cognitive motor dual task interference
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
attention
information processing capacity of an individual
concepts: has a limit (capacity); performing a task requires given portion of capacity
if 2 tasks are perforemd together that require more than available capacity of attention
task performance on either or both tasks deteriorates
cognitive-motor interference
possible outcome when a cognitive task and motor task are performed simultaneously
cognitive-motor interference in healthy adults
limited by ability to process info (attentional capacity)
system requires switching attention to most task-relevant info
cognitive-motor interference in neuro disease
capacity available for attention to task may be decreased
executive function deficits may=incorrect alocation of attention
single task may require incr attention
combining task=compromise 1 or both tasks
where would you see deficits with cognitive-motor interference?
reaction time (preparation-initiation) and/or movement sequence (initiation-execution-termination)
attention must be able to be appropriately switched and allocated
balance, coordination, UE manip for tasks of walking, talking, step down curb, avoiding people, carrying things, texting, etc.
prioritization of dangers of oncoming traffic, bumping into things/ppl, falling, wrong turn, etc.
stimuli can be numerous and conflicting
attention types: divided, alternating, selective
how does pathology affect cognitive-motor interference?
capacity of executive function: attention not allocated properly
capacity of speed of processing available for attention to task
dual tasking
2 tasks that can be performed independently, measured separately, have distinct goals
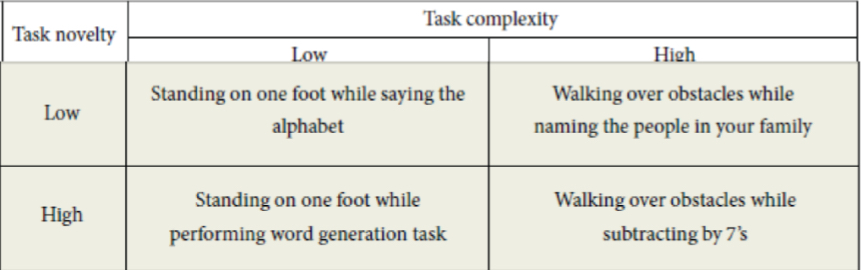
complexity
related to # of task components and attentional demands
novelty
related to performer experience
low novelty low complexity task
task is easier
ex. walking on a level surface
high novelty low complexity task
task is of moderate difficulty
ex. walking on an icy surface
low novelty high complexity task
task is of moderate difficulty
ex. walking on a level surface while carrying a glass of water
high novelty high complexity task
task is harder
ex. walking on an icy surface while carrying a glass of water
motor-motor tasks
two motor tasks combined in a dual task
cognitive-motor tasks
a motor and a cognitive task combined in a dual task
dual cognitive-motor task (1)/novelty of cognition
dual cognitive-motor (2)/novelty of motor

measures of dual task performance
y axis: cognitive performance
x axis: motor performance
perform each single task, then dual task
horiz distance btwn single task perform and dual perform=motor interference
vert distance btwn single task perform and dual perform=cog interference
area between single task lines and dual task lines=automaticity
smaller area between cog single/cog dueal or motor single/motor dual=attention allocation
task specific interference: motor dual ttask effect (DTE)
[(motor DT-motor ST)/motor ST]*100%
+=facilitation
-=interference
task specific interference: cognitive dual task effect
[(cog DT-cog ST)/cog ST]*100%
+=facilitation
-=interference
task prioritization: motor priority trade off
+motor DTE
-cog DTE
task prioritization: cognitive priority trade off
-motor DTE
+cognitive DTE
task prioritization: mutual interference
-motor DTE
-cognitive DTE
task prioritization: mutual facilitation
+motor DTE
+cognitive DTE
modified attention allocation index
motor DTE-cognitive DTE
+motor priority
0 no priority
-cognitive priority
calculating DTE
use negative multiplier (± 100%) if inverse/opposite relationship (ex. incr time=worse perform)
negative values always indicate decline in performance
DTE considerations
cognitive task must be continuous
cognitive task msut be completed using same method but diff specific responses (like different numbers to count down from)
do not provide number until ready to begin motor task
task prioritzation
mutual interference: both -
motor priority trade off: motor +, cog -
cog priority trade off: motor -, cog +
mutual facilitation: botth +