Physical Science Unit 3
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Aluminium
Al
Argon
Ar
Barium
Ba
Boron
B
Bromine
Br
Calcium
Ca
Carbon
C
Chlorine
Cl
Chromium
Cr
Cobalt
Co
Copper
Cu
Fluorine
F
Gold
Au
Helium
He
Hydrogen
H
Iodine
I
Iron
Fe
Lead
Pb
Lithium
Li
Magnesium
Mg
Mercury
Hg
Neon
Ne
Nickle
Ni
Nitrogen
N
Oxygen
O
Phosphorus
P
Platinum
Pt
Potassium
K
Radium
Ra
Silicon
Si
Silver
Ag
Sodium
Na
Sulfur
S
Tin
Sn
Uranium
U
Zinc
Zn
Dalton’s Model/Billiard Ball Model
What did Dalton believe about the atom?
it is the smallest indivisible particle of atom
they are identical in mass and properties
uniform spheres
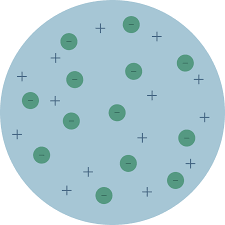
Thompson’s model/plum pudding model
What did Thompson believe the atom was?
A homogeneous or uniform mixture of positively charged and negatively charged electrons
they are electrically neutral
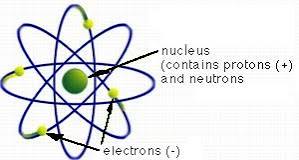
Rutherford Model/nuclear model
What did Rutherford believe about the atom?
It consists of a central core, or nucleus, of positively charged particles that electrons circulate around
Bohrs theory of the hydrogen atom
Electrons revolve about the nucleus of the atom in
discrete, specific orbits of certain radii
Jump energy levels (n1, n2, ect)
According to Bohr, each orbit (N=1, N=2, ect) represent what?
Quantum principle numbers that represent energy levels where electrons exist
According to Bohr, electrons are able to make ____ and when they do so ____ is emitted or absorbed
Quantum jumps, electromagnetic radiation
In Bohrs theory, when an electron jumps from a high energy level to a low one what occurs?
a photon is emitted (kicked out kinda)
When an electron jumps from a low level to a high one what occurs?
a photon is absorbed
What is energy in Max Planck’s quantum hypothesis?
quantized, meaning it has a specific number of energy levels
In planck’s quantum theory an oscillating electron has _____ of energy
discrete, specific amounts of energy
quantized energy only has ___ values
specific
continuous energy can have ____ value
any
what type of energy is this?
quantized
what type of energy is this?
continuous
what is the electronic charge of an electron?
-1
where are electrons located?
outside the nucleus
what is the electronic charge of a proton?
+1
where are protons and neutrons located?
the nucleus
what is the electronic charge of a neutron?
0
what does the atomic number represent? what does it determine of an element?
it represents the number of protons in the nucleus, and it determines the identity of the element
Are atoms electrically neutral, positive, or negative? Why?
They are neutral because protons and electrons are equal
what is the mass number of an atom equal to?
The number of protons + neutrons
what is the neutron number?
the number of neutrons in the nucleus
what are isotopes?
atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different atomic masses/neutrons
what is radioactive decay?
the process in which a nucleus spontaneously (aka naturally) decays, giving off particles of radiation
what are the types of radioactive decay?
alpha, beta, and gamma
what is alpha decay?
the disintegration of a nucleus into a nucleus of another element, with the emission of helium nucleus (aka an alpha particle)
what is beta decay?
the disintegration of a nucleus into a nucleus of another element, with emission of an electron (aka a beta particle)
what is gamma decay?
the emission of a gamma ray from an excited nucleus to form a stable nucleus
what does the star in the gamma decay equation represent?
the highest energy level or an excited/energetic nucleus
What is half life?
The time required for half of the nuclei of a radioactive substance to decay
How are half life's measured?
With a geiger counter that measures the rate of emission of decay particles
What is nuclear fission?
The process in which a large nucleus is split into two smaller nuclei with th emission of neutrons and the conversion of mass into energy
Do nuclear processes abide by the law of conversation of mass and energy?
No!!
What is nuclear fusion?
The process in which smaller nuclei combine to form larger nuclei, with the release of energy
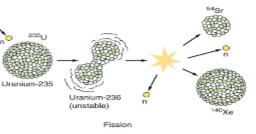
What nuclear reaction is occuring here?
Nuclear fission
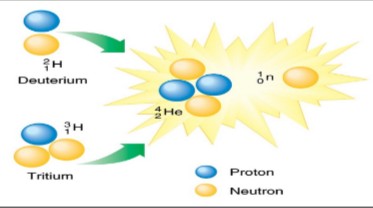
What process is this?
Nuclear fusion