Sensation, Perception, and Consciousness
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Do overlapping confidence intervals mean the difference is not statistically significant?
Overlapping confidence isn't conclusion. Confidence intervals give insight—but significance needs a test.
How is the absolute threshold determined in sensory psychology?
Vary the stimulus intensity across trials
Record whether the stimulus is detected
Identify the level of intensity detected ≥50% of the time
Example: A tone is played at different volumes—if a person detects the sound at 50% of trials when it’s at 10 dB, that’s the absolute threshold for hearing at that frequency.
How does Signal Detection Theory explain decision-making under distractions?
Signal Detection Theory (SDT) quantifies how people detect stimuli in the presence of distracting noise
What are the four possible outcomes in Signal Detection Theory?
Hit (Signal present, correctly detected)
or Miss (Signal present, not detected)
False (Signal absent, incorrectly detected)
or Fix (Signal absent, correctly deteremined to be absent)
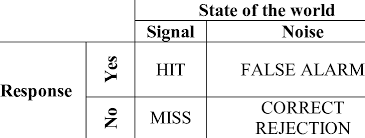
What is the absolute threshold in psychology?
The absolute threshold is the lowest level of stimulus intensity that a person can detect at least 50% of the time under controlled conditions.
What does "threshold" mean in psychology? (Threshold = Tiny Tune-up in Awareness)
A threshold is the point at which a stimulus becomes strong enough to be noticed or produces a response.
What is top-down processing in psychology? (Mind over matter)
Top-down processing is when your brain guides perception using prior knowledge, experiences, expectations, and context—rather than relying solely on raw sensory input.
Your brain fills in the gaps, even when the senses don’t spell it out clearly.
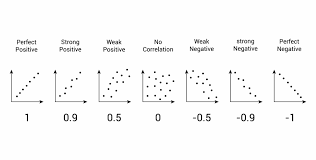
What do correlation coefficients reveal?
Correlation measures the strength and direction of a relationship between two variables—represented by a coefficient rr from −1 to +1
What is Emotional Intelligence? (“Feel smart: sense, stay, strive.”)
Emotionally intelligent people sense emotions, stay grounded, and strive beyond impulse.
What is confirmation bias? (“Confirm what comforts.”)
Confirmation bias is the tendency to favor information that supports one’s existing beliefs while ignoring or dismissing opposing evidence.
What is hindsight bias? (“Past feels predictable—after the fact”)
Hindsight bias is the tendency to believe—after an event has occurred—that one "knew it all along" or could’ve predicted the outcome.
Which category of psychoactive drugs has the lowest risk of dependence?
“Hallucinogens open minds, not cravings.” They’re trippy, but not typically addictive.
What is habituation in psychology?
“Repeat, retreat.” Habituation is a reduced response to a repeated, harmless stimulus over time.
What is craving in psychology and substance use?
“Craving = Call from within.” The body and brain signal a powerful urge to return to a substance.
What is interference in memory psychology?
Interference occurs when existing or new information disrupts the processes of:encoding, consolidation, and retrieval
What are memory schemas in psychology?
Memory schemas are mental frameworks built from past experiences that help us organize, store, and retrieve information efficiently.
What is a Source Monitoring Error in psychology?
A Source Monitoring Error occurs when a person misattributes the origin of a memory—confusing where, when, or how they learned the information.