Bio Chapter 7 Lymphatic system
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the 4 main functions of the lymphatic system?
Absorbs excess interstitial fluid and returns it to the blood,
absorb fats from the small intestine,
produce and distributes lymphocytes,
defend the body against pathogens.
What body system to Lymphatic vessels move lymph to?
cardiovascular
What are the secondary lymphatic organs?
spleen
lymph nodes
The type of immunity that is fully functional without previous exposure to various foreign invaders is
innate immunity
Tears, saliva, and perspiration contain an enzyme called ? that helps kill or inhibit bacteria.
lysozyme
Which human organ system returns excess interstitial fluid to the blood?
lymphatic system
The two main phagocytic cells that are involved in the inflammatory response are
neutrophils and macrophages
what vessels form a one-way system of vessels which transport lymph to the cardiovascular veins
lymphatic vessels
A group of protective plasma proteins designated by the letter C and a number are all part of what system?
complement
The primary lymphatic organs are
thymus and red bone marrow
The adaptive immune system responds to foreign molecules, typically protein components of bacteria, viruses, molds, or parasites, which are collectively known as
antigens
The components of innate immune defenses are
protective proteins
chemical barriers
inflammatory response
What is lysozyme?
antibacterial enzyme
The complement system is actually composed of
a number of blood plasma proteins
A molecule recognized as being foreign to the body is
antigen
The cell type that is mostly responsible for antibody-mediated immunity is
b cell
Cloned B cells that produce antibodies specific to a particular antigen are called
plasma cells
How do T and B lymphocytes recognize different antigens?
Each lymphocyte has antigen receptors in its plasma membrane, which can bind to only one specific antigen.
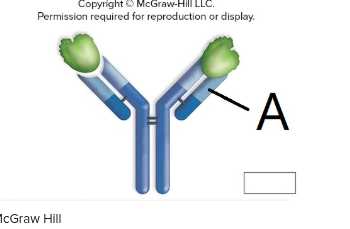
The letter a is pointing to a
variable region of a light chain
Which two types of cells can undergo clonal expansion after a specific antigen binds an antigen receptor on their surface?
B and T cells
The most unique and significant feature of monoclonal antibodies is that they are
produced by plasma cells derived from the same B cell
What are some major characteristics of B cells?
carry out antibody-mediated immunity
Cell-mediated immunity most directly involves the destruction of diseased and/or cancerous cells by
T cells
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) present fragments of pathogens to T cells on APC cell surface molecules called
major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs)
Antibodies that are produces by a plasma cell derived from a single B cells an bind to exactly the same antigen are called
monoclonal antibodies
The type of immunity that results from the production of antibodies by an individual following an infection or vaccination is which immunity?
active immunity
Adaptive immunity in which T cells destroy diseased or cancer cells is
cell-mediated immunity
Two scenarios that result in active immunity
immunization with a vaccine
infection with a pathogen
Two examples of cytokines are
interferons and interleukins
Which type of cells display fragments of antigens to T cells?
antigen presenting cells
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is caused by
the human immunodeficiency virus
The type of immunity that results from the administration of prepared antibodies by injection is
passive immunity
Because substances like pollen, food, and animal hair can provoke hypersensitivity reactions, they are called
allergens
To minimize organ transplant rejection, which type of molecules must be cross-matched between the donor and the recipient?
MHC molecules
Why is passive immunity always temporary?
The antibodies are not produced by the body.
The signaling molecule that regulates white blood cell formation and activation is called
cytokines
A reaction that is defined as a hypersensitivity to substances that normally pose no serious risk to the body, such as pollen, food, or animal hair is called a(n)
allergic reaction
Select the two most common strategies that are currently used to control rejection of organ transplants.
Matching MHC types between organ and recipient
correct
Administration of immunosuppressive drugs