Lecture 27 ADHD Medicinal chemistry
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Why is it difficult to diagnose
there are no biological markers only standardised rating scales
What are some neurotransmitter theories
Functional differences in some neurotransmitter systems
e.g. dopamine and norepinephrine
some differences in volume in some brain regions and connectivity
Treatment guidelines
Adults:
Offer Methylphenidate or lisdexamfetamine (environmental modifications no effect + sig impairment
dexamphetamine if patient cannot tolerate longer profile
Atomoxetine if no response or cannot tolerate
Trial in 6 weeks and review efficacy
Trial and error basis
What are stimulant medications
•Methylphenidate: dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
•Amphetamine: dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and releaser
What are some non-stimulant medication
•Atomoxetine – norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (useful when stimulant medications are contraindicated) (NRI)
•Guanfacine and clonidine – norepinephrine receptor agonists (a2-adrenoceptor agonists) (NRA)
What is the effect of cocaine and amphetamine on neurotransmitters
Increase dopamine release or inhibit re-uptake
Psychostimulants
Release more DA into synaptic cleft
What are some adverse effects
Decreased appetite, deficits in height/weight gain
Increased blood pressure or heart rate
Sleep disturbance
Tics
Seizures
Psychotic symptoms
Some patients may try to self medicate to reduce symptoms
Why are medications discontinued
side effects not tolerated
perceived lack of effectiveness
dislike of taking medications
stigma
What is lisdexamfetamine
An Amphetamine prodrug
Describe the immediate release profile of lisdexamfetamine
short Tmax
rapid symptom control
effects not long lasting
Describe the extended release profile
formulations of amphetamine and methylphenidate
•Methylphenidate (extended release): 12h
•Methylphenidate (delayed and extended release): 11h after 10-12h delay
Describe the structure of lisdexamfetamine
Amide bond

Which enzyme is used in hydrolysis
cytosolic amino peptidase
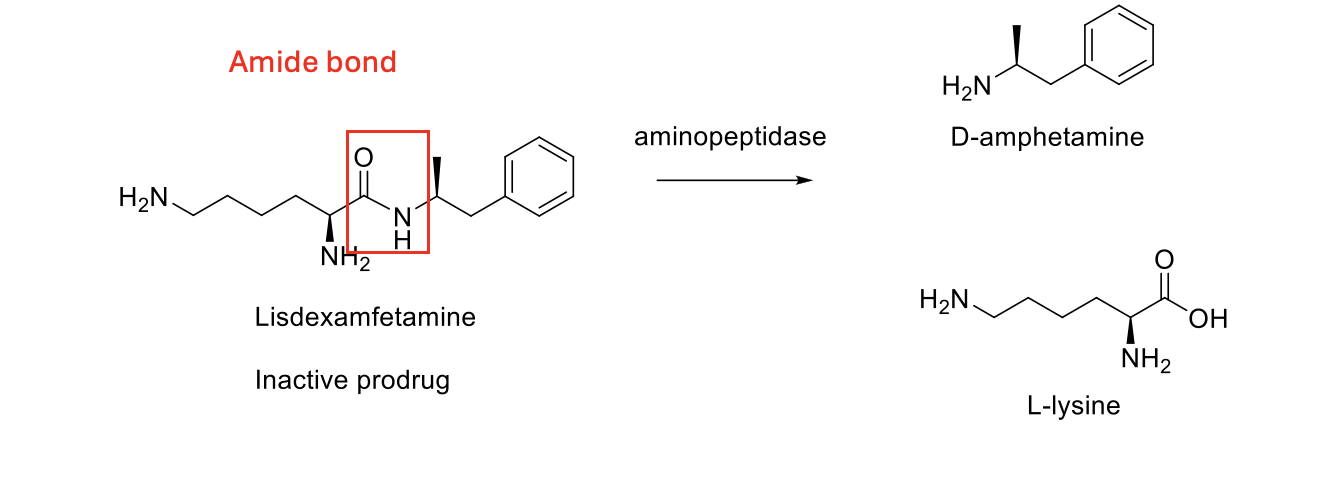
Describe hydrolysis pathway
Describe the stability of amide bonds
not very reactive as they are stable
Therefore require a lewis acid
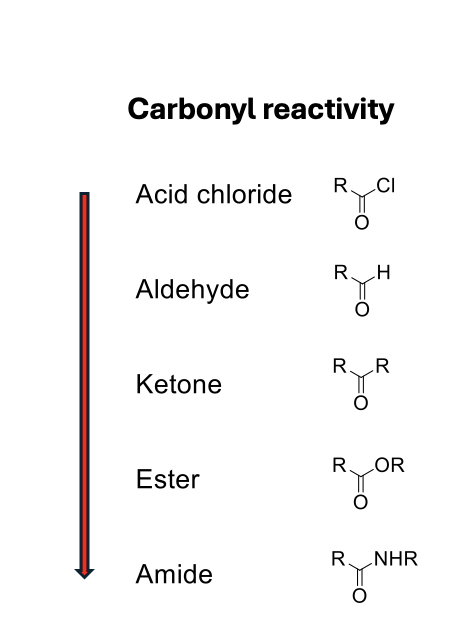
What lewis acid is used
Zn2+ or H+
What mechanisms cross BBB
Passive, transcellular diffusion: more lipophilic drugs
Active transport: needs glucose or amino acid to cross
Receptor-mediated transport: needs a receptor to be released by endocytosis
Describe how lisdexamfetamine is absorbed
High aqueous solubility and low lipophilicity
Rapid absorption through PEPT1 high affinity receptor in the small intestine
Converted into dextoamphetamine and L-lysine
Poorly diffused from GI tract
What is the active form of lisdexamfentamine
D-Amphetamine
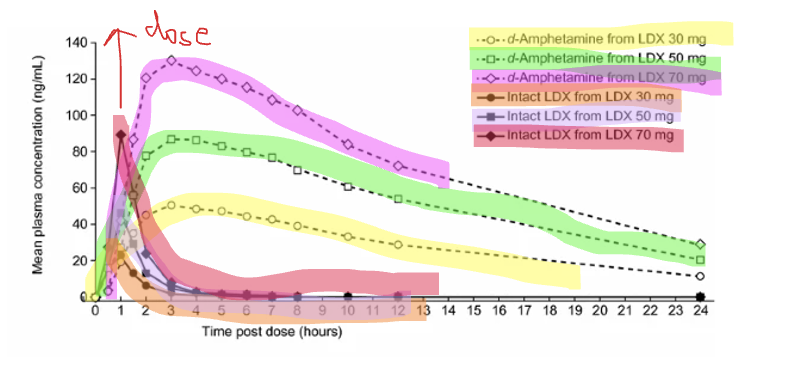
D-amphetamine vs LDX
D-amphetamine is the active form so it well and rapidly absorbed
resulting in a high mean plasma concentration from 2 hours
This increases with higher doses
VS
LDX poor absorbed
mean plasma concentration declines quite raiply
take 1 hour longer to reach peak levels
Long lasting Lisdexamfetamine
Typically only extended release has a prolonged effect but Lisdexamfetamine is the only exception
But this may be due to slow onset of the drug rather than extended half life
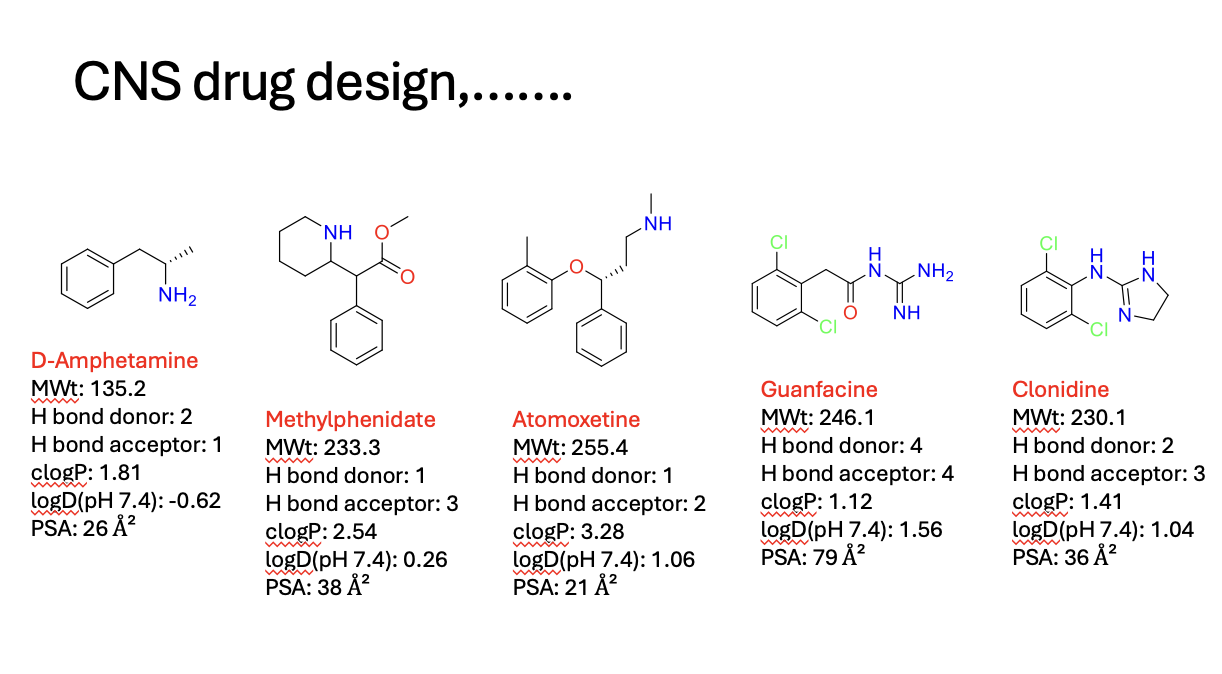
Chemical structures of CNS drugs
beware sometimes the lipinski rules don’t always apply
1 hydrogen bonds
lipophilic (positive log P)
Issues with tolerance
One explanation is that the slower onset and lower Cmax of LDX causes less acute tolerance than immediate release preparations, leading to an extended duration of action
so even though the given dose via immediate or oral release has the same AUC and t1/2
there may be underlying effects that induce tolerance quicker