Electromagnetic Spectrum (Yr 9)
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
EM Spectrum
The collection of all the EM (electromagnetic) waves.
Similarities of EM Waves:
They can all travel through a vacuum
They all travel at the same speed in a vacuum
They are all transverse waves.
Differences of EM Waves:
Different wavelengths
Different frequencies
Different energies
EM Spectrum: (Increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength L to R)
Radio, Microwave, Infrared, Visible light, Ultraviolet, X-Ray, Gamma
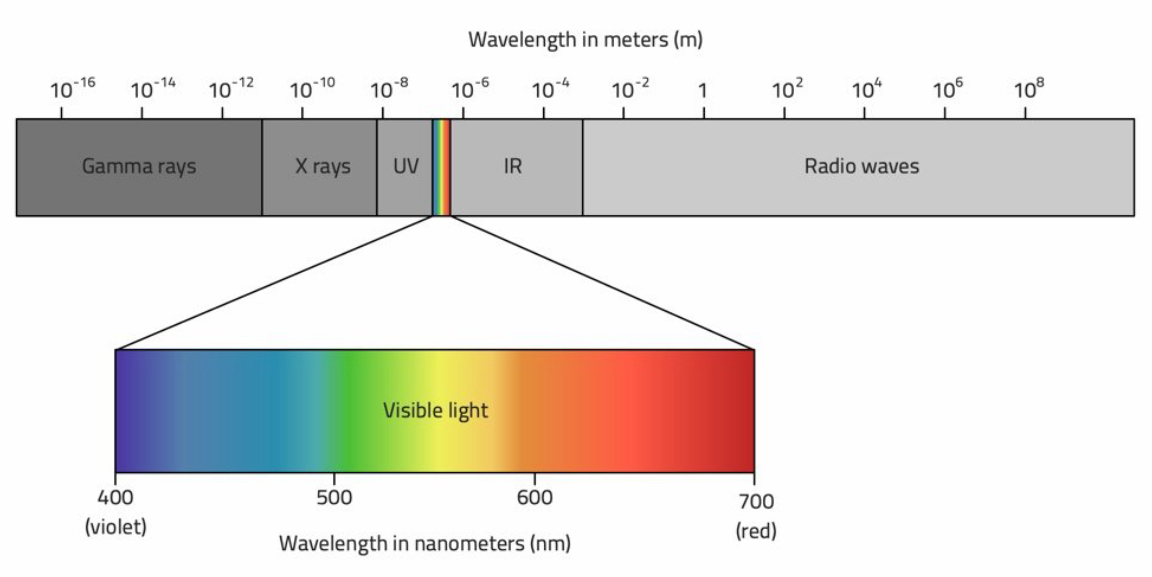
Visible Light Spectrum: (Increasing Frequency)
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet
Uses of each wave:
Radio - Communication, TV and radio signals.
Microwave - Satellite communication, Cooking
Infrared - Cooking, Heaters, Thermal Imaging
Visible - Fibre optic communication, Endoscopes
Ultraviolet - Fluorescent lamps, Tanning
X-Rays - Medical imaging of body
Gamma - Sterilising food/medical equipment
Dangers of each wave:
Radio - No proven dangers
Microwave - Heating of internal tissue
Infrared - Skin burns
Visible - Damage to retina
Ultraviolet - Skin cancer, damage to eyes
X-Rays - Cancer
Gamma - Cancer
Key Wavelengths:
Radio - Metres
Microwaves - Millimetres/Centimetres
Visible Light - 700 nanometres to 400 nanometres (1nm = 10(-9))
X-Rays - 10(-10) metres