MACRO Quiz (EXAM 4)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Biological Importance of Lipid Metabolism:
Lipids perform several essential functions:
_______
_______ storage of _______
_______ of several important _______ and _______ molecules
Lipid metabolism includes both the _______ and _______ of fatty _______ and/or more complex _______ molecules.
The choice between synthesis and degradation reflects the level of energy stores available to the _______.
Biological membranes, Efficient, energy, Components, structural, functional, synthesis, synthesis, fatty, lipid, body,
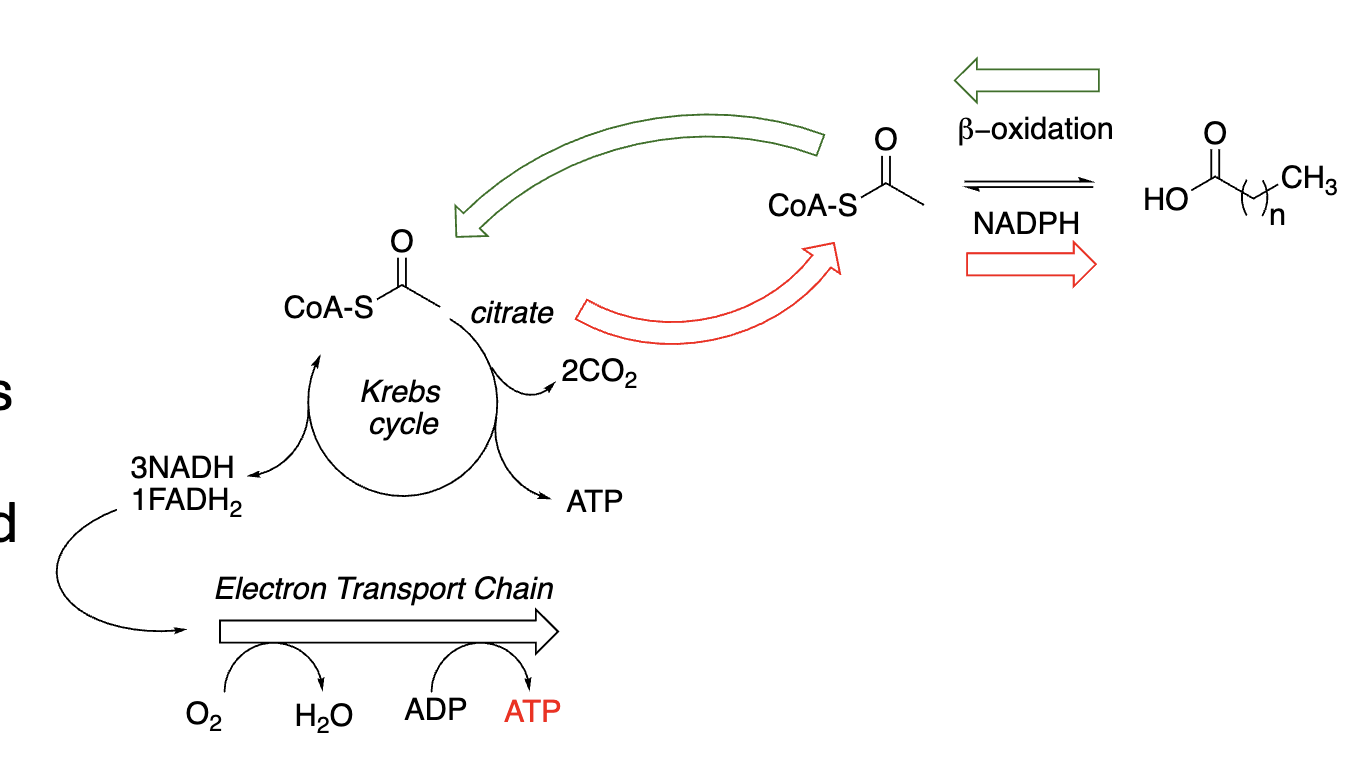
________ are an important source of carbon fuel (________):
________
________ Cycle, ________
Important building blocks for membranes, hormones, and other lipid molecules (________):
Requires ________
Consumes ________
Also, the Krebs Cycle, ETC occur in the ________
Fatty acids, catabolism, beta-oxidation, Krebs, ETC, anabolism, NADPH, ATP, mitochondria
STUDY
Like carbohydrates, fatty acids are oxidatively cleaved to _______
Acetyl-CoA feeds into _______ (Citric Acid Cycle & ETC)
TCA intermediates (e.g., _______) serve as precursors to the _______ of other molecules, including fatty acids
acetyl-CoA, cellular respiration, citrate, biosynthesis
What’s the reducing agent for acetyl-CoA?
NADPH
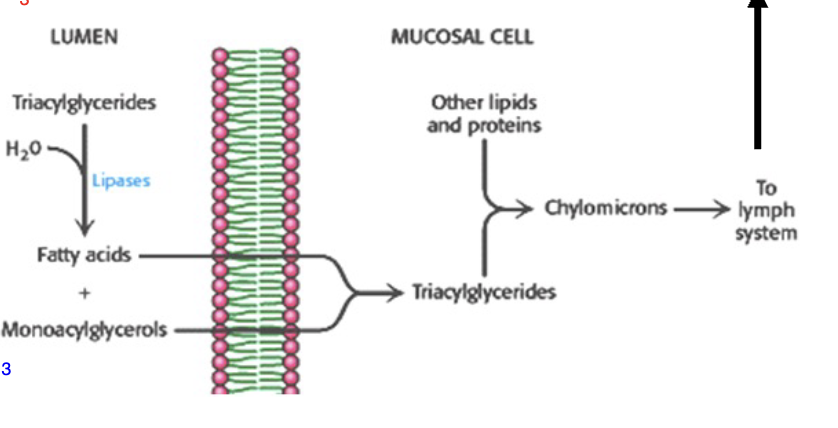
Digestion of Lipids
Minimal digestion of lipids in _______
Fats are mainly converted to _______ and _______ in GI tract by _______ from pancreas
Bile from liver aids in _______ & _______
Free fatty acids and monoglycerides are absorbed by _______ cells; then _______ resynthesized, packaged as _______ (less readily mobilized), & released into _______ system
< 5% of _______ is excreted; it’s mainly stored in _______ cells till needed as fuel
Glycogen is more readily and easily mobilized
stomach, monoglycerides, fatty acids, lipase, digestion, absorption, intestinal epithelial, triglycerides, chylomicrons, lymph, fat, adipose
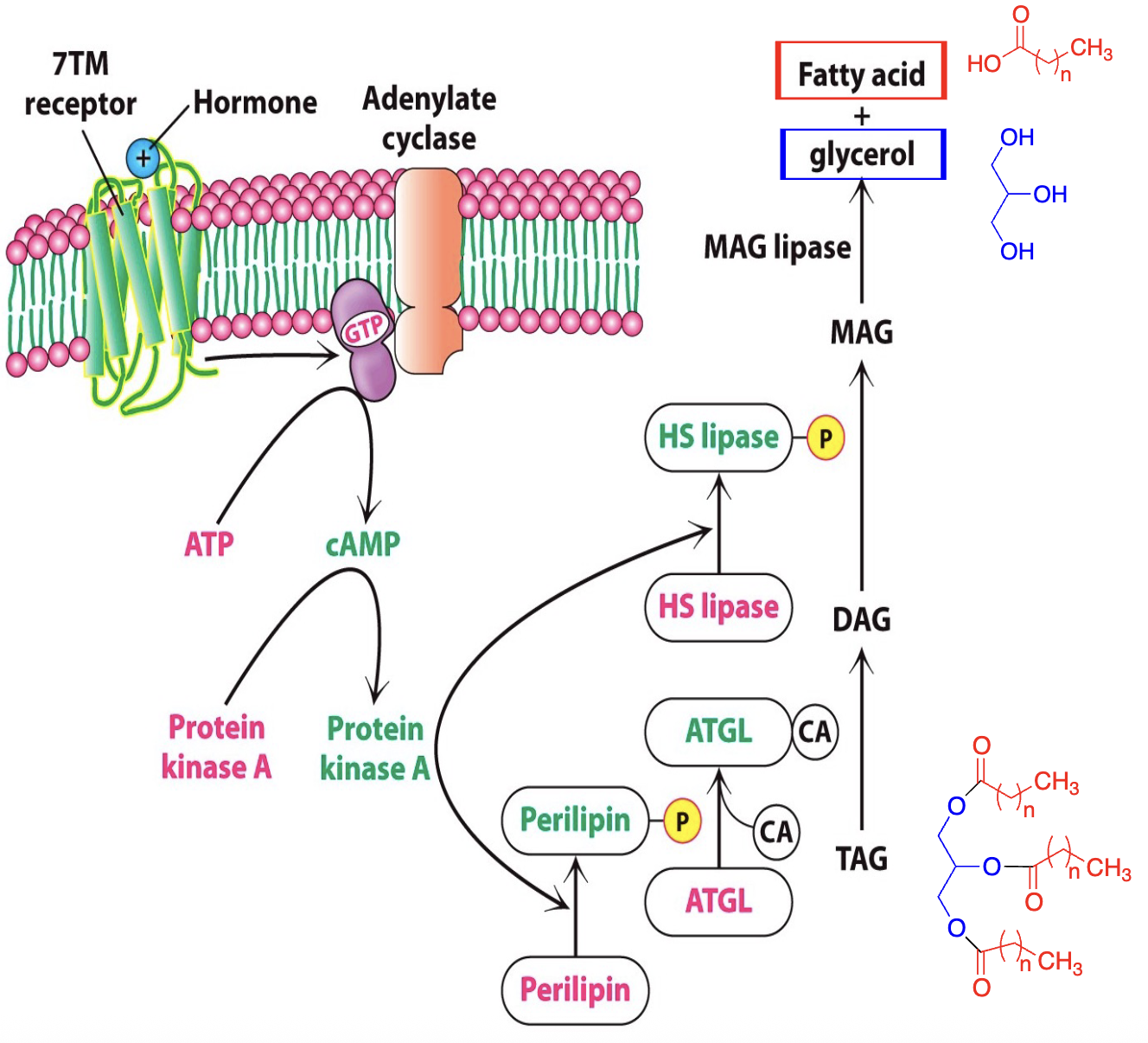
Preparation for Catabolism
• Before they can be used as fuel, stored fats must be hydrolyzed to ________ and ________
• Hormones (________, ________) initiate signal for lipase to break down triacylglycerols (TAG) —> _____ —> _____ —> _____ and _____
fatty acids, glycerol, glucagon, epinephrine, DAG, MAG, glycerol, fatty acids
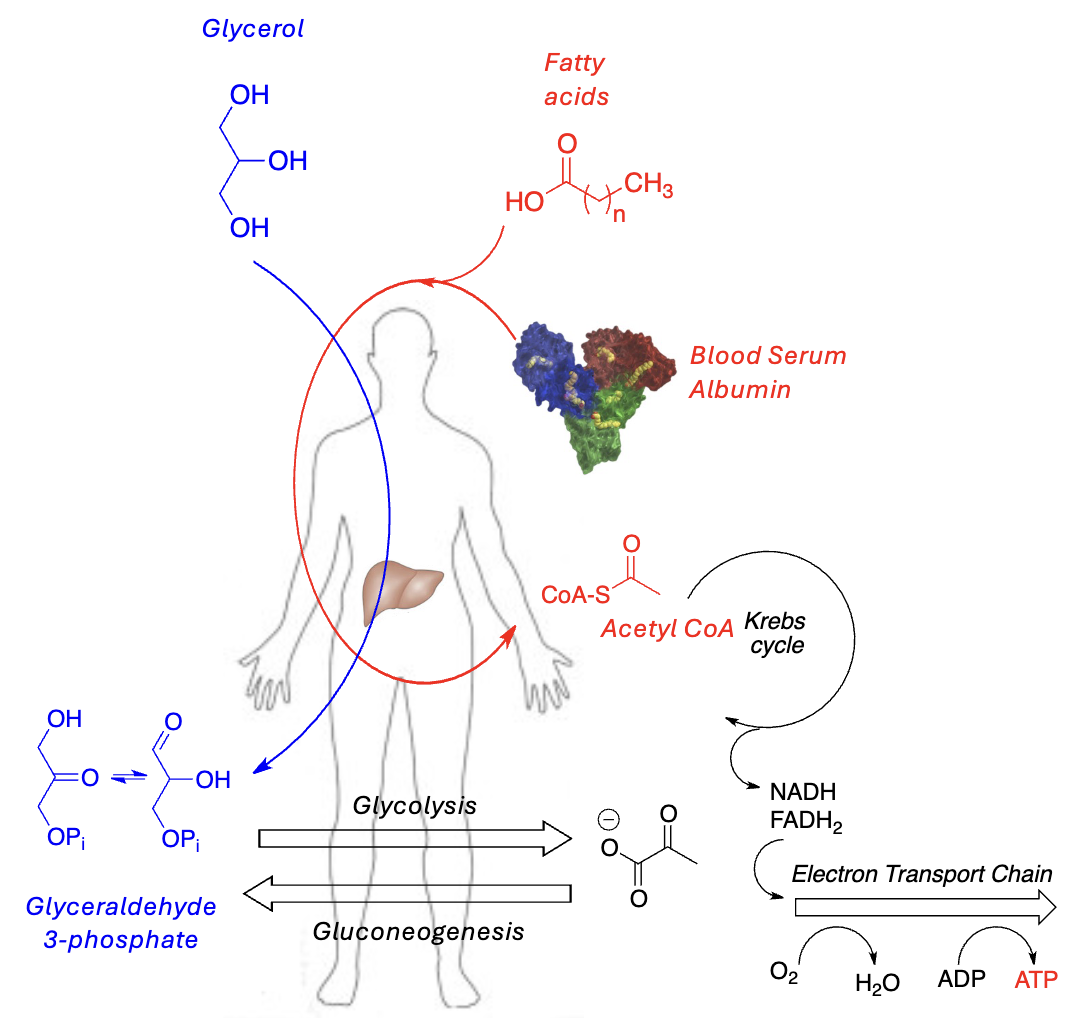
Fatty acids are _______ in blood plasma
Must “bind” to _______ to circulate
Ultimately metabolized (_______) to acetyl CoA —> feeds into _______
Glycerol metabolized in liver (CAP) to _______ —> contributes to _______ or _______
not soluble, blood serum albumin, beta-oxidation, cellular respiration, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis
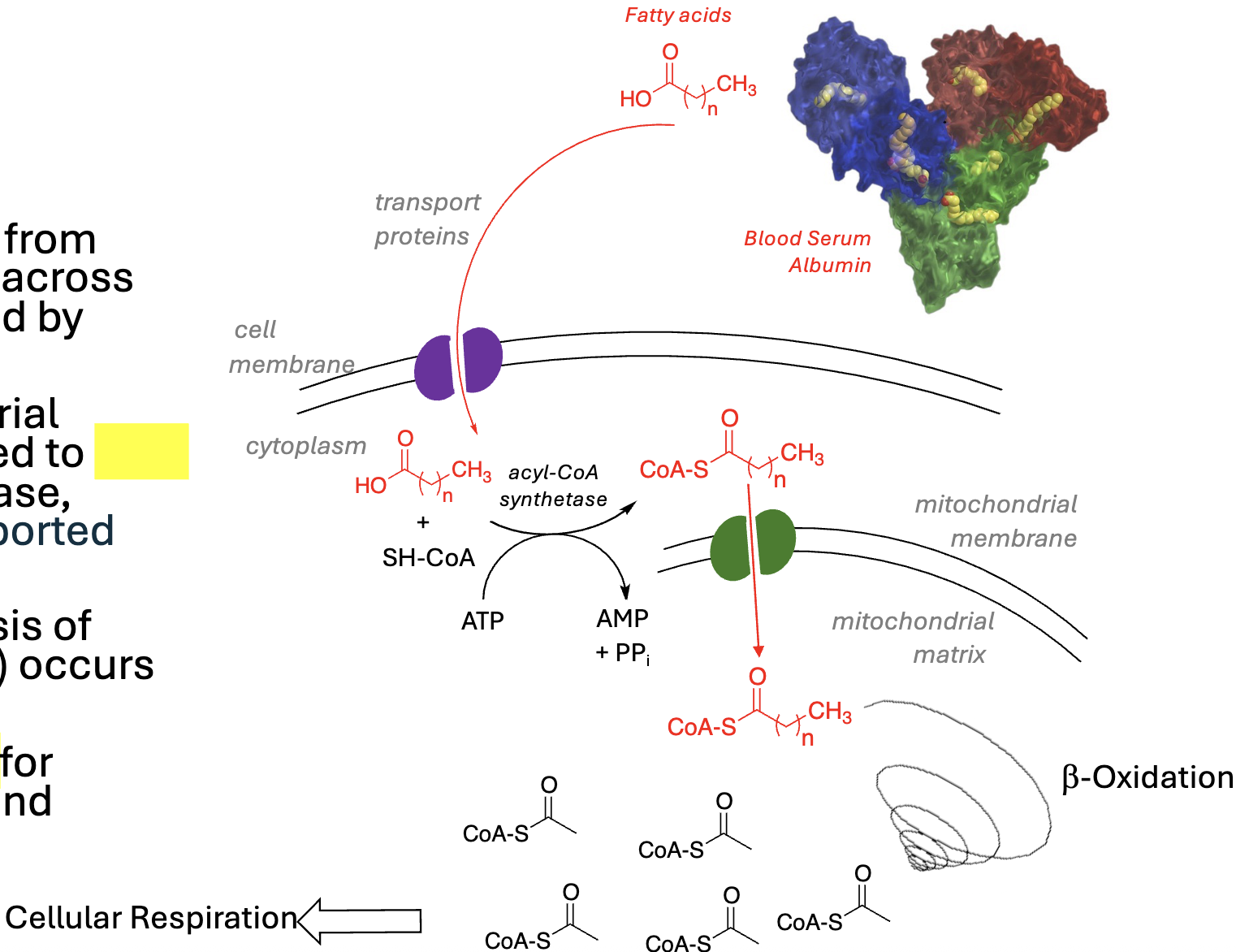
Overview of Beta-Oxidation:
Fatty acids separate from albumin and diffuse across cell membrane, aided by _________
On outer mitochondrial membrane, FAs linked to ______ by acyl-CoA synthetase, fueled by ATP; transported into the _________
_________ (breakdown of acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA) occurs in mitochondria
Provides _________ for cellular respiration and synthesis of ATP
transport proteins, CoA, mitochondria, beta-oxidation, acetyl-CoA
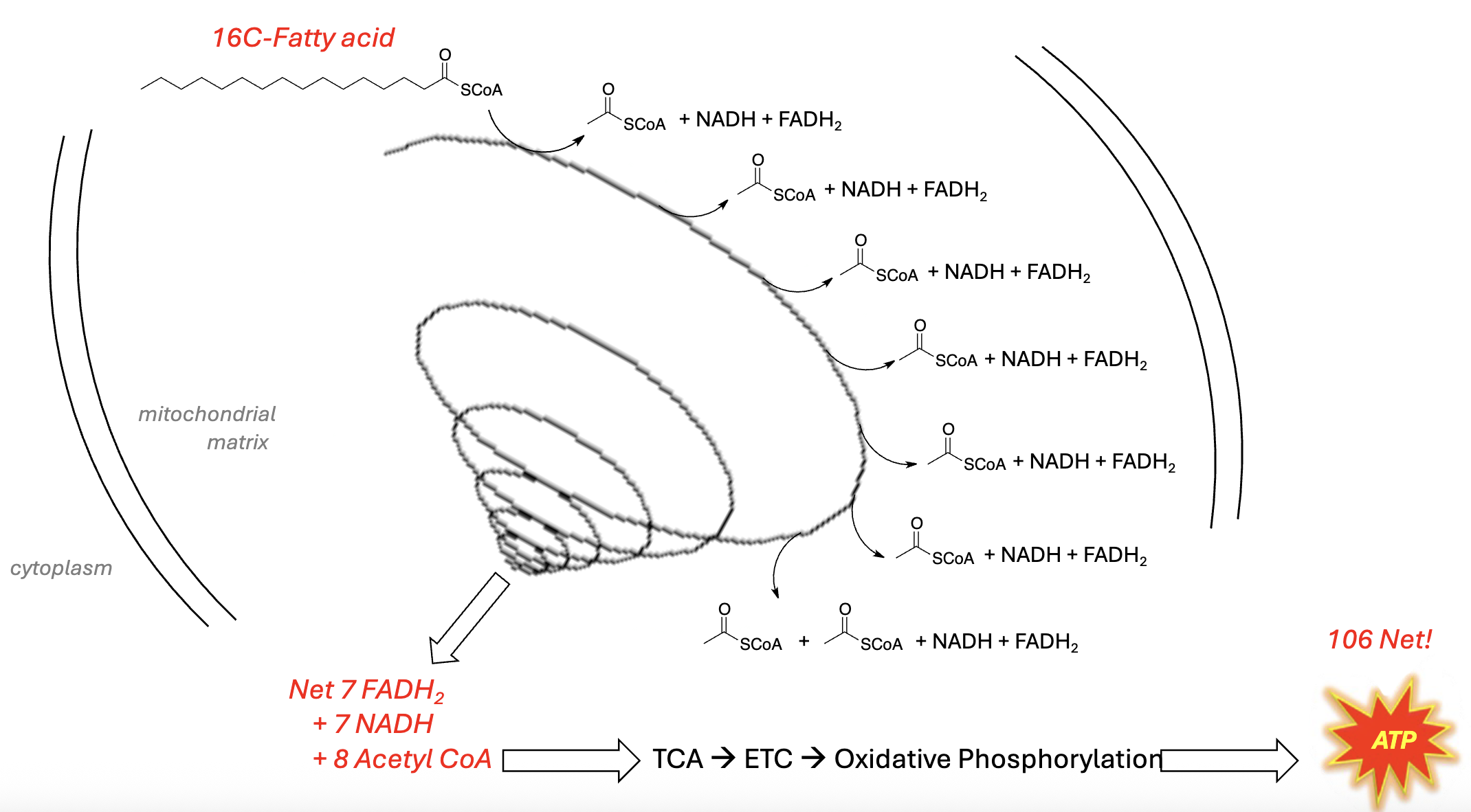
Steps of Beta-Oxidation:
Sequential breakdown of ______ to acetyl-CoA in mitochondrion
Iterative 4-step process:
Decreases C-chain by _____ (Acetyl-CoA)
Yields _ FADH2 & _ NADH
For a 16-C fatty acid:
_ rounds of b-oxidation yield:
_ Acetyl CoAs
_ FADH 2 (1 per round)
_ NADH (1 per round)
acyl-CoA, 2Cs, 1, 1, 7, 8, 7, 7
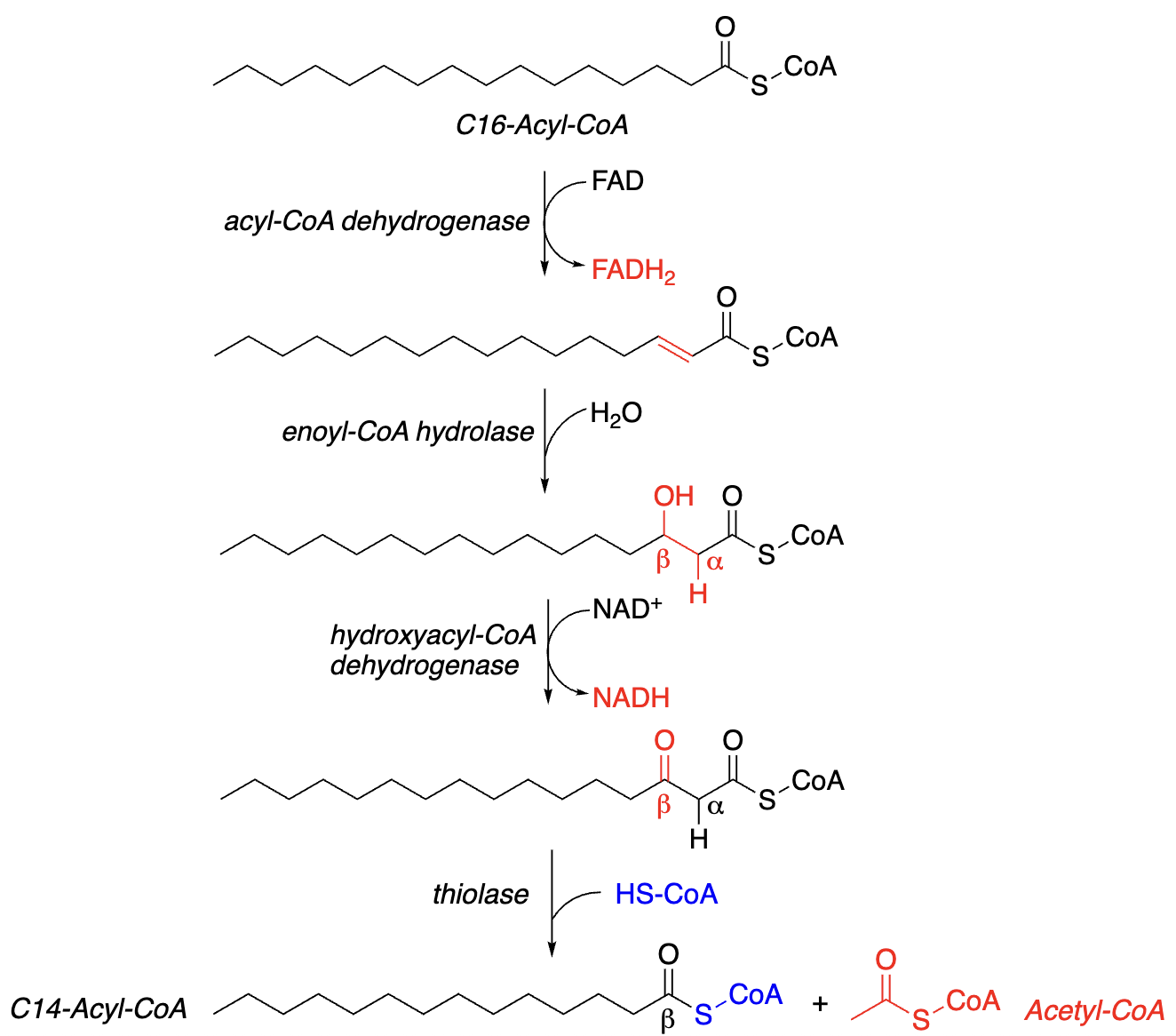
4 Steps of each “Round” of Beta-Oxidation:
__________ (oxidation) of acyl-CoA, reduction of FAD —> FADH2
__________ (addition of H2O)
________ of beta-carbon, ________ of NAD+ —> NADH
Reaction w/________ —> 2C-shortened acyl-CoA + 1 acetyl-CoA
Dehydrogenation, Hydration, Oxidation, reduction, CoA-SH
STUDY
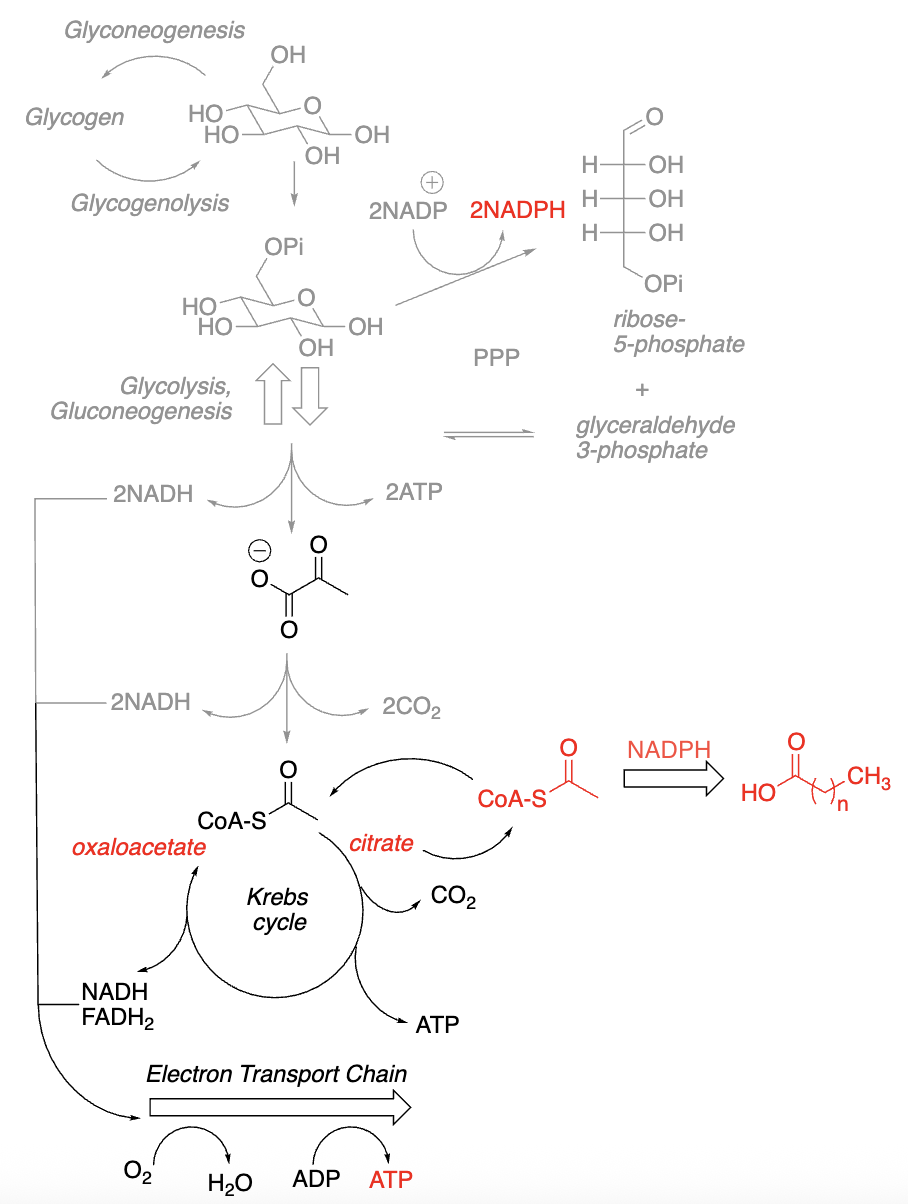
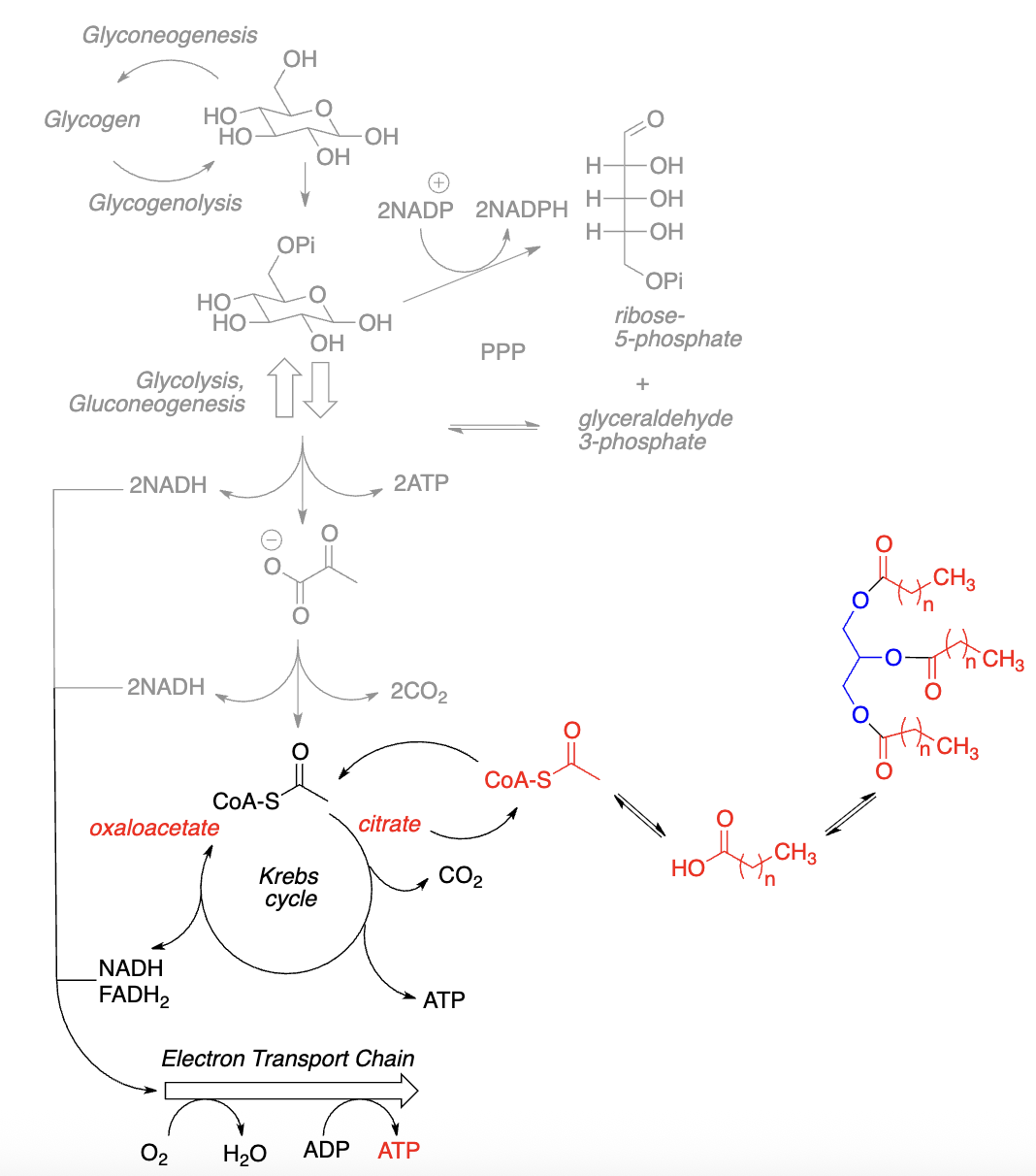
Overview of Fatty Acid Synthesis:
Sequential buildup of fatty acids from ______
_ carbon units added at a time
Requires reducing agent, ______ (from ______)
Acetyl CoA is located mainly in mitochondria w/no ______ out
Acetyl CoA “transported” out of mitochondria as ______
acetyl-CoA, 2, NADPH, PPP, transporter, citrate
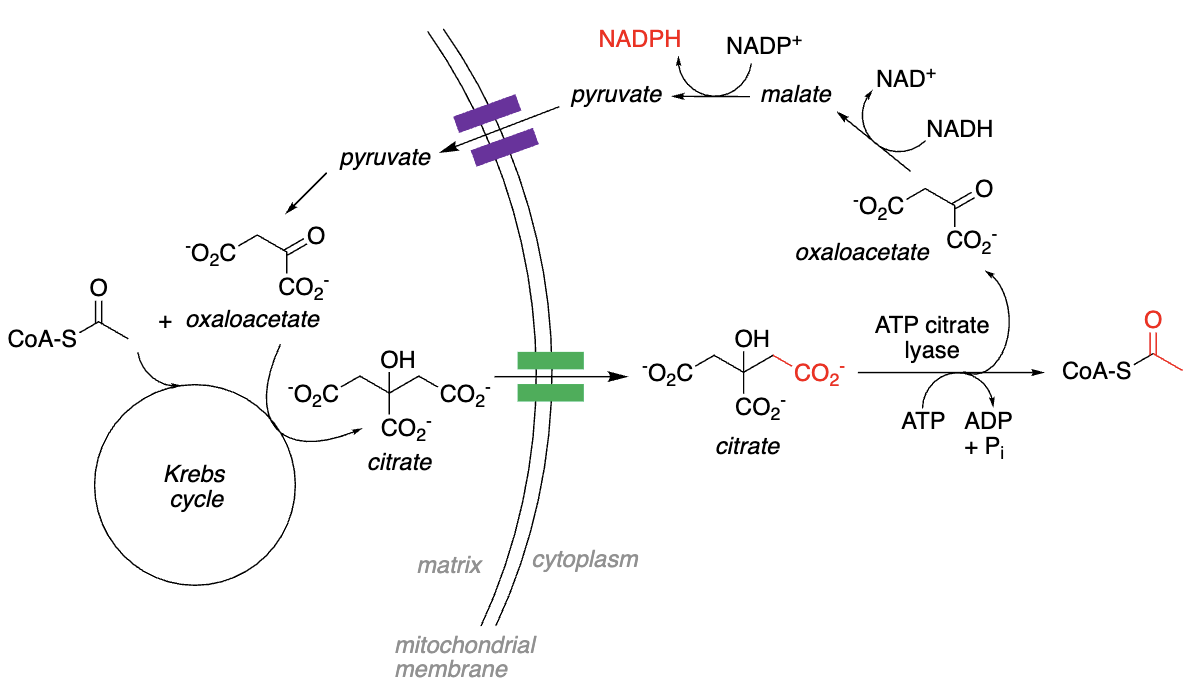
Transporting Acetyl-CoA out of Mitochondria:
Acetyl CoA + oxaloacetate —> citrate, which can be _________ across mitochondrial membrane
In the _________, citrate converted to acetyl- CoA + oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetate reduced by _______ to _______
Malate oxidized to _______ by _______; yields _ NADPH
Pyruvate transported back into mitochondrion, converted back to _______, etc...
transported, cytoplasm, NADH, malate, pyruvate, NADP+, 1, oxaloacetate
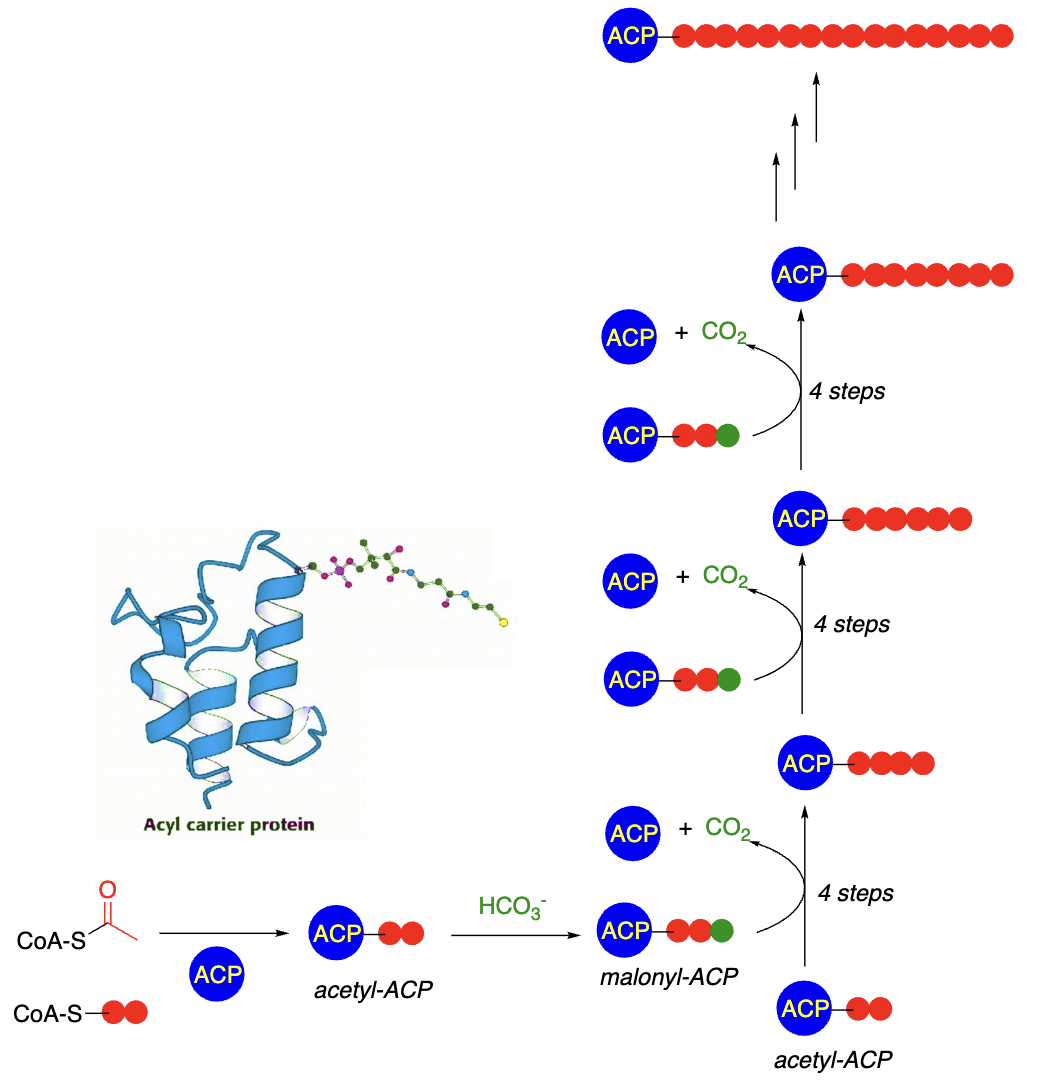
Simplified Steps of Fatty Acid Synthesis:
Acetyl-CoA (__) transferred ____________ (ACP) —> acetyl-ACP
Acetyl-ACP activated by condensation with ______ (1C) —> malonyl-ACP (__)
Malonyl-ACP (3C) condenses with another _________ (__)—> 4C acyl-ACP + CO2
Several steps yield a ____ extended fatty acid-ACP
All of the above are repeated many times to produce __________ of the desired length
2C, acetyl carrier protein, HCO3, 3C, acetyl-ACP, 2C, 2C-, fatty acids
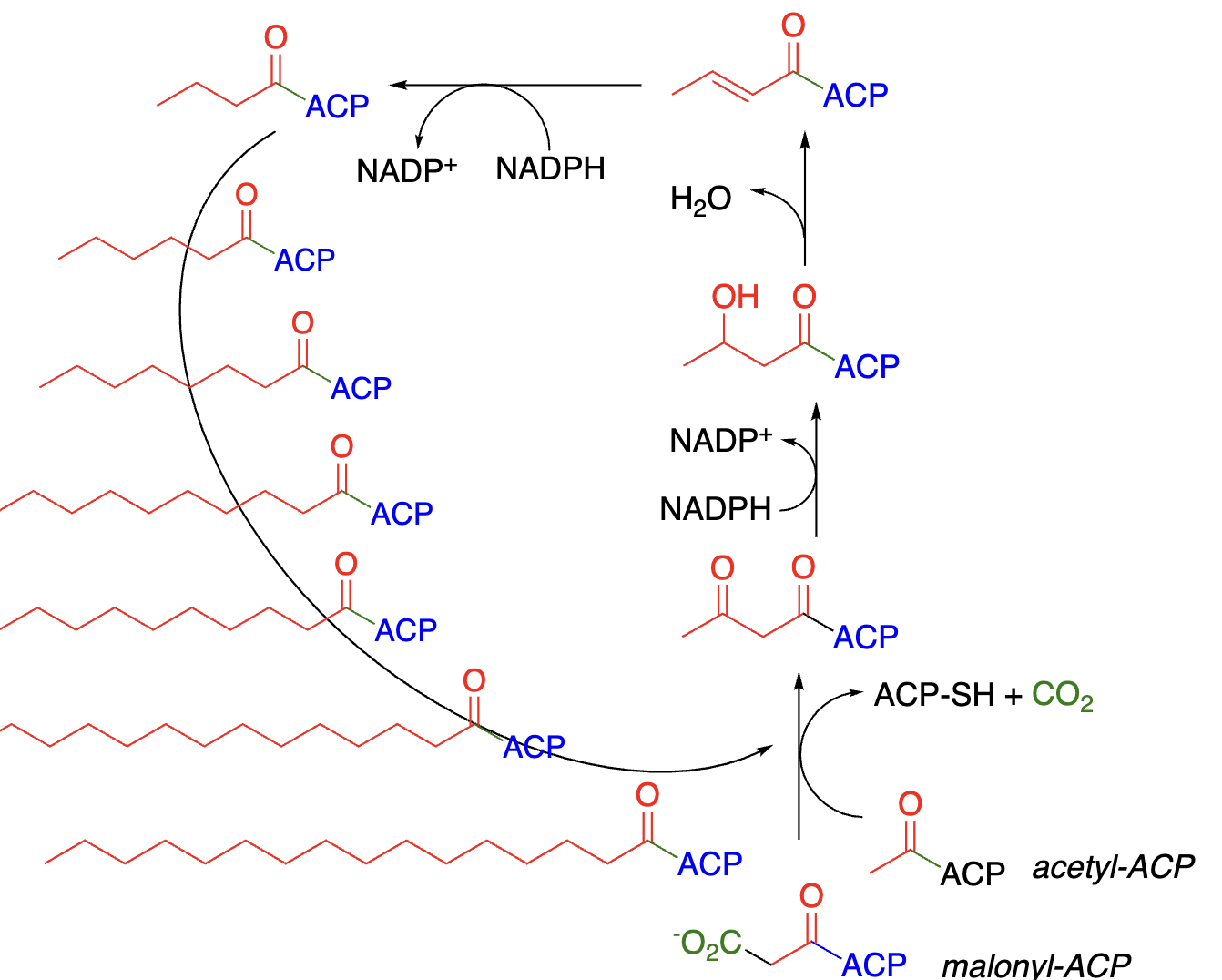
Steps of Fatty Acid Synthesis:
4-step iterative process, repeated over multiple rounds to build up fatty acids _ carbons at a time:
_________ of acyl-CoA + malonyl-CoA —> beta-diketone + CO2
beta-diketone _______ by ______ —> beta-hydroxy-ketone + NADP+
beta-hydroxyketone _________ —> alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone
alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone _______ by ______ —> fatty acid-ACP + NADP+
2, Condensation, reduced, NADPH, dehydrated, reduced, NADPH
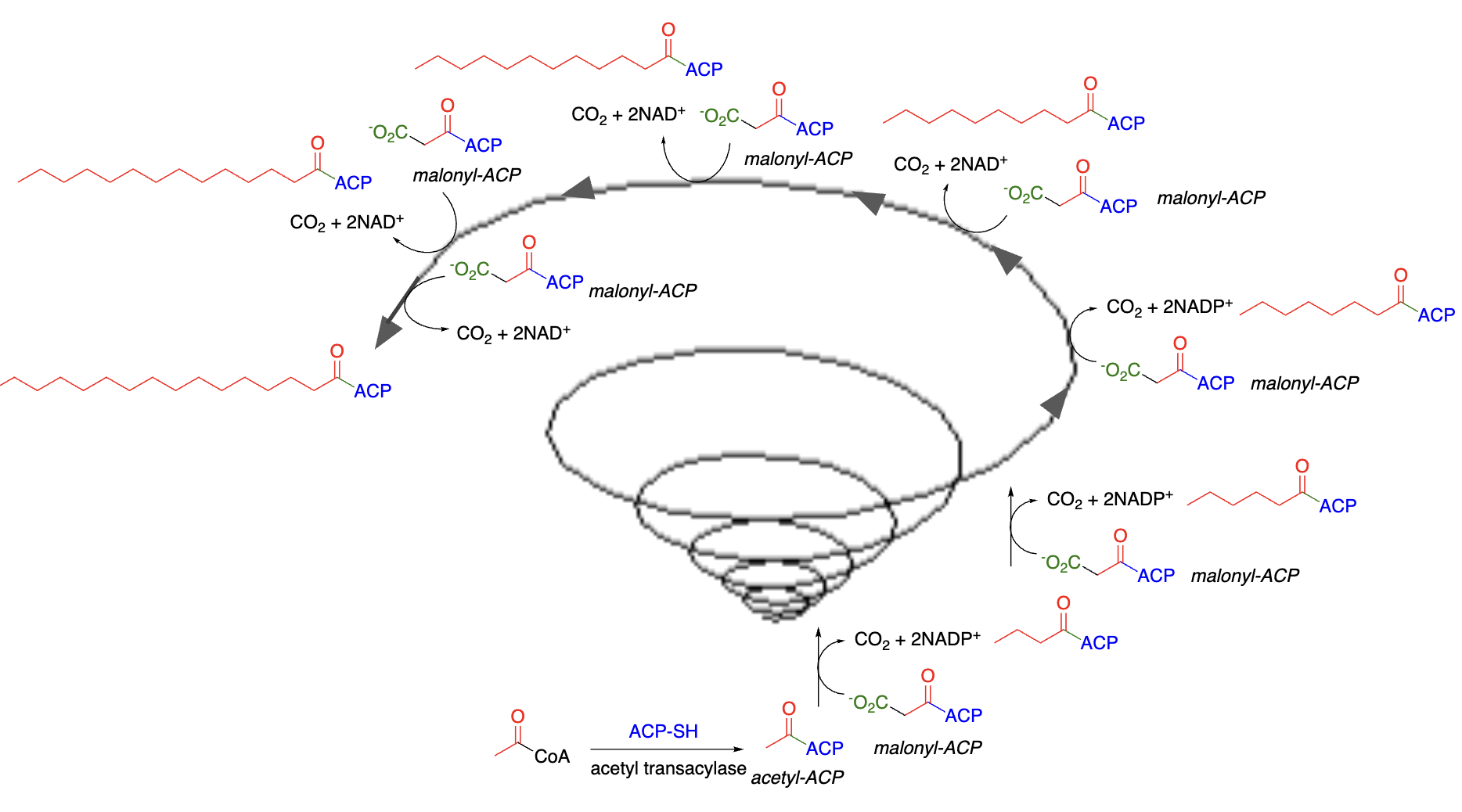
STUDY
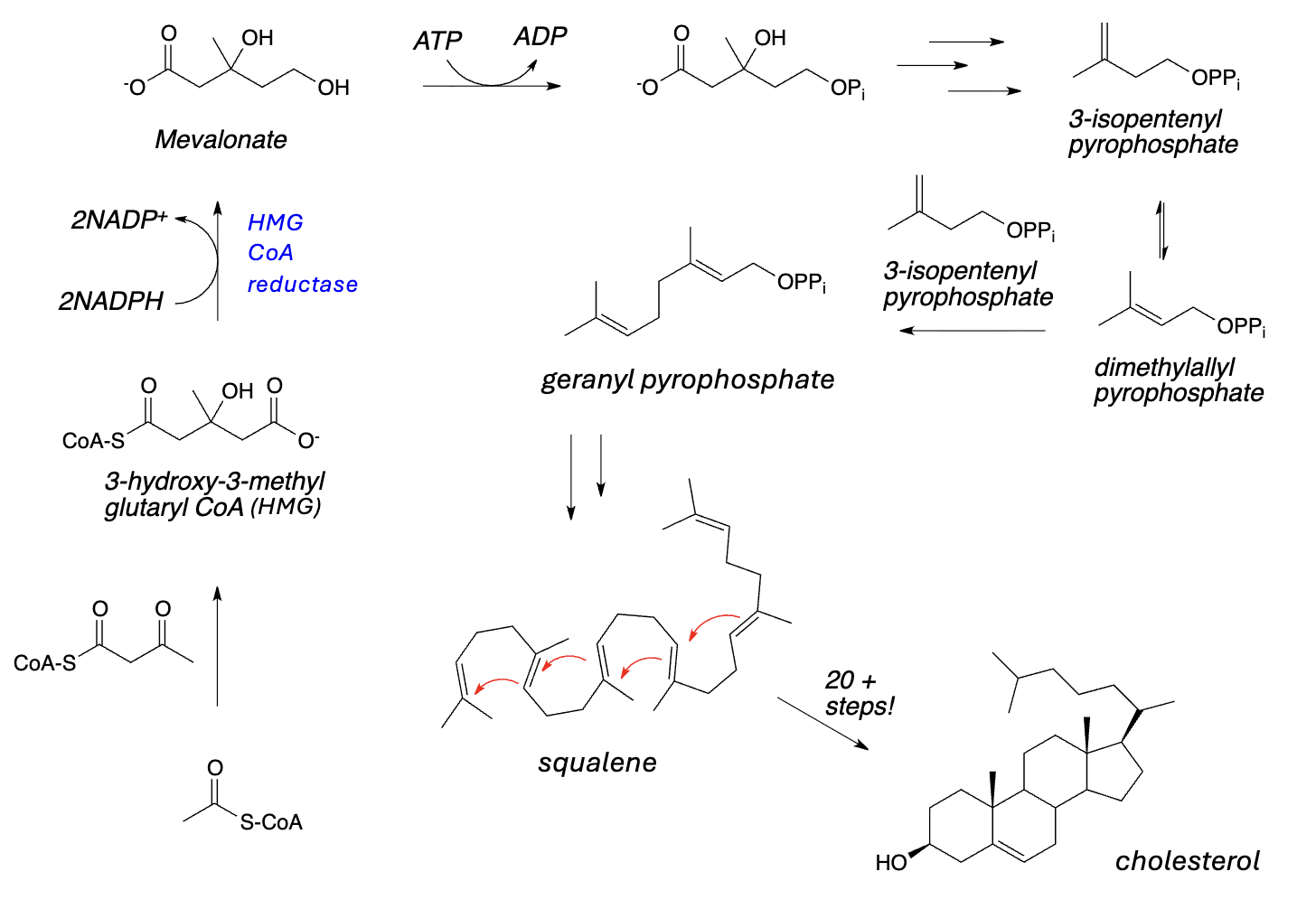
Synthesis of Other Lipids:
Acetyl-CoA is the precursor/building block for other lipids, as well, e.g., _________ and _________
cholesterol, steroid hormones
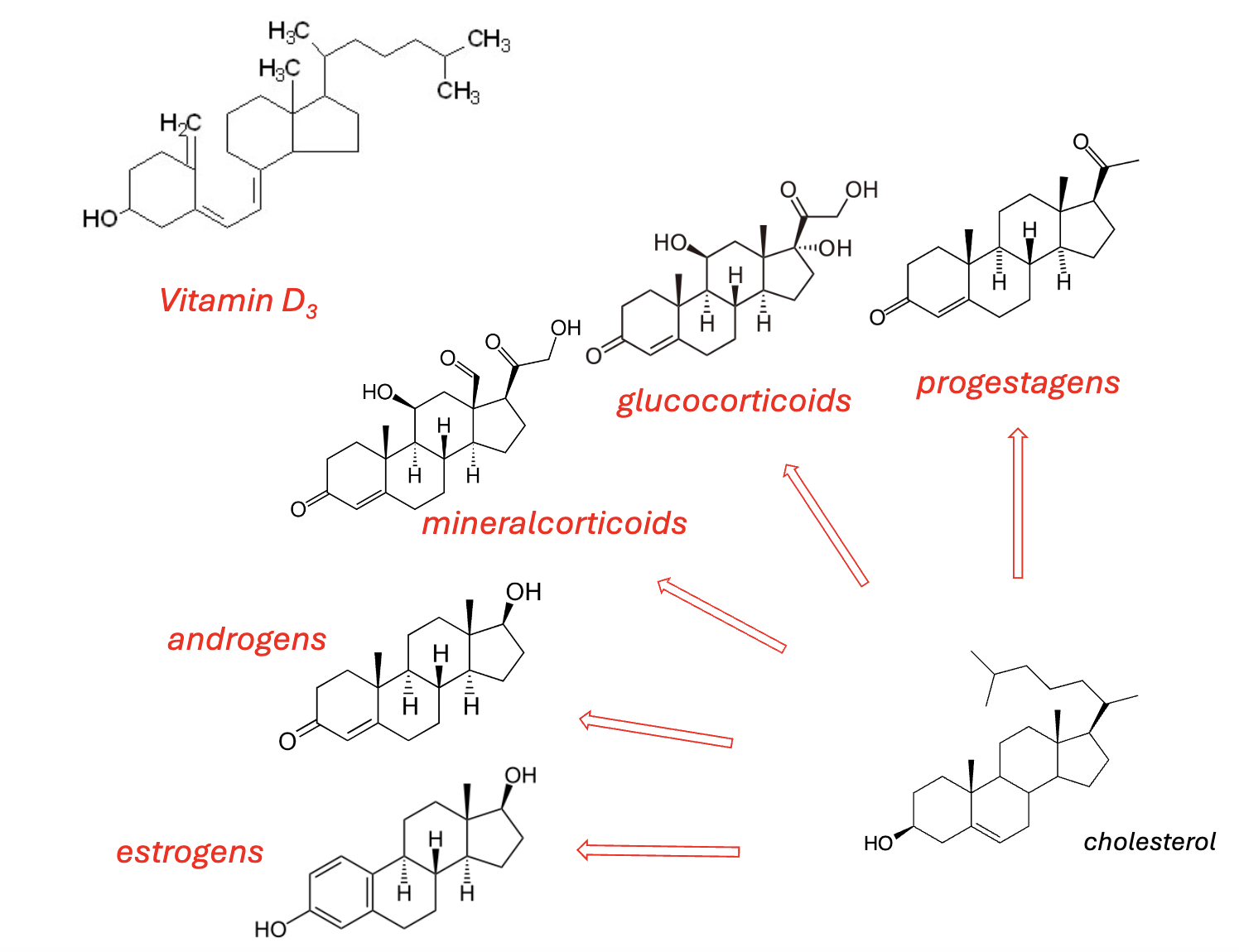
STUDY
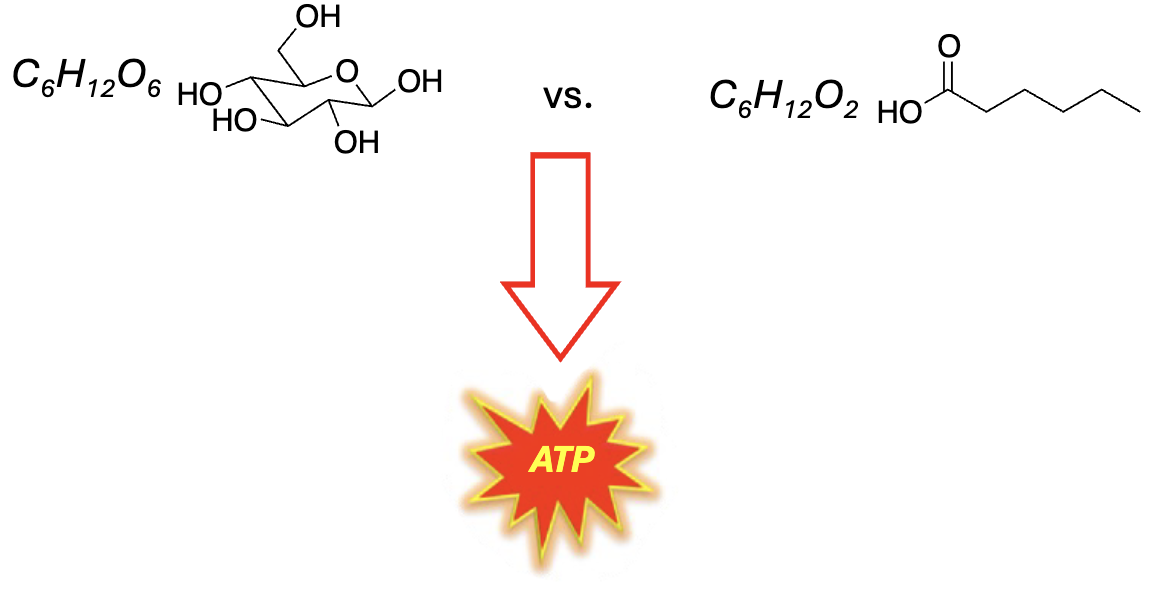
Sample Problem
Quantitatively compare the ATP yield from the complete oxidation of glucose, a six-carbon carbohydrate, and hexanoic acid, a six-carbon fatty acid. Hexanoic acid is also called caproic acid and is responsible for the “aroma” of goats. If fats are better fuels than carbohydrates, why does the body use carbohydrates (glucose) as its primary source of energy/ATP?
37 ATPs total fro 1 C6-FA
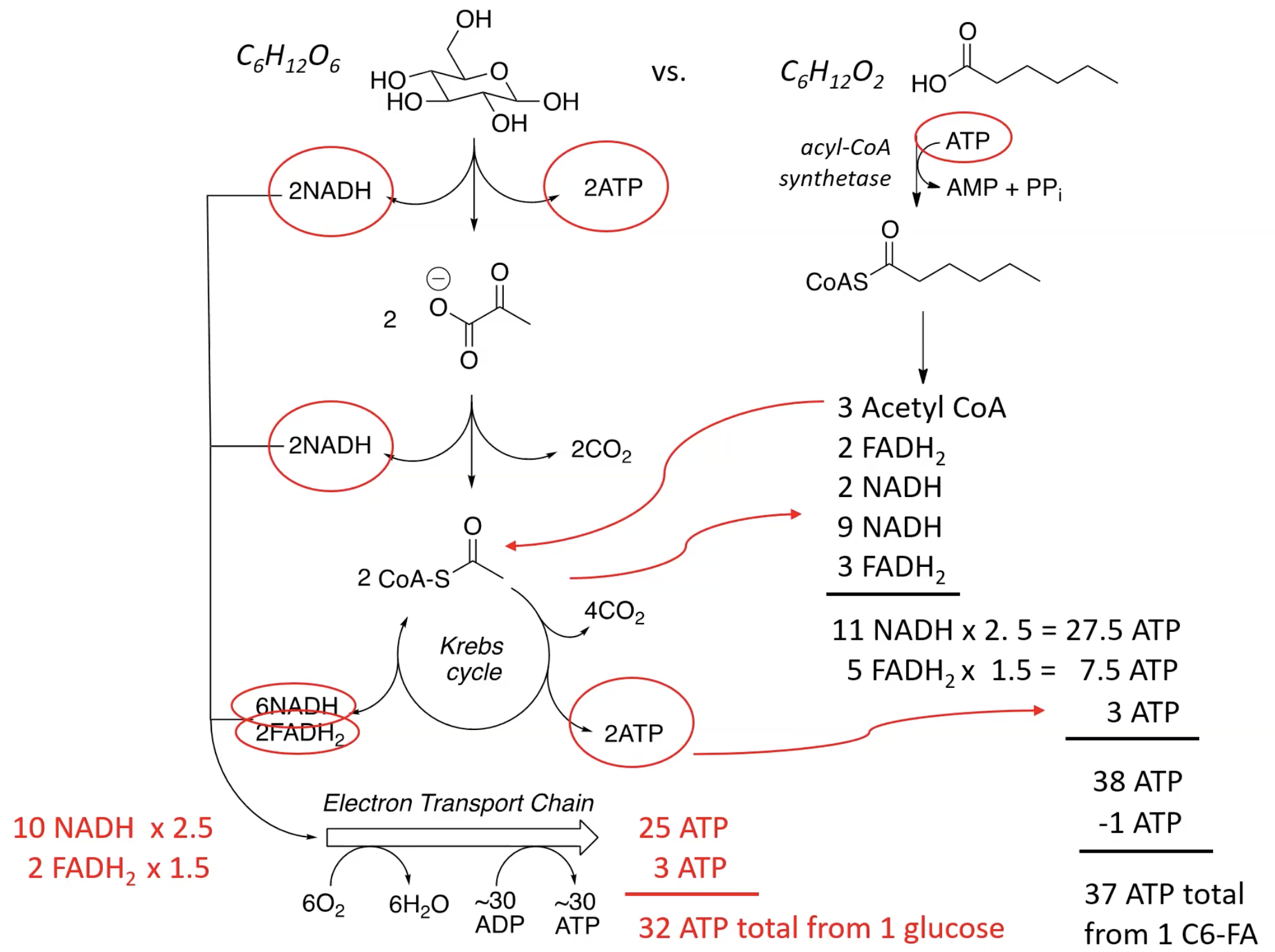
Sample Problem Solved
STUDY
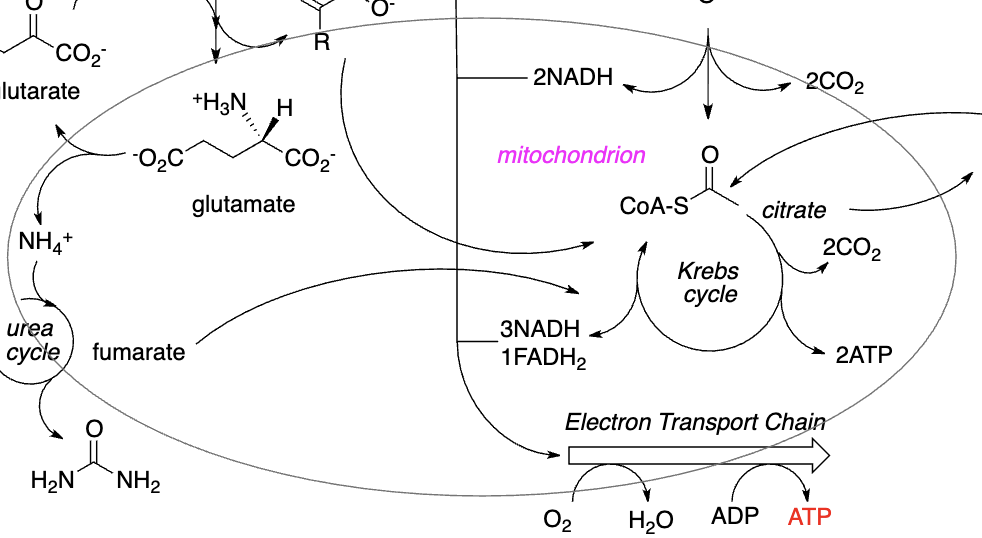
Biomedical Importance of the Metabolism of Nitrogen-Containing Compounds
In normal adults, nitrogen intake = nitrogen excreted; exceptions:
Nitrogen intake _ Nitrogen excreted, during growth and pregnancy
Nitrogen intake _ Nitrogen excreted, may follow surgery, advanced cancer or other disorders
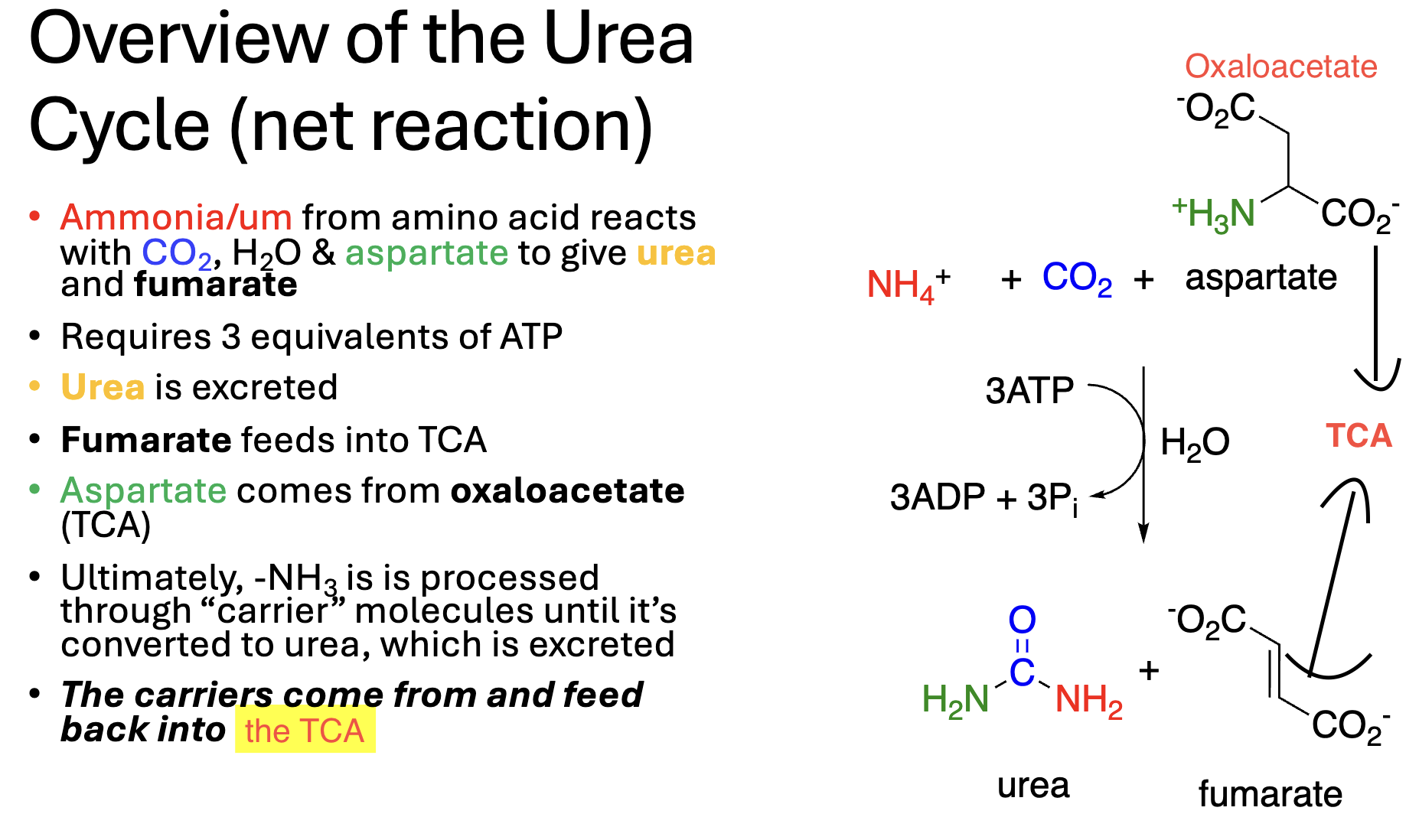
Most Nitrogen in humans comes from _________, which are catabolized to urea through the _________
>, <, amino acids, Urea Cycle
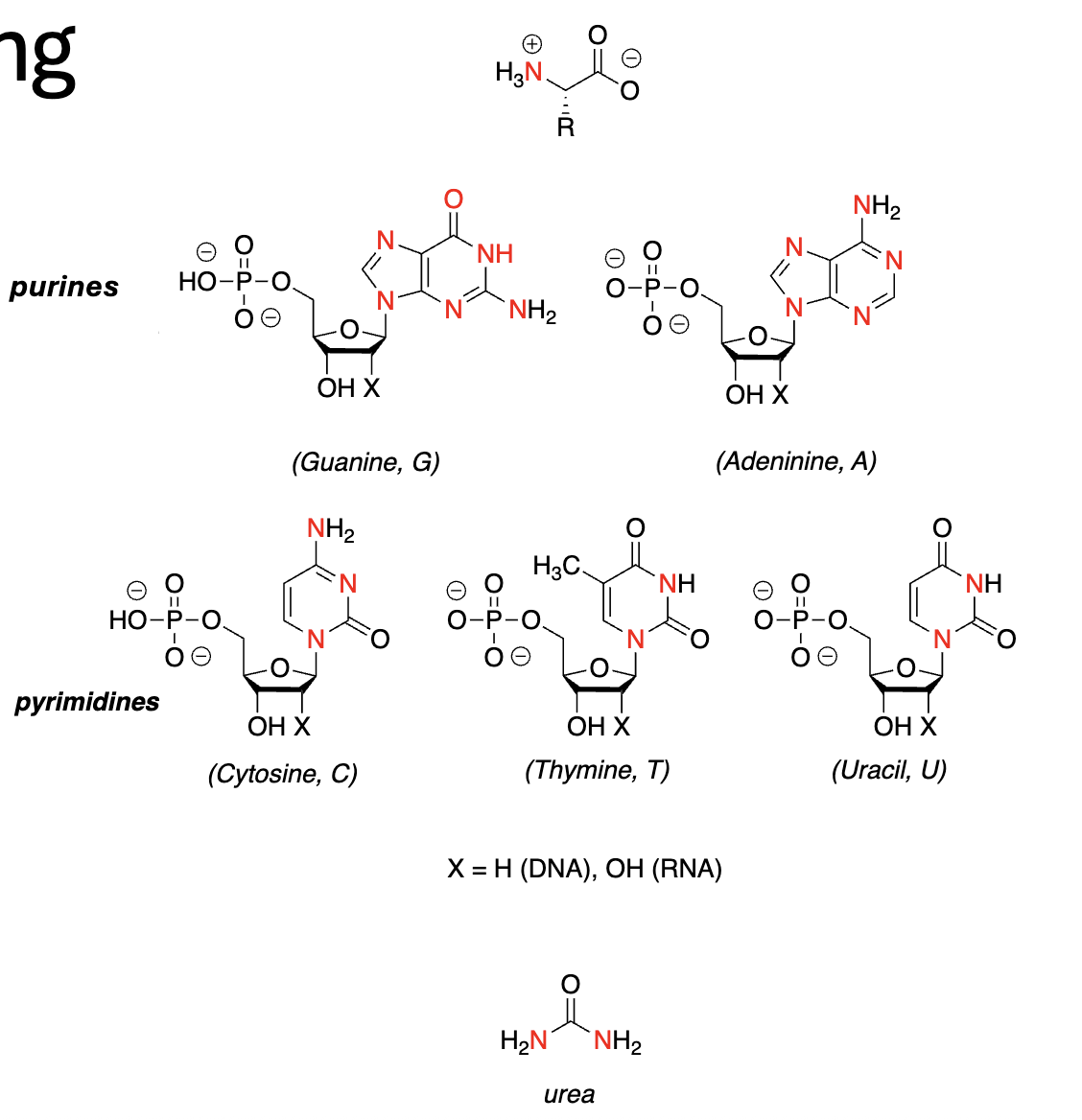
Nitrogen-Containing Compounds:
Amino Acids
_________
_________ (of other AAs & nucleotides)
Nucleotides
Comprises nucleic acids (_________ & _________ bases)
_________
Urea
the Waste product of _________ of _________
_________
Fuel, building blocks, purine, pyrimidine, Genetic code, catabolism, amino acids, Urea Cycle
Why is Nitrogen Unique?
• Our nutrients/fuels come mainly from plants (and animals that eat plants)
• Plants can readily synthesize C,H,O- containing compounds (_______) from environmental ____ and ____ (photosynthesis)
• But atmospheric ________ (___) is inert
glucose, CO2, H2O, Nitrogen, N2
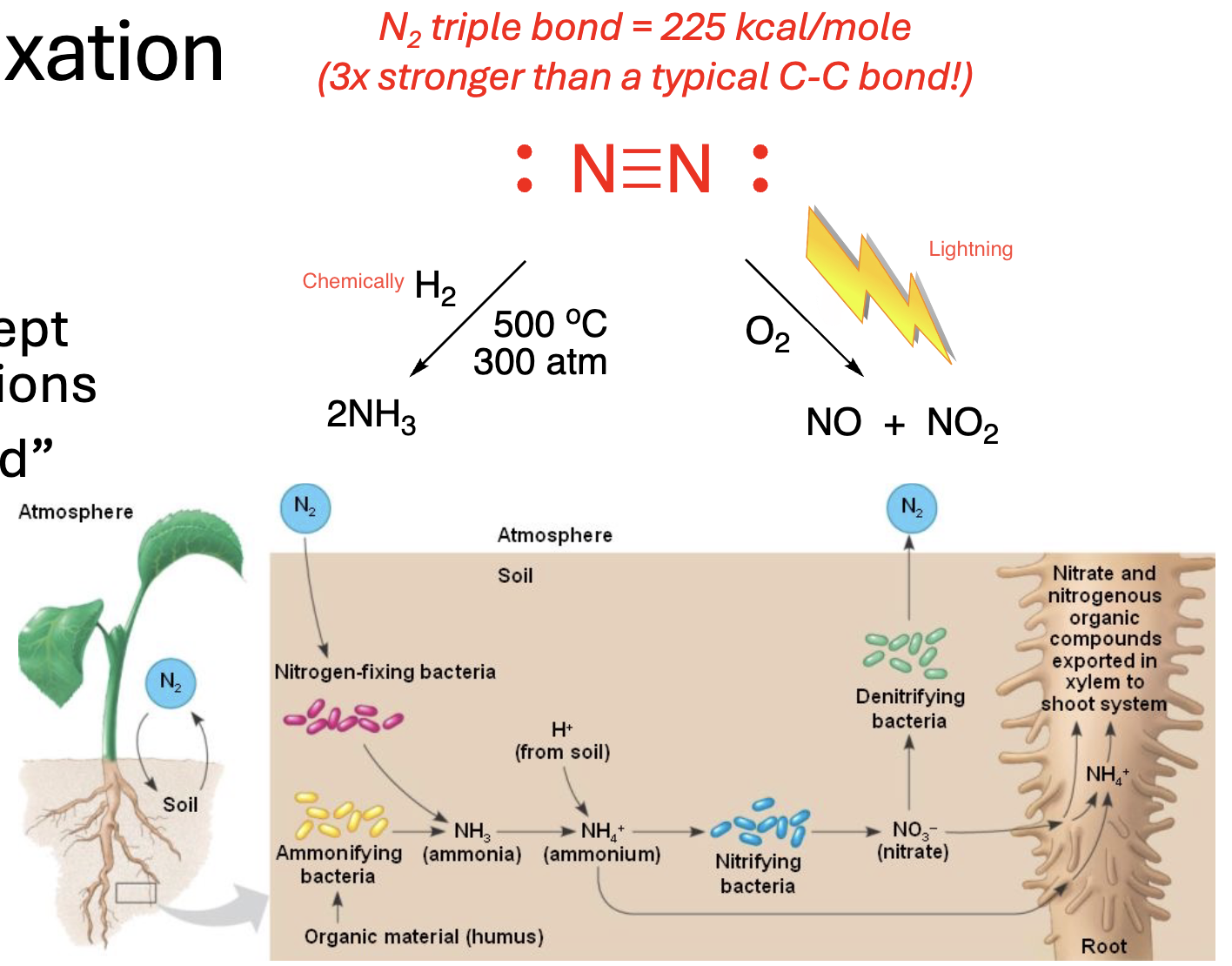
Nitrogen (N2 ) Fixation
__% of Earth’s atmosphere, but it’s __________, except under special conditions
Nitrogen can be “fixed” in 3 ways:
__________ (Haber Process)
__________
__________
80, inert/unreactive, Chemically, Lightning, Nitrogen-fixing Bacteria
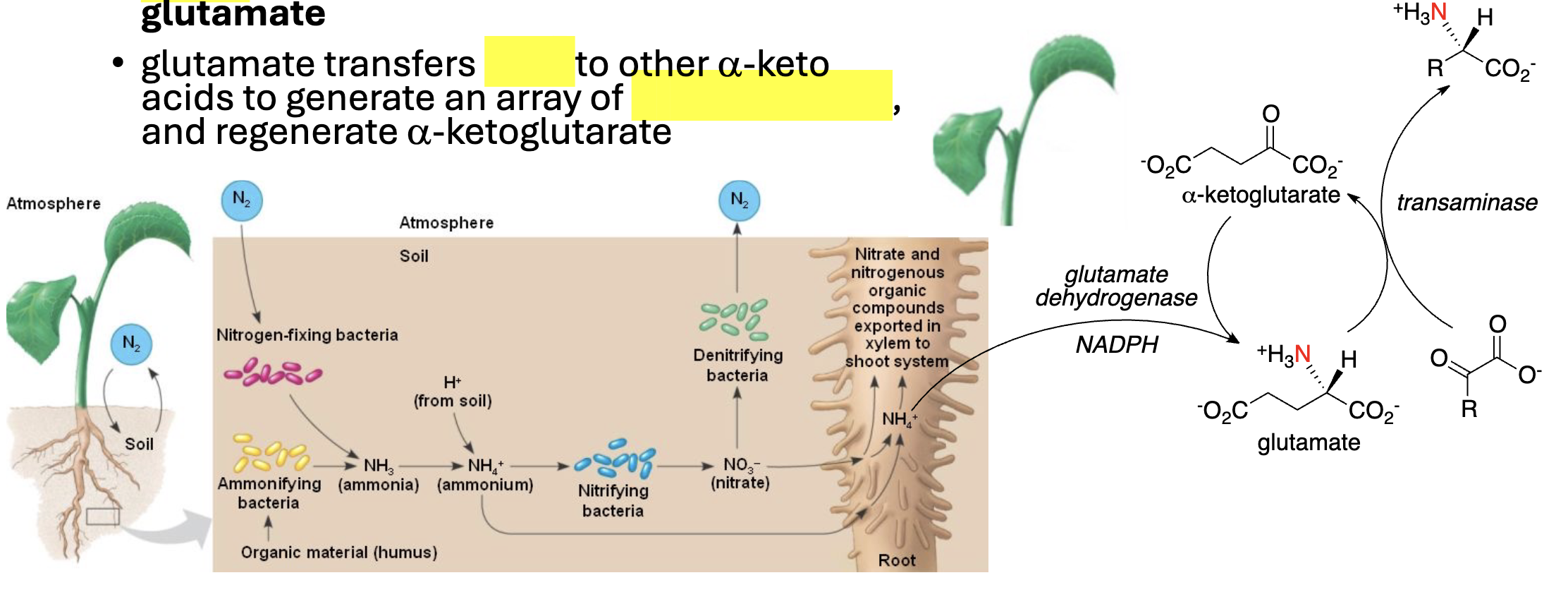
Nitrogen Assimilation in Plants
____ in soil is assimilated into amino acids by _____: picked up by a-ketoglutarate to give ________
glutamate transfers ______ to other a-keto acids to generate an array of ___________ (___________), and regenerate a-ketoglutarate
NH4+, plants, glutamate, :NH3, alpha-amino acids, transamination
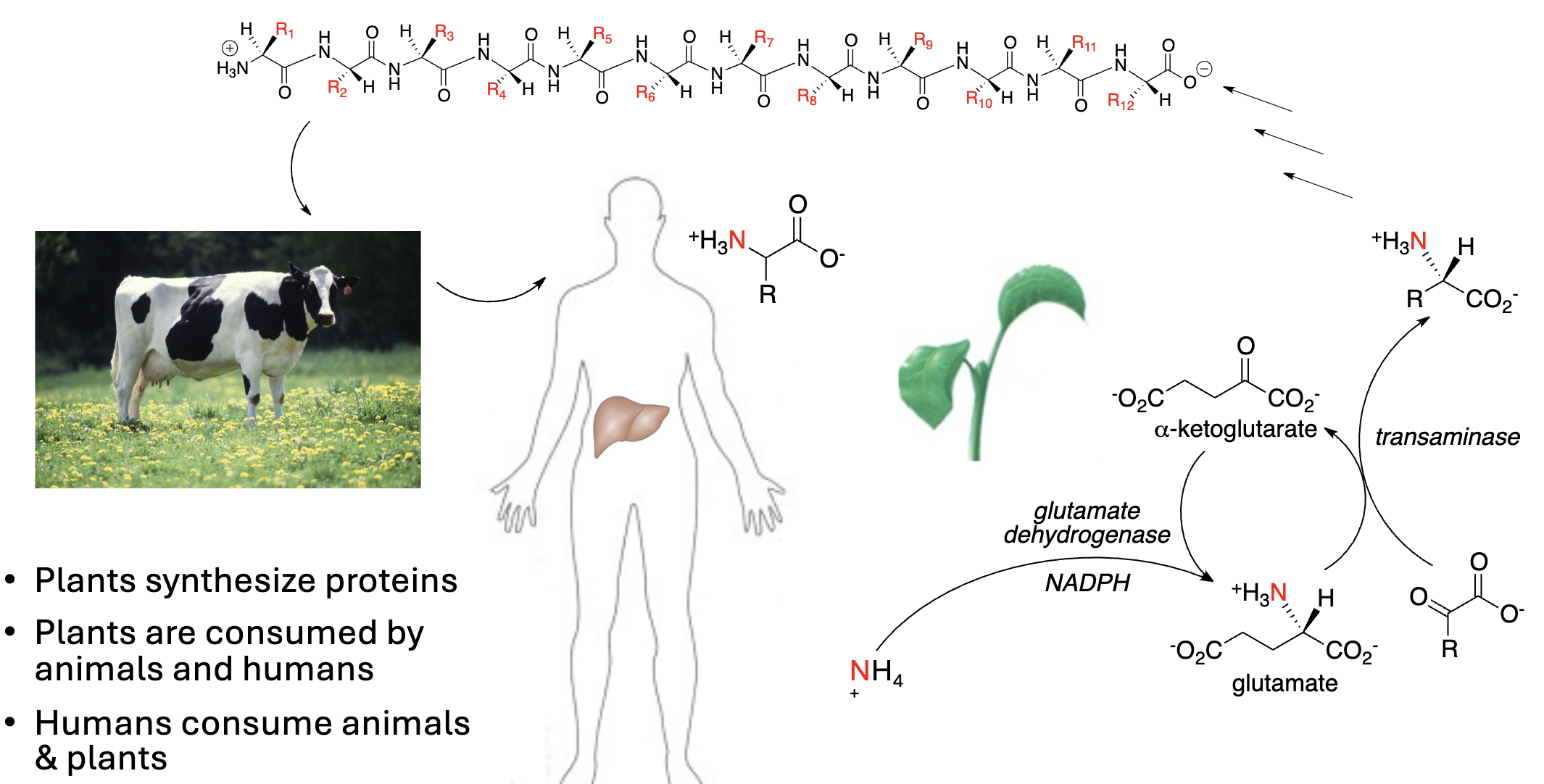
STUDY
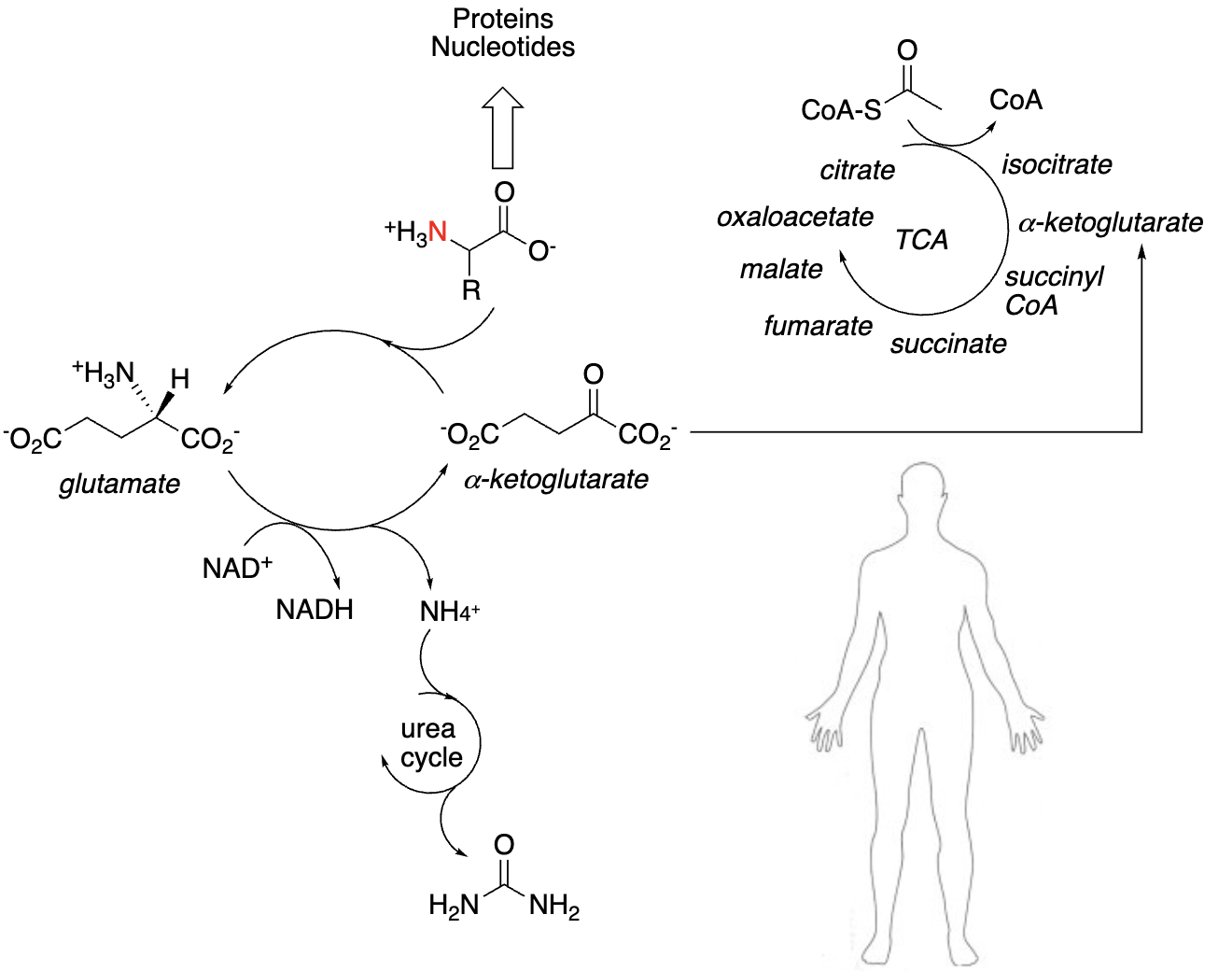
Amino Acids in the Body:
Unlike carbohydrates and fats, amino acids are _______; they’re _______:
Used for the synthesis of _______ and/or _______
Or catabolized to:
_______ & processed through _______
Carbon fuels & fed into the _______
not stored, either, proteins, nucleotides, Ammonium, Urea Cycle, TCA
STUDY
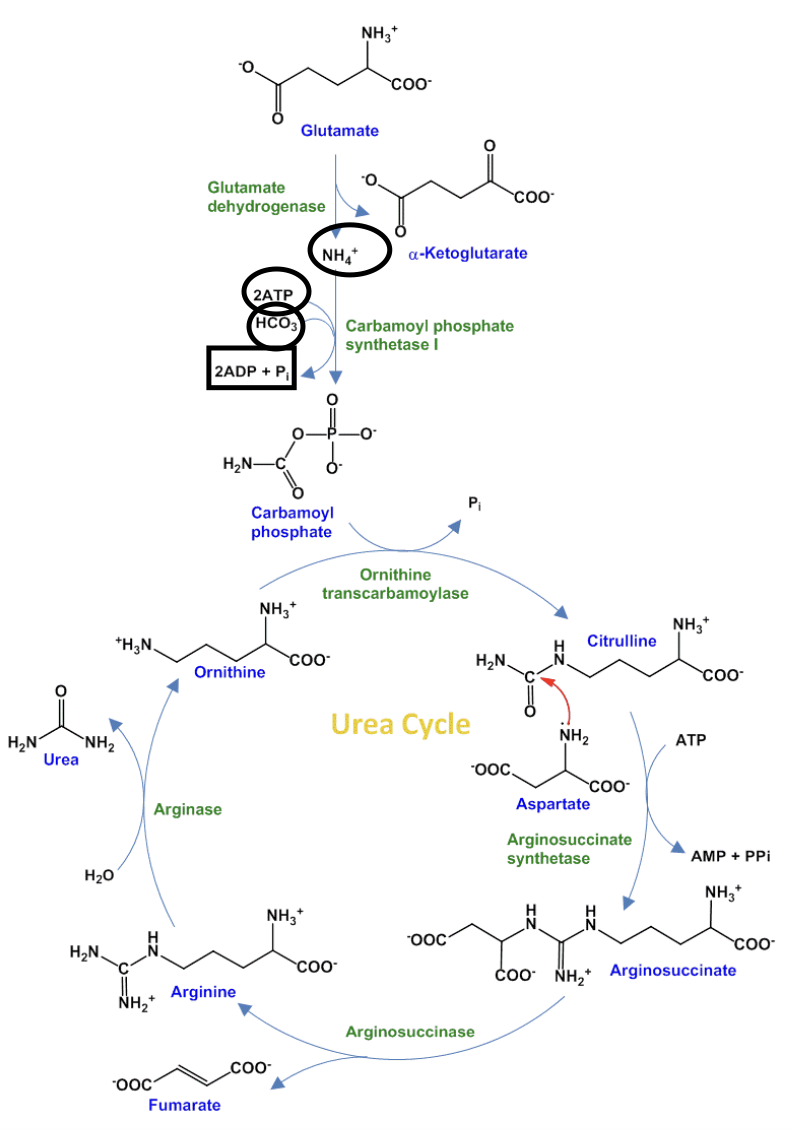
STUDY
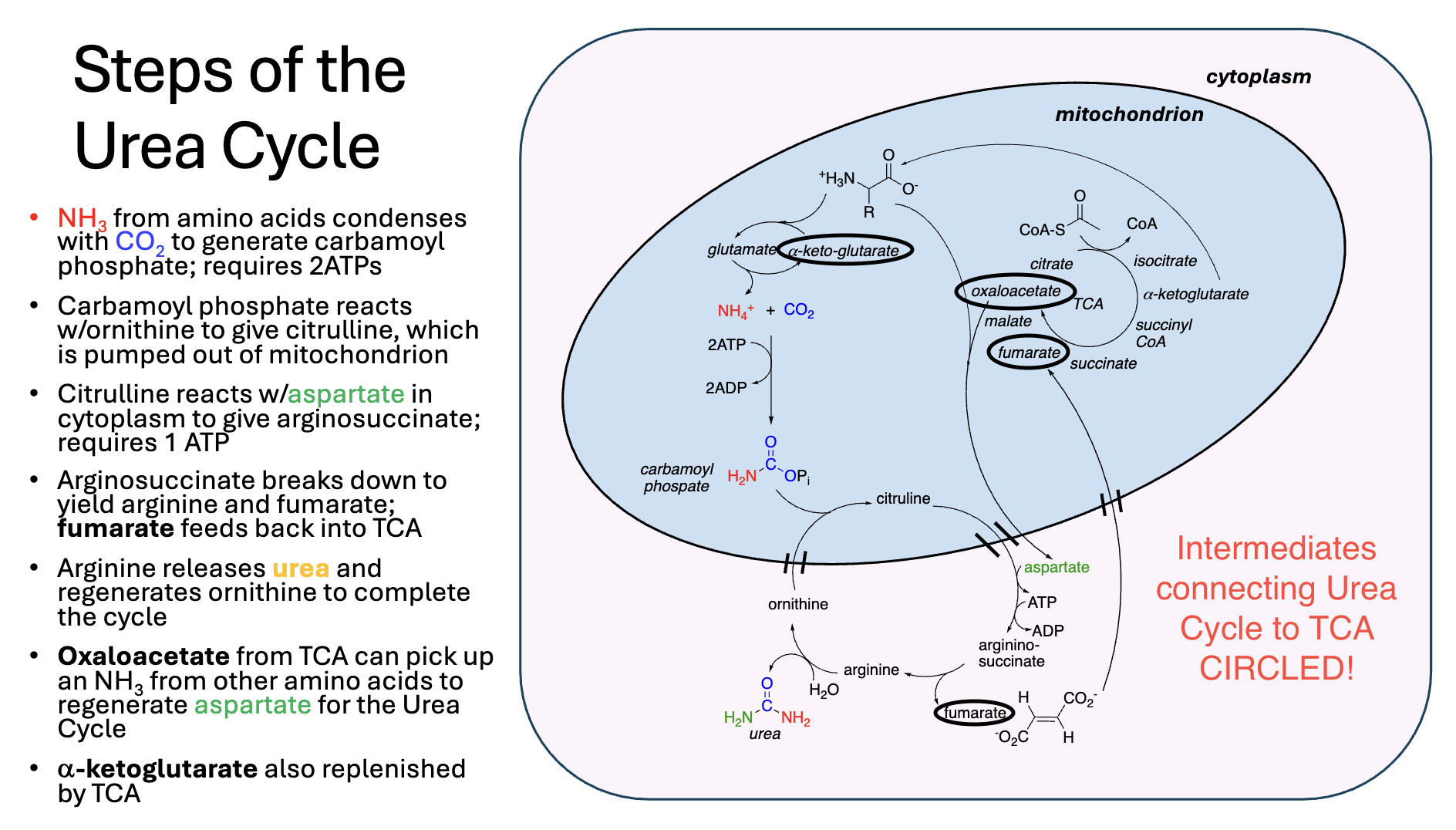
KNOW THE IDEA, don’t memorize specific substrate names
STUDY
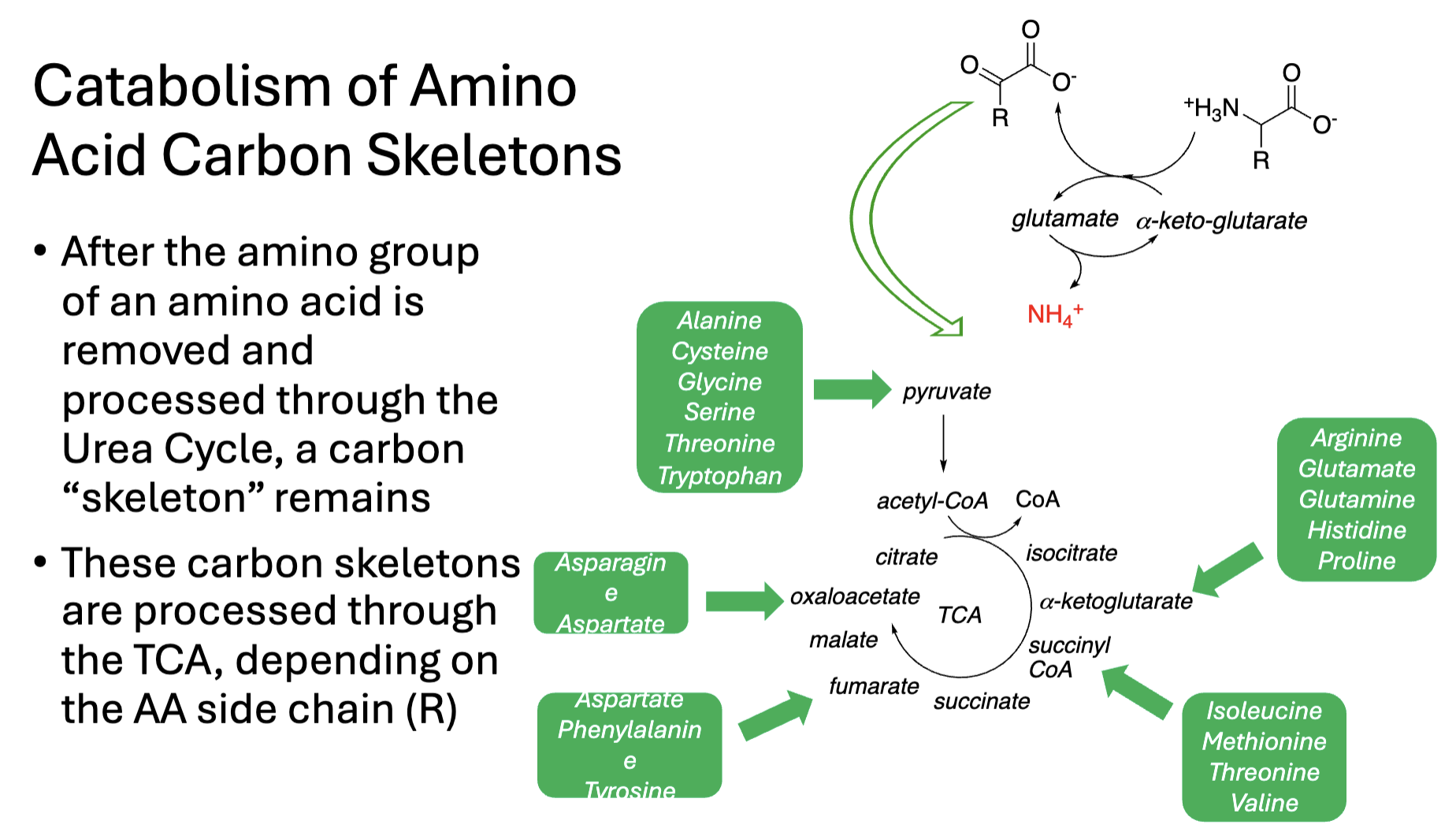
DON’T MEMORIZE GREEN AA
STUDY
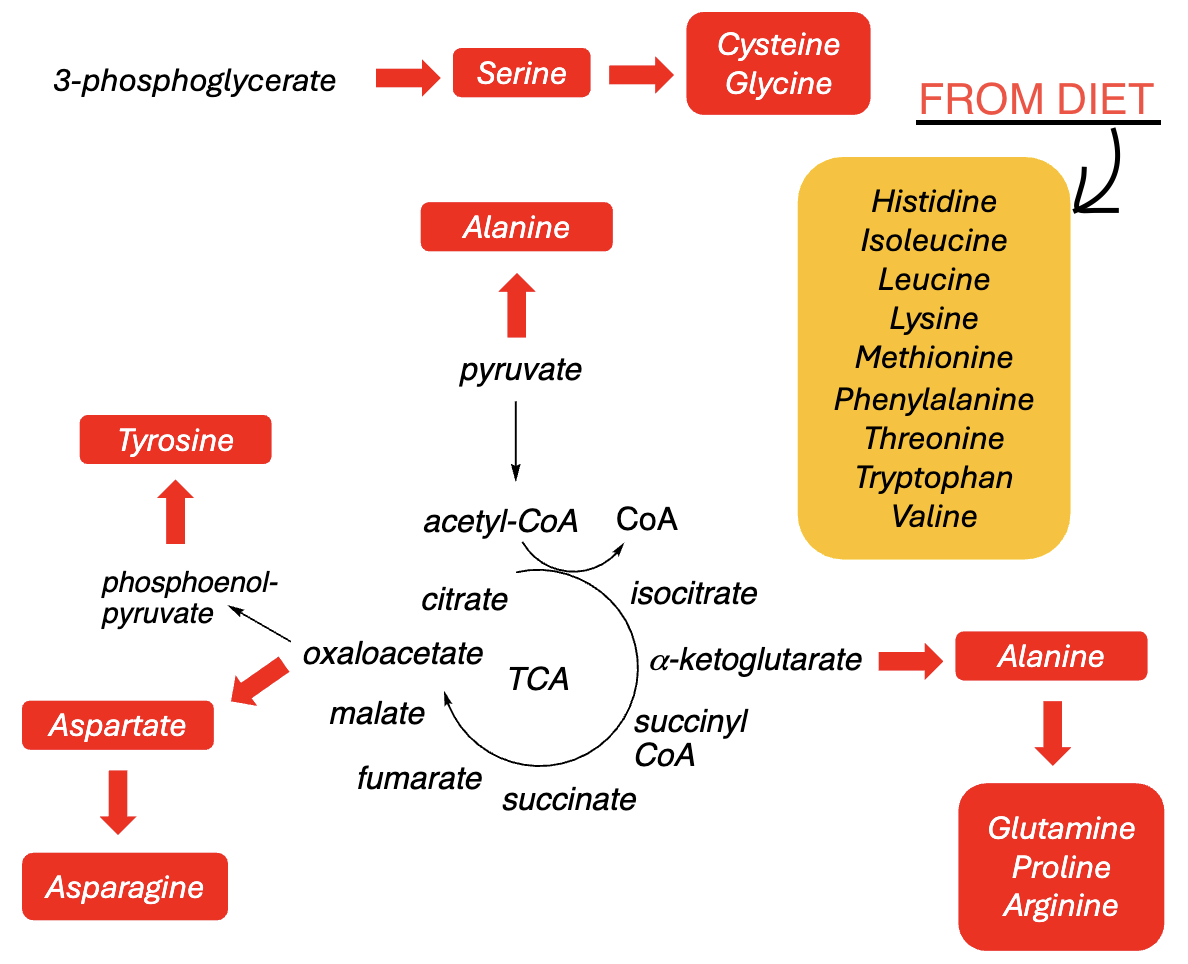
Amino Acid Synthesis:
• Humans can synthesize __ amino acids from _____ or _____ intermediates (amino _ comes from glutamate)
• The other _ are “essential” amino acids that must be obtained from the ____
11, TCA, glycolysis, N, 9, diet
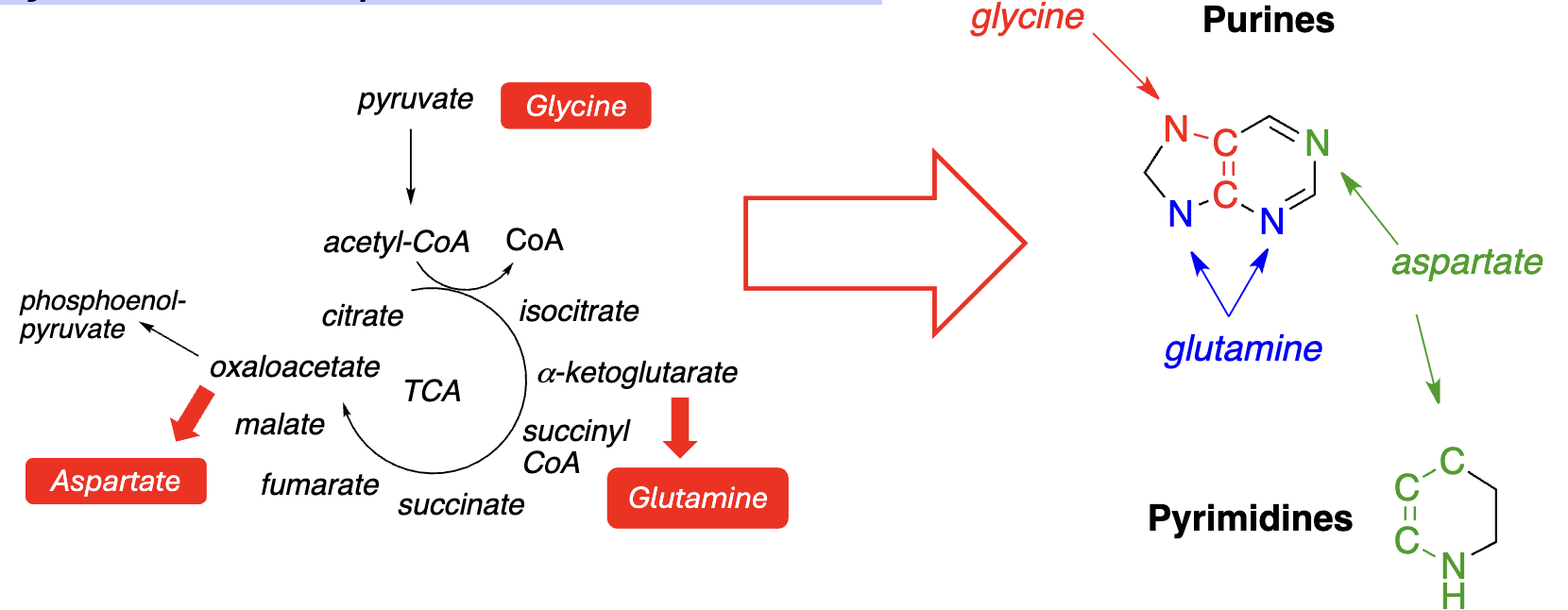
Purine & Pyrimidine Synthesis:
The ______ bases of nucleotides (purines & pyrimidines) are synthesized, in part, from amino acids
amine
STUDY
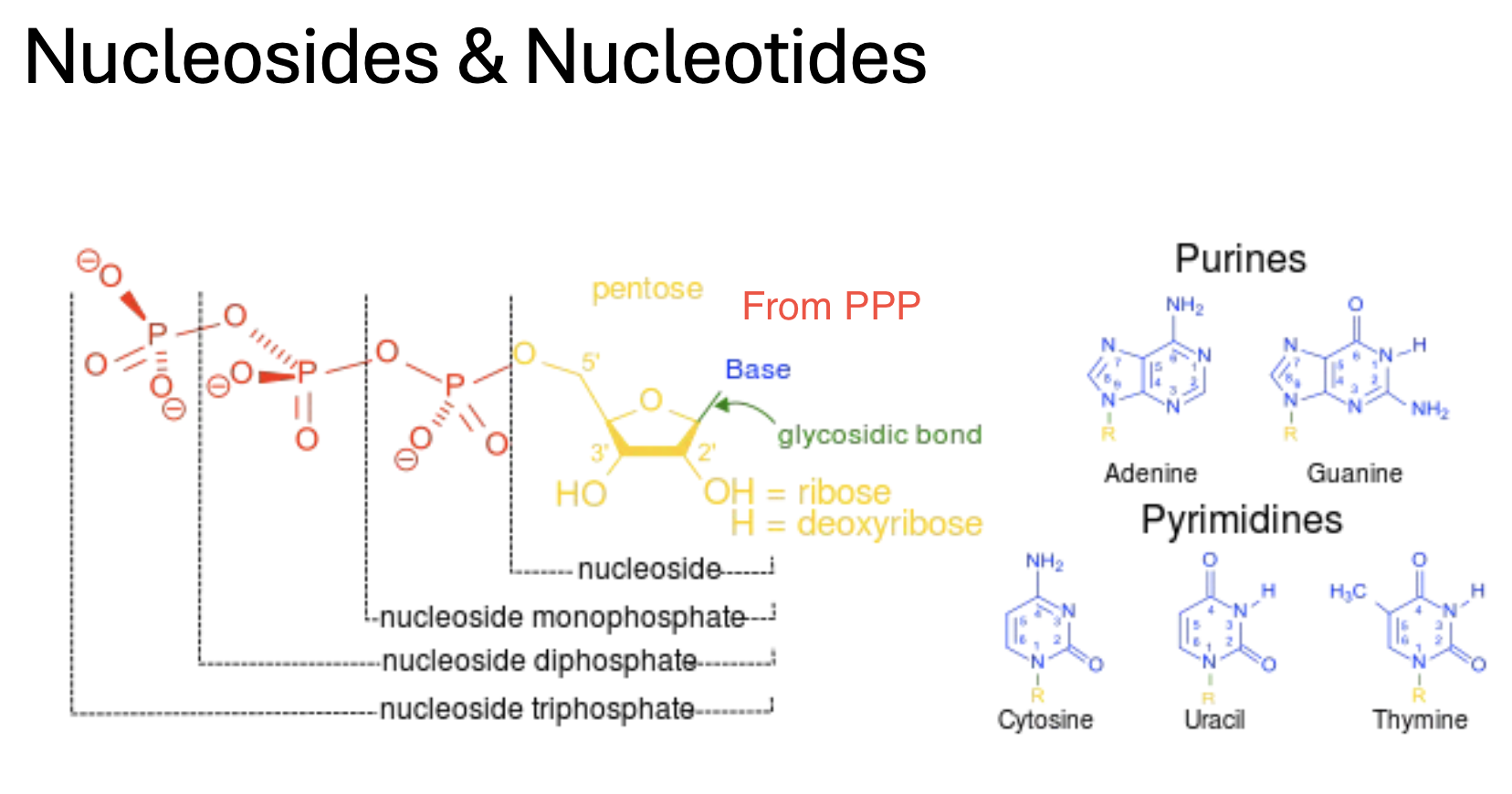
Amino acids are incorporated into ________ and ________
________ come from the PPP
Nucleic acids (DNA & RNAs) are synthesized from ________
...nucleic acids carry the “code” for ________
pyrimidines, purines, Ribose sugars, nucleotides, protein synthesis