Introduction to Pathology and Pathophysiology – Key Vocabulary
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
25 vocabulary flashcards summarizing the essential terms and examples introduced in the Pathology and Pathophysiology lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms

Objectives
.
Pathophysiology
The study of the disruption of normal bodily function (homeostasis) caused by disease; the physiology of abnormal function.
Pathology
The study of structural or morphological abnormalities expressed as diseases of cells, tissues, organs, and systems.
Disease
An impairment of cellular, tissue, organ, or system functions that challenges body homeostasis; synonymous with illness.
Homeostasis
A dynamic steady state maintained by appropriate regulatory responses—essentially, the condition of good health.
Etiology
The cause of a disease or disorder (e.g., genetic, acquired, infectious).
Idiopathic Disease
A disease whose cause is unknown or unidentifiable.
Iatrogenic
A condition that results from medical or surgical treatment.
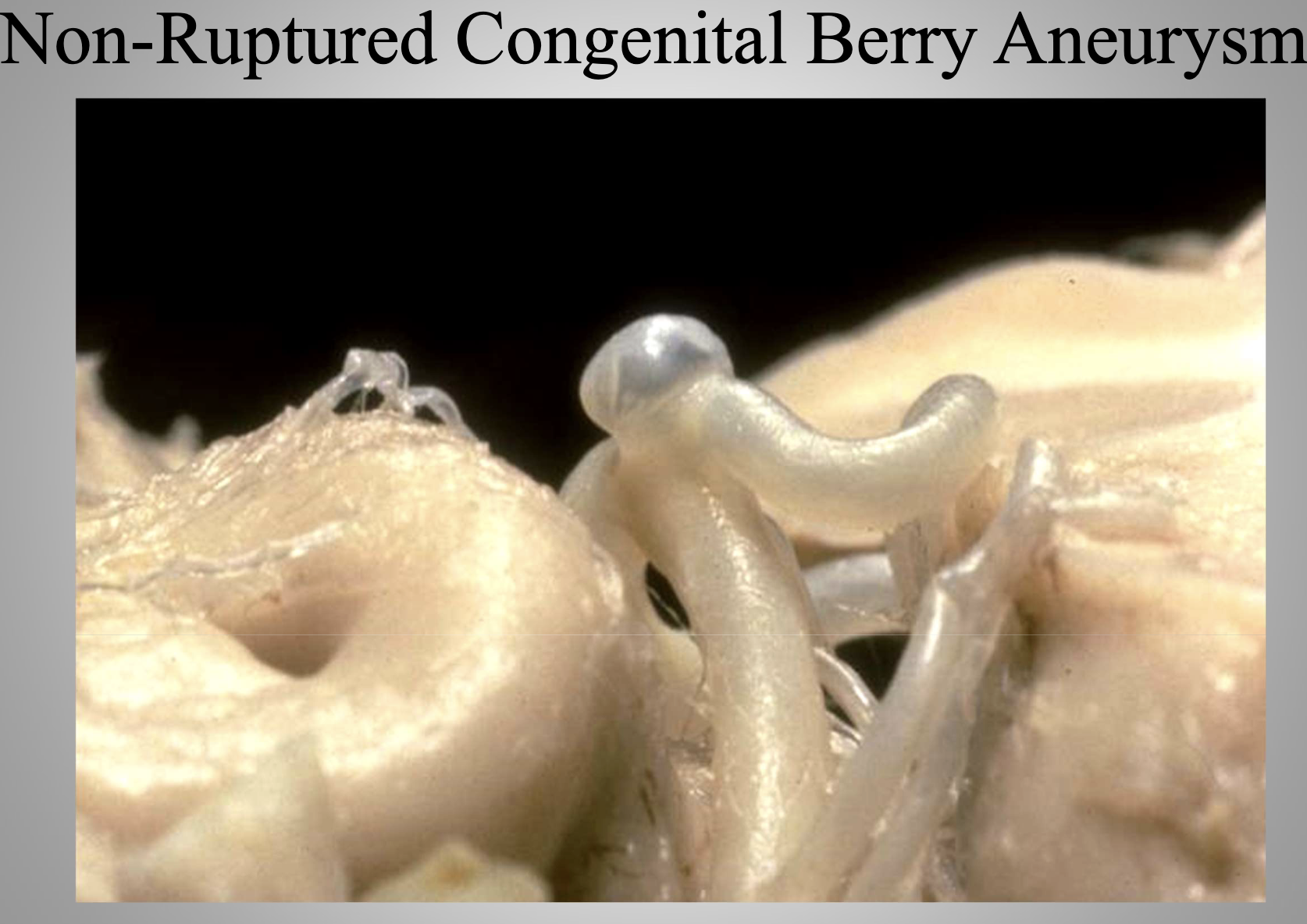
Congenital
A disorder present at birth, arising during fetal development (e.g., congenital berry aneurysm).
Nosocomial
An infection or disorder acquired while in a hospital setting.
Genetic Disease
A disease inherited through gene abnormalities.
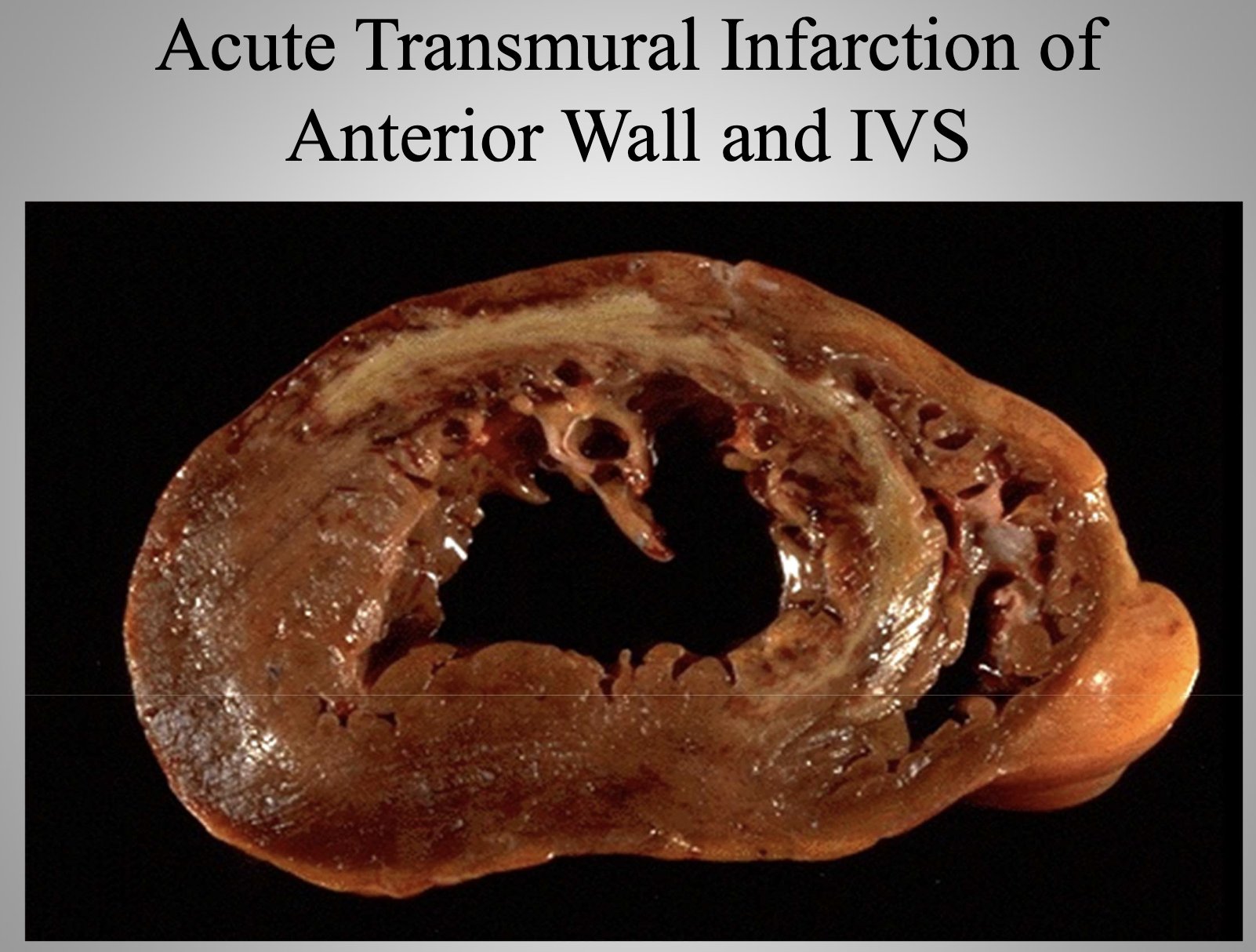
Acute Disease
A severe disorder with rapid onset and usually short duration; often self-limiting (e.g., acute myocardial infarct).
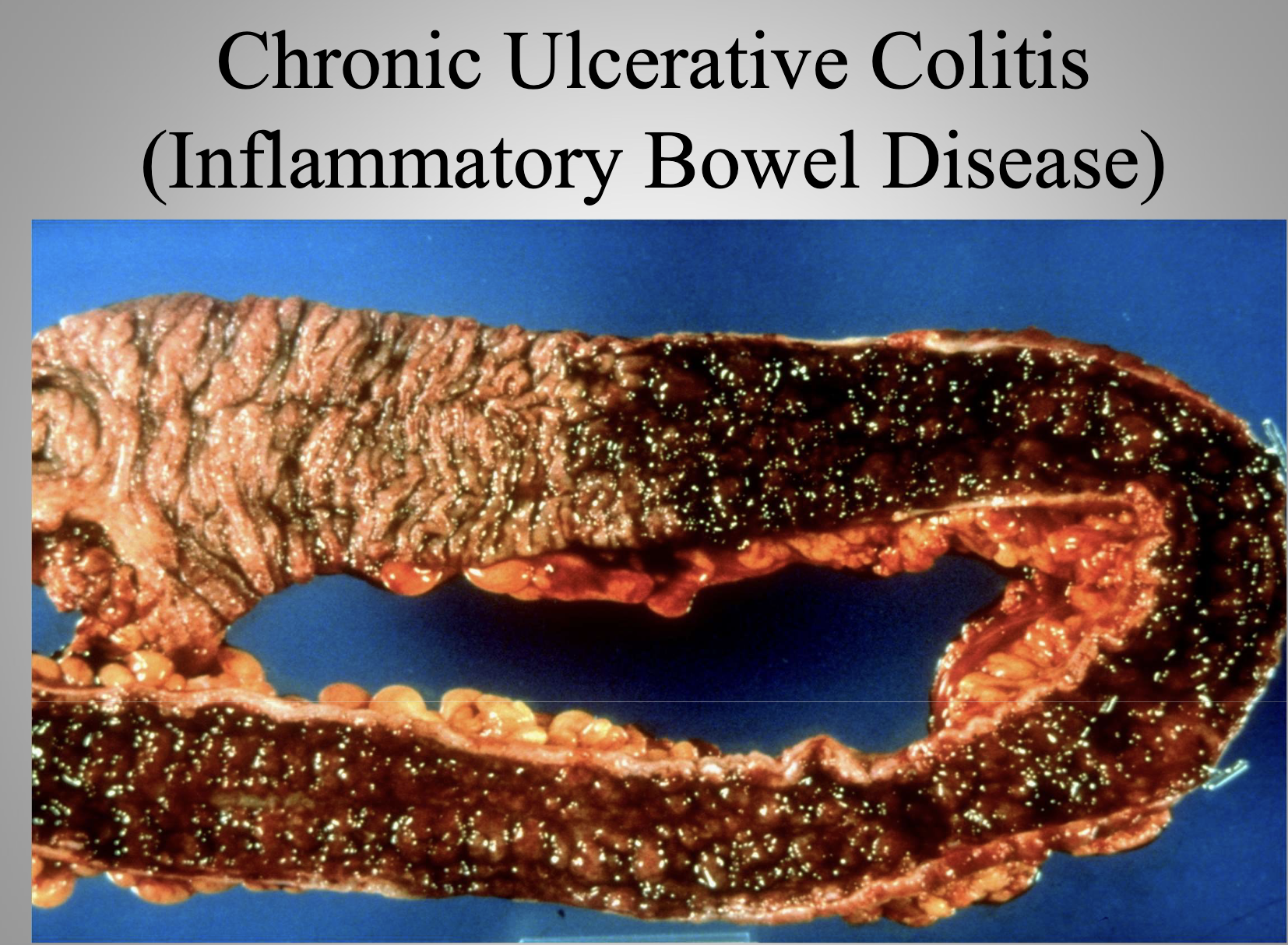
Chronic Disease
A long-term, continuous disease with exacerbations and remissions, usually not curable (e.g., chronic ulcerative colitis).
Subacute Disease
A disorder whose duration and severity fall between acute and chronic.
Subclinical Disease
A disease without observable signs or symptoms that typically does not progress, but they have the disease
Carrier State
The condition in which an individual harbors a pathogen without symptoms but can transmit it (e.g., “Typhoid Mary”).
Disease
impairment of cells, etc. Results of altered functions of the body
Syndrome
A group of clinical symptoms and physical features that collectively characterize a particular disorder.
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
A chromosomal disorder with intellectual disability, characteristic facial features, simian crease, cardiac defects, and other anomalies. The most common
Cushing Syndrome
A condition of excess cortisol/ACTH causing central obesity, ‘buffalo hump,’ thin limbs, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and skin changes.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
A constellation of defects from prenatal alcohol exposure: ethanol in pregnancy facial anomalies (smooth philtrum, thin upper lip), growth retardation, and neurodevelopmental issues.
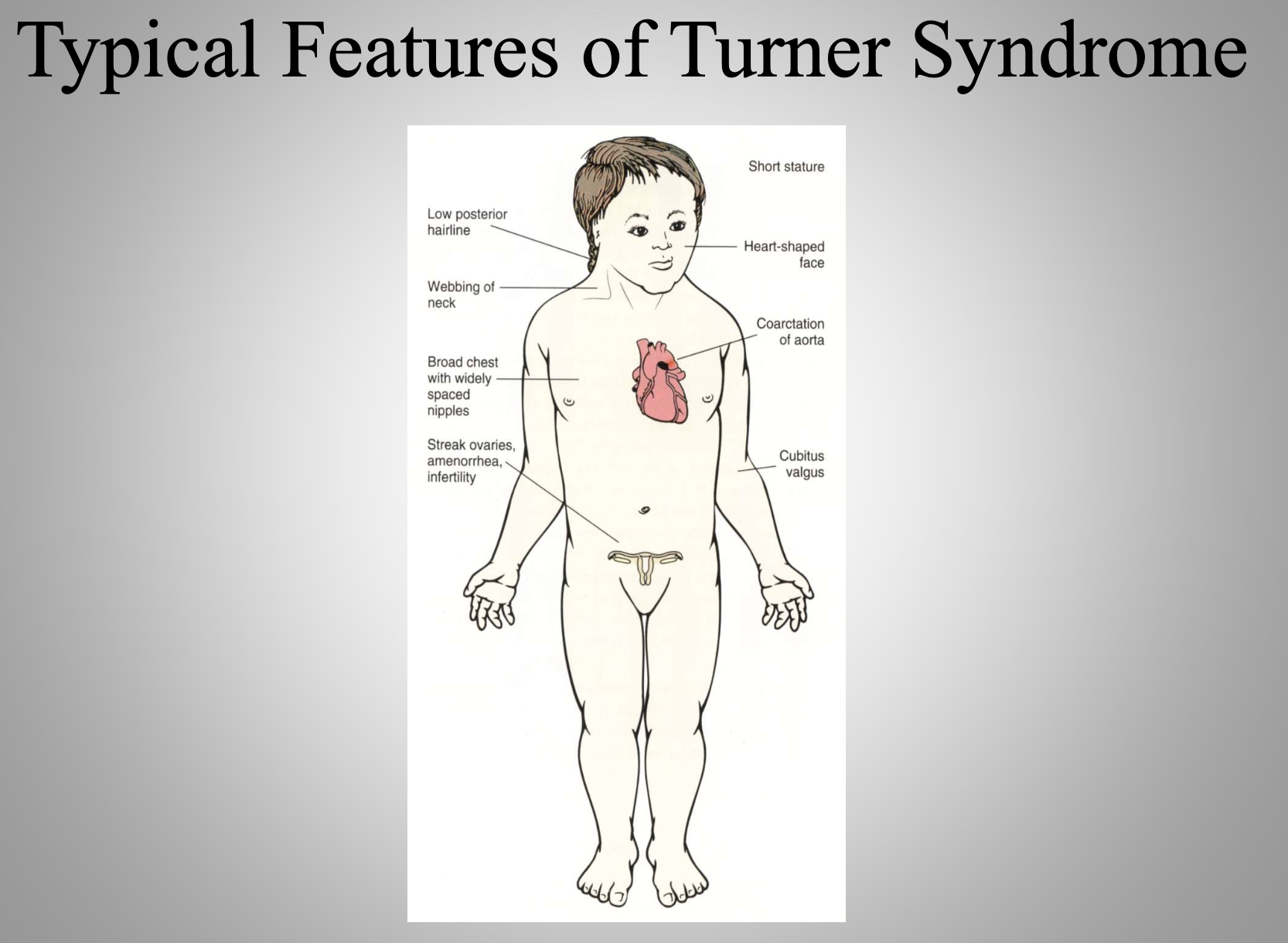
Turner Syndrome (XO)
Monosomy X leading to short stature, webbed neck, broad chest, streak ovaries, amenorrhea, and possible aortic coarctation. XO karyotype
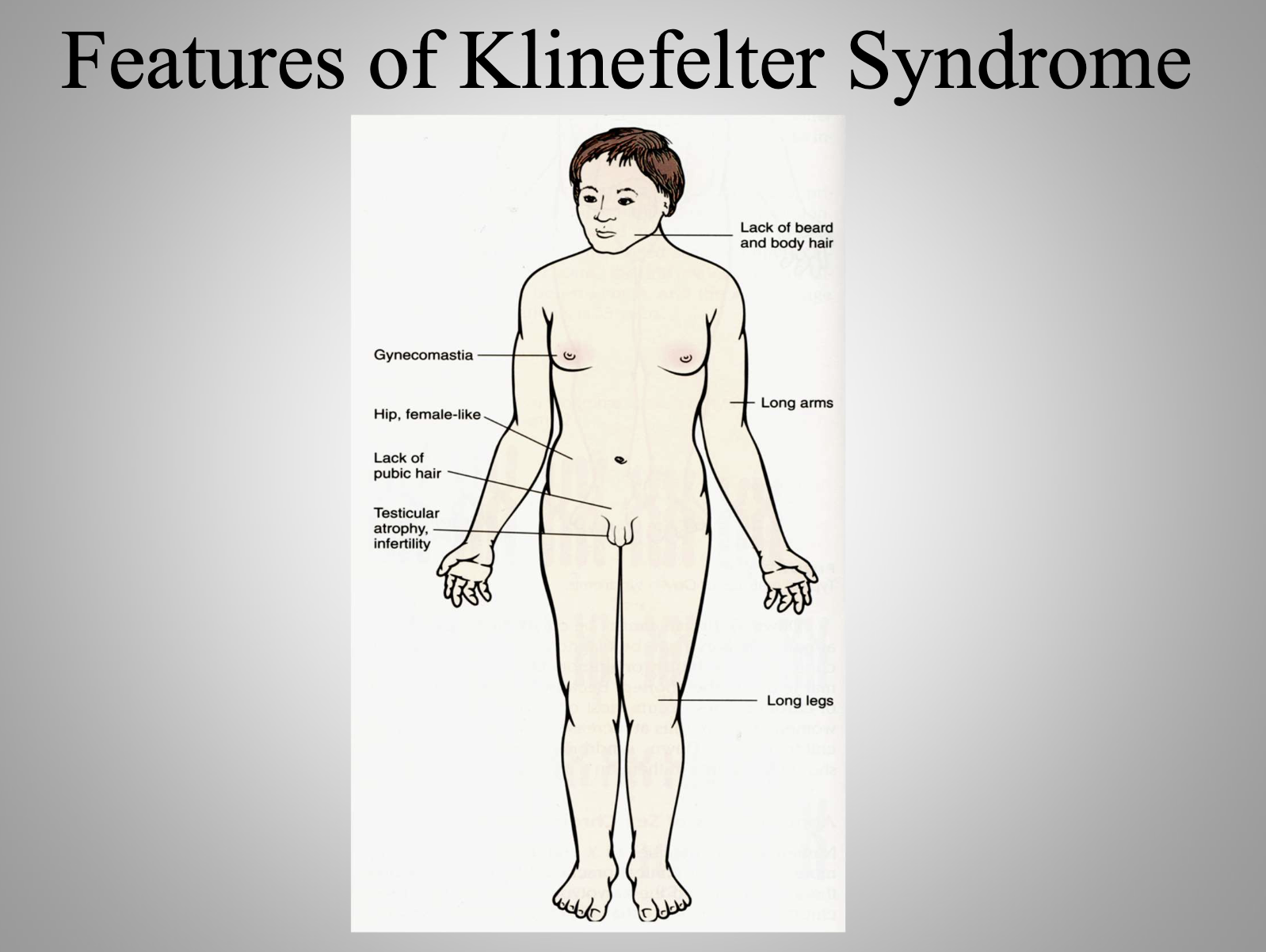
Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY)
A karyotype disorder causing tall stature, long limbs, gynecomastia, testicular atrophy, infertility, and sparse body hair. XXY karyotype
Toxic Shock Syndrome
An acute, toxin-mediated illness (often Staphylococcus aureus) featuring high fever, rash, hypotension, and multi-organ dysfunction.
Congenital Berry Aneurysm
A saccular aneurysm of cerebral arteries present from birth; risk of rupture leads to subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Acute Myocardial Infarct
Sudden necrosis of heart muscle due to coronary artery occlusion (e.g., thrombosis in the left anterior descending artery).
Ulcerative Colitis
A chronic inflammatory bowel disease with continuous colonic mucosal inflammation, marked by remissions and exacerbations.