Exam 2
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What contents of field notes are required to draw lithostratigraphic columns
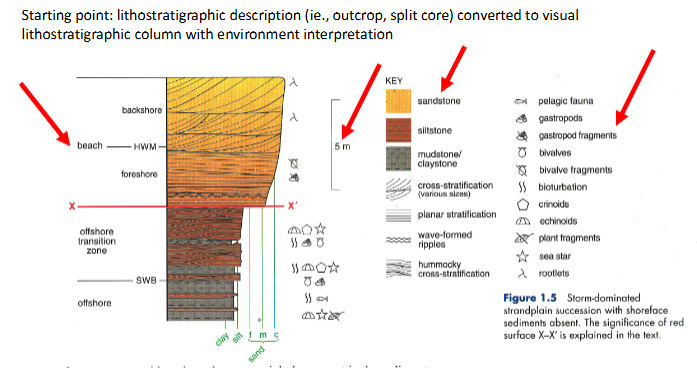

What lithology is this?
Conglomerate
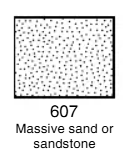
What lithology is this?
Sandstone
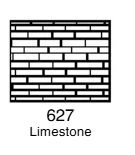
What lithology is this?
Limestone

What lithology is this?
Dolomite

What lithology is this?
Shale
Lithostratigraphic Hierarchy
Super group: largest unit, made of two or more groups or formations that share lithological characteristics
Group: mode of two or more formations with shared lithological features
Formation: the primary and most essential unit, defined by its lithological properties and map ability.
Member: subdivision of formation, with distinct characteristics but not mappable at scale of formation
Bed: smallest unit, representing distinct depositional layer
Taxon-range Zone
Single taxon
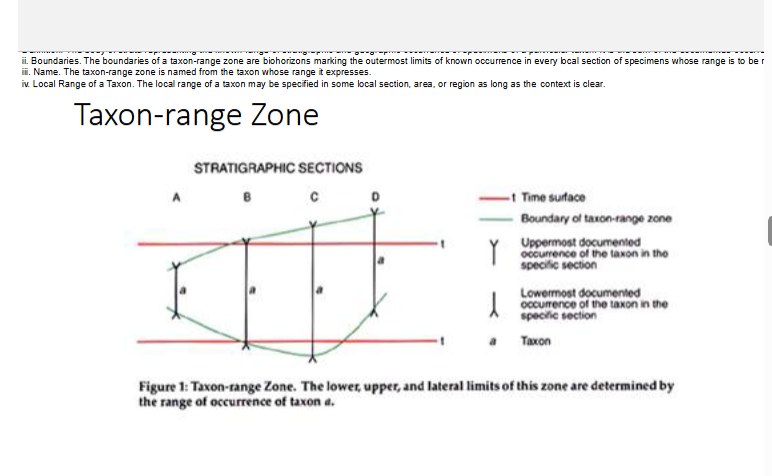
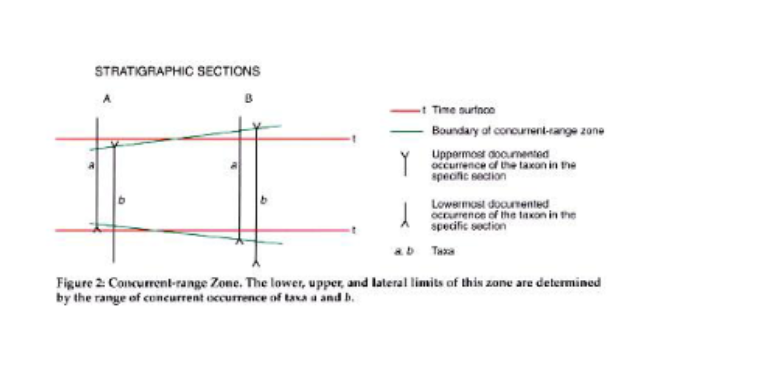
Concurrent-range Zone
Uses two taxa
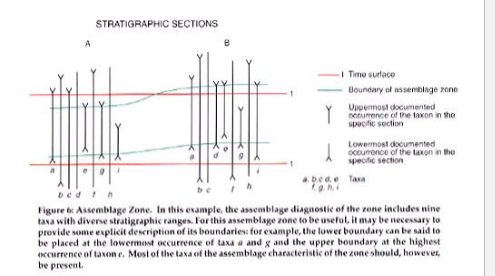
Assemblage Zone
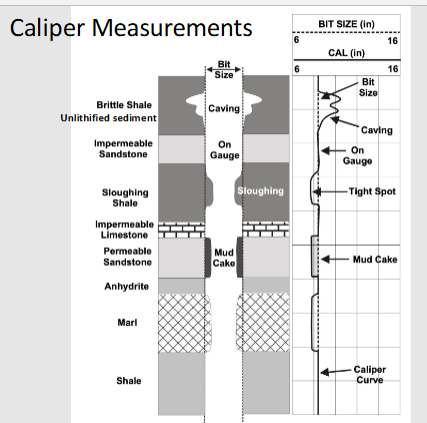
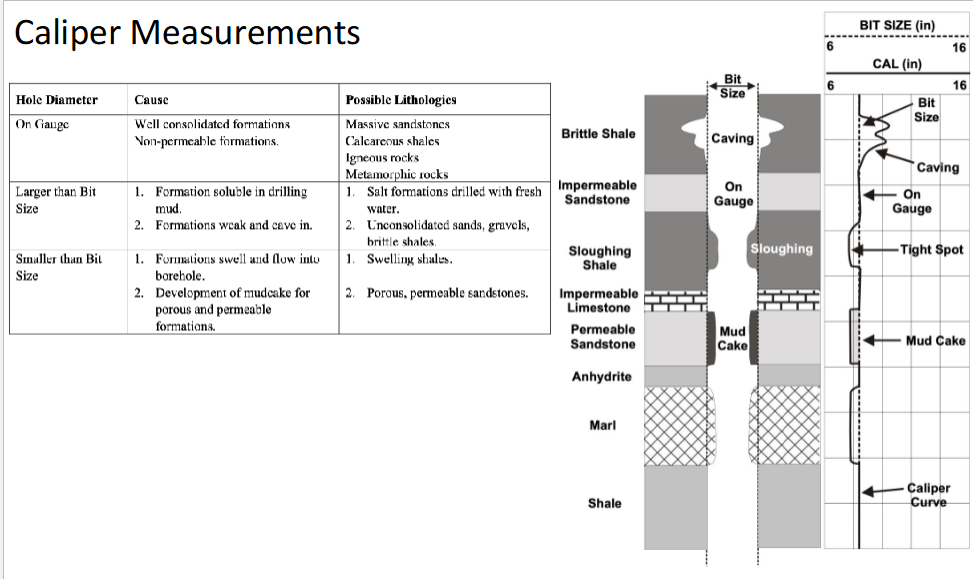
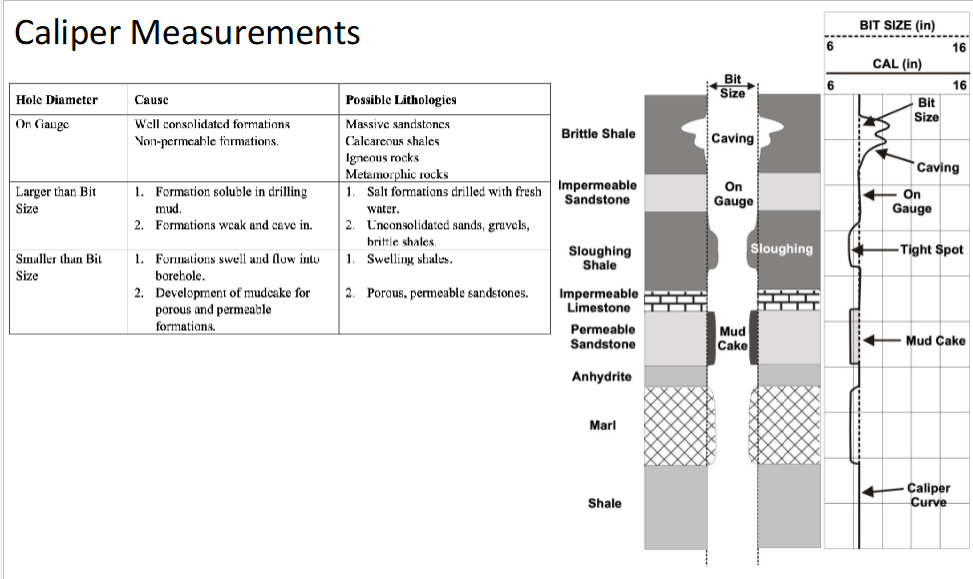
What does the Caliper sensor measure?
The size of the drilled borehole
Electrical Sensors measure?
Detects porewater amount, permeability, and ionic concentration of sediment and porewater
Gamma-ray sensors measure?
Measure the amount and type of radioactive elements (U, Th, K) in sediment
What is drilling mud composed of?
Functions of Drilling Fluids
Provide hydrostatic pressure to control the well
Create a seal between borehole and formation
Remove rock cutting from the well
Lubricate and cool the drill string
Types of Drilling Fluids
water-based muds
oil-based muds
Properties of Drilling Fluids
mud weight
viscosity
pH
Fluid Loss
Salinity
Composition of Drilling Muds
bentonite clay to increase viscosity and suspend cuttings, and barite to add weight.
Bed strength/induration/cemented
Caliper measures this.
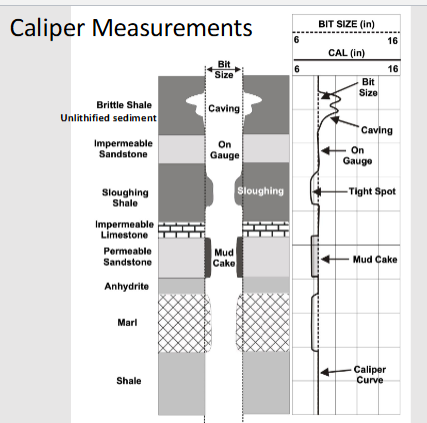
Caliper Measurements
on gauge: well consolidated formations, non-permeable formations
massive sandstones
calcareous shales
Larger than bit size: Formation soluble in drilling mud or formations weak and cave in.
Salt formations drilled with fresh water
unconsolidated sands, gravels, and brittle shales
Smaller than bit size: formations swell and flow into borehole or development of mudcake for porous and permeable formations
swelling shales
porous, permeable sand stones

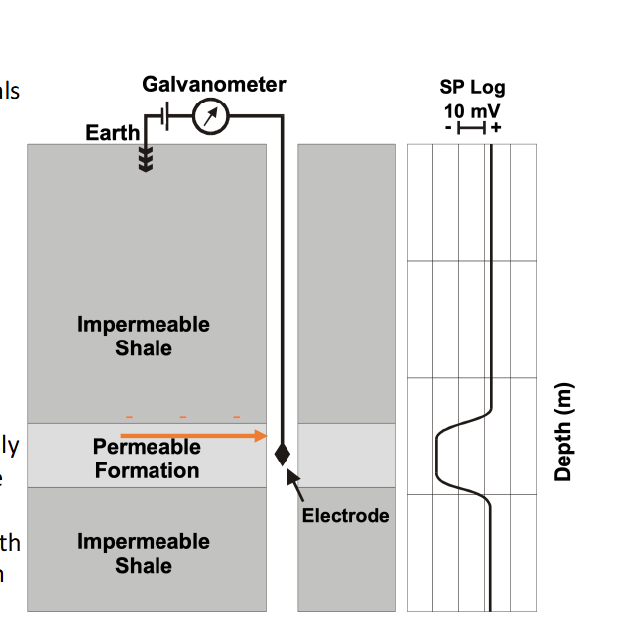
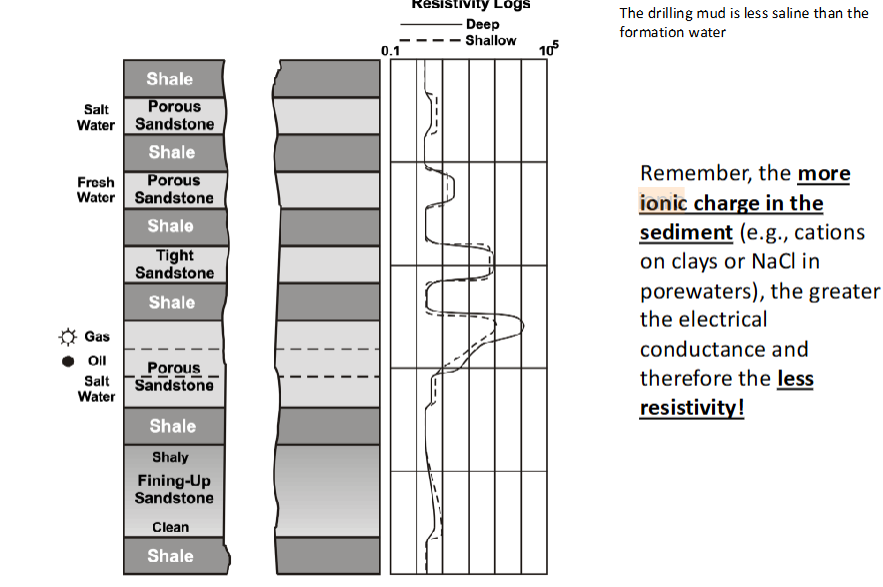
Spontaneous Potential (SP) Logs
measures natural electric potential
permeable formation, Low SP
Impermeable= higher SP
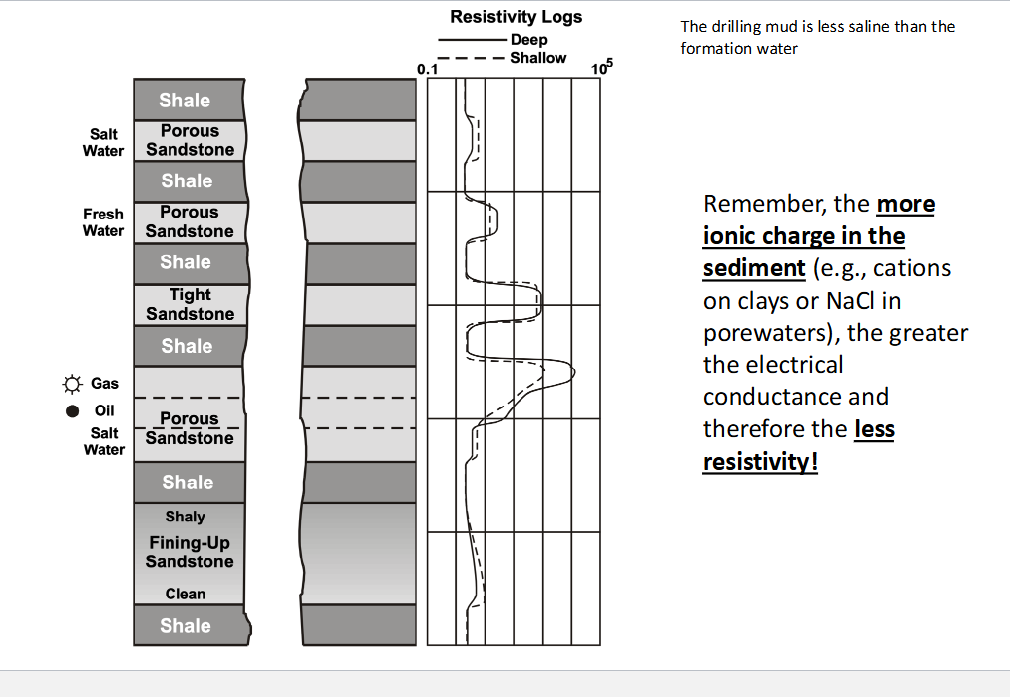
Resistivity Logs
is function of permeability, porosity and pore fluid salinity in rock
Frequently used to identify lithology that varies based on permeability
High Resistivity=little porewater
Low resistivity =more porewater
Remember, the more ionic charge (saline) in sediment (cations on clays or NaCl in porewaters), the greater the electrical conductance and less resistivity
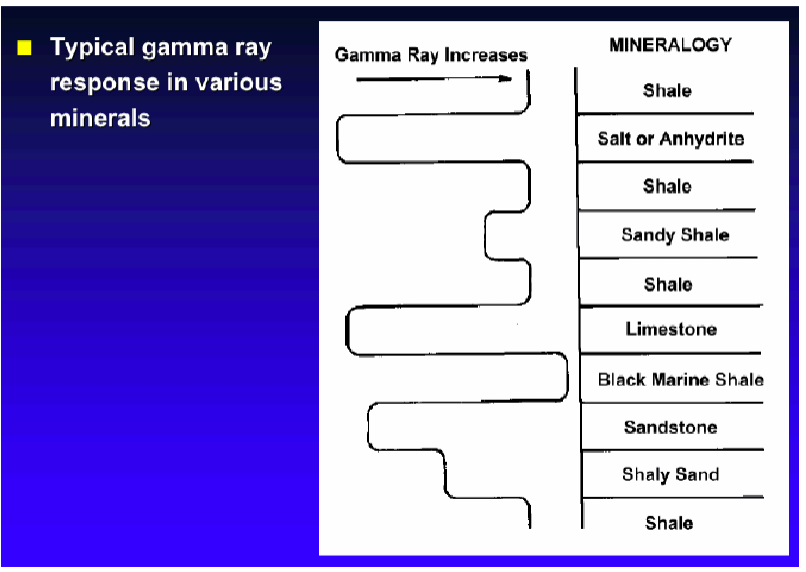
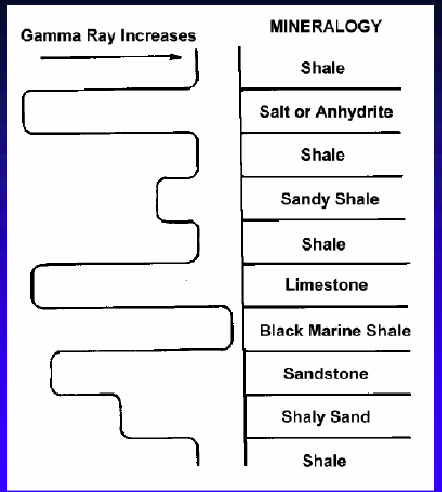
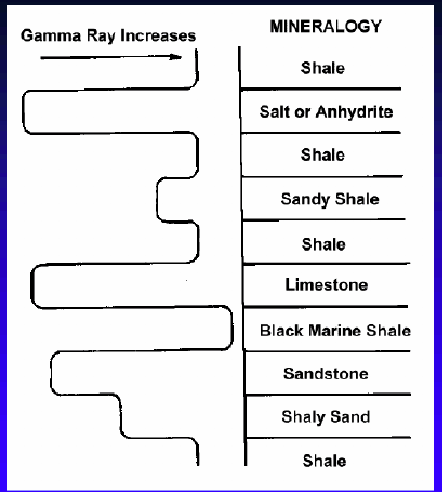
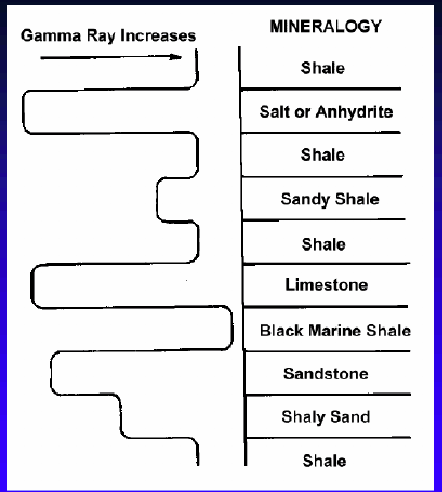
Gamma Ray Logs
Shales have high gamma radioactivity
Lithology from lowest to highest gamma radiation
Limestone: 5-10
Dolomite: 10-20
Sandstone: 10-30
Shale: 80-140
Gamma Ray Logs Interpretations
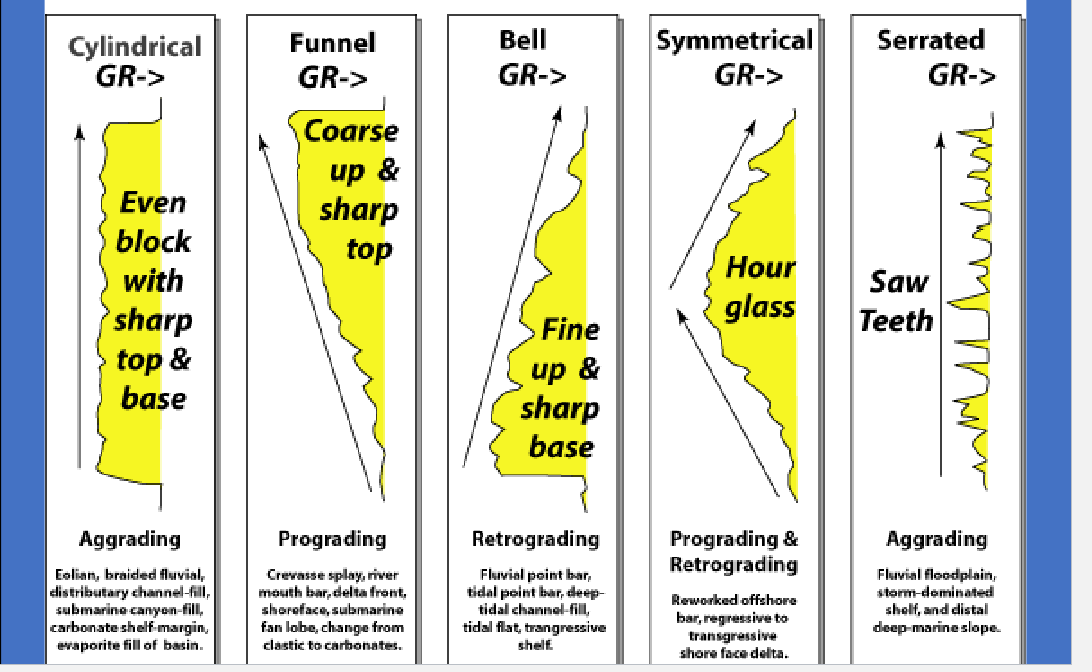
Cylindrical GR
Even block with sharp top and base
Eolian
Braided Fluvial
distributary channel-fill
submarine-canyon-fill
carbonate-shelf-margin
evaporite fill or basin

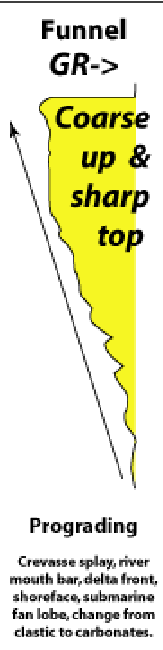
Funnel GR
Coarse up and sharp top:
crevasse splay
river mouth bar
delta front
shoreface
submarine fan lobe
change from clastic to carbonates
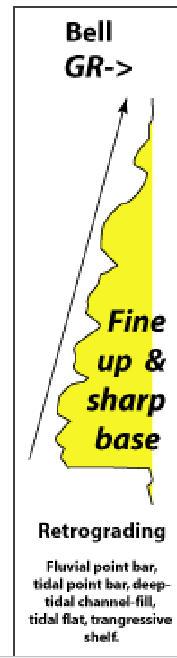
Bell GR
Fine up and sharp base:
fluvial point bar
tidal point par
deep tidal channel
tidal flat
transgressive shelf
Symmetrical GR
Prograding and retrograding
reworked offshore bar, regressive to transgressive shore face delta
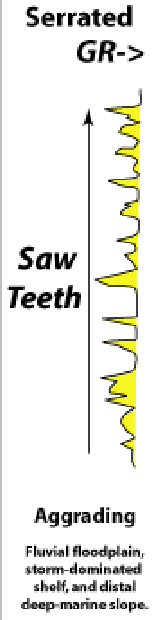
Serrated GR
Saw teeth
fluvial floodplain
storm dominated shelf
distal deep-marine slope
Dotted contact
Diffuse/gradual
Sharp Contact
Straight Line
Angular Unconformity
Tilted or folded, with new horizontal layer on top
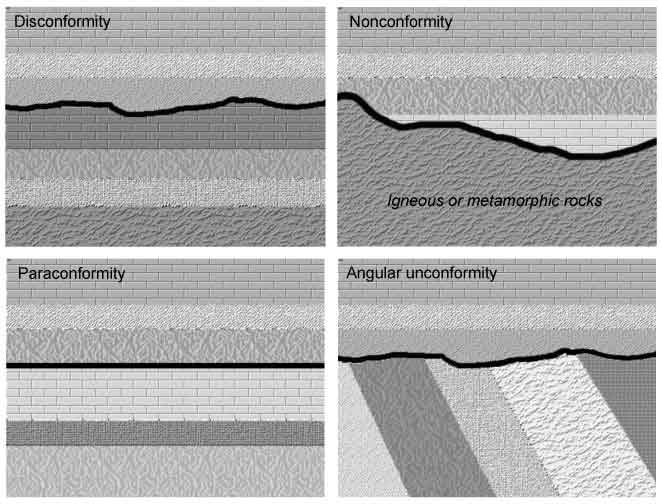
Disconformity
Clear erosion between sedimentary layers

Nonconformity
Where sedimentary rock is deposited on top of igneous rock
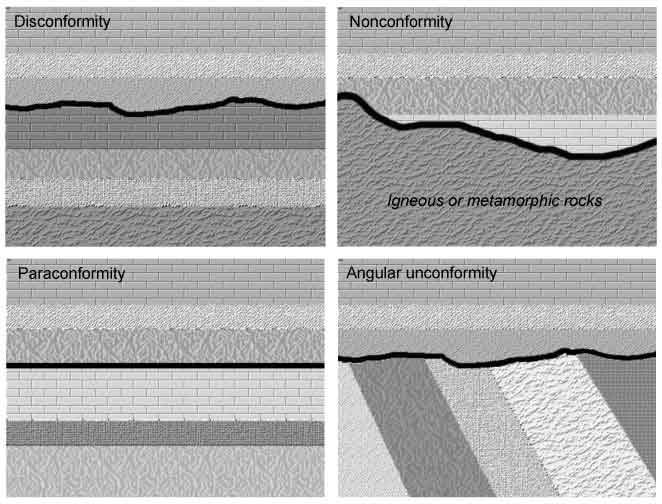
Paraconformity
Similar to a disconformity, this is a gap between parallel rock layers. The key difference is that there is no obvious erosional surface or discolored contact; it is a gap where beds are parallel and little apparent erosion has occurred.
Sandstone on shale
Sharp Contact
Sandstone on Conglomerate
Diffuse contact
Bed strength/induration/cemented
Use Caliper
On gauge: Well consolidated
Larger than bit: Formation weak and cave in
Smaller than bit: Formations swelling or development of mud cake for porous and permeable formations
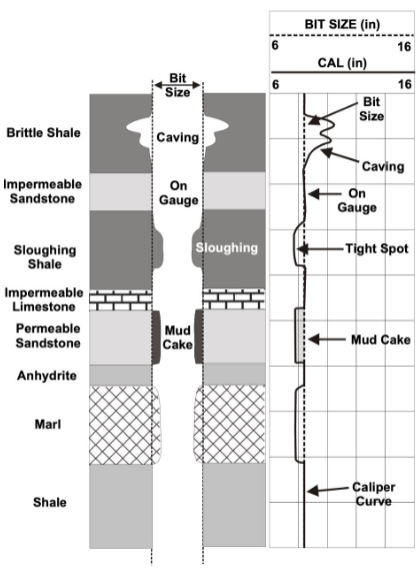
Permeable vs. impermeable beds
Caliper: non permeable formations are on guage, permeable form mudcakes and show smaller than bit size
Spontaneous Potential (SP): permeable= low SP
impermeable= high SP
Resistivity Logs: HLow resistivity =more porewater (permeable)
Low resistivity=little porewater (impermeable)
Swelling lithologies
Caliper: smaller than bit size= swelling
High ionic strength pore fluids
Resistivity Logs: the more ionic charge in the sediment, the less resistivity
Fining/coarsening upward sequences
Gamma Ray Log
Gamma ray logs infer grain size (and so subsequently inferred depositional energy)
Gamma Ray Logs: Shale
Value: 80-140
Shale has high gamma radioactive Response
Caliper Log: Shale
most shales are on gauge
Larger than bit= brittle shales (caving)
Smaller than bit= swelling shales (sloughing)

Spontaneous Potential (SP) Log: Shale
Impermeable Shale= Higher SP Value
Give an indication of shaliness (maximum negative deflection is clean porous, permeable sand; minimum/low SP is shale or cemented limestone)
Resistivity Logs: Shale
Low resistivity
Deep and shallow are the same
Caliper Logs: Sandstone
On gauge: Impermeable sandstone
Smaller than bit size: Permeable sandstone
Larger than bit size: unconsolidated sands
Spontaneous Potential (SP) Logs: Sandstone
Low SP, because sand is permeable
Resistivity Logs: Sandstone
Tight Sandstone: Higher than shale, higher than porous sandstone
Porous Sandstone: Higher than shale, lower than tight sandstone
Gamma Ray Log: Sandstone
Low gamma ray value, but higher than limestone
Acts as representation of grainsize
Gamma Ray Log: Limestone
Very low
Lower than sandstone and shale
Caliper Log: Limestone
Probably on gauge
Spontaneous Potential (SP) Logs