3.2.2 Reaction Rates
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Define rate of chemical reaction
the change in concentration of a reactant or a product per unit of time
Give 5 factors that affect the rate of reaction
temperature
pressure
concentration
surface area
use of a catalyst
What does simple collision theory state is neccessary for a reaction?
molecules must collide with each other
they must have energy greater than or equal to activation energy
molecules must collide in the correct orientation
What does ‘correct orientation’ refer to?
organic mechanisms
What happens if molecules collide with less energy than reaction energy?
no reaction takes place
What happens if molecules collide in the incorrect orientation?
no chemical reactions take place
What is a collision that doesnt result in a reaction called?
unsuccessful collision
How does concentration effect reaction rate?
increasing concentration increases rate
Why does concentration increase reaction rate?
more molecules in a given volume and thus more frequent successful collisions
How does increasing pressure effect reaction rate?
increasing pressure increases rate of reaction
Why does increasing pressure increase rate of reaction?
more molecules in a given volume, more frequent successful collisions
How does increasing temperature affect rate of reaction?
it increases rate of reaction
Why does increasing temperature increase reaction rate?
the average energy of the molecules increases as kinetic energy increases, a greater proportion of molecules have eenergy greater than or equal to activation energy → more frequent successful collision
Define activation energy
the minimum energy required for a reaction to take place by the breaking of bonds in the reactants
What is a catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of reaction without being consumed by the overall reaction. It allows the reaction to proceed via a different route with lower activation energy.
Give 2 types of catalyst
homogeneous and heterogeneous
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
a catalyst that exists in a sifferent physical state from the reactants
What is a homogeneous catalyst?
a catalyst that exists in the same physical state from the reactants
How does a catalyst increase rate of reaction?
lowers activation energy
greater proportion of the molecules have energy greater than or equal to activation energy
more frequent successful collisions occur
What are the advantages of using a catalyst?
lower temperature can be used
reduced energy demand
less CO2 emissions
less cost
increased sustainability
alternate pathway
higher atom econcomy
less waste
What conditions do enzymes operate at?
30-40*C
room pressure (1 atm)
What type of catalyst are enzymes?
homogenous
Give 3 examples of heterogeneous catalysts?
(iron) in manufacture of ammonia
ziegler-natta
Rh/Pd/Pt as catalytic converter
Describe the distribution of energies of the molecules of a reaction mixture
few molecules have very high activation energy
the majority of molecules have medium to ow activation energy
What is a boltzmann distribution?
shows the distribution of energies of molecules at a particular temperature
Draw a boltzmann distribution
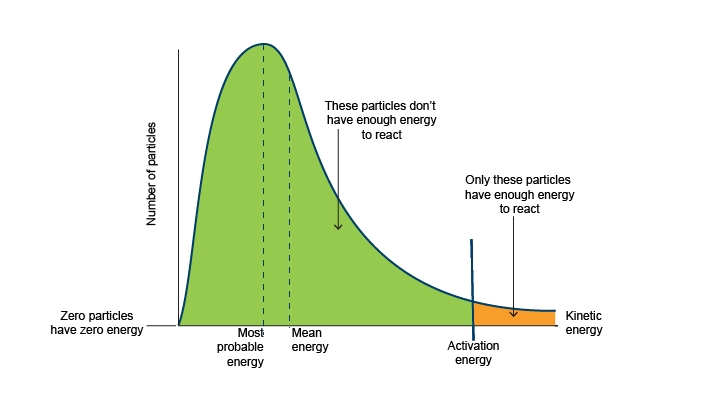
What is the modal energy?
the energy that the greatest number of molecules occupy
What is the total area under a curve equal to?
the number of molecules
What does the shaded area under a boltzmann curve?
the number of molecules with energy greater than or equal to activation energy
Describe the shape of a boltzmann curve?
unsymetrical
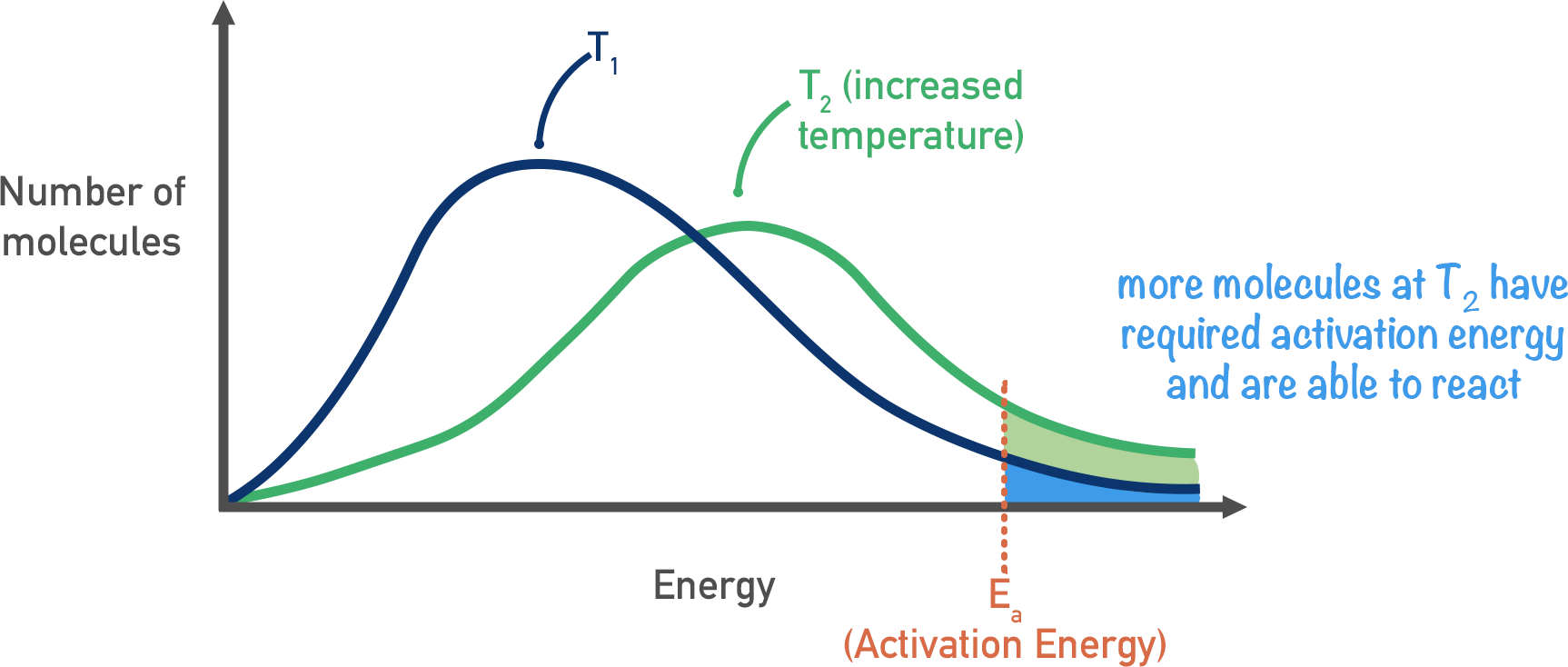
How does a boltmann curve change when tempterature increases?
lower peak
total area is the same
shifts to the right
Draw a boltzmann distribution with lower and higher temperature
How do you show a catalyst on a botlzmann distribution curve?
Ea shifts to the left
Give 5 ways of measuring rate of reaction
change of mass
titration
colorimeter
volume of gas released
change in pH or electrical conductivity
What is continuous monitoring?
measuring concentration/mass/volume at regular time intervals
If a gas is a product, how is rate measured?
change of mass
volume of gas evolved
How is change in mass measured?
placing the beaker of the reaction on a balance and measuring mass at regular time intervals
How is volume of gas lost measured?
gas syringe
upside down measuring cylinder
If a coloured solution is used/produced how can rate be measured?
colourimeter
If a reaction involved acid or base how can rate be measured?
pH meter at regular time intervals
samples taken at regular time intervals and titrated
Which way to measure change in pH is more accurate?
samples taken, via titration
What does a concentration time graph involve?
change in concentration of a reactant or product with time
How can you calculate rate of reaction at t using a conc-time graph?
drawing a tangent, and change in y over change in x
How can you calculate initial rate of reaction using a conc-time graph?
tangent at 0, change in y over change in x