ITM706 Symbols
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms

BPMN Activity

BPMN Start Event

BPMN End event

Gateway
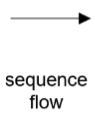
BPMN Sequence Flow
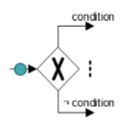
XOR-Split (takes one outgoing branch)
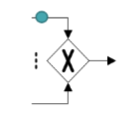
XOR-Join (proceed when one incoming branch has completed)
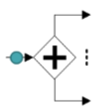
AND-Split (takes all outgoing branches)
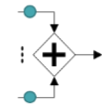
AND-Join (proceed when all incoming branches have completed)

Object
- It is a particular instance of a class
- It has some properties and methods
- It exposes its behavior through the methods
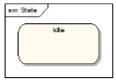
State
- A state represents a situation where some invariant condition holds
- For example, if a printer is not printing a document, then the state of the printer is ‘Idle’

Transitions
Transitions from one state to another in a State Machine Diagram are denoted by lines with arrowheads. A transition may have a trigger, a guard and an effect.
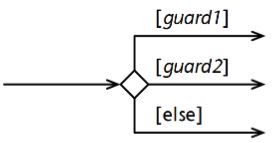
Guard
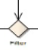
Choice

Junction
- Junction pseudo-states are used to chain together multiple transitions
- A single junction can have one or more incoming, and one or more outgoing, transitions;
- a guard can be applied to each transition
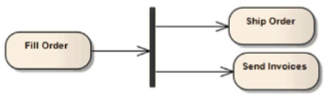
Fork
Fork or split the flow into a number of concurrent flows
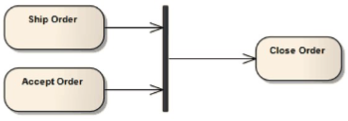
Join
Join the flow of number of concurrent flows

Abstract Task
An Abstract task is a placeholder task used in high-level modeling where the specific type of work isn’t defined yet
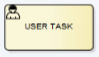
User Task
A User Task is a task performed manually by a human, typically using a software interface or system screen
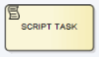
Script Task
A Script Taks is a task executed automatically by the workflow engine using a predefined script (no human involvement)

Service Task
A Service Task is a task performed by an automated service,such as calling an API, web service, or system function

Business Rule Task
A Business Rule Task is a task where business rules or decision logic (like a decision table or rule engine) are evaluated automatically
Send Task
A Send Task is a task that sends a message to an external participant or system and then immediately completes
Receive Task
Receive Task is a task that waits to receive a message before the process can continue
Subprocess
subprocess is a grouped set of activities represented as a single task; used to organize complexity and hide detailed steps
Activity with Loop-Standard
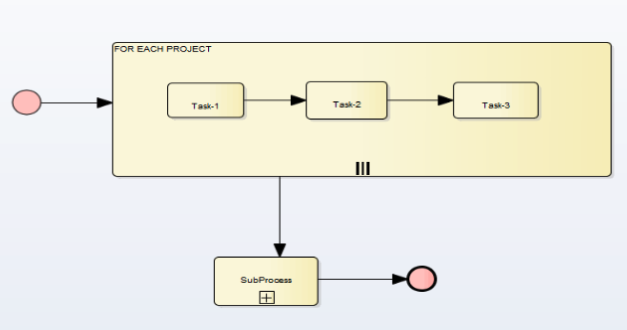
Activity with Loop-Multiinstance

Data Object Input
A data object provides or stores information for an activity

Data Object Output
A data object provides or stores information for an activity

Data Store
A data store represents a mechanism for an activity to retrieve or update stored information
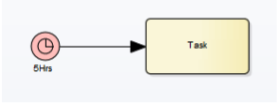
Timer Start Event
It starts the process at a specific time, date, or interval. It’s use case is for scheduled processes.
It can’t be edge mounted
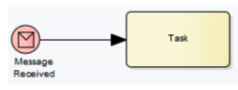
Message Start Event
The process starts only when a specific external message is received. The use case: triggered by another system or participant.
It can’t be edge-mounted.
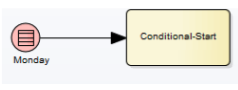
Conditional Start Event
A Conditional Start event starts when a condition becomes true (e.g. “inventory < threshold”). The use-case is data-driven workflows.
It can’t be edge-mounted
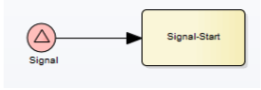
Signal Start Event
A signal start event is triggered by a broadcast signal that can be caught by multiple processes. The use case is global triggers, many processes can listen.
It can’t be edge-mounted
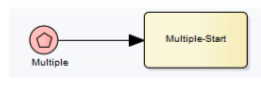
Multiple Start Event
Process can start from one of several possible triggers (message OR timer OR signal OR conditional). The Use case is flexible start logic.
It can’t be edge-mounted
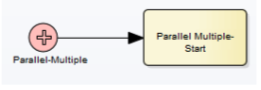
Parallel Multiple Start Event
Process starts only when All specified triggers occur together. Use: synchronization of multiple independent start conditions.
It can’t be edge-mounted.

Catching Message Event
Waits to receive a message from another participant/system.This is an intermediate event.

Catching Link Event
Receives a “jump” from another point in the process flow. This is an intermediate event.

Catching Signal Event
Waits for a broadcast signal by any process. This is an intermediate event.

Throwing Message Event
Sends a message to another participant/system. This is an intermediate event.

Throwing Link Event
Emits a “Jump” to another link event elsewhere in the diagram. This is an intermediate event.

Throwing Signal Event
Broadcasts a signal that any catching event can receive. This is an intermediate event.
Boundary Event
A boundary event is an event attached to the border of an activity. It monitors that activity and reacts if something happens while the activity is running.

Message End Event
When the process ends, it sends a message to an external participant or system.

Escalation End Event
Ends the process by escalating an issue to a higher-level handler without marking it as a failure. This is common in approval workflows.

Error End Event
Ends the process with an error, interrupting the current flow. Must be caught by an Error Boundary Event.

Signal End Event
Broadcasts a signal to any process that is listening (catching signal events). Triggers global reactions.

Exclusive Gateway (XOR)
From multiple outgoing paths, the process takes only one path based on conditions.

Parallel Gateway (AND)
Activates all outgoing paths simultaneously with no conditions.

Inclusive Gateway (OR)
Allows one or more outgoing paths to be taken depending on conditions.
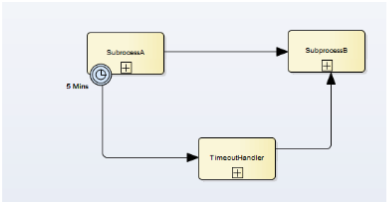
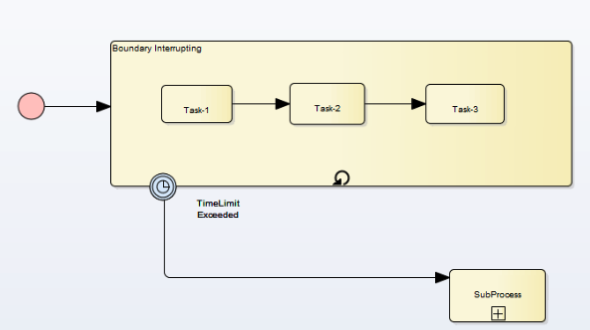
Boundary Interrupting Event
After 5 minutes, Execution of Subprocess A is cancelled. TimeoutHandler subprocess starts execution.
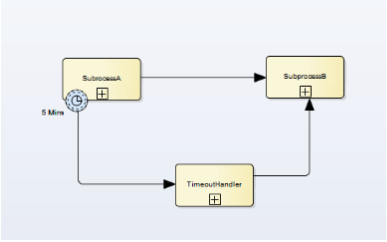
Boundary Non-Interrupting Event
After 5 minutes, execution of Subprocess A is still continued. TimeoutHandler sub-process starts execution
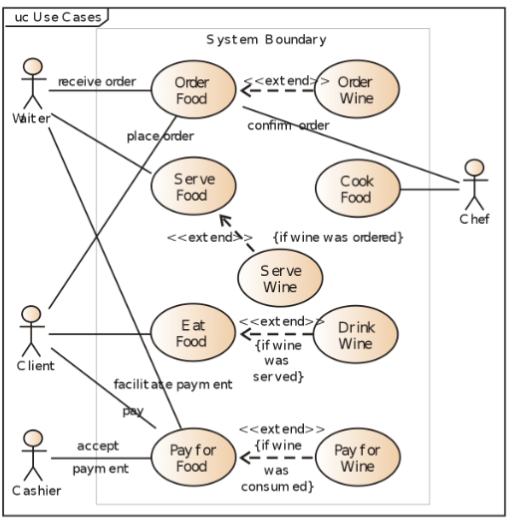
UML Diagram: Use Case Diagram
UML Diagrams: Sequence Diagram
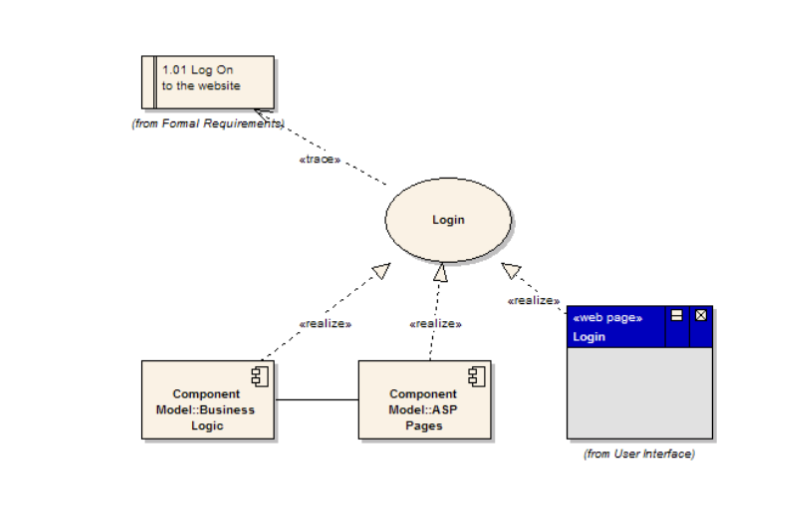
UML Diagrams: Implementation Diagram
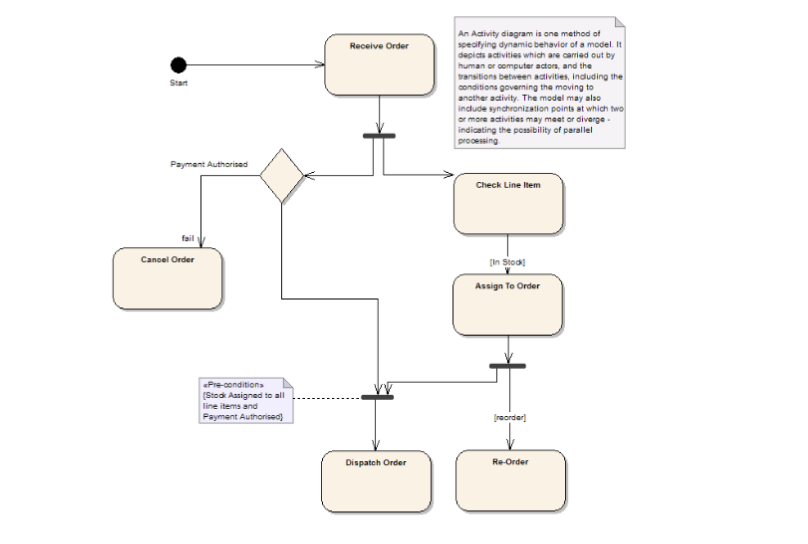
UML Diagrams: Activity Diagram
Archimate Layers
The Business Layer: It offers products and services to the external customers
The Application Layer: It supports the business layer with application services
The Technology Layer: It offers infrastructural services (like: processing, storage and communication services) needed to run applications
Core Concepts of Archimate Language
Active Structural Elements: The business actors, application components, and devices are active structural elements
Behavioral Elements: The processes and functions performed by the actors
Passive Structural Elements: Objects on which behavior is performed. For example, information objects in the business layer, data objects in the application layer and physical objects in the technology layer.

Business Actor
A business actor represents a business entity that is capable of performing behavior. Actors may, however, include entities outside the actual organization.

Business Role
A business role represents the responsibility for performing specific behaviour, to which an actor can be assigned, or the part an actor plays in a particular action or event.

Business Collaboration
A business collaboration represents an aggregate of two or more business internal active structure elements that work together to perform collective behavior. A business collaboration is a specialization of the business role.

Business Interface
A business interface represents a point of access where a business service is made available to the environment.

Business Process
A business process represents a sequence of business behaviors that achieves a specific result such as a defined set of products or business services.

Business Function
A business function represents a collection of business behavior based on a chosen set of criteria (typically required business resources and/or competencies), closely aligned to an organization, but not necessarily explicitly governed by the organization.

Business Interaction
A business interaction represents a unit of collective business behavior performed by (a collaboration of) two or more business actors, business roles, or business collaborations.

Business Event
A business event represents an organizational state change. It may originate from and be resolved inside or outside the organization.

Business Service
A business service represents an explicitly defined exposed business behavior

Business Object
A business object represents a concept used within a particular business domain.

Business Contract
A contract represents a formal or informal specification of an agreement between a provider and a consumer that specifies the rights and obligations associated with a product and establishes functional and non-functional parameters for interaction. A contract is a specialization of a business object

Representation
A business representation represents a perceptible form of the information carried by a business object.

Business Product
A product represents a coherent collection of services and/or passive structure elements, accompanied by a contract/set of agreements, which is offered as a whole to (internal or external customers).

Application Component
An Application Component is a modular, deployable, and replaceable part of a system that encapsulates its contents and exposes its functionality through a set of interfaces

Application Collaboration
Application Collaboration is an aggregate of two or more application components that work together to perform collective behavior

Application Interface
Application Interface is a point of access where an application service is made available to a user or another application component

Data Object is a passive element suitable for automated processing

Application Service
Application Service is a service that exposes automated behavior
Application Function is a behavior element that groups automated behavior that can be performed by an application component
Application Interaction
Application Interaction is a behavior element that describes the behavior of an application collaboration

Application Process
An application process represents a sequence of application behaviors that achieves a specific result.

Application Event
An application event represents an application state change

Technology Node:
A node is a computational resource upon which artifacts may be stored or deployed for execution. A node represents a computational or physical resource that hosts, manipulates, or interacts with other computational or physical resources. Nodes are active structure elements that perform technology behavior and execute store and process technology objects such as artifacts. ,

Technology Device
A device is a hardware resource upon which artifacts may be deployed for execution. A device represents a physical IT resource upon which system software and artifacts may be stored or deployed for execution.

System Software
A software environment for specific types of components and objects that are deployed on it in the form of artifacts. System software represents the software that provides or contributes to the environment for storing, executing, and using software or data deployed within it.

Technology Collaboration
A technology collaboration represents an aggregate of two or more technology internal active structure elements that work together to perform collective technology behavior. It specifies which nodes cooperate to perform some task.
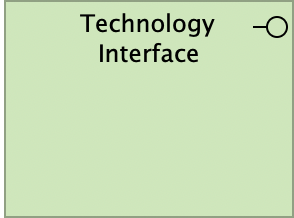
Technology Interface
A technology interface represents a point of access where technology services offered by a node can be accessed. It specifies how the technology services of a node can be accessed by other nodes. A technology interface exposes a technology service to the environment.
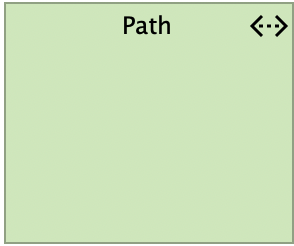
Technology Path
A path represents a link between two or more nodes, through which these nodes can exchange data, or material. A path is used to model the logical communication (or distribution) relations between nodes.

Communication Network
A communication network represents a set of structures that connects nodes for transmission, routing, and reception of data.
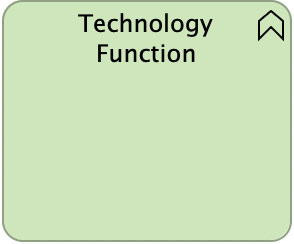
Technology Function
A technology function represents a collection of technology behavior that can be performed by a node. A technology function describes the internal behaviour of a node; for the user of a node that performs a technology function, this function is invisible. If its behavior is exposed externally, this is done through one or more technology services.
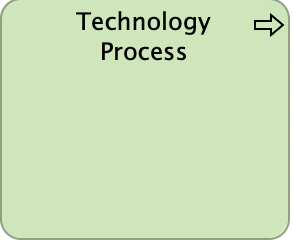
Technology Process
A technology process represents a sequence of technology behaviors that achieves a specific result. It describes the internal behavior of a node; for the user of that node, this process is invisible. If its behavior is exposed externally, this is done through one or more technology services.
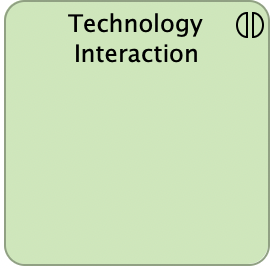
Technology Interaction
A technology interaction represents a unit of collective technology behavior performed by (a collaboration of) two or more nodes. A technology interaction describes the collective behavior that is performed by the nodes that participate in a technology collaboration.
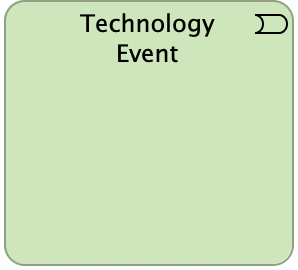
Technology Event
A technology event represents a technology state change. Technology functions and other technology behavior may be triggered or interrupted by a technology event. Also, technology functions may raise events that trigger other infrastructure behavior. A technology event may trigger or be triggered (raised) by a technology function, process, or interaction.

Technology Service
A technology service represents an explicitly defined exposed technology behavior. A technology service exposes the functionality of a node to its environment. A technology service is realized by a technology function or process.

Artifact
An artifact represents a piece of data used or produced in a software development process or by the deployment and operation of an IT system.

Association model is a relation between objects that is not covered by another, more specific relationship

The influence relation model that an element affects the implementation or achievement of some motivation element

Access
The access relation models that behavioural elements can observe or act upon passive structure elements.

Serving
The serving relation models that an element offeres its functionality to another element.
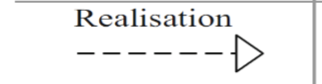
Realisation
The realisation relation indicates that an entity plays a critical role in the creation, achievement, sustenance, or operation of a more abstract entity.

Specialisation
The specialisation relation indicates that an element is a particular kind of another element

Assignment
The assignment relation expresses the allocation of responsibility, performance of behaviour, or execution.