IB BIOLOGY A1.2 NUCLEIC ACIDS
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Nucleic Acid
Polynucleotide chain of one two types; deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Genetic Code
The order of bases in DNA that determines the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide
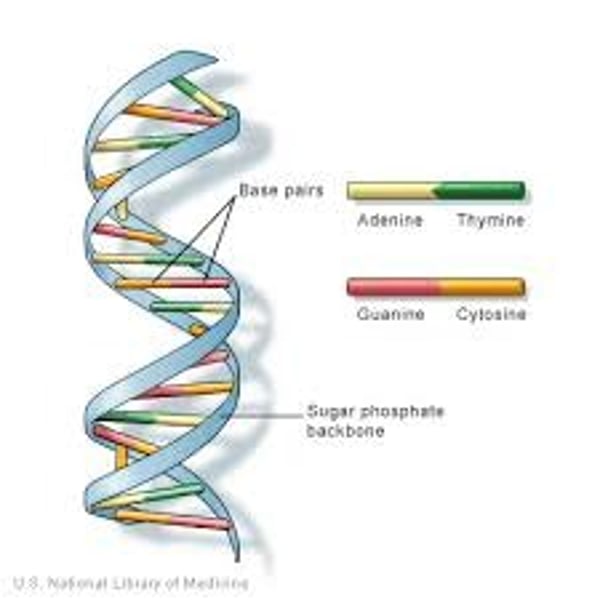
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
A form of nucleic acid consisting of two complementary chains of deoxyribonucleotide subunits, and containing the bases adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine.
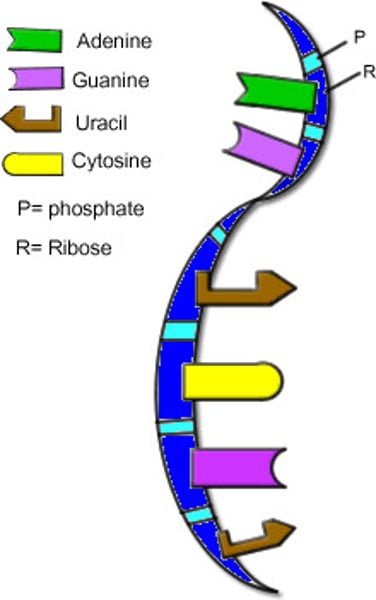
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
A form of nucleic acid containing the pentose sugar ribose, and the organic bases adenine, guanine, uracil and cytosine. SIngle stranded
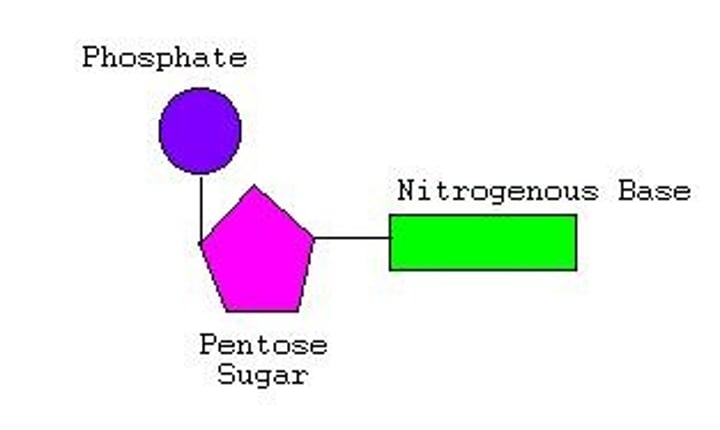
Nucleotide
Phosphate ester of the nucleoside - an organic base combined with pentose sugar and a phosphate (Pi)
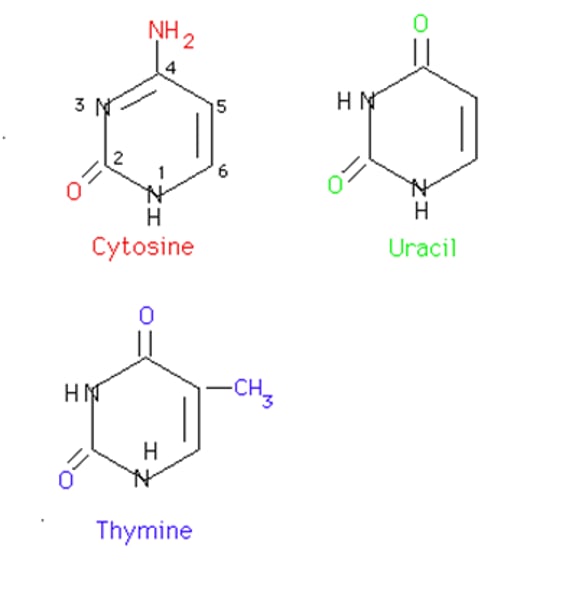
Cytosine
A pyrimidine nitrogenous base found in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) that pairs with guanine
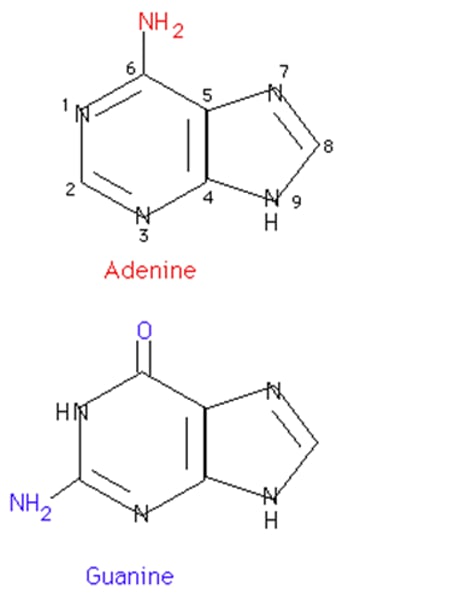
Guanine
A purine nitrogenous base found in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) that pairs with cytosine.
Adenine
A purine nitrogenous base, found in the coenzyme ATP and NADP and in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) that pairs with thymine.
Thymine
A pyrimidine nitrogenous base found DNA that pairs with adenine
Pentose
A 5 carbon monosaccharide sugar
Condensation
Formation of larger molecules involving the removal of water from smaller component molecules.
Purine
One of two types of chemical compound used to make nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA and RNA. EG. Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidine
One of two types of chemical compound used to make nucleotides. EG Cytosine, Thymine and Uracil.
Polynucleotide
A long, unbranched chain of nucleotides, as found in RNA and DNA
Codon
three consecutive bases which specify an amino acid
Uracil
A pyrimidine nitrogenous base found in RNA; pairs with adenine.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
a single-stranded RNA molecule formed during transcription
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Short lengths of RNA that combine with specific amino acids prior to protein synthesis
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Molecule that forms part of the protein-synthesising organelle known as the ribosome.
Phosphodiester bond
The linkage between the 3' carbon atom of of sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another. A type of covalent bond
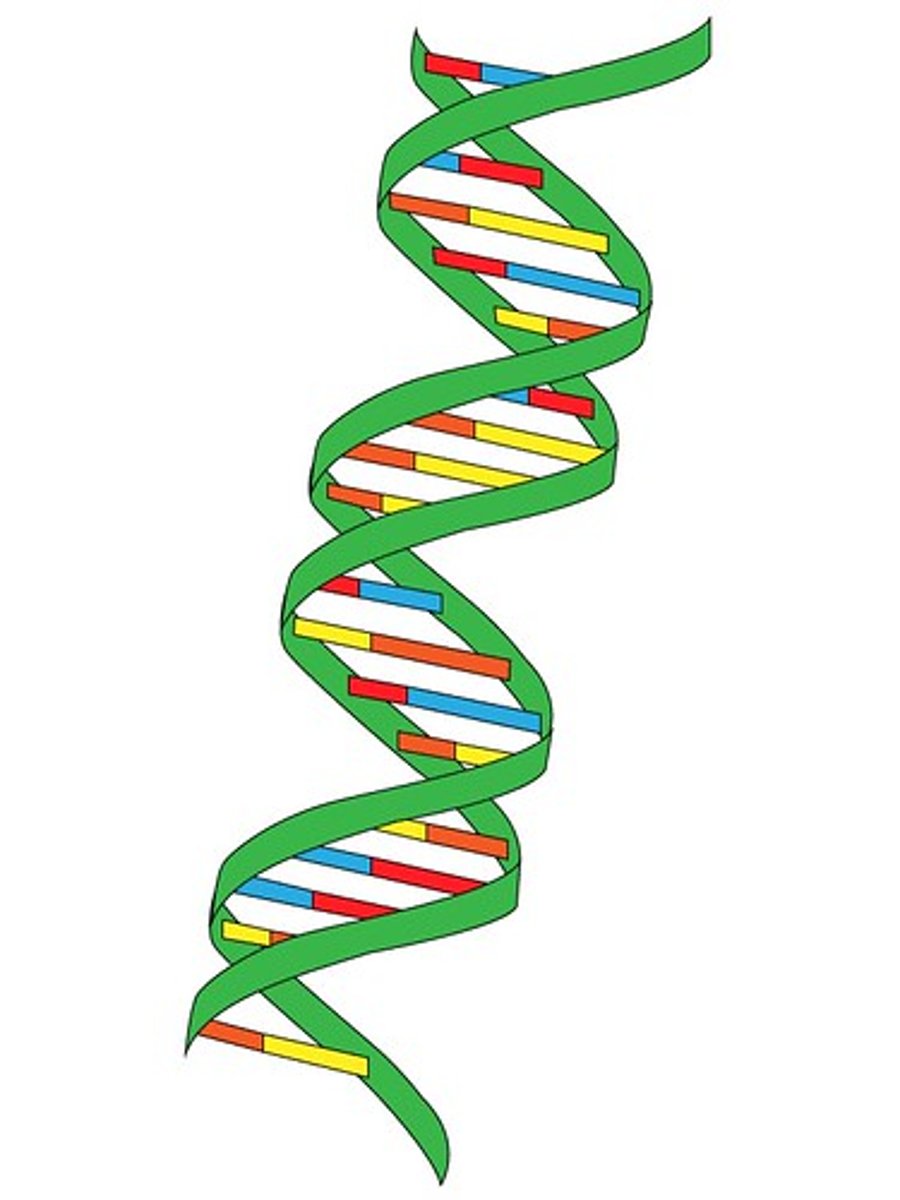
Double helix
Two interlocking helices joined by hydrogen bonds between the pairs of purine-pyrimidine bases.
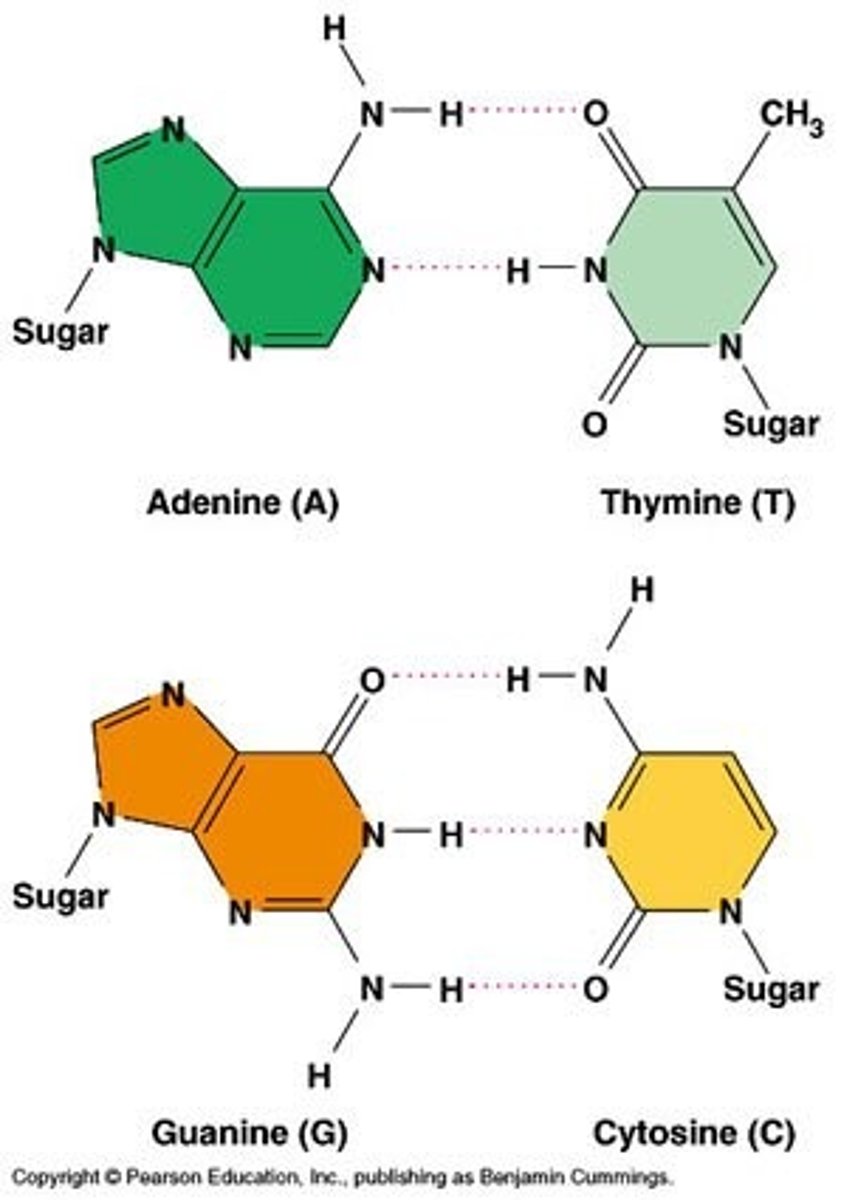
Complementary base paring
How nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids align with each other ie A-T/U and C-G. Complementary pairs are held together by hydrogen bonds.
Nucleosome (HL)
A sequence of DNA wound around 8 histone protein cores - a repeating unit of eukaryotic chromatin.
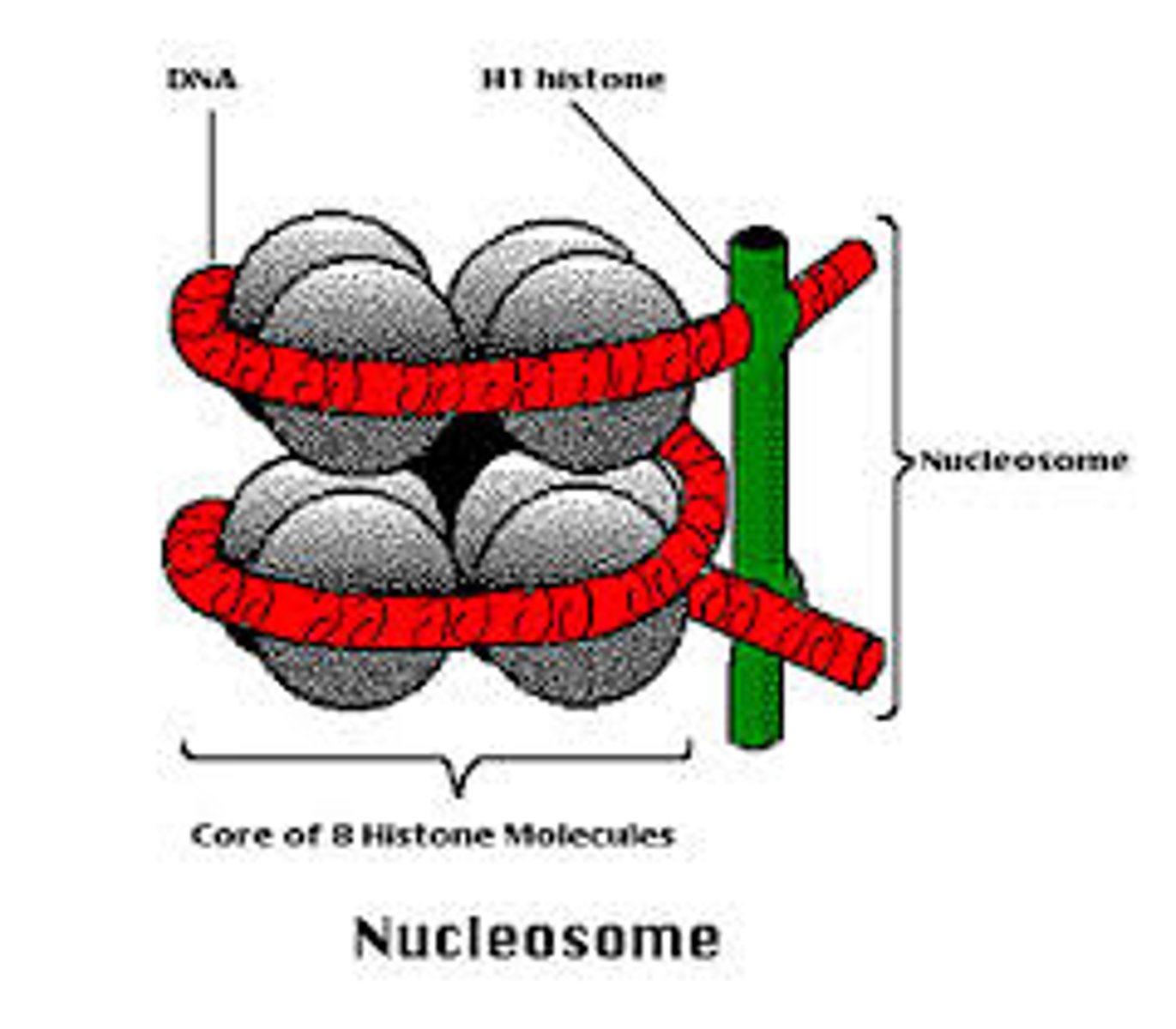
Histone (HL)
Protein that forms the scaffolding of chromosomes and us used un chromosome condensation to form nucleosomes.