RADT 142 - Week 10: Magnetism Study Guide
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is magnetism?
Charged particles in motion exhibit magnetism.
Ex.) Electrons-
What is magnetic domain?
Accumulation of many atomic magnets.
Electrons/particles need to be in motion to exhibit magnetism
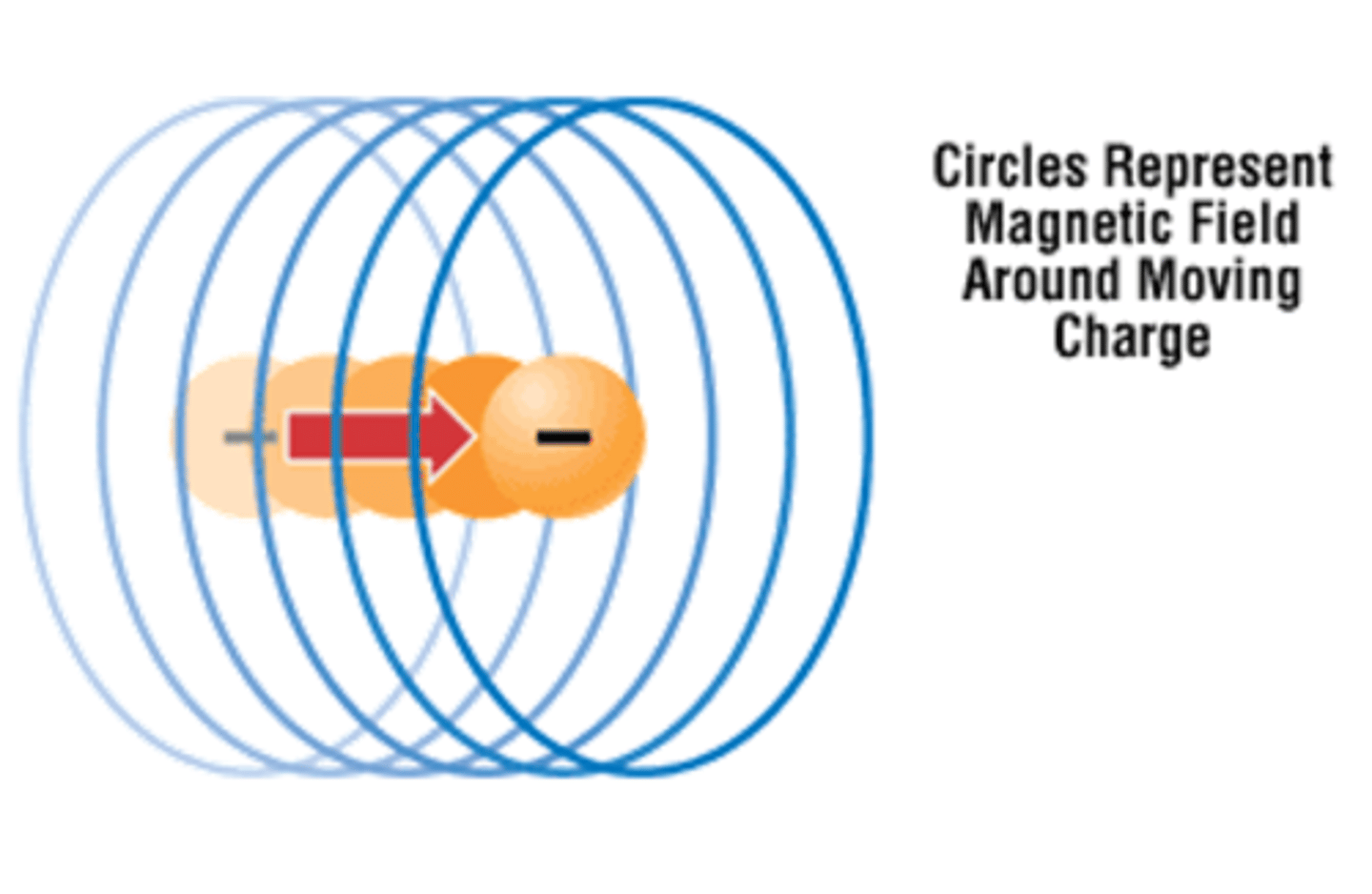
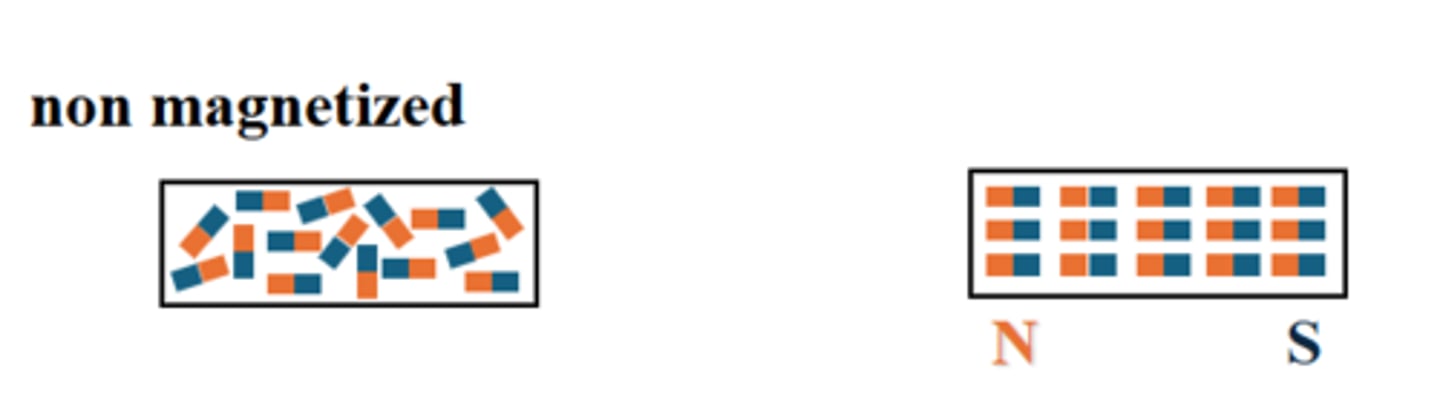
What is the nature of magnetism?
Magnetic materials are usually in a non-magnetized state where domains are in random arrangement
Random domains = No magnet
A _________is a small region within a material where the atoms all align with each other.
A magnetic domain is a small region within a material where the atoms all align with each other.
Domains align when a _____ is introduced.
Domains align when a magnetic field is introduced.
- Results in a magnetized material with a N to S orientation
- Effectively one North pole and one South pole

What are the SI units of Tesla (T) & Gauss (G)?
1 G = 1x10^-4 T or 0.0004 T
Tesla - MRI
They do not equal one another
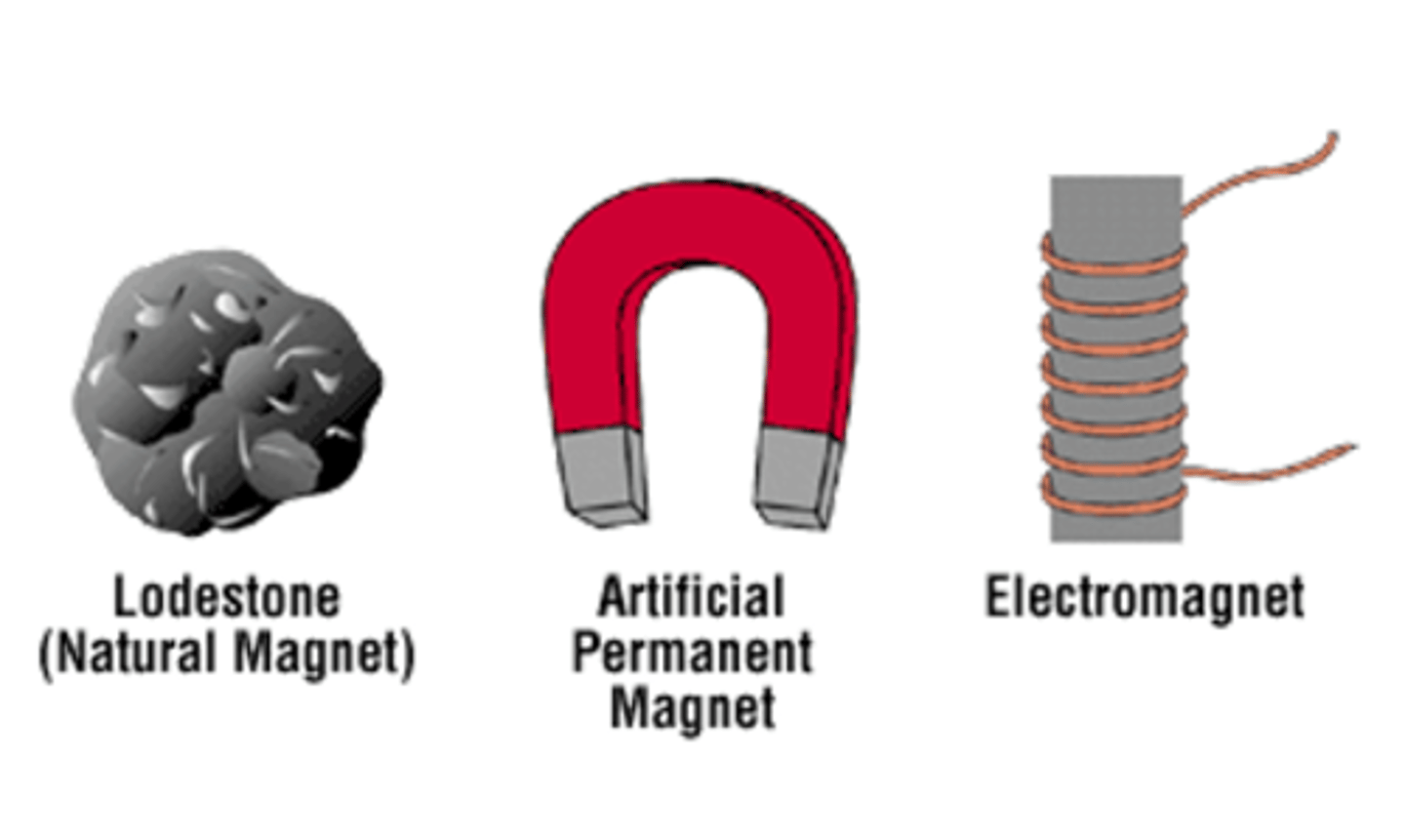
What are the 3 classifications of magnets?
1. Natural (found in nature)
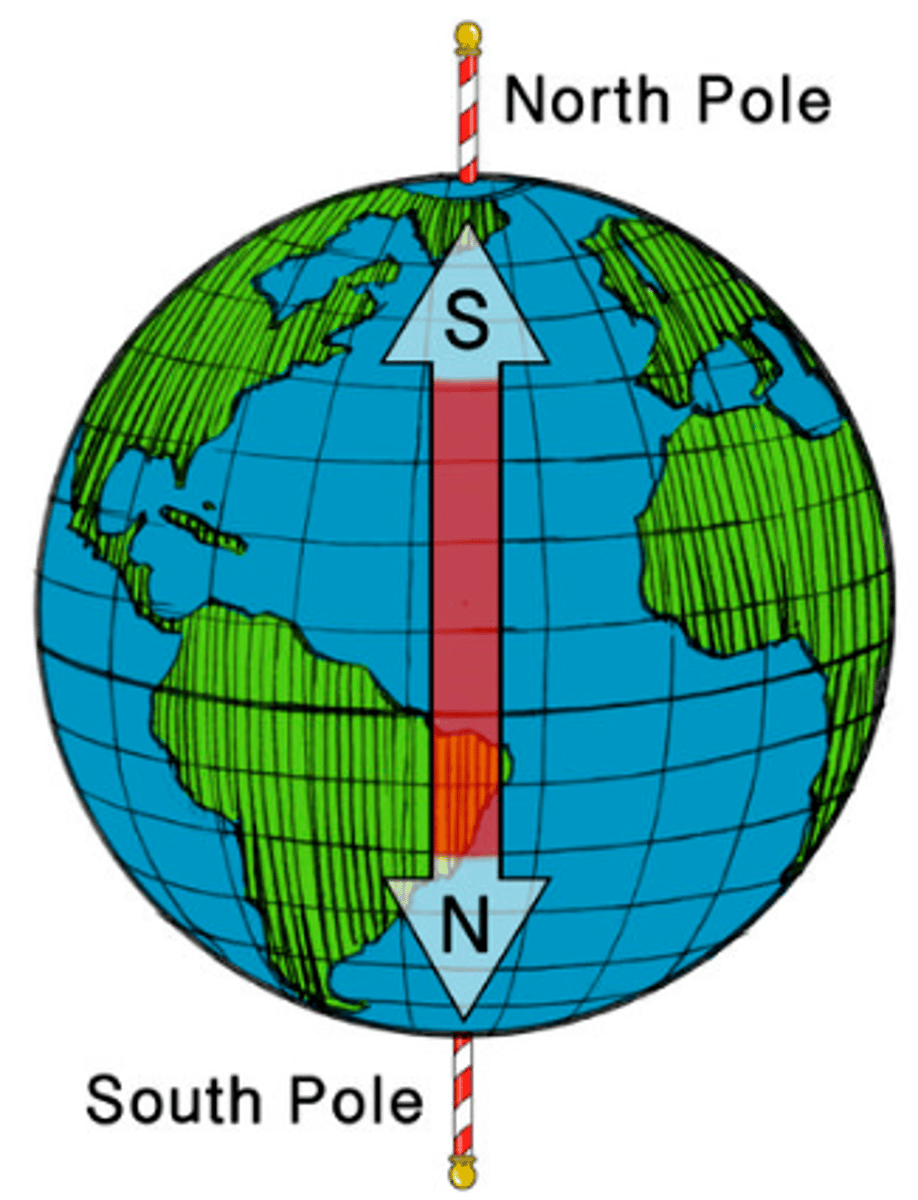
- Earth is dipole: has 2 poles (N & S)
- Magnetite (Iodoestone or Iron Oxide) is natural ore that exhibits magnetism
2. Artificial Magnets (man made)
- Hardened steel or alloy
- Compass
3. Electromagnetics (temporary)
- Created by a current of e- and iron core
The earth is _______. But is it a weak one or a strong one?
The earth is a magnet but a weak one.
What is permeability (susceptibility)?
How easily a material can be magnetized
High permeability → easy to magnetize
Low permeability → hard to magnetize.
What is retentivity?
The ability of a material to hold magnetization.
What is the relationship between permeability and retentivity?
Inversely related
What are the four magnetic classifications of matter?
1. Ferromagnetic: Materials that can be magnetized, exhibit strong magnetic properties and are strongly attracted to a magnet.
Ferromagnetic ability goes up, the strength of the magnet goes up. direct relationship
2. Paramagnetic: Materials that are only weakly attracted to a magnetic field and loosely influenced by a magnetic field.
3. Diamagnetic: Materials that are weakly repelled by a magnetic field, cannot be magnetized, and are not attracted to a magnet.
Most elements in periodic table are diamagnetic like silver and gold
Silver & gold are not attracted to magnets
4. Nonmagnetic: Materials that are unaffected by a magnetic field
What is the magnetic force field?
Lines of force (magnetic flux lines)
Direction:
N→S outside the magnet
S→N inside the magnet
Form a closed loop
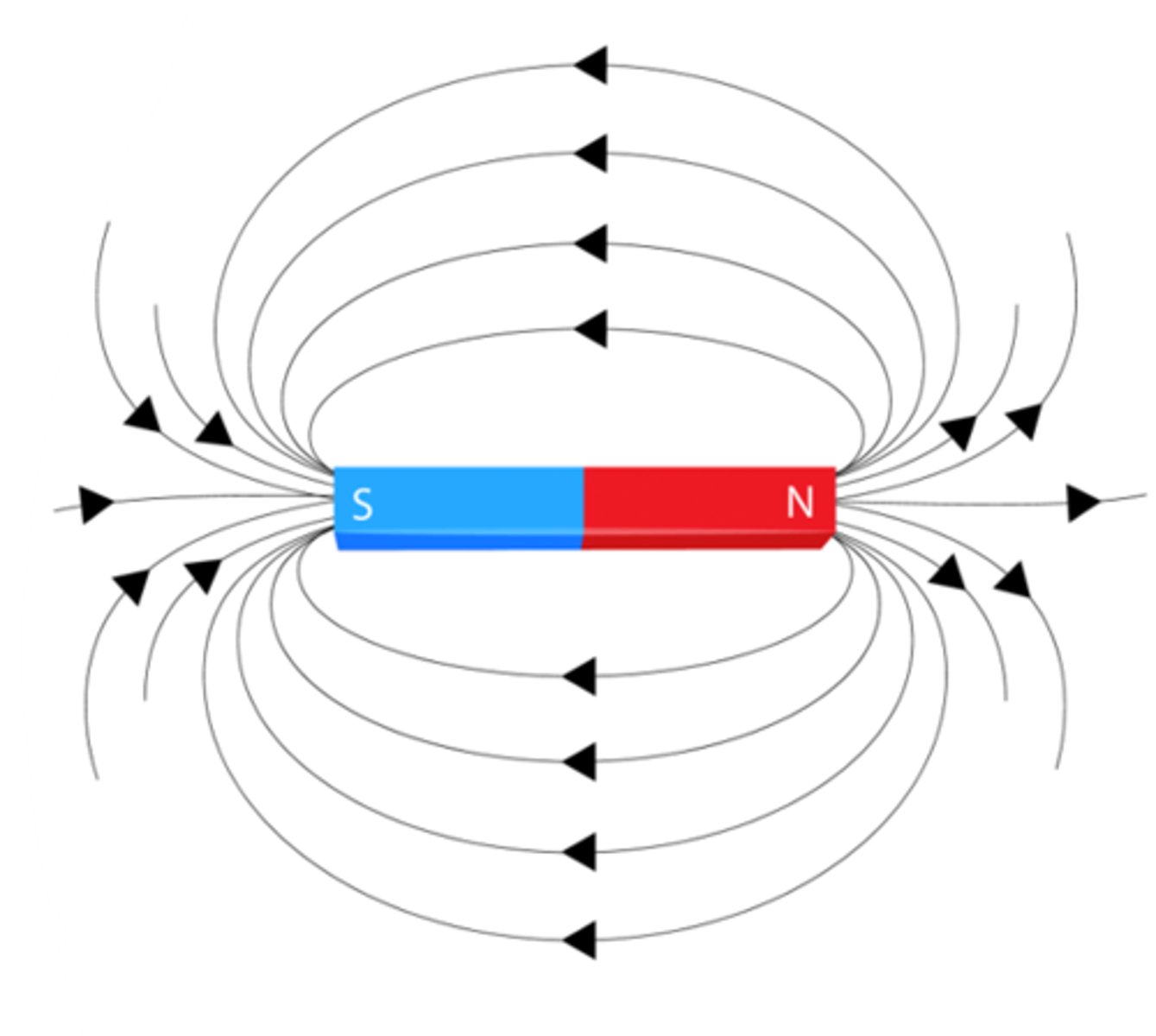
What is magnetic field?
Field lines pass through both magnetic & non-magnetic materials.
concentrated by magnetic materials
unaffected by non-magnetic materials
**Blue highlighted represents the green line in the image**
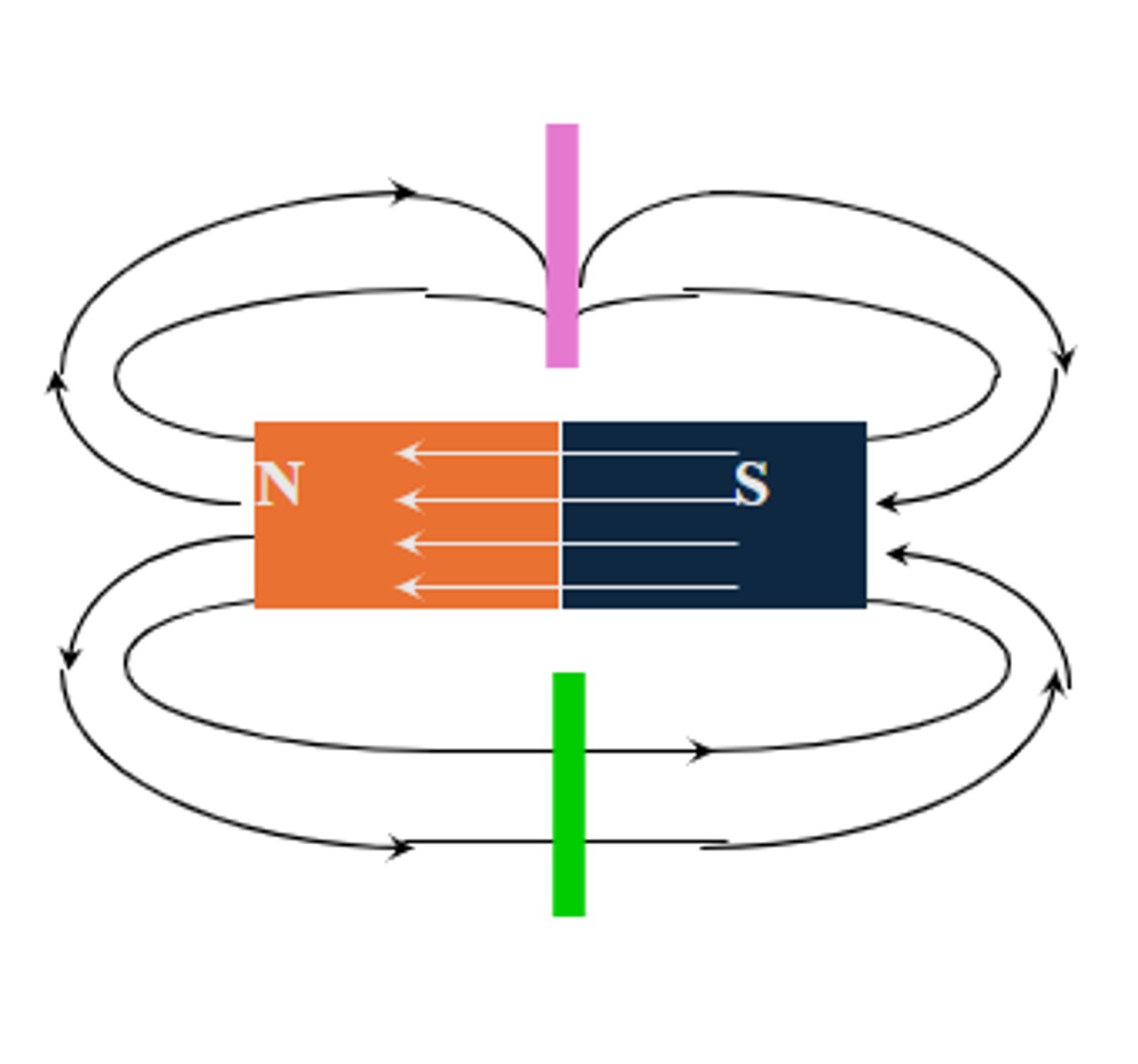
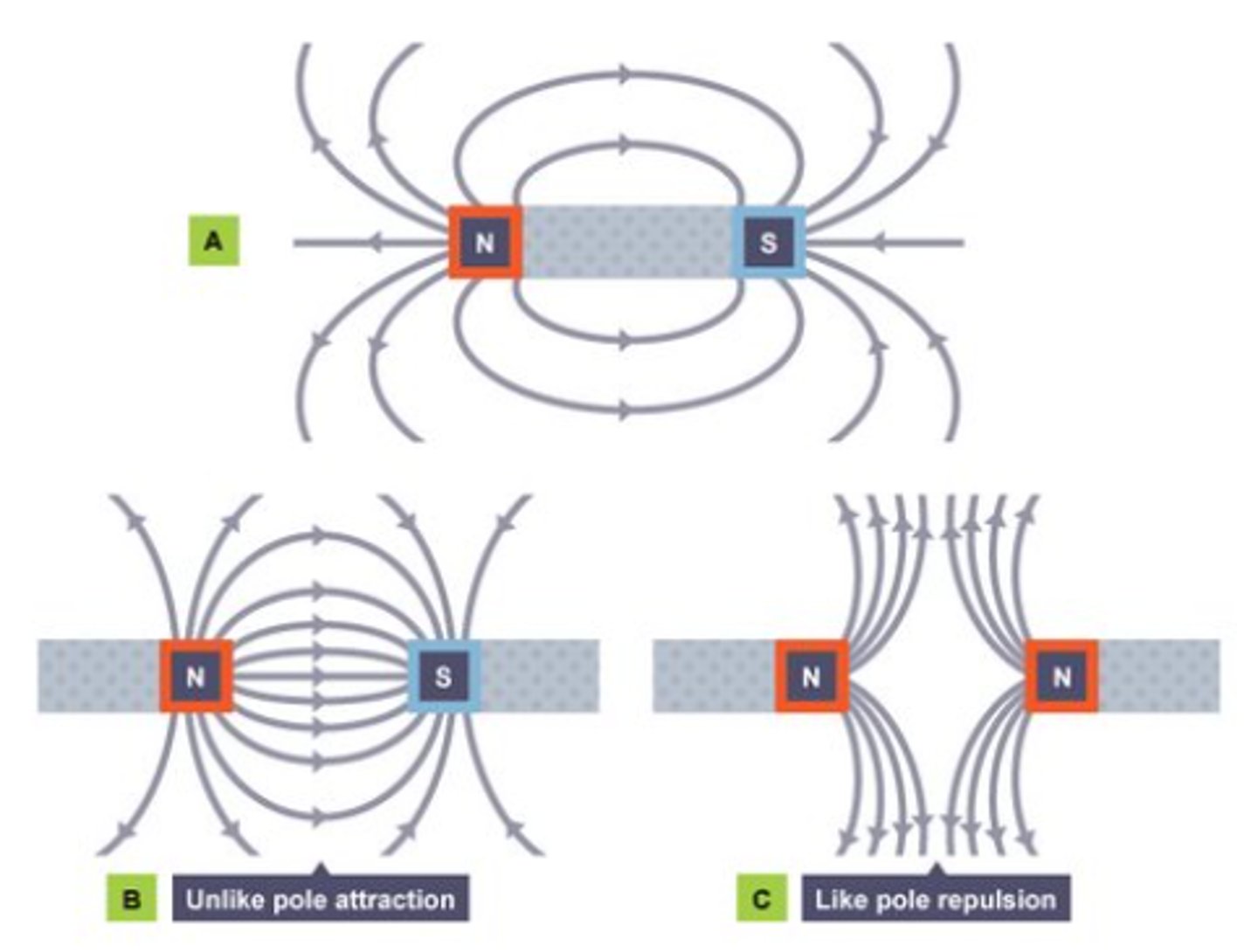
What is the Law of Magnetism?
Every magnet has two poles. Designated N & S.
What is magnetic law #2?
Like poles repel, unlike poles attract.
Attraction: When opposite magnetic poles are brought near each other — North (N) → South (S) — they pull together.
Repulsion: When like poles are brought near each other — North (N) → North (N) or South (S) → South (S) — they push apart.
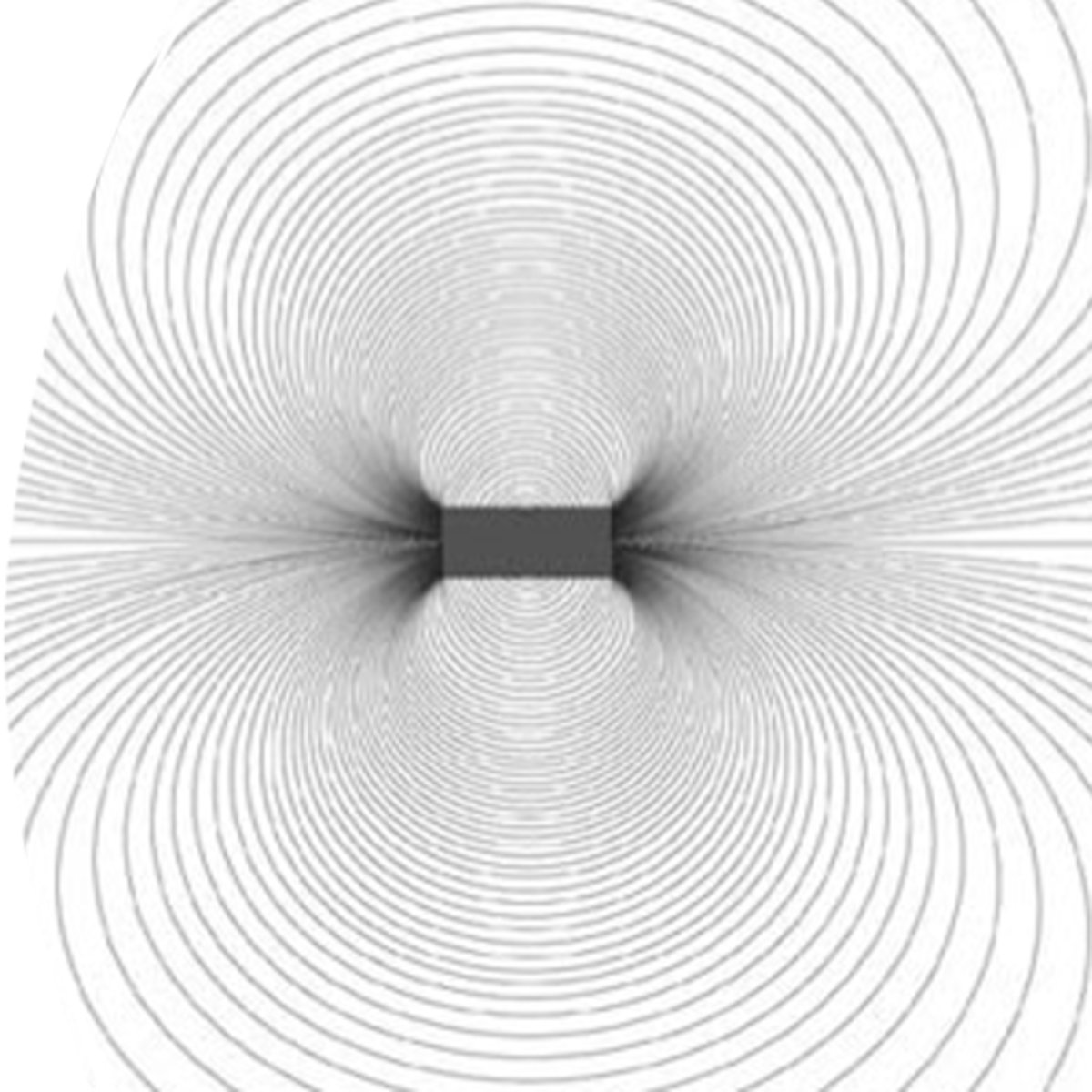
What determines the strength of magnetism?
The number of field lines per unit area.
More lines means it's a stronger field closer to the source.
Less lines means weaker field further from the source.
How do you create a magnet?
By stroking an iron bar repeatedly with a magnet.
Iron has high permeability and can easily turn into a magnet. It also has low retentivity and loses its magnetism quickly.
permeability & retentivity relationship - inversely proportional