Metabolic Rate & Temperature Regulation
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 7: Tuesday, October 7th: Review & Midterm Exam 1; Thursday, October 9th: Endocrine Glands & Dysfunction: The Thyroid Gland (cont.); Week 9: Tuesday, October 21st: Metabolic Rate & Temperature Regulation (cont.); Thursday, October 23rd: Growth
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
the following are _______ effects of the thyroid gland:
metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
basal metabolic rate (how quickly our body metabolized energy at rest/baseline)
temperature
growth and nature
physiological
effector organs of the hypothalamus, which all have thyroid receptors, are (5 in total):
bones, the brain, nerves, the heart, and body cells
pressure on the eyes that causes bulging, and excessive thyroid hormone in the blood describes _______
exophthalmos
_______ is also known as hypothyroidism, and has the following characteristics:
. metabolic dysregulation
an autoimmune disease
High basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Increased sweating
Weight loss
Graves’s disease
_______ is also known as hyperthyroidism, and has the following characteristics:
1. Still causes goiter
metabolic dysregulation
low basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Decreased sweating
Weight gain
Hashimoto’s disease
in 1814, Gay-Lussac discovered that _______ deficiency caused goiter, so he fed those with the disease seaweed and marine products
iodine (I2)
in 1895, Kocher found high amounts of iodine (I2) in the _______
thyroid gland
in 1918, Kendall found and named _______, which has four iodine atoms bound to a tyrosine
thyroxine/tetraiodothyronine (T4)
in 1952, Gross and Pitt-Rivers found and named _______, a more active form of thyroid hormones that has three iodine atoms bound to a tyrosine
triiodothyronine (T3)
_______ can remove iodine form tetraiodothyronine (T4) to create triiodothyronine (T3)
Deionodases
the thyrid gland developed from the embyro’s _______
digestive tube
true or false: if the thyroid gland weighs more than 20g, this indicates a thyroid disease
true
the thyriod gland communicates and delivers hormones via
large sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves, and blood and lymph
_______ are special cuboidal/columnar epithelial cells in the thyroid gland that make T3 and T4
thryoid follicles
the lumen around each thyroid follice cell is filled with a glycoprotein colloid called _______
thyrogobulin (TG)
_______ produce calcitonin, which is involved in calcium homeostasis
parafollicular c cells
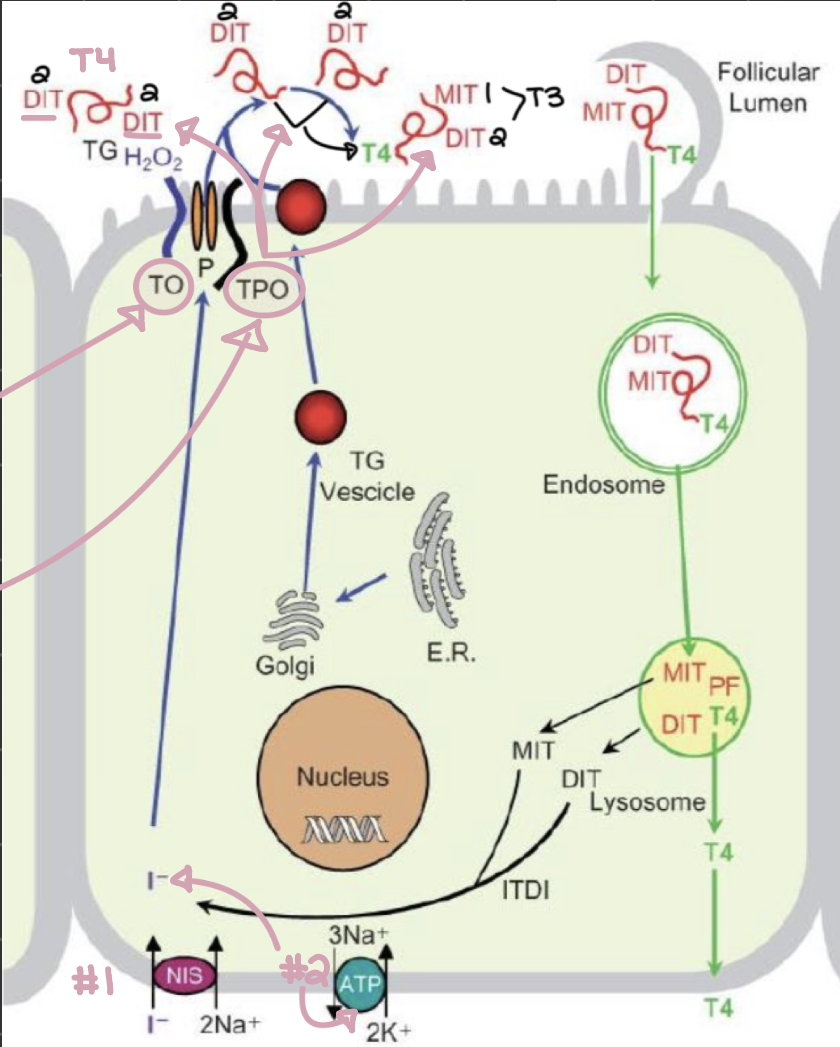
describe the process of thyroid hormome secretion, starting with iodide entering the cell:
iodide (I-) enters the cell bound to _______
The cell charge changes once I- enters, _______ out, and _______ in
I- is oxidized by _______ to become I²
_______ attaches I² to Thyroglobulin (TG)
triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4) are produced from _______ and _______
_______ binds to these cells to release triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4)
Na+
Na+, K+
thyrooxidase (TO)
thyroid peroxidase (TPO)
diiodotyrosine (DIT), monoiodotyrosine (MIT)
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
_______ stimulates T3 and T4 production
TSH
T3 and T4 are lipid soluble, but they reqiure _______ receptors to enter cells and control when they can enter
transmembrane
_______ is the thyroid hormone that can enter the nucleus because its the actice form
T3
when hormones levels are too high, T3 will turn off the anterior pituitary to stop TSH, which is a _______ negative feedback
direct
when hormones levels are too high, T3 will turn off the hypothalamus to stop TRH, which is an _______ negative feedback
indirect
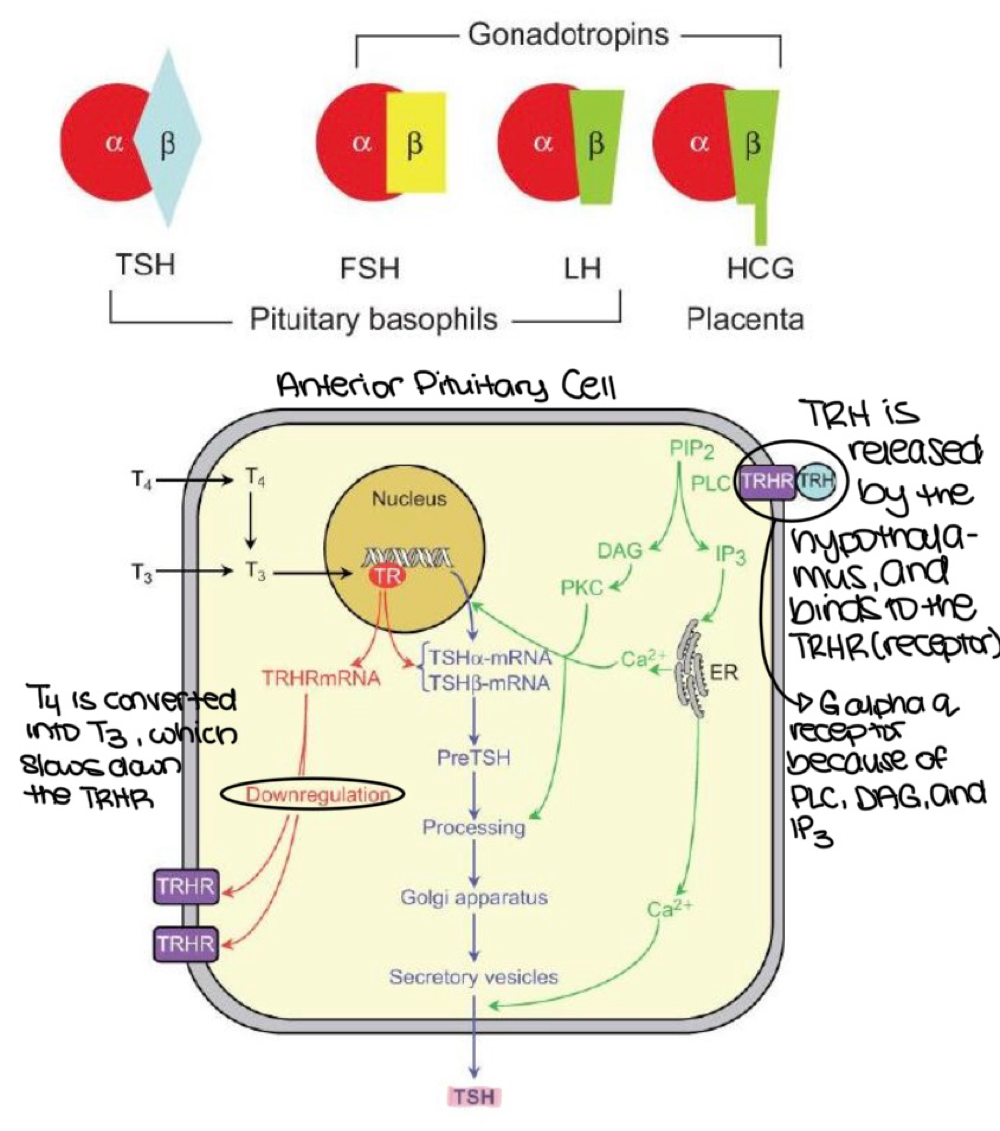
TRHR (TRH receptor), which is located on anterior pituitary cells, is what type of G-protein receptor?
G alpha q
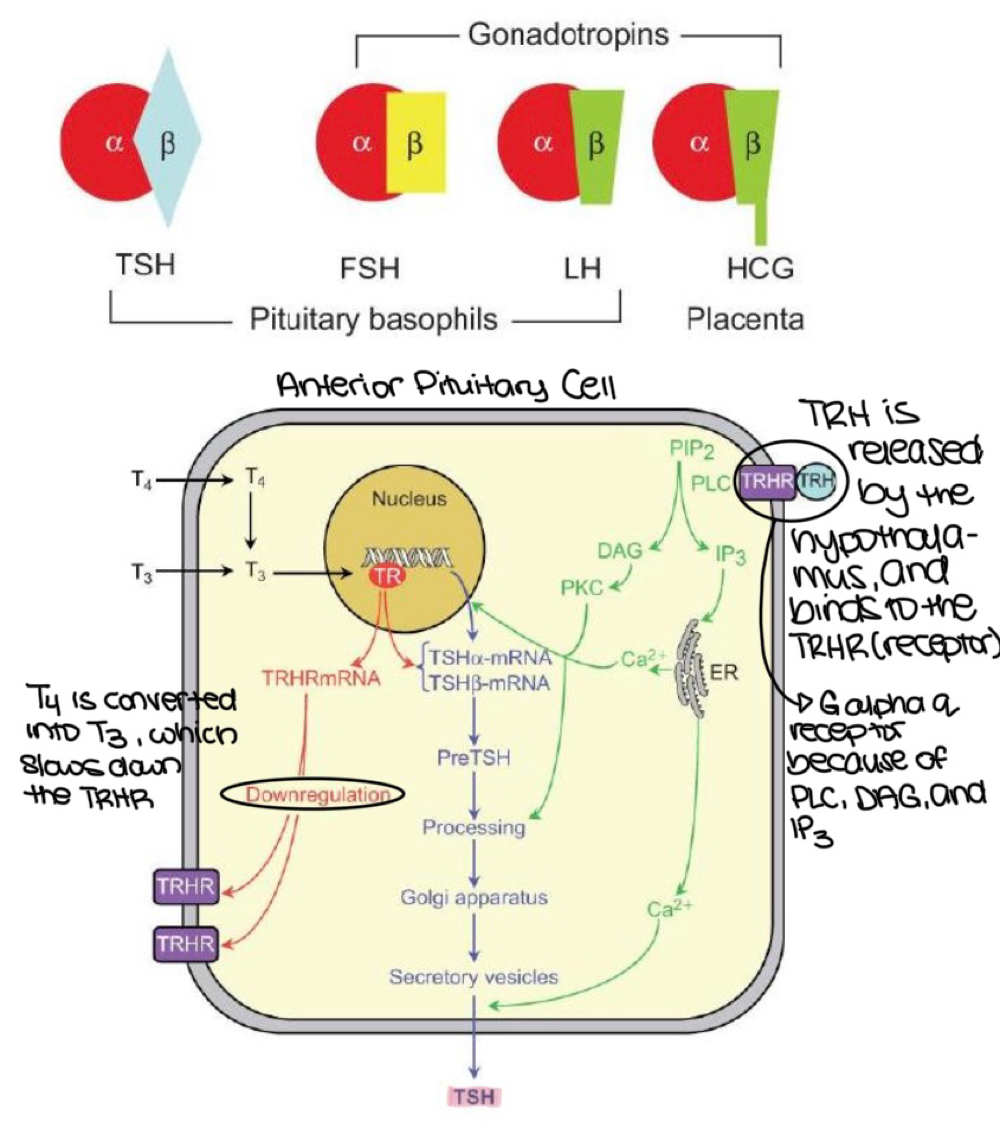
T4 is converted into T3, which does what to the TRHR on anterior pituitary cels
slows down/downregulates
during fetal development, nervous system maturation depends on _______ and _______
T3 and T4
In adults, thyroid hormones increase sympathetic activity by upregulating _______ receptors
adrenergic
Thyroid hormones increase heart rate and contractility by affecting _______ channels
ion
T3 acts permissively with _______ to promote bone formation.
growth hormone
T3 determines when bone growth _______ (ends).
stops
Thyroid hormones increase oxygen consumption and heat production by increasing _______ use.
ATP
Uncoupling proteins in mitochondria produce _______ instead of ATP.
heat
Hyperthyroidism causes muscle _______ due to excess protein breakdown.
wasting
Conversion of T4 to T3 in the pituitary provides _______ feedback to reduce TSH release.
negative