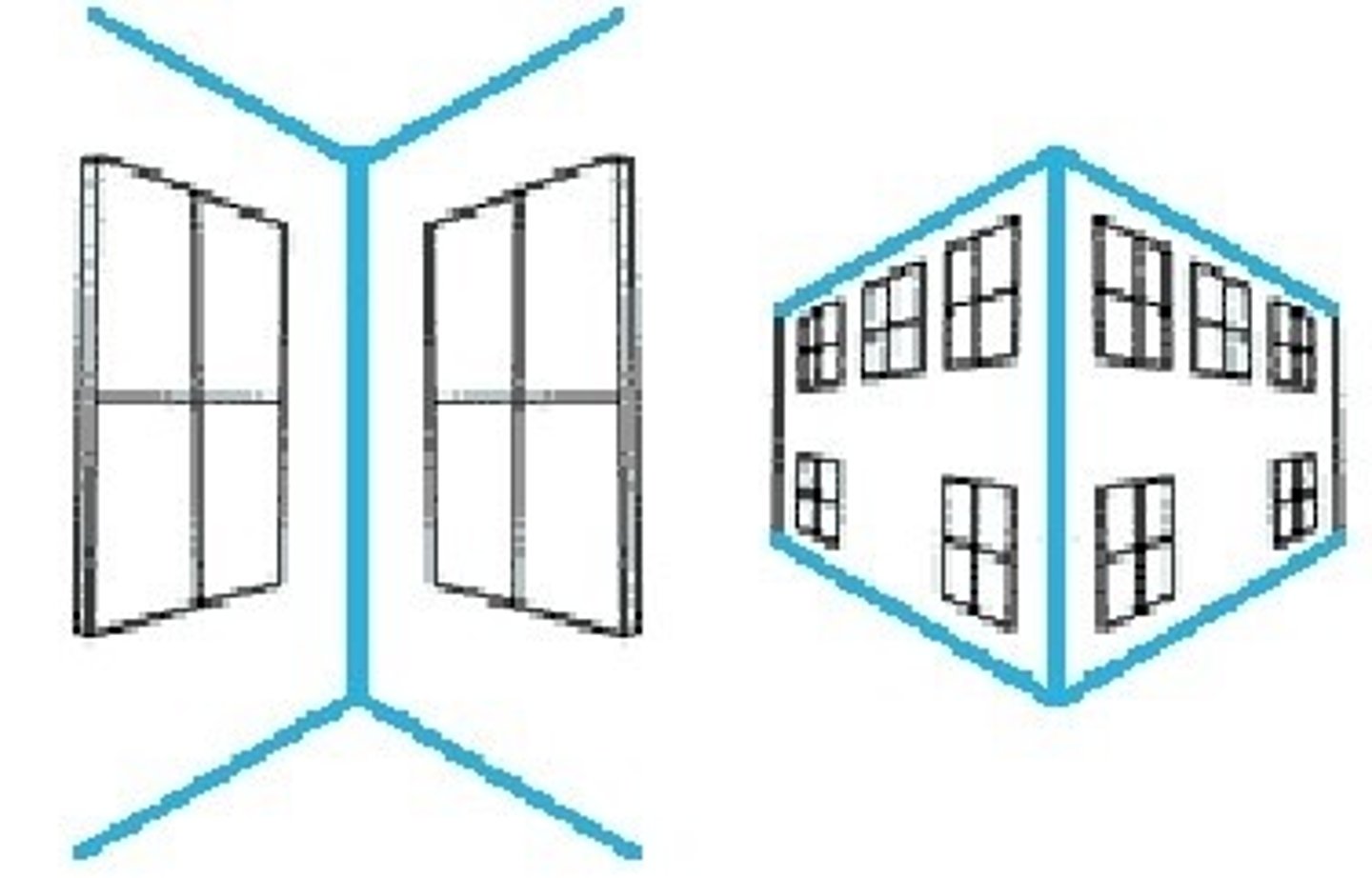
horizontal-vertical illusion
The front-horizontal foreshortening theory
- People interpret vertical lines as horizontal lines extending into the distance
- More common among those living in rural/ non- industrialized area
Non industrialized "fooled" by horizontal vertical
Segall et al 1963, 1966
Industrialized groups more fooled by muller lyer
Non industrialized groups fooled by vertical horizontal
Hudson (1960)
A study in which compared the ability of a range of African tribe members to differentiate between 2D and 3D perception. Found that education and cultural assumptions influences the perception of images.
Categorization
Grouping based on perceived similarities
universal tendency of categorization
Emotions, primary colors, shapes, stereotypes
gender stratification hypothesis
the idea that gender differences are related to cultural variations in opportunity structures for girls and women.
Else-Quest et al. (2010)
- 69 nations
-Results: greater gender gaps in math best predicted by
- ↓ Gender equality in school enrollment ◦ ↓ Women's share of research jobs
- ↓ Women's parliamentary representation
dialectical thinking
The tendency to accept what seem to be contradictions in thought or beliefs. Common in Asia. good and evil, masculinity and femininity, yin and yang. Example: i feel too tired to work, and i can still do my work anyways
positive logical determinism
A tendency to see contradictions as mutually exclusive categories, as either-or, yes-no, one-or-the-other types of categories. Example: mother and daughter conflict. Mother raised the daughters in a specific way but they are now rejecting mothers values. one of the parties, either the mother or daughter are in the wrong. It would prescribe that perhaps the mother is being stubborn, or the daughter to wilful. Western thought
Peng and Nisbett (1999)
American responses more non-dialectical
- ex "mothers have to recognize daughters' rights to their own values
Chinese responses more dialectical
- ex"Both the mothers and the daughters have failed to understand
each other"

Naive Dialecticism
Ying Yang. Have to accept contradictions and change, world is made of opposites.
Doctrine of the mean- the truth is in the middle. Goldilocks
Bruner et al Western cultures vs Africa sorting
Africa: both children and adults sort by color.
Western: children sort by color. Adults sort by shape then function.
Chiu 1972 sorting American vs Chinese children
Cow, Chicken, Grass
American: cow and chicken go together bc shared features
Chinese: cow and grass go together bc of relationship
Memory: universal tendencies
- memory processes (encoding, storage, retrieval, etc.)
- memory decline with age
- hindsight bias
Effects of oral traditions on memory
Ghanaian students better at remembering verbal stories.
Math
Universal number line left - right, big - small
Many languages use base 10, English does 1-19 unique and additive starting at 20. Makes it more confusing
Time orientation: long term vs short term cultures (hofstede)
Long term: focus on past and future. Japan, china, India
Short term: focus on present. United States, New Zealand, Canada
Levine and Norenzayan 1999 time orientation
3 things reflective of pace of life:
- how fast people walk
- transaction at a post office
- accuracy of clocks
Results
Fastest- Switzerland, Ireland, Germany, Japan, Italy
Slowest- Mexico, Indonesia, Brazil, El Salvador
Colder cities faster
Bright economies faster
Individualistic faster
Basic emotions
Innate, evolutionary adaptive.
Anger, joy
Universal
Self conscious emotions
Embarrassment, pride
Ekman 1969 facial expressions
Tribes of New Guinea
Showed facial expressions universally recognized
Universality in spontaneous expression of emotion
Sighted Olympic athletes vs congenitally blind Paralympic athletes
spontaneous facial expressions of emotion is not dependent on observational learning but simultaneously demonstrates a learned component to the social management of expressions, even among blind individuals.
Universality in emotion response system coherence
Various response components (e.g., face, voice, physiology) are
related to each other in a meaningful way
Universal correlations in
-verbal & nonverbal expressions
- emotion intensity and physiological sensations
Universality in emotion antecedents
Emotional antecedents- events or situations that elicit an emotion
Results: no culture-specific category of antecedents needed
o Happiness: relationships with friends, achievements
o Anger: relationships, injustice
o Sadness: relationships, death
Front end calibration vs back end calibration
Front end: culture regulates what people become emotional about in the first place
Back end: culture regulates how people express emotion (cultural display rules)
Cultural display rules
Deamplifications, amplification, neutralization, qualification, masking, simulation
Collectivist show deamplification of emotion when older person around
Individualist show more encouragement for emotional expression
Models of emotion: internal vs relational
Internal: rage room. Inside out. Individualistic
Relational: lack of stress when deamplifying emotions. Collectivistic
Hypercognized vs. hypocognized emotions
Hypergognized: thought about a lot example: love in the US and shame in china
Hypocognized: little attention/ knowledge about an emotion, no words to describe it. Example: Tahitians have no words for grief, instead they say their sick
Socially engaging vs socially disengaging emotions
Socially engaging- collectivistic, social interdependence. Happy, sad, respect, sympathy, guilt
Socially disengaging- independence, autonomy, individualistic, pride, anger
Emotional dialecticism
Co occurrence of pleasant and unpleasant emotions
lexicon
Vocabulary
Phonology
study of speech sounds
Semantics
Meaning of words and sentences
Morphology
Formation of words over time p
Pragmatics
the appropriate use of language in different contexts
Reciprocity between culture and language
Learning culture helps language acquisition
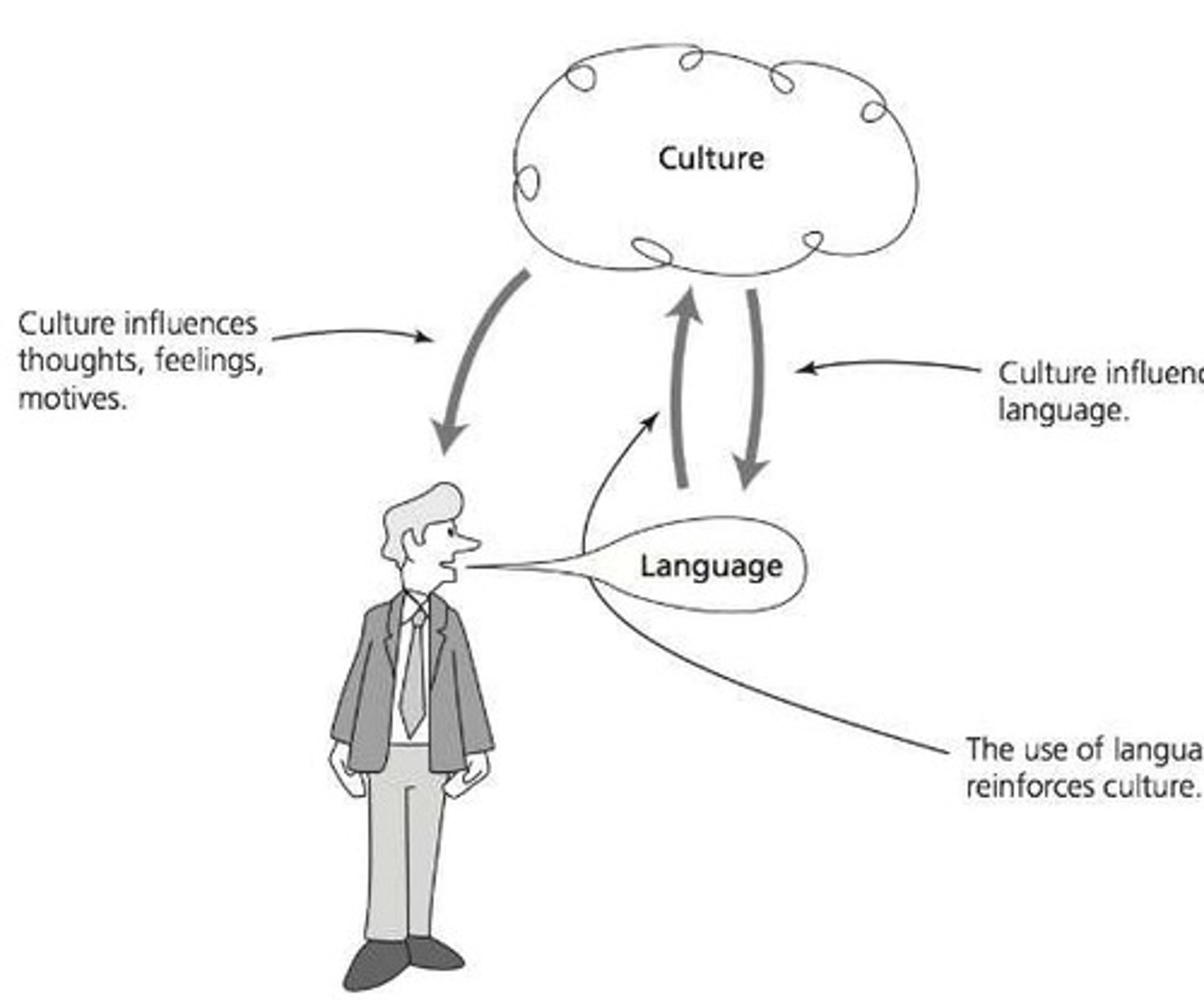
culture and pragmatics
Low context cultures- interpret messages independent from context. Individualist
High context cultures- interpret messages considering context. Collectivist
Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis
Linguistic relativity.
The idea that different languages create different ways of thinking.
*hypothesis not true-Lexical differences do not influence cognition, babies with no language think. The same
Different forms of nonverbal behaviors
Speech illustrators: gestures
Emblems: peace sign, ok sign
Gaze: in us eye contact is respectful, but not for Asia
Paralinguistic cues: tone, intonation, pitch
Proxemics: how close you are to someone
Haptics: touch. High moderate and low contact cultures
code frame switching
the process by which bilinguals switch between one cultural meaning system and another when switching languages
Hong et al code frame switching
When Primed with American images: internal attributions
o The big fish leading the others
When Primed with Chinese images: external attributions
o The big fish being chased by the others
Biomedical model of health
Focuses on the physical or biological aspects of disease and illness. It is a medical model of care practised by doctors and health professionals and is associated with the diagnosis, cure and treatment of disease.
biopsychosocial model of health
The integration of biological, psychological, and social factors in dealing with health related behaviors
Holistic approach to health
Emphasizes the integration and balance of mind, body, and spirit. Considers needs of the person as a whole. Goal of homeostasis. Ying yang
complementary and alternative medicine (CAM)
Acupuncture, homeopathy. No scientific backing, but usually works
pluralistic culture
A modern society composed of groups who see the world from different perspectives, value different activities, hold disparate religious beliefs, and aspire to different goals
Three indicators of health worldwide
-life expectancy
-infant mortality
-subjective well-being
cultural neuroscience
studies the ways that cultural variables affect the brain, the mind, genes, and behavior.
Neuroscience+ cultural psychology+ population genetics
People living in countries with a high prevalence of pathogens are more likely to be more collectivistic.
Example: 5-HTTLPR short allele= increased risk of depression in face of stressful events
Link between prevalence of 5- HTTLPR short allele and collectivism "culture- gene coevolution"
Health practices and prevalence of pathogens/ genes across cultures
People living in collectivistic places likely to have high number of pathogens, also likely to wear masks for the safety of others.
Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions
power distance, individualism, masculinity, uncertainty avoidance, long-term orientation
Social isolation/ support health
Fewer social ties= higher mortality rate, unemployment, stress, pessimistic attribution styles
Perceived support may be more important than actual support
International body project
26 countries from 10 world regions, Participants all females, Ask participants to pick the picture that resembles their body shape and the picture that shows the ideal body shape
Results:
America- highest levels of dissatisfaction
Asia- lowest
Acculturation and the immigrant paradox
Immigrants have better mental and physical health among immigrants compared to non immigrants despite challenges
Further acculturation= worse health outcomes
What explains it?
Healthy behaviors
Social support
Immigrant selectivity
Abnormality: traditional view vs cultural realism
Traditional view- there's cultural similarities even universality on psychological mechanisms
Cultural relativism- psych disorders can only be understood in cultures where they occur
diathesis-stress model
suggests that a person may be predisposed for a psychological disorder that remains unexpressed until triggered by stress
Reliability
Getting the same diagnosis each time
Validity
Diagnosis accurately portrays clinical symptoms
Etic
Focus on similarities and universality. Outsider perspective (reliability and validity easy to achieve)
cultural concepts of distress (CCD)
Syndromes- patterns of symptoms that cluster together for individuals in specific groups
Idioms- how groups communicate their distressing thoughts and emotions
Explainations- causes of the distress
Emic
Focusing on differences. Insider perspective
Cultural Formulation Interview (CFI)
a set of questions that assess the impact of culture on key aspects of the client's health, help diagnose properly
Underpathologizing
indiscriminately seeing behavior as cultural when in fact, behavior may reflect abnormal psychological response. Saying they're fine when they may not be
Overpathologizing
misinterpreting culturally sanctioned behavior as expressions of abnormal symptoms
Schizophrenia
Positive symptoms- delusions and hallucinations
Negative symptoms- lack of speech, social withdrawal, no motivation
International pilot study of schizophrenia
Similarities between cultures: hallucinations and delusions
Differences: developing countries have faster recovery rates, hallucinations more accepted in Nigeria
Depression
Physical, emotional, motivational changes, women more vulnerable, vegetative symptoms, must deviate from the cultural norm
Culture specific symptoms of depression
Chinese:
Embodied emotional experience more than physical
Impaired social relations
Insomnia is a cause not a symptom
ADHD
Must have inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity.
2 veins on etiology (causes):
"ADHD is biologically based" - both chinese and us agree
"ADHD kids are just bored and need more to do"- chinese agree 71%
evolutionary attractiveness
Must signal reproductive success
Low waist to hip ratio
Average face= attractive
Desireable personality traits- sensitive, kind, sociable, pleasant, likable, interesting, competent, intelligent, sexual interest
Attribution
explaining one's own behavior and the behavior of others
internal (dispositional) attribution
attributing one's behavior to his or her personality; for example, attributing a child's hostility to their aggressive personality
external (situational) attribution
inference that a person's behavior is caused by something about the situation
fundamental attribution error
Attribution error made about someone else's behavior
- good behavior= external attribution
- bad behavior= internal attribution
fundamental attribution error- cultural differences
Miller 1984
Americans: internal/ dispositional attributions "that's just the type of person she is"
Hindu: external/ situational attributions " he is unemployed so he's having a hard time"
Peng 1994
American: internal/ dispositional - he's psychologically disturbed
Chinese: external/ situational - he was isolated
social identity theory
the idea that ingroups consist of individuals who perceive themselves to be members of the same social category and experience pride through their group membership.
Cultural differences in in group/ out group relationships
Individualistic
- more in groups
- weaker attachment
- individual success> sacrificing for ingroup
- less distinction between groups, more inclusive
collectivistic
- fewer ingroups
- stronger attachment
- group success important, more willing to sacrifice for group
- more distinction and discrimination against groups
contact hypothesis
The idea that stereotypes and prejudice toward a group will diminish as contact with the group increases.
To work it needs:
Equal status
Common goals
Cooperation