Bio 1220 Practical II
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Gametophyte (haploid)
produces gametes
stage they spend most of their time
Sporophyte (diploid)
produces spores
Hepaticophyta (Liverworts)
gametophyte dominant
Bryophyta (Mosses)
gametophyte dominant
Lycophyta (Club Mosses)
Sporophyte dominant (2n)
Psilotophyta (Whisk Fern)
Sporophyte dominant (2n)
Sphenophyta (Horsetails)
Sporophyte dominant (2n)
Pteridophyta (Ferns)
Sporophyte dominant (2n)
Gymnosperms (Seed Plants)
Sporophyte dominant (2n)
Saprophytic
obtains nutrients from dead organisms (most fungi)
Mucoromycota
Mostly soil dwelling saprophytes
Example: Bread and fruit mold, rhizopus
To sexually reproduce, they form
diploid zygospores in the
zygosporangium that will
undergo meiosis yielding haploid
zygomycete spores
Basidiomycota
Mainly saprophytic species
Reproduce sexually via the formation of
specialized club-shaped cells called a
basidium that bear basidiospores
Example: mushrooms, toadstools,
puffballs, shelf fungi, and rusts
Ascomycota
Largest fungal group
• Example: morels, molds, lichens,
truffles and single celled yeasts
• The defining feature of this group is
the ascocarp which contain the
ascus, a microscopic sexual
structure in which ascospores are
formed
Lichen
Crustose: flat
Foliose: flat with leaf like lobes
Fruticose: bushy or shrub like
Mutualistic symbiotic relationship between
cyanobacteria or green algae and a fungus
(Ascomycota)
Taphrina deformans
parasitic fungus infects peach trees causing “leaf curl disease”
sycamore trees parasitic fungus
Anthracnose fungi
Cordyceps
“mind control” ascomycota
Ectoderm
skin and nervous system
Mesoderm
muscles, connective tissue, skeleton, kidneys, circulatory and reproductive organs
Endoderm
lining of the gut and major organs derived from it
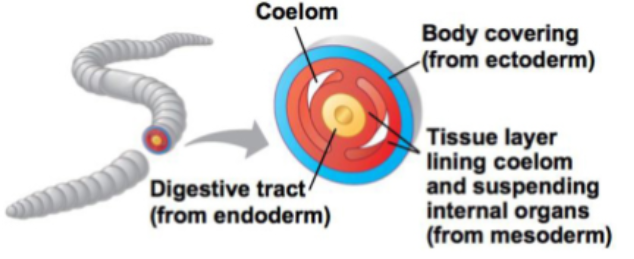
Acoelomate

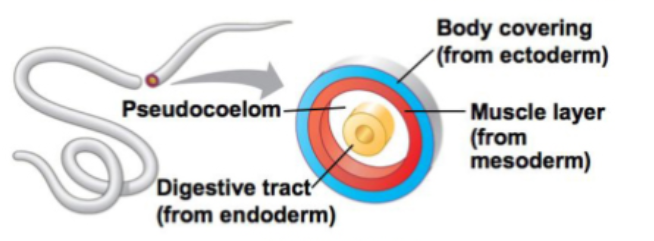
Pseudocoelomate

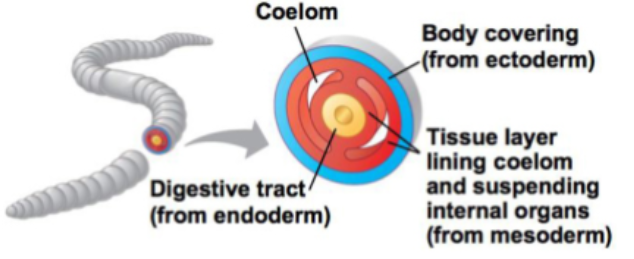
Eucoelomate

Fertilization
egg (n) and sperm (n) unite to form a diploid zygote (2n)
• n = one set of chromosomes
• 2n = two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent)
Gametes
are produced in the gonads via meiosis
Protostomes
Develops mouth before anus as an embryo
Deuterostomes
Develops anus before mouth as an embryo
Porifera
Sponges, lack tissues, are sessile (immobile) filter feeders
Cnidaria
(jellies, coral, anemones) Radial symmetry, diploblastic (2 tissue layers) = Ectoderm and Endoderm
Possess muscle & nerve tissue = they can
move! Have tentacles with cnidocytes (stinging cells)
that are used to capture prey
Protostome traits
bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, organ systems, cephalization
2 lineages of protostomes
Lophotrochozoa (flatworms, earthworms, leeches, mollusks) and Ecdysozoa (Nematoda and Arthropoda)
Platyhelminthe
Flatworms (lophotrochozoan), acoelomate, incomplete digestive system (except tapeworms)
Three groups of Platyhelminthes
Free living planarians, parasitic flukes, and parasitic tapeworms
Annelida
Segmented worms (Lophotrochozoa), Eucoelomates, complete one-way digestive tract, metameric (segmented) body
3 groups of annelids?
Terrestrial earthworms, leeches, and marine polychaetae worms
Mollusca
Mollusks (lophotrochzoans), Eucoelomate, Complete digestive tract (alimentary canal), Many possess a tongue-like structure with rows of teeth, called a radula (Except for bivalves which filter feed)
Ventral region mollusks
(underside) forms a muscular foot (arms & tentacles
in cephalopods)
Dorsal region mollusk
(top) forms into a soft mantle (folds around mantle
cavity where organs are); the mantle is surrounded by a shell (in
some organisms
4 main groups of mollusks
Chitons, gastropods (snails & slugs),bivalves (oysters & clams), cephalopods (squid & octopuses).
Incomplete metamorphosis
Juvenile stages resemble adults,
differing only in size and sexual maturity
Complete metamorphosis
Organisms undergo dramatic
transformations in form and ecology as they move from the juvenile (larval) stages to adult stages
Ecdysozoans
Grow by ecydysis (process of molting) an exoskeleton/cuticle (support and protection, but it’s not
composed of living tissue, so it does not grow and expand with
the organism, which is why they shed)
•have a three-layered cuticle
Nematoda
Nematodes or Roundworms (ecdysozoans), Pseudocoelom & complete digestive tract
Arthropod
Arthropods (ecdysozoans): includes insects, chelicerates (scorpions, spiders, ticks), myriapods (centipedes,
millipedes), and crustaceans Growth by ecdysis, Characterized by jointed limbs, Cuticle (exoskeleton) made of chitin
Tagmata
Body segments, each with a pair of appendages
4 subphyla of arthropoda
Chelicerates, myriapods, crustaceans, and insects
Chelicerates
Horseshoe crabs, spiders, ticks, mites, and scorpions, Ancient, Have 2 tagma (Cephalothorax
Abdomen)
• Have 6 pairs of appendages
• 1 pair of fanged chelicerae—feeding, defense, copulation,
movement, sensory reception
• 1 pair of pedipalps
• 4 pairs of walking legs
Myriapoda
Millipedes and centipedes, 2 tagma: head and trunk, Paired appendages per trunk segment, Centipedes are Carnivorous and often poisonous (1 pair of walking legs per segment), Millipedes are detritivores (two pairs of walking legs per segement)
Crustacea
Lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, crabs, water fleas,
isopods (woodlice), and barnacles. tagma: cephalothorax and abdomen, Unique in that they have 2 pairs of antennae
Insecta
Beetles, grasshoppers, butterflies, bees, flies,
cockroaches, ect. Most abundant and diverse 3 tagma: Head Thorax and Abdomen, 3 pairs of walking legs and Usually have 2 pairs of wings
Antennules crayfish
sensory functions, touch, smell, balance
somites crayfish
body segments
swimerettes crayfish
used for swimming, carry (and aerate) eggs in females, and help circulate water past gills
uropods crayfish
rudders and backwards swimming
telson crayfish
forms tailfan w/ uropods, has anus, backwards swimming
pyloric stomach
second part of digestive system, food is further filtered and digested
cardiac stomach
the initial, anterior part of the stomach where food is stored and mechanically ground by a gastric mill with calcified teeth
green glands
aka antennal glands, are the excretory organs of crayfish that function like kidneys to filter waste from the blood and maintain water/salt balance
gastric mill
grinding apparatus in a crayfish's stomach that uses a system of hard, ossified teeth to crush and break down food into smaller particles for digestion
Deuterostomes
triploblastic, eucoelmate, and bilaterally symmetric
Gastrulation
cells migrate to form the three
tissue layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm)
Neurulation
Leads to development of the nervous system
(a neural tube is formed that eventually becomes the brain
and spinal cord)
Two groups of deuterostomes
Chordates and echinoderms
Echinodermata
As adults, bodies are radially symmetrical
Larval forms are bilaterally symmetrical
Most have “spines” extending from their body (projections of
internal endoskeleton)—endoskeleton is not bone, it’s calcium
carbonate
Echino = “spiny”
Derm = “skin”
Water-vascular system (series of internal water-filled canals
that end in structures called tube feet) used for movement
Trace the path of water through the water vascular
system
madreporite → ring canal → radial canals →
ampullae → tube feet
4 key characteristics of Chordata
1. Notochord—forms part of vertebral column
2. Dorsal hollow nerve cord—becomes brain & spinal cord
3. Pharyngeal gill slits—become openings to the outside of the body
for gas exchange (only seen during embryonic development for
terrestrial vertebrates)
4. Post-anal tail—a tail, posterior to the anus (in apes and humans, this
is only seen during embryonic development)
Urochordata
Tunicates (chordata)
Sessile (immobile) marine organisms
Examples: Sea squirts and salps
Cephlacordata
(chordata)
Lancelets: small, elongated “fish-like” marine
invertebrates w/ a complete digestive system that lack jaws and sense organs
Adults wriggle into the sand, leaving only its
anterior (front) end exposed
Chondrichthyes
Cartilaginous fishes (ex: sharks and rays)
Vertebral column made of cartilage (not bone)
Notochord
forms vertebral column (surrounds spinal
cord)
3 chordate subphylas
Urochordata [invertebrates] Cephalochordata [invertebrates] Vertebrata [vertebrates]
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Dorsal hollow nerve cord (Chordata)
forms spinal cord and brain
Pharyngeal pouches form
Aquatic: open into gill slits = gills (gas exchange organ) Terrestrial: gill slits do not form after pharyngeal pouches form (vestigial trait—no function)
Post-anal tail
lost in some species
Families/Classes:
Chordata families/classes
• Myxinoidea
• Petromyzontoidea
• Chondrichthyes
• Actinopterygii
• Amphibia
• Reptilia
• Mammalia
Myxinoidea
hagfish, No vertebral column, has skull, slime defense mechanism—slime repels
other scavengers when a hagfish is feeding
Petromyzontoidea
Lampreys
Skull and vertebral column
Parasitic
Two families of jawless fish
Myxinoidea and Petromyzontoidea
Two families of jawed fish
Actinopterygii and Chondrichthyes
Actinopterygii
Ray-finned fishes
Bone
Operculum (bony flap that covers and
protects the gills)
Tetrapods (3)
amphibia, reptilian, mammalian