Spinal Cord
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering spinal cord anatomy, meninges, spinal nerves, gray and white matter structures, and reflex physiology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
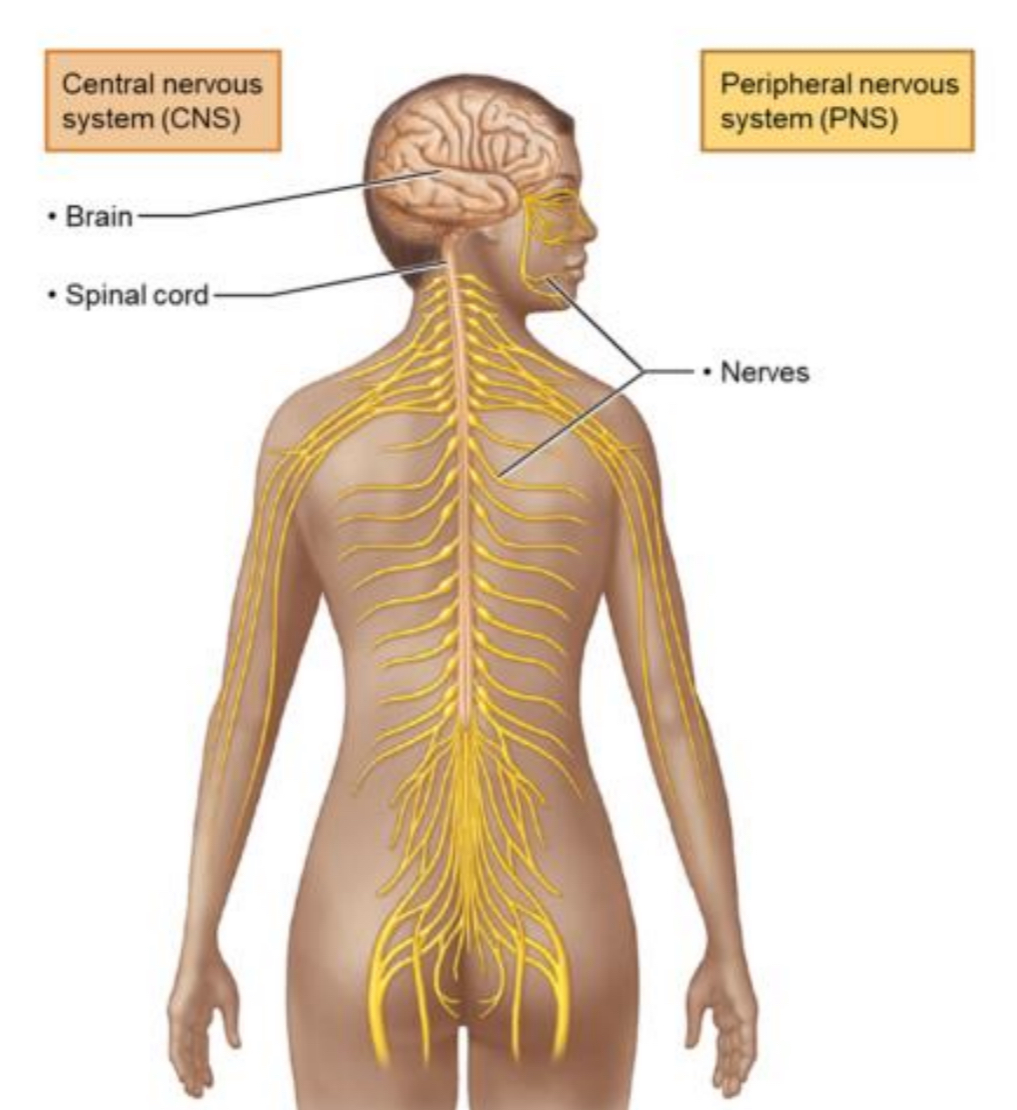
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Comprises the brain and spinal cord; responsible for integrating sensory information and coordinating motor output.
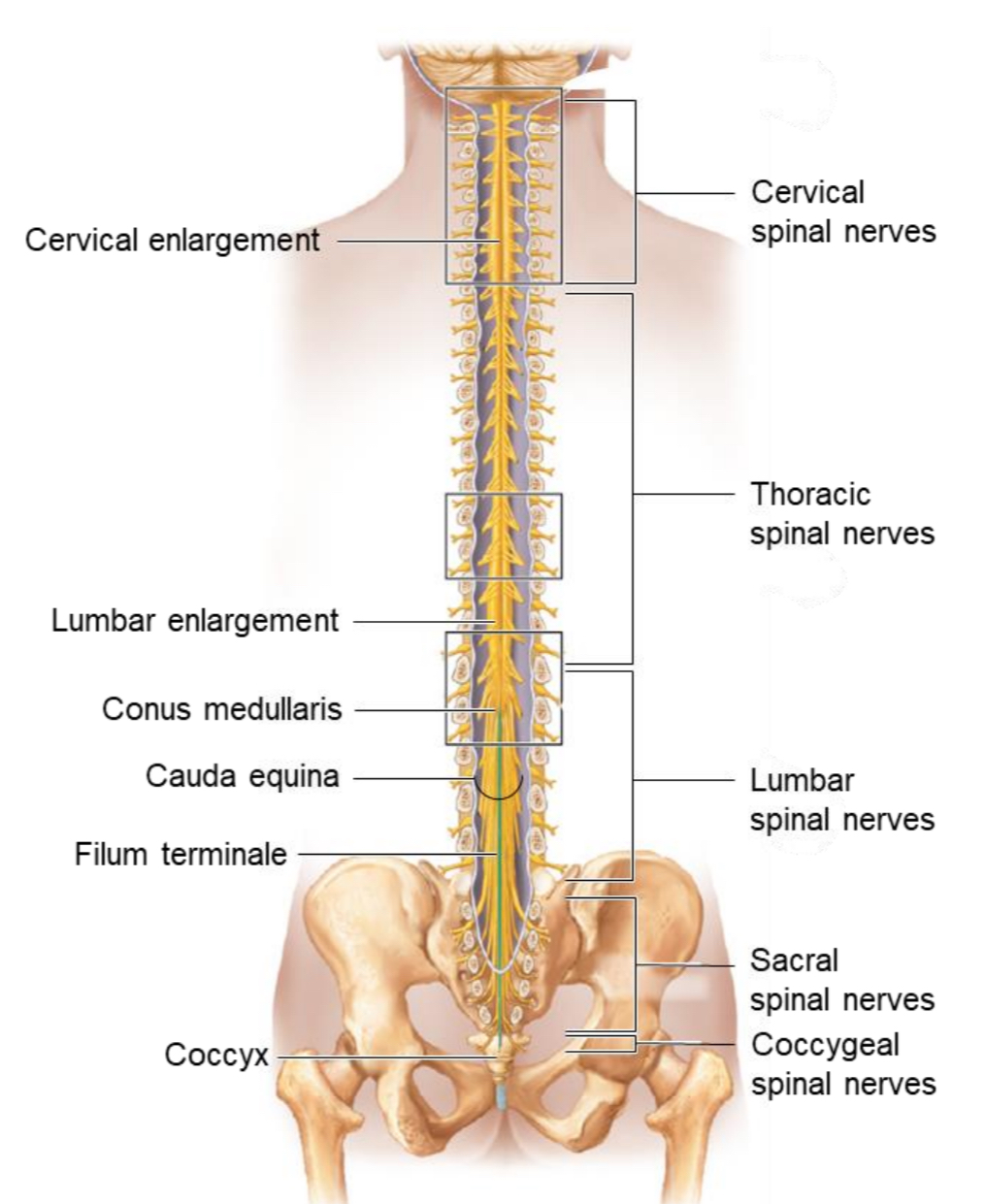
Spinal Cord
Location: CNS structure extending from the foramen magnum C1 → L2 vertebra
Function: conducts impulses to/from the brain and mediates spinal reflexes.
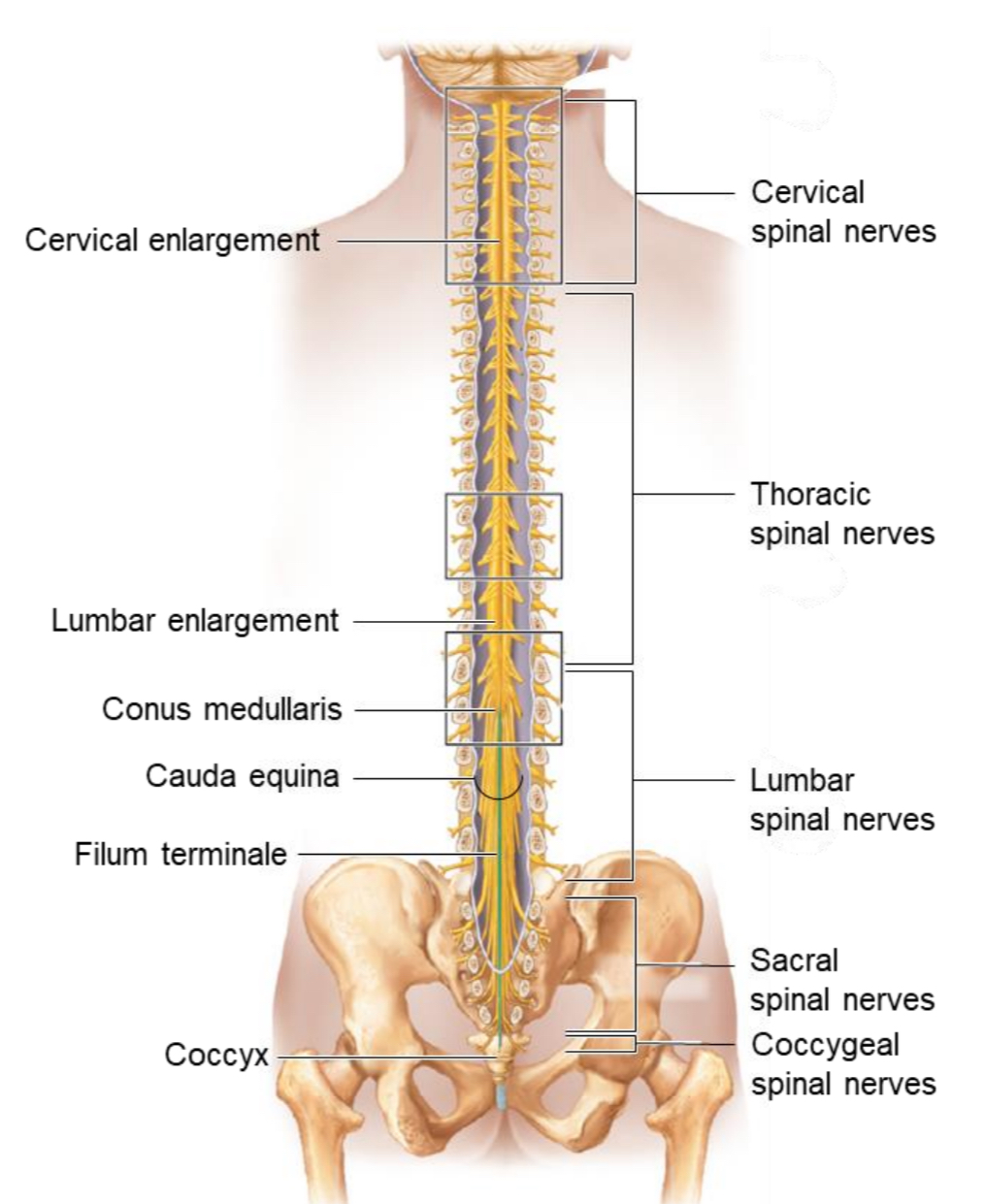
Conus Medullaris
The tapered, cone-shaped end of the spinal cord around L1–L2.
Anterior median fissure aka cleavage
Anterior deep crevasse in the middle of the spine
Posterior median sulcus aka butt crack
Posterior shallow depression in the middle of the spine.
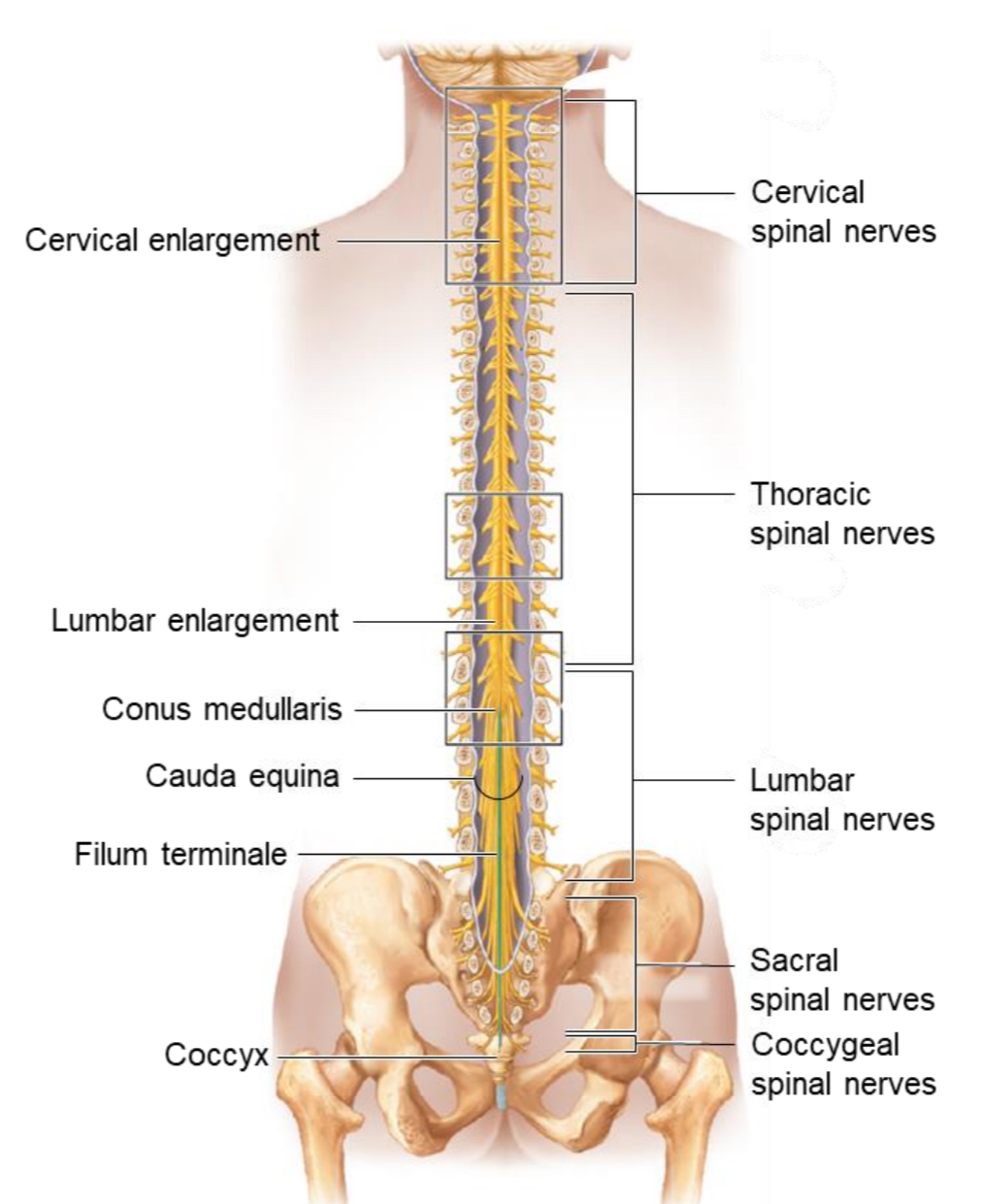
Filum Terminale
A thread-like extension of pia mater that anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx.
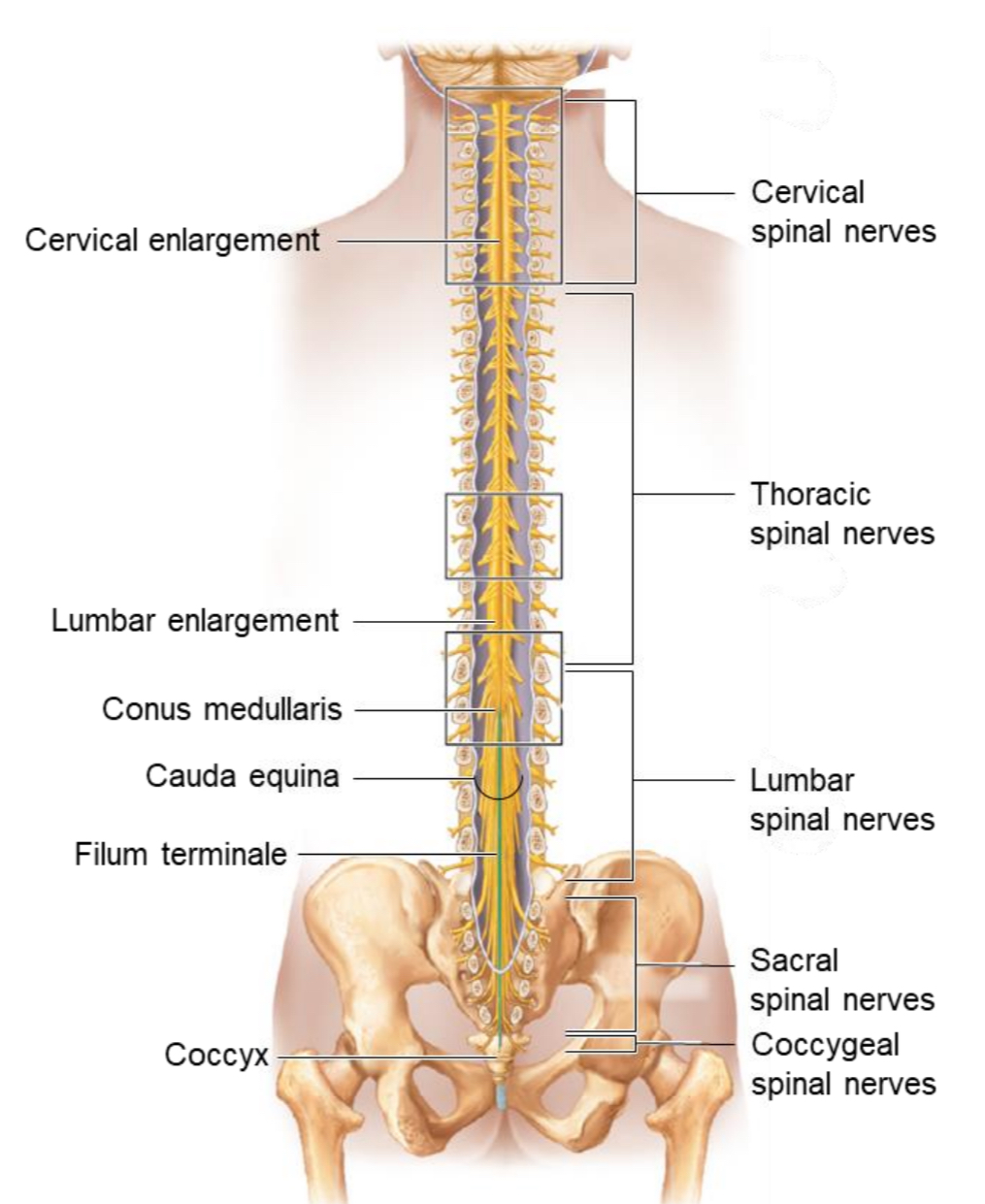
Cauda Equina
A bundle of spinal nerve roots below L2 resembling a horse’s tail; site for lumbar puncture (spinal tap).
Cervical Enlargement
Widened region of the spinal cord
Function: gives rise to nerves supplying the upper limbs.
Lumbosacral Enlargement
Widened region of the spinal cord
Function: gives rise to nerves supplying the lower limbs.
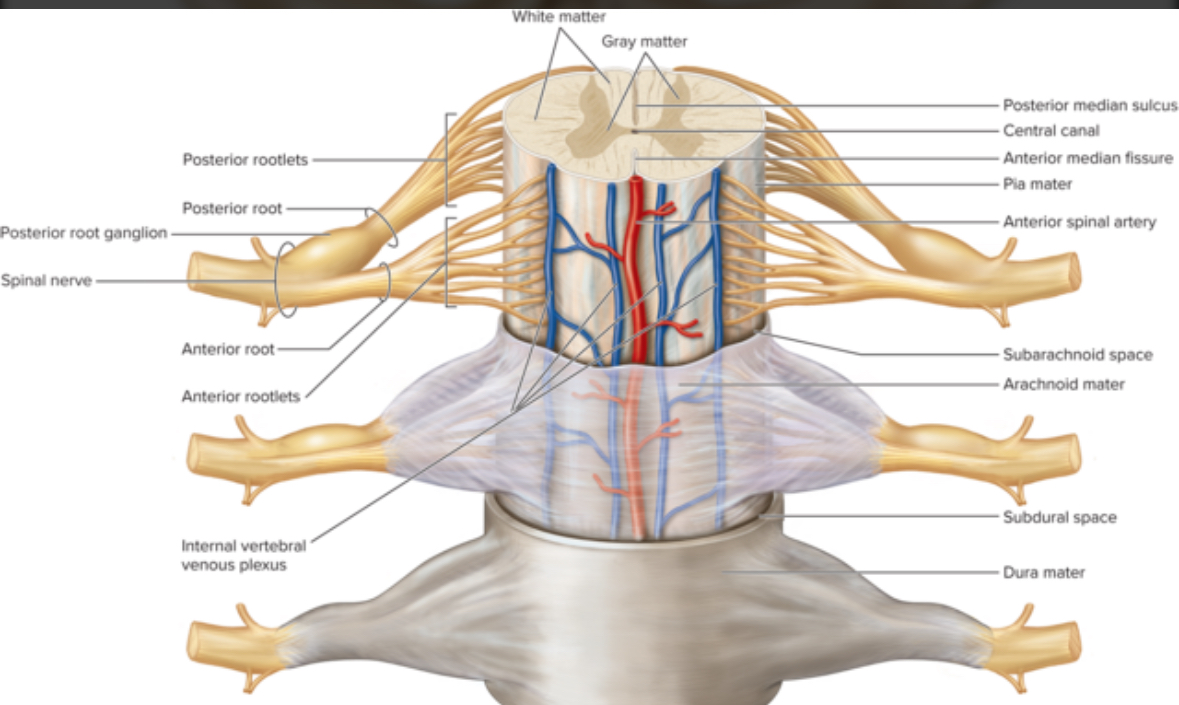
3 Layers of the spinal cord, meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
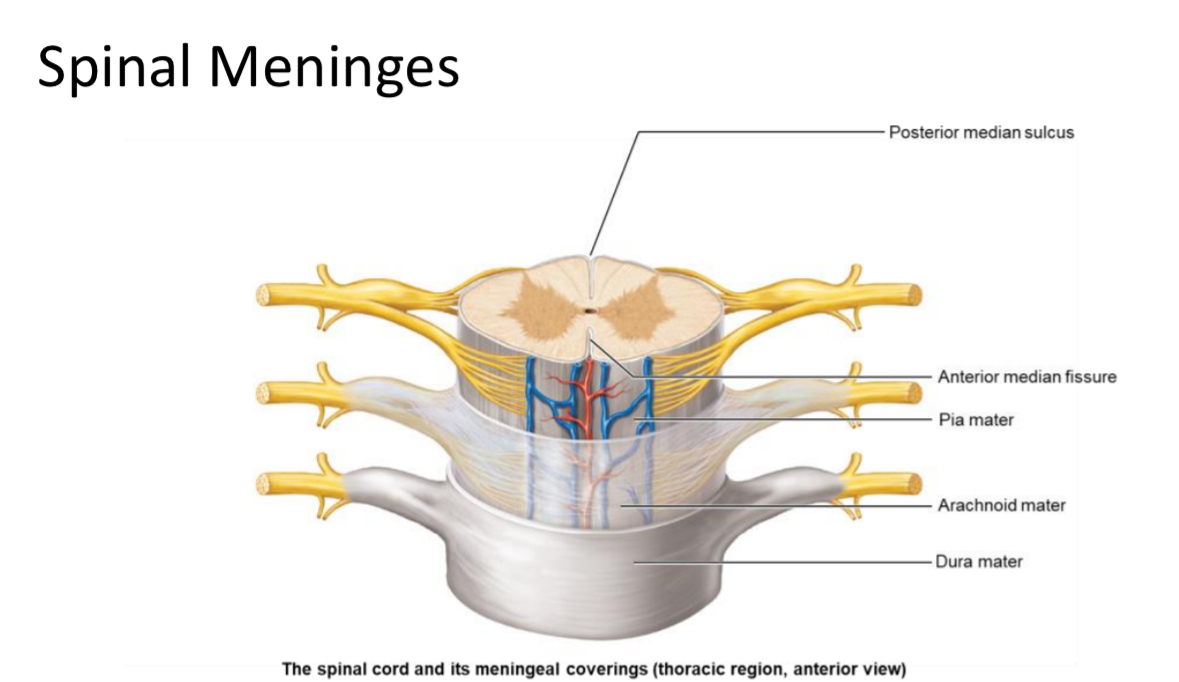
Dura Mater
Location: most superficial spinal meninx
Structure: dense irregular CT
Function: support and structure
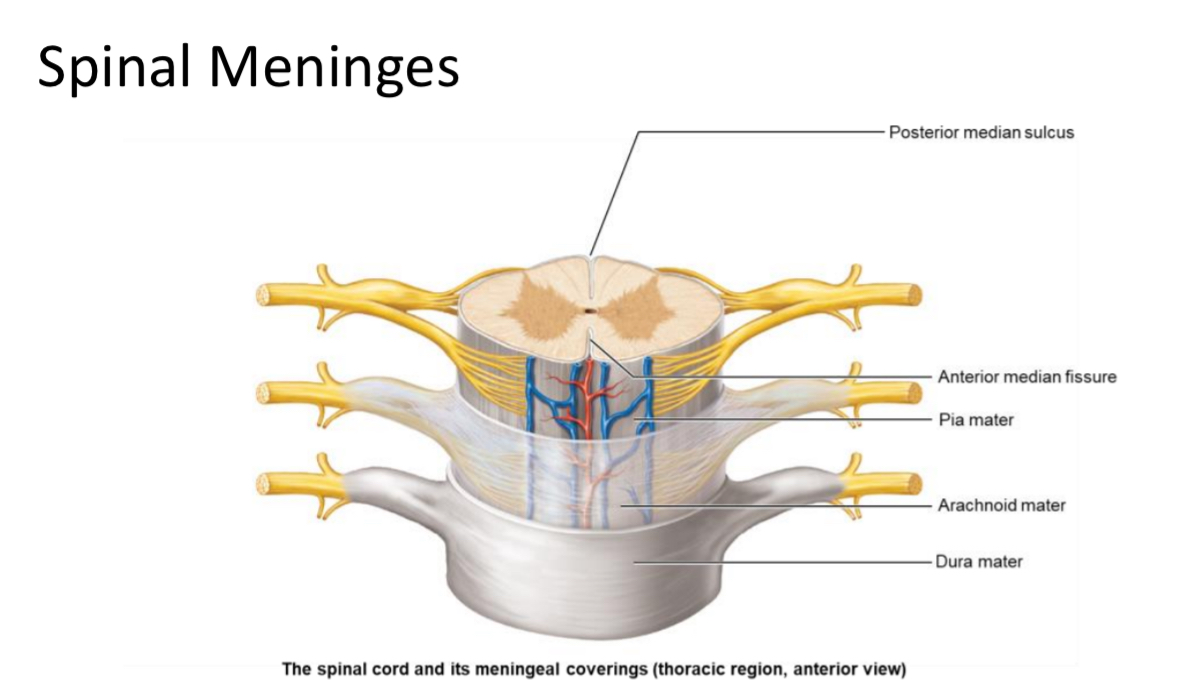
Arachnoid Mater
Location: Middle meninx
Structure: dense irregular CT and elastic fibers
Function: support
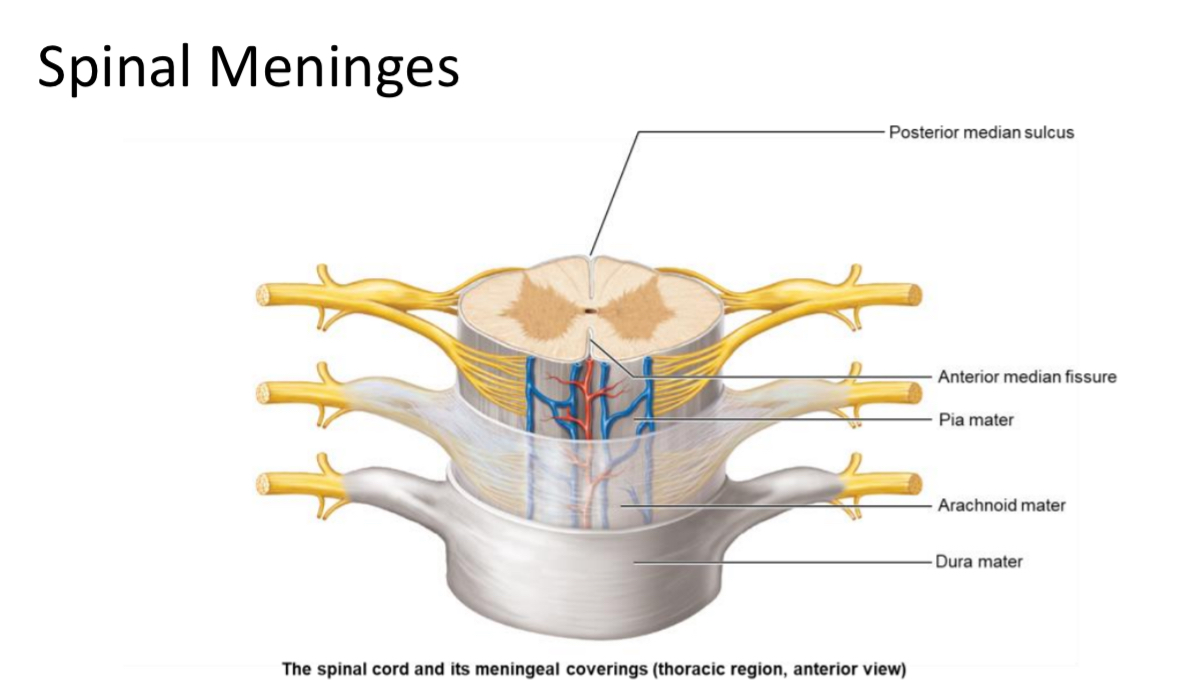
Pia Mater
Location: deepest meninx
Structure: areolar CT
Function: metabolic support.
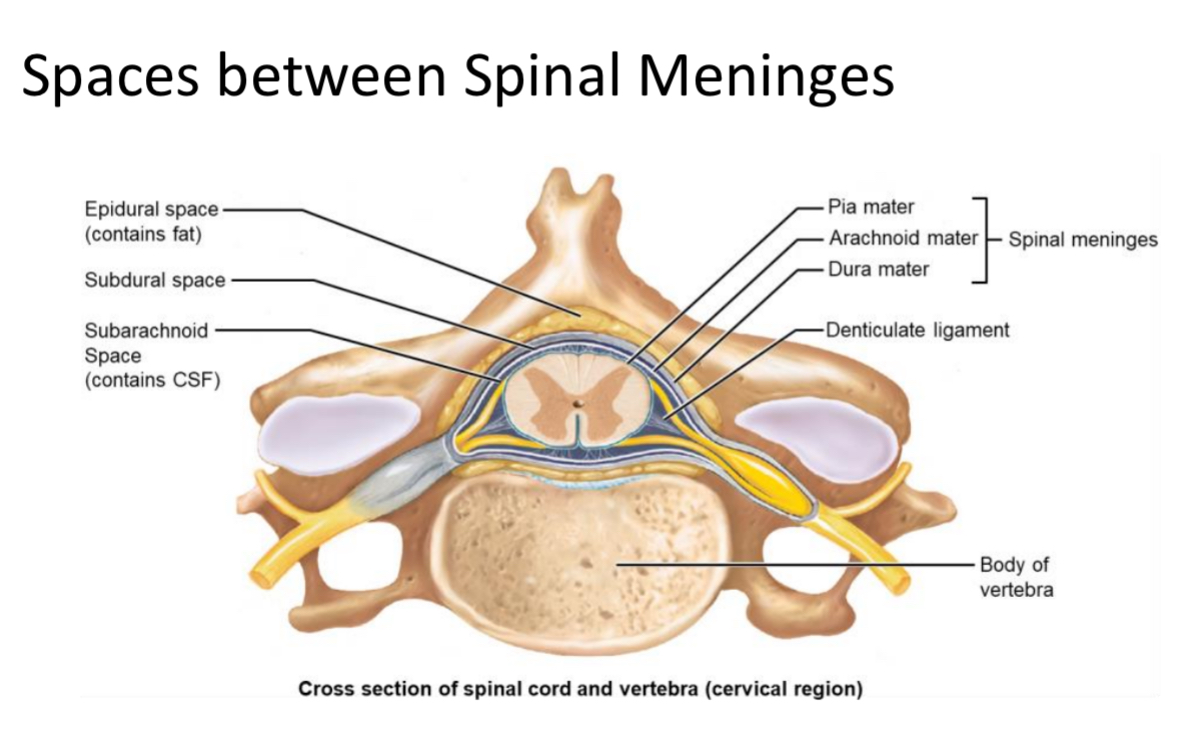
Denticulate Ligaments
Triangular extensions of pia mater that laterally anchor the spinal cord to the dura mater.
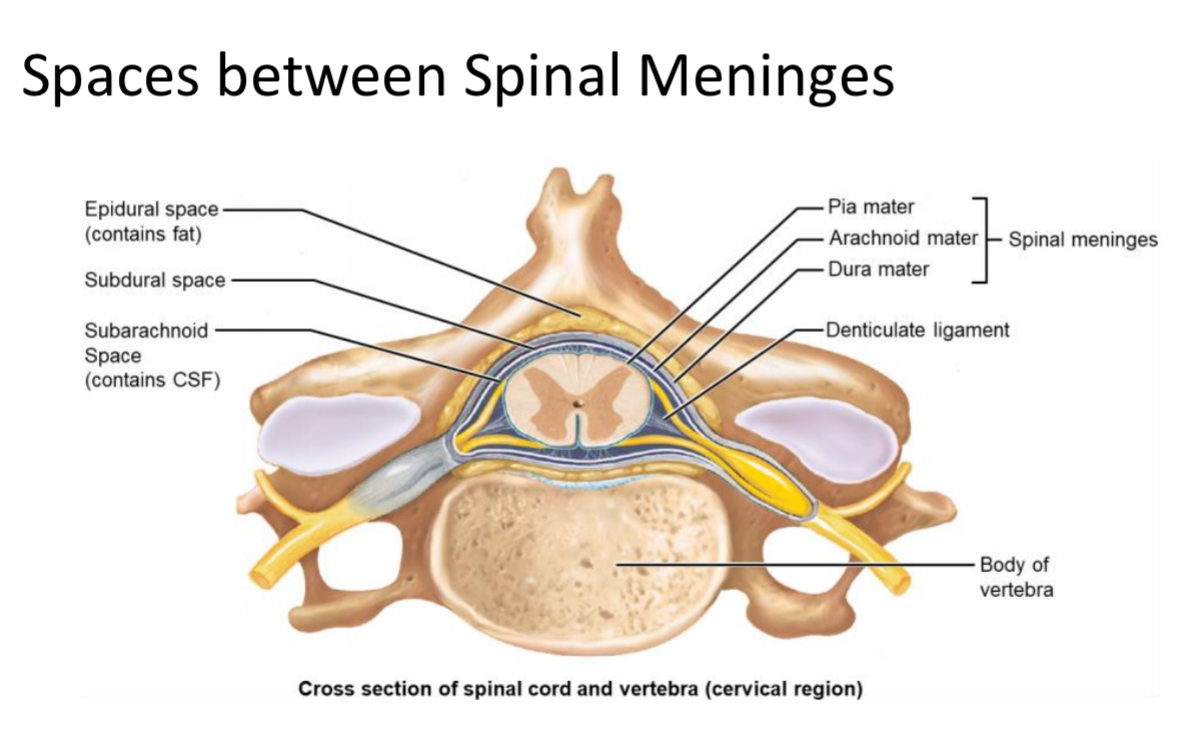
Epidural Space
Space between vertebrae and dura mater filled with adipose tissue; site of epidural injections.
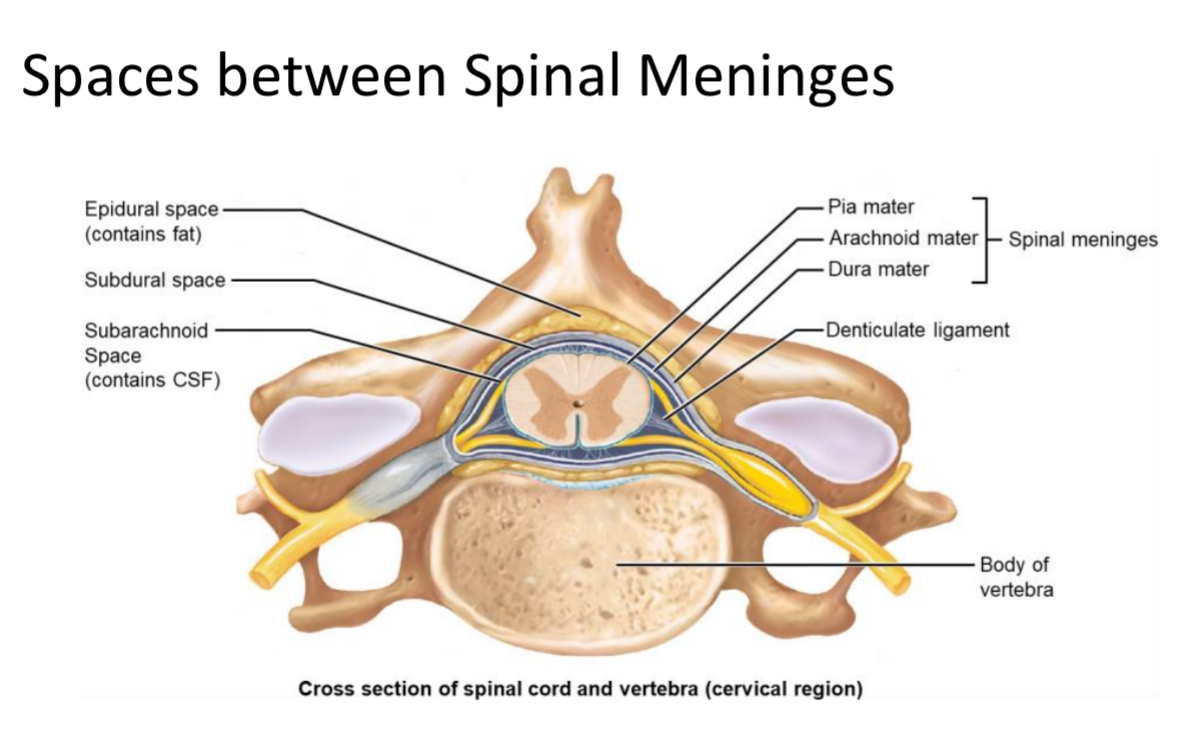
Subdural Space
Potential space between arachnoid mater and dura mater.
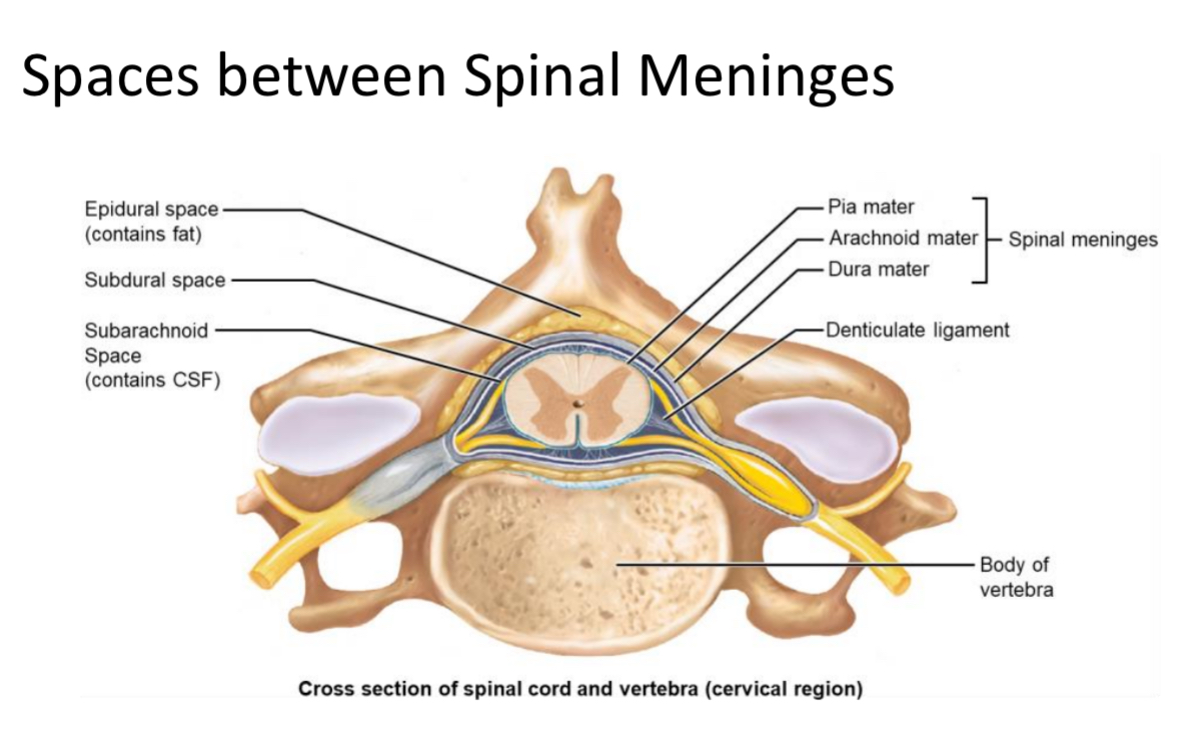
Subarachnoid Space
Space between arachnoid and pia mater containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for metabolic support and buoyancy.
Spinal roots
nerves stemming from spinal cord surface
Bunch of axons
Rootlets
Smaller spinal roots
Project from the surface of spinal cord
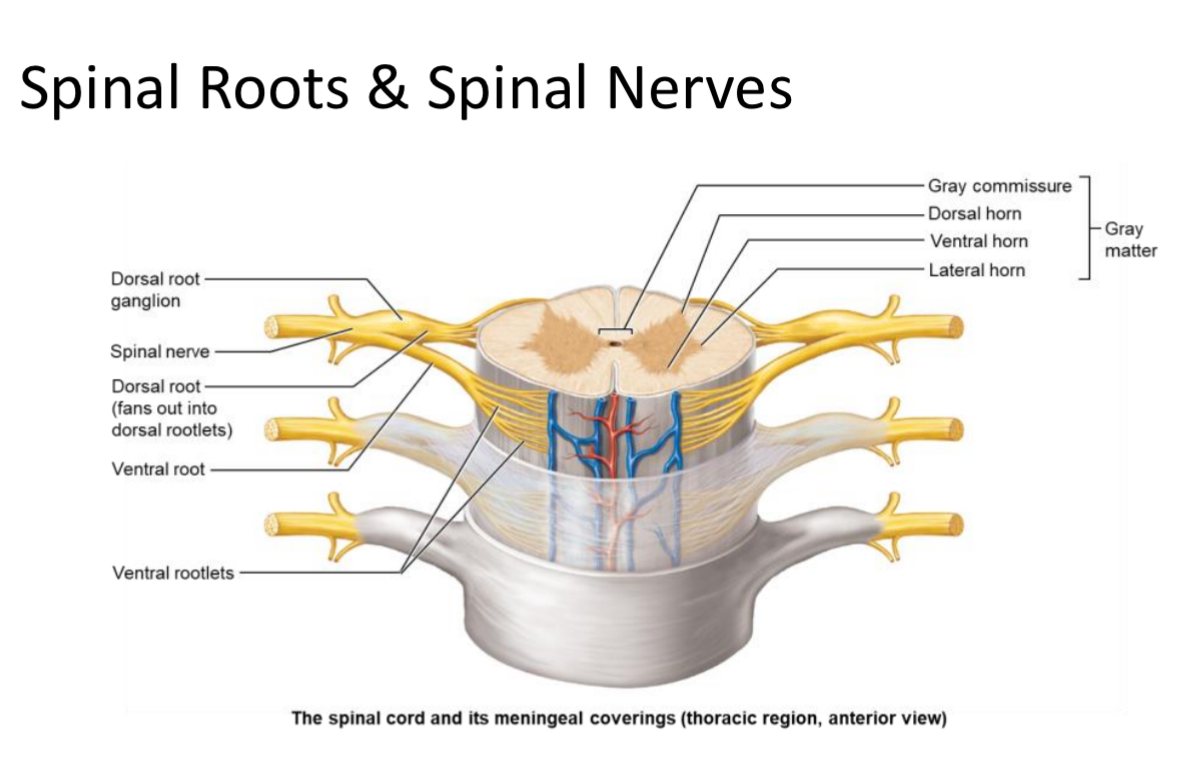
Ventral Rootlets
Small bundles of motor neuron axons exiting the spinal cord surface from the front; merge to form a ventral root.
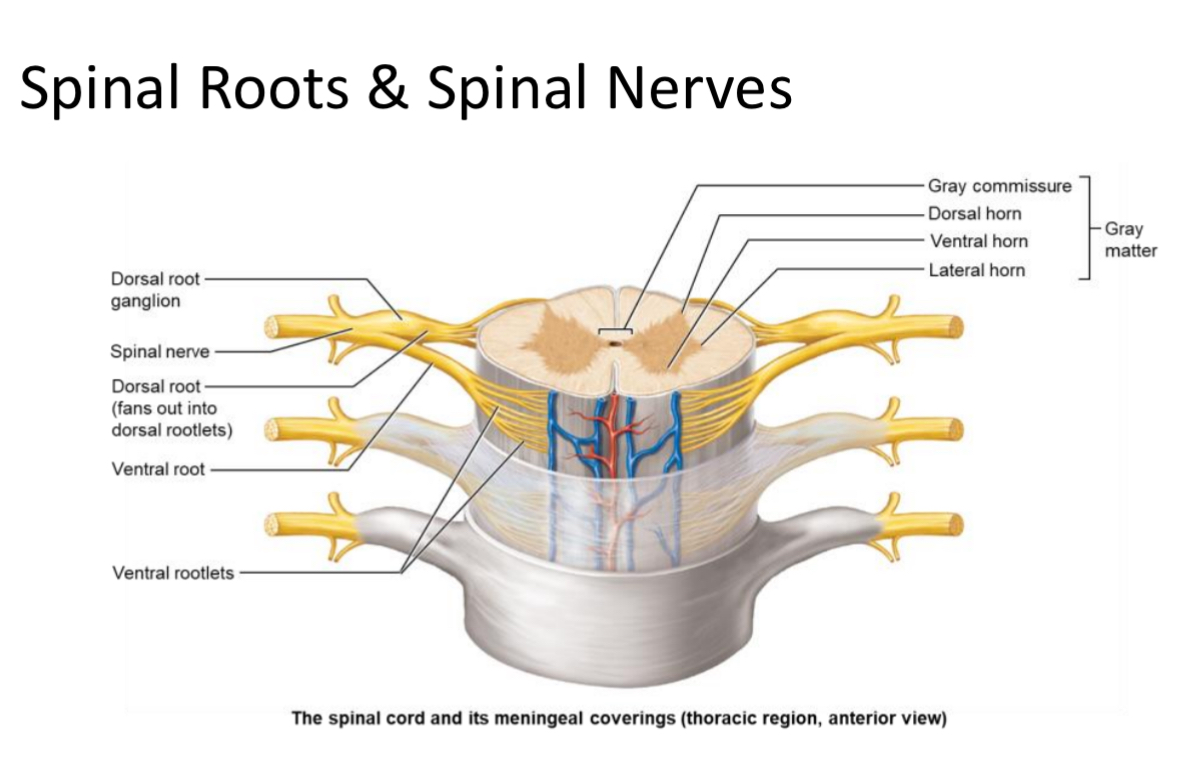
Ventral Root
Bundle of ventral rootlets carrying efferent (motor) axons from the spinal cord.
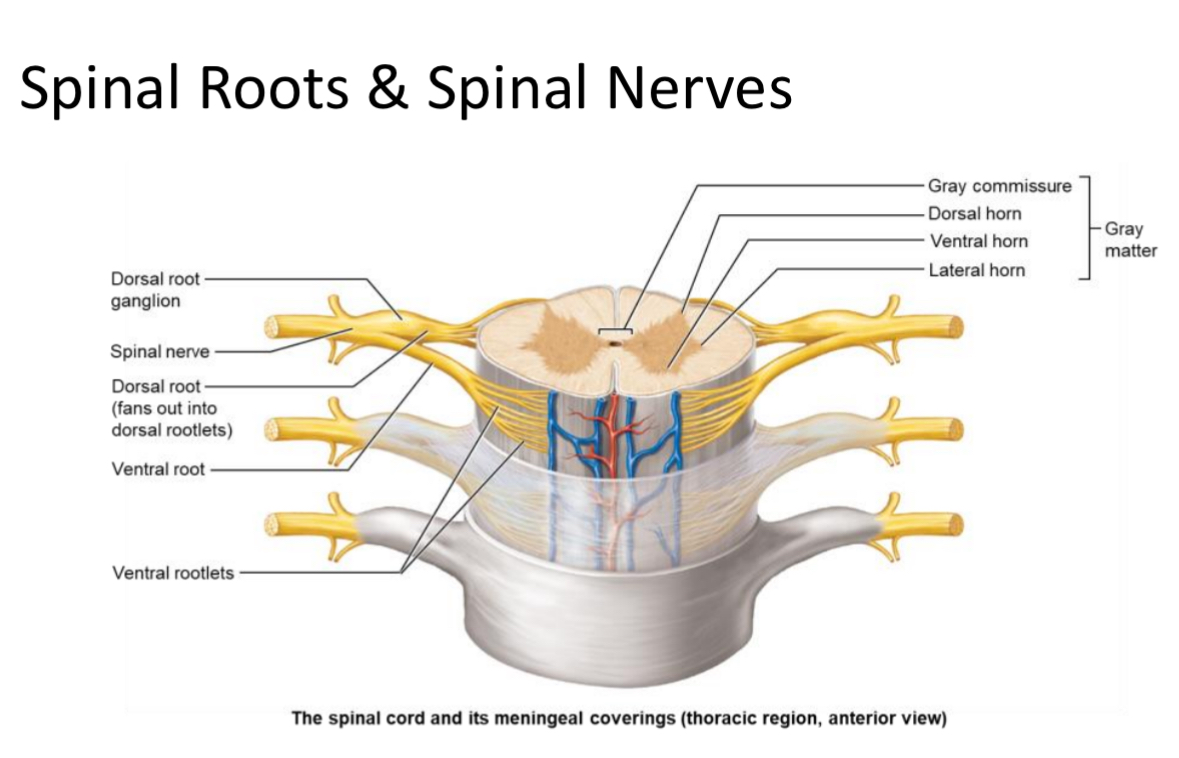
Dorsal Rootlets
Small bundles of sensory neuron axons entering the spinal cord from the back; merge to form a dorsal root.
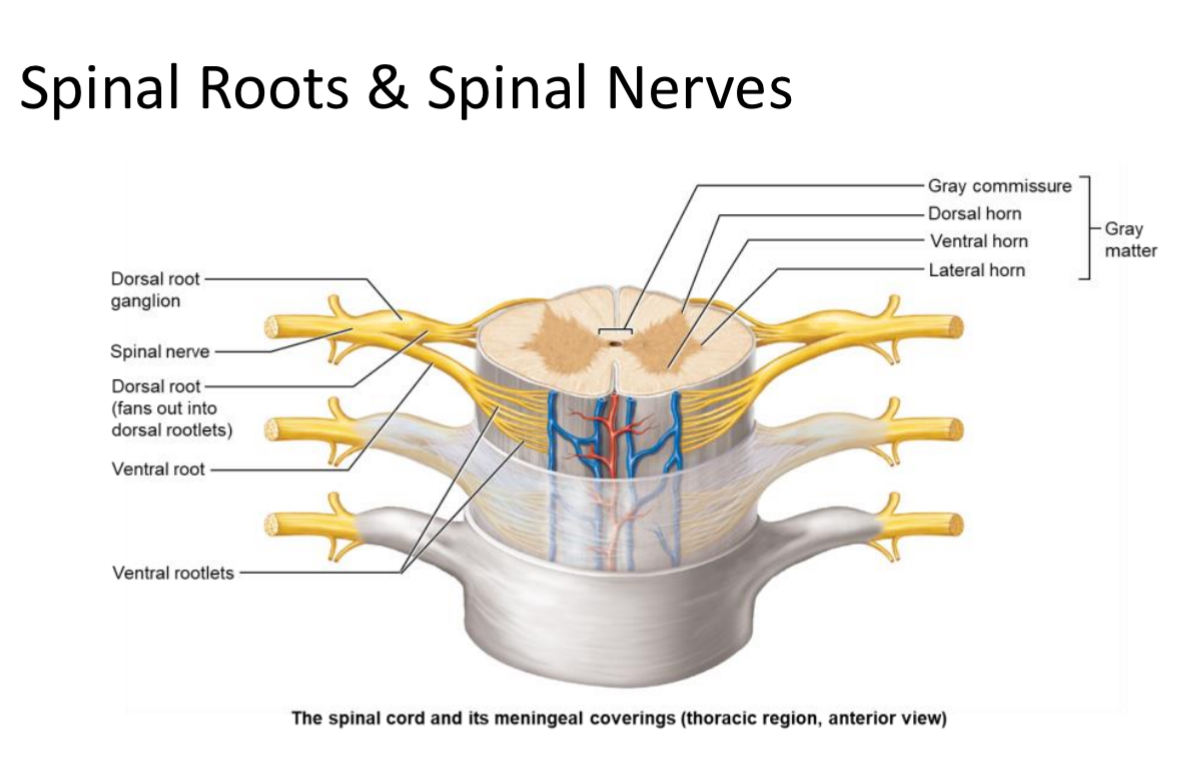
Dorsal Root
Bundle of dorsal rootlets carrying afferent (sensory) axons to the spinal cord; contains the dorsal root ganglion.
Spinal root
Contains both ventral and dorsal roots
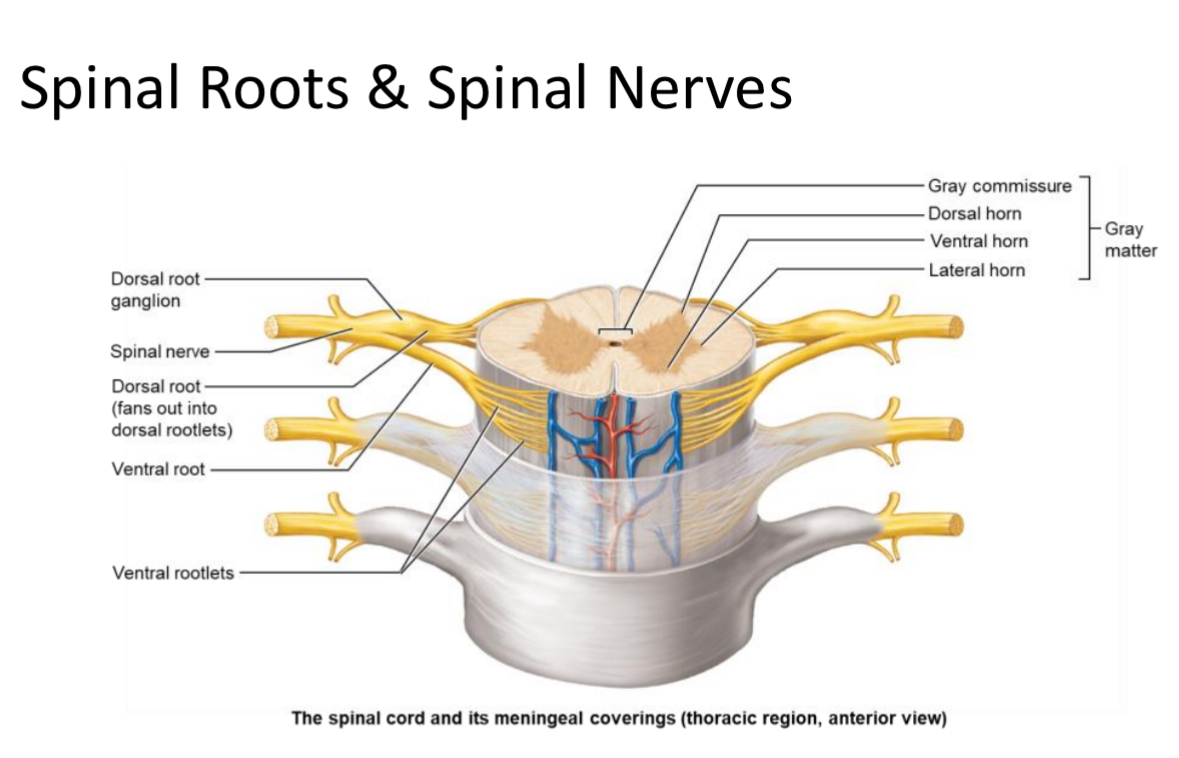
Spinal Nerve
Mixed nerve formed by union of a dorsal and ventral root; there are 31 pairs named by vertebral region.
Regions of spinal nerves that stick out
Cervical spinal nerves
Thoracic spinal nerves
Lumbar spinal nerves
Sacral spinal nerves
Coccygeal spinal nerves
2 types of tissue make up the spinal cord
Grey matter
White matter
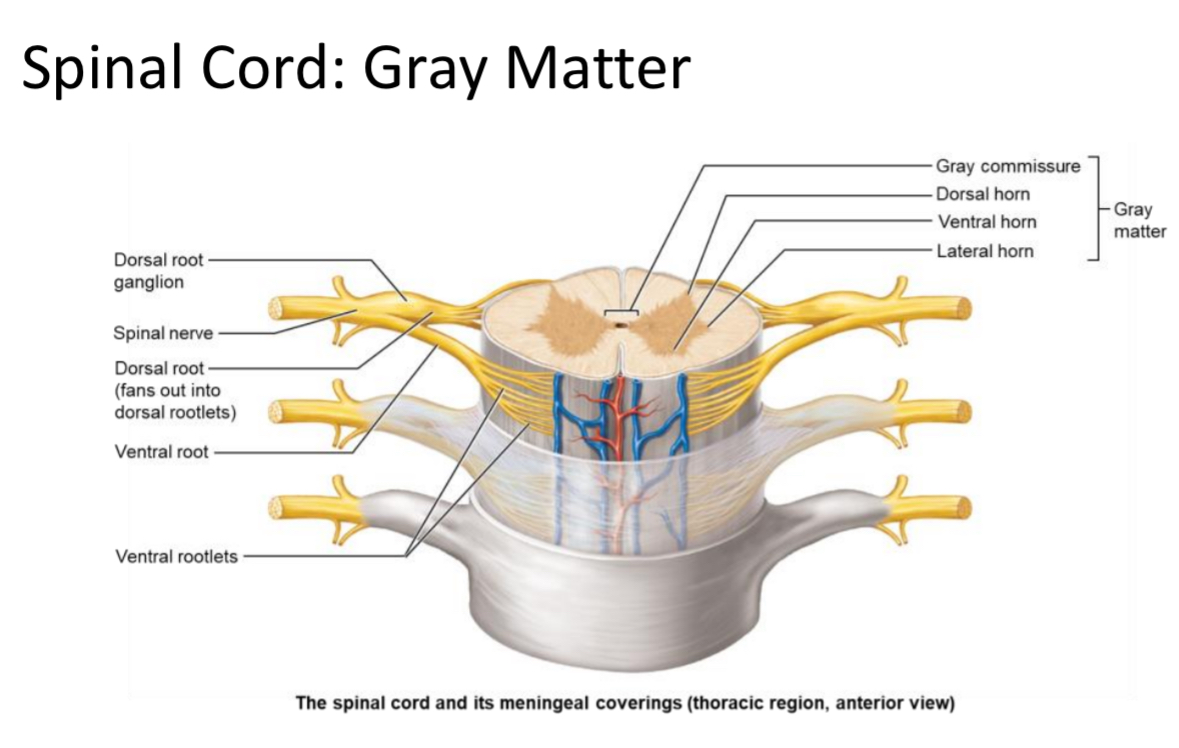
Gray Matter
Location: Inner spinal cord tissue
Structure: butterfly containing neuron cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons; arranged in ‘horns.’
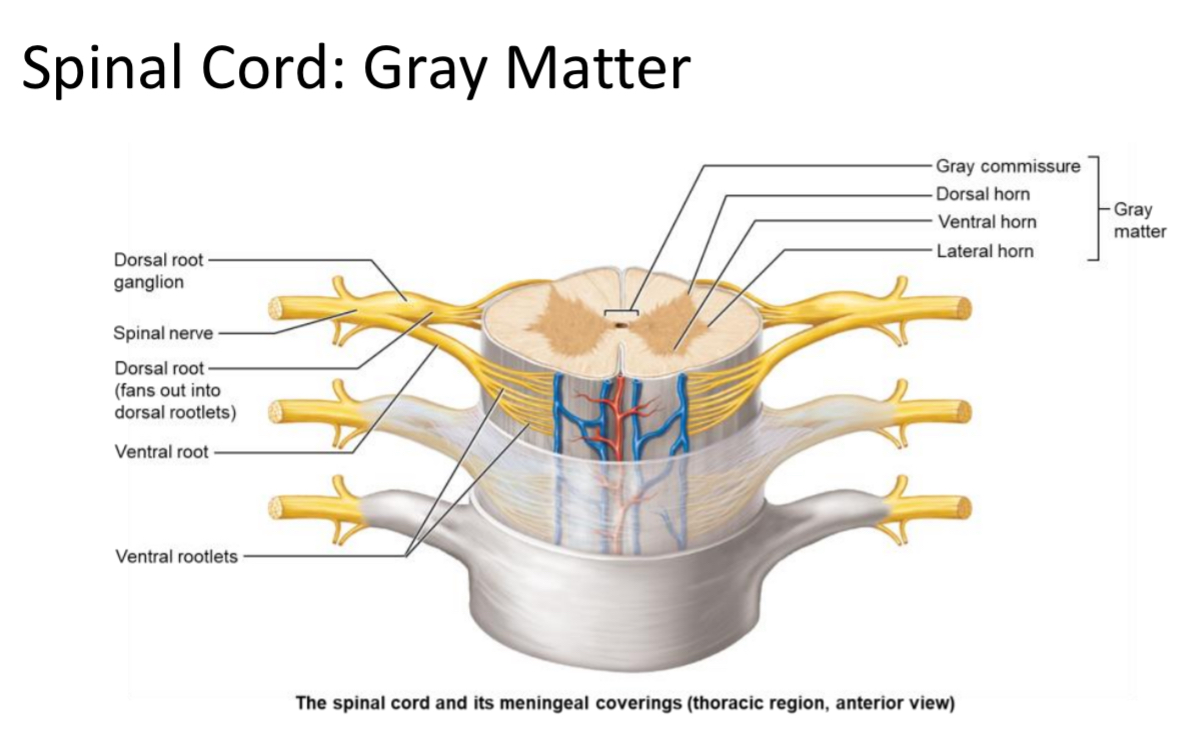
Gray Commissure
Cross-bar of gray matter connecting the two spinal cord wings; surrounds the central canal.
Central Canal
CSF-filled channel in the center of the spinal cord lined by ependymal cells.
Divided regions of the grey matter, horns
Ventral grey horn
Dorsal grey horn
Lateral grey horn
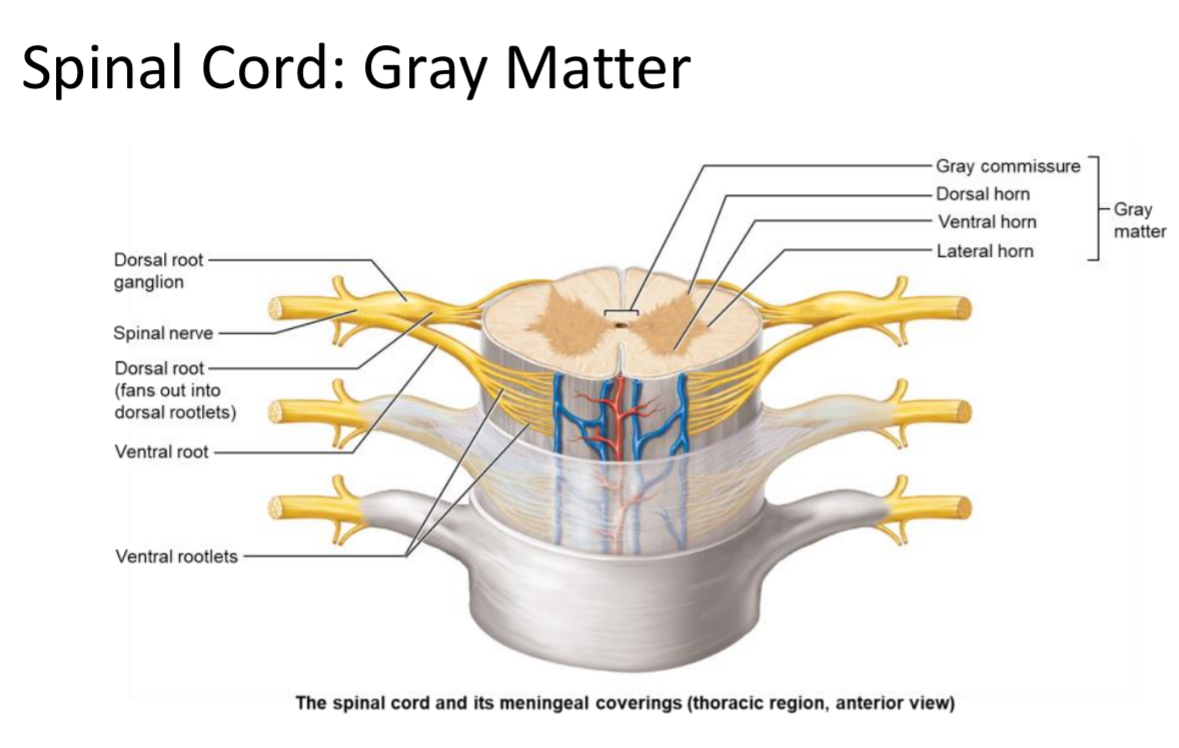
Ventral Horn
Location: Gray matter region of spinal cord
Structure: houses somatic motor neuron cell bodies. multipolar neurons
Function: send motor output to skeletal muscle. Somatic motor output.
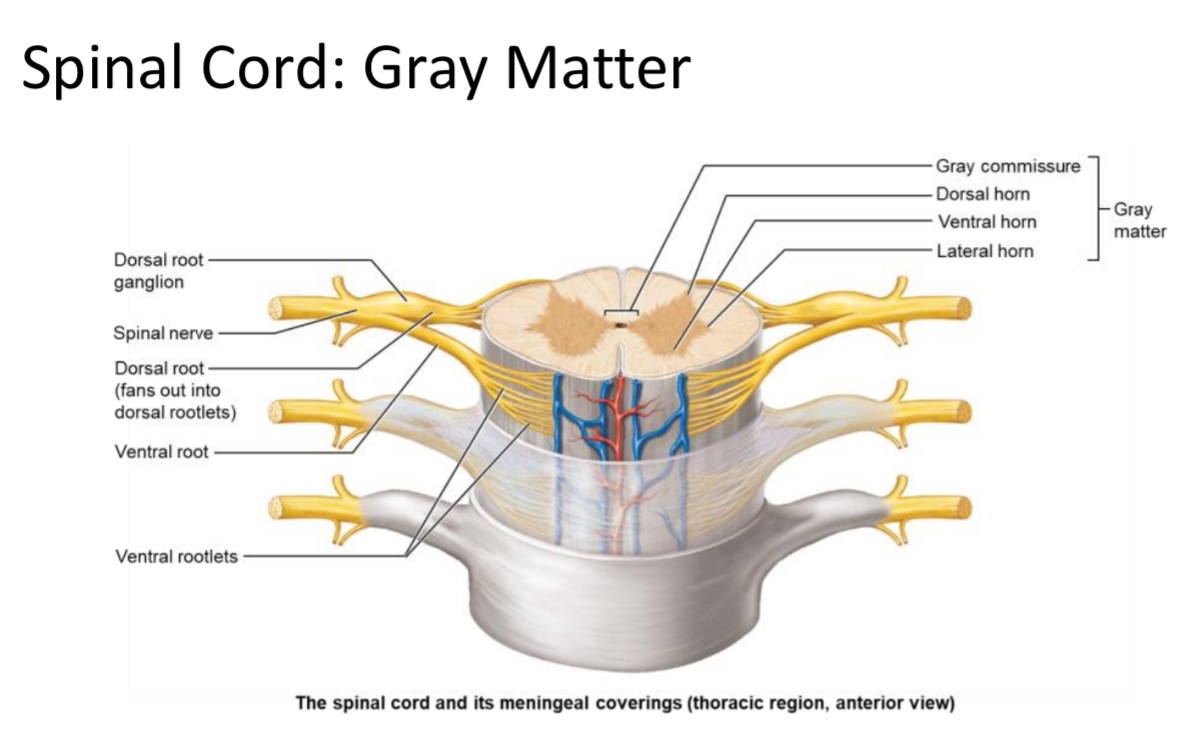
Dorsal Horn
Location: Gray matter region of spinal cord
Structure: unipolar sensory neurons with cell bodies living in the dorsal root
Function: receive sensory input from the body but not from special senses: eyes, ears, or taste buds
Dorsal root ganglion
A collection of cell bodies of sensory neurons
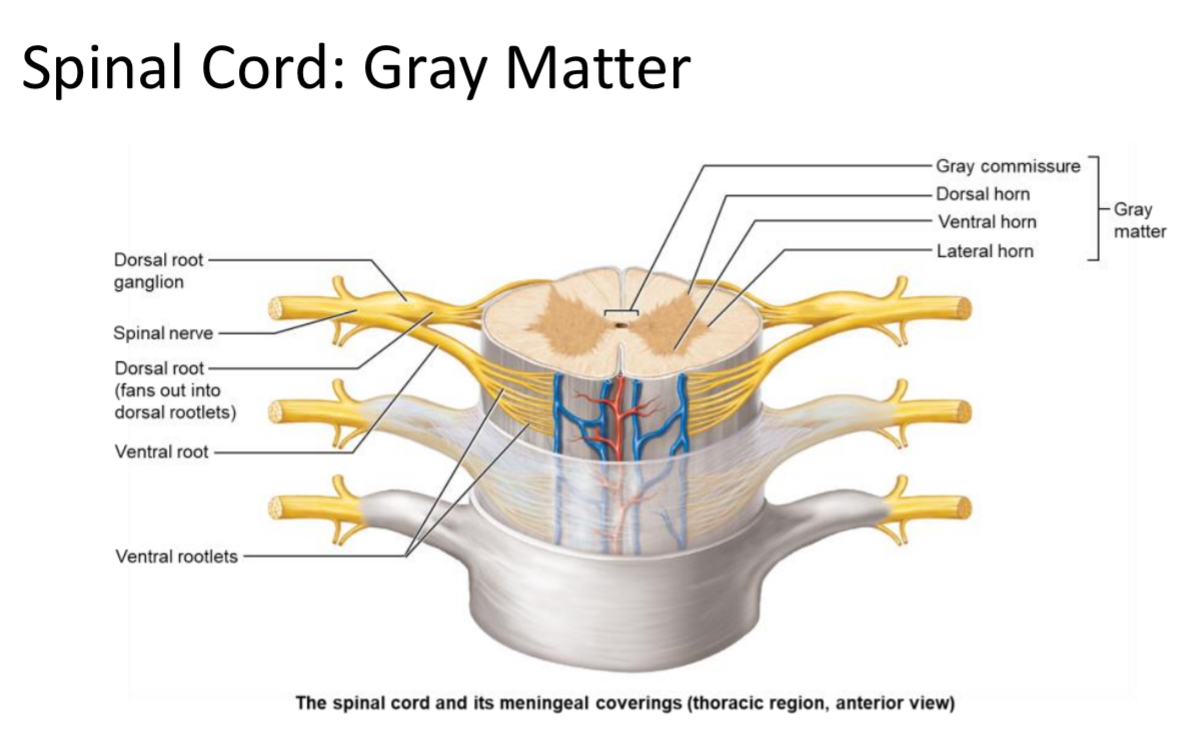
Lateral Horn
Location: Gray matter region between T1–L2
Structure: contains autonomic multipolar motor neuron cell bodies
Function: send output to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
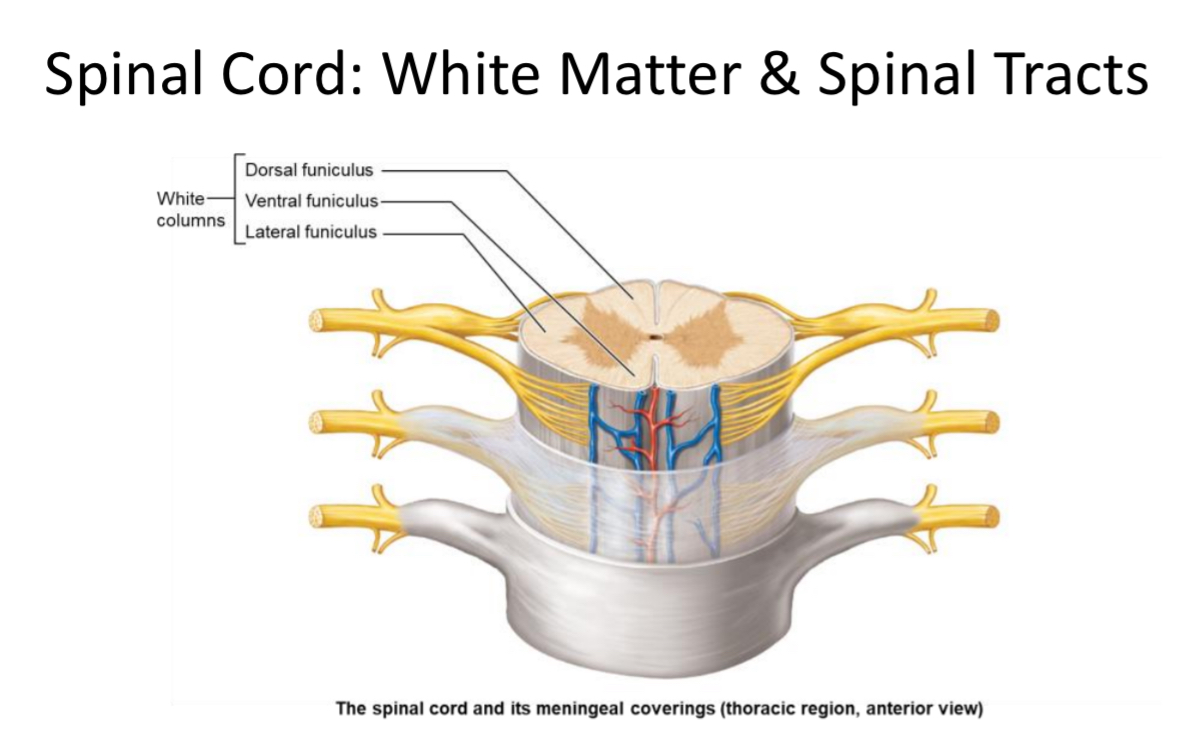
White Matter
Location: Outer spinal cord tissue
Structure: composed of tracts organized into funiculi. Like cables
Function: axons transmit information to and from the brain
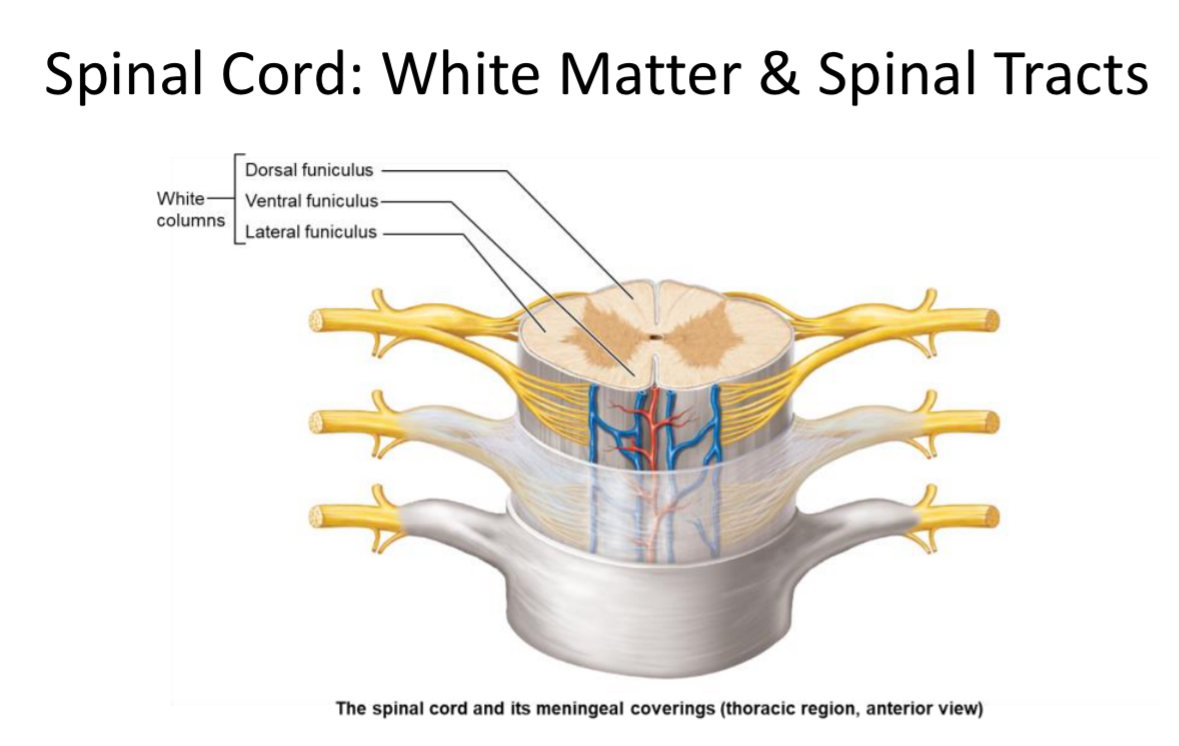
Funiculus (White Column)
One of three major regions (anterior, lateral, posterior) of spinal cord white matter carrying ascending/descending tracts.
Tract
Bundle of myelinated axons within the CNS transmitting specific information.
Nucleus (CNS)
Cluster of neuron cell bodies within the central nervous system gray matter.
Ganglion (PNS)
Cluster of neuron cell bodies located outside the CNS, e.g., dorsal root ganglion.
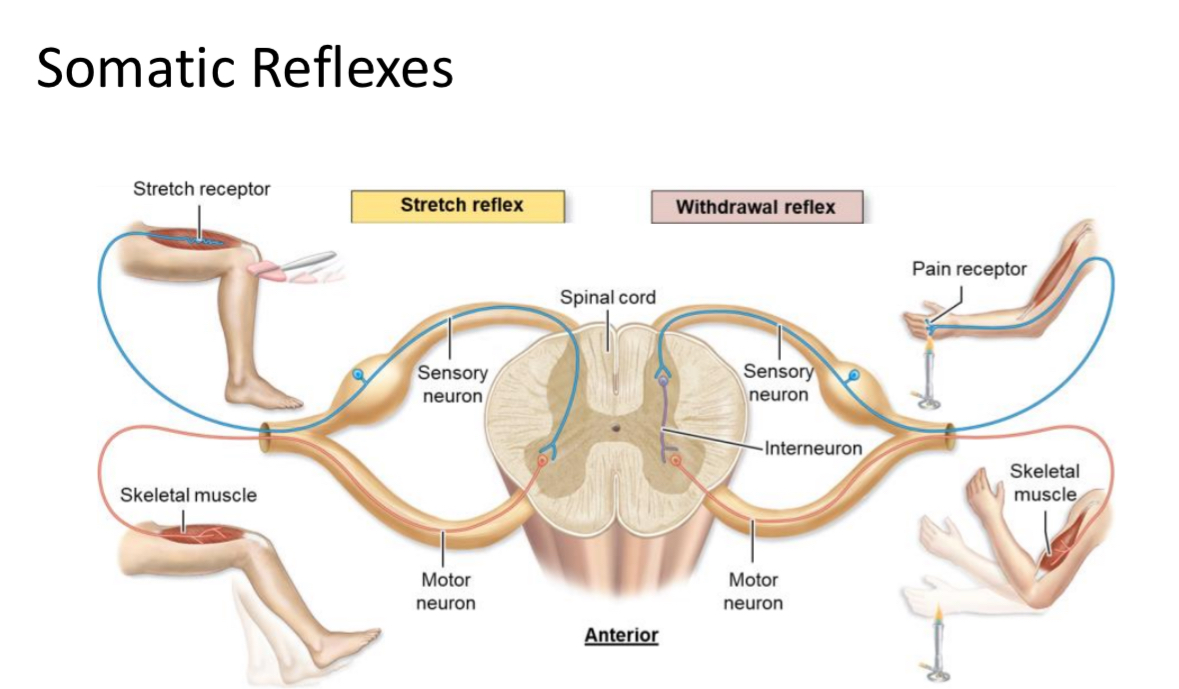
Reflex
A rapid, automatic motor response to a specific sensory stimulus.
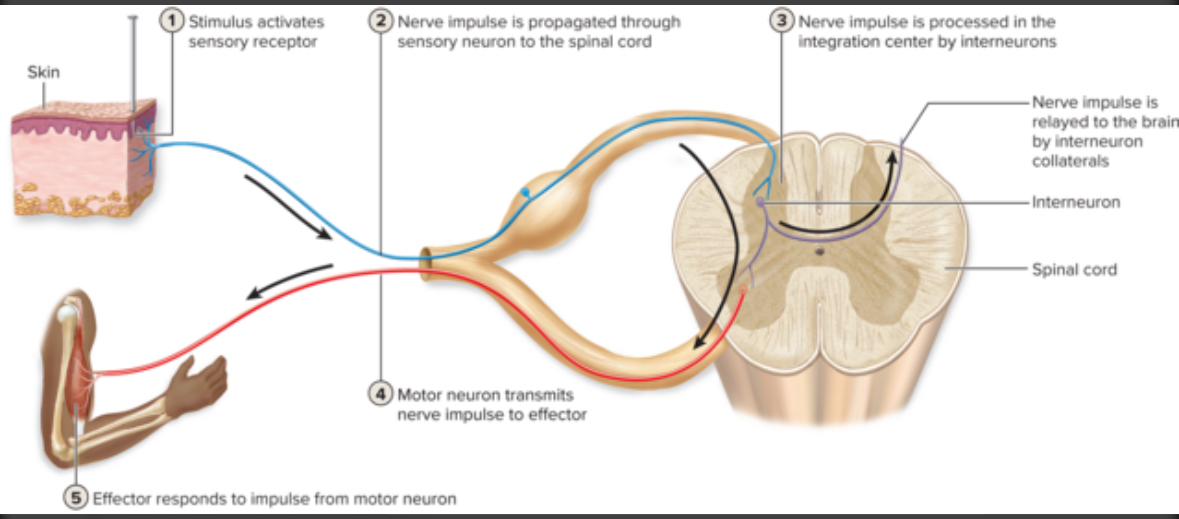
Reflex Arc
Neural pathway of a reflex involving a sensory neuron, integration center (± interneuron), and motor neuron.
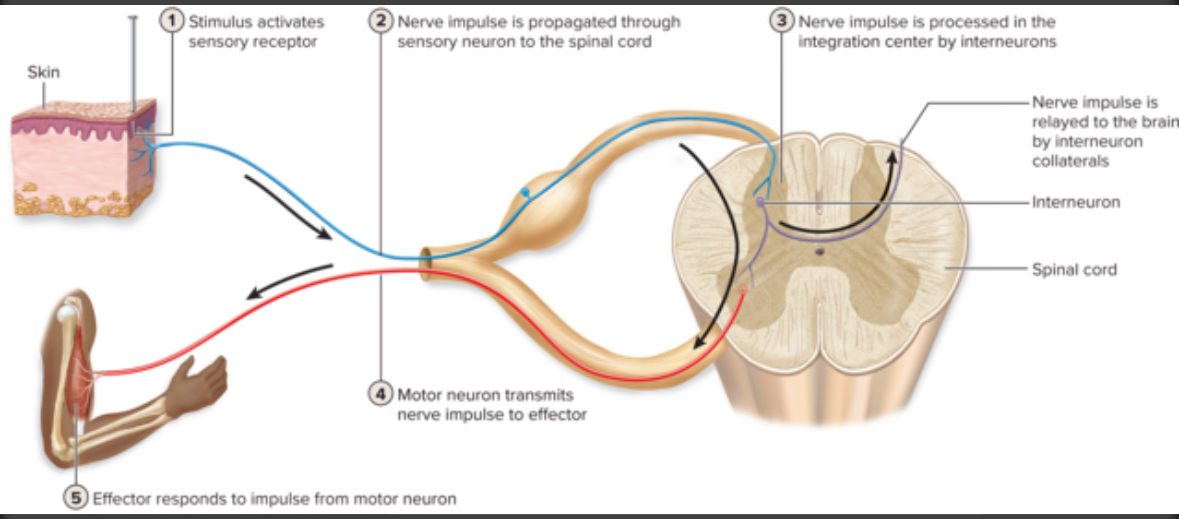
3 components of reflex
Sensory neuron talking to interneuron
Interneuron takes information and decides what to do
Interneuron tells motor neuron what to do
2 types of reflex
Somatic
Autonomic
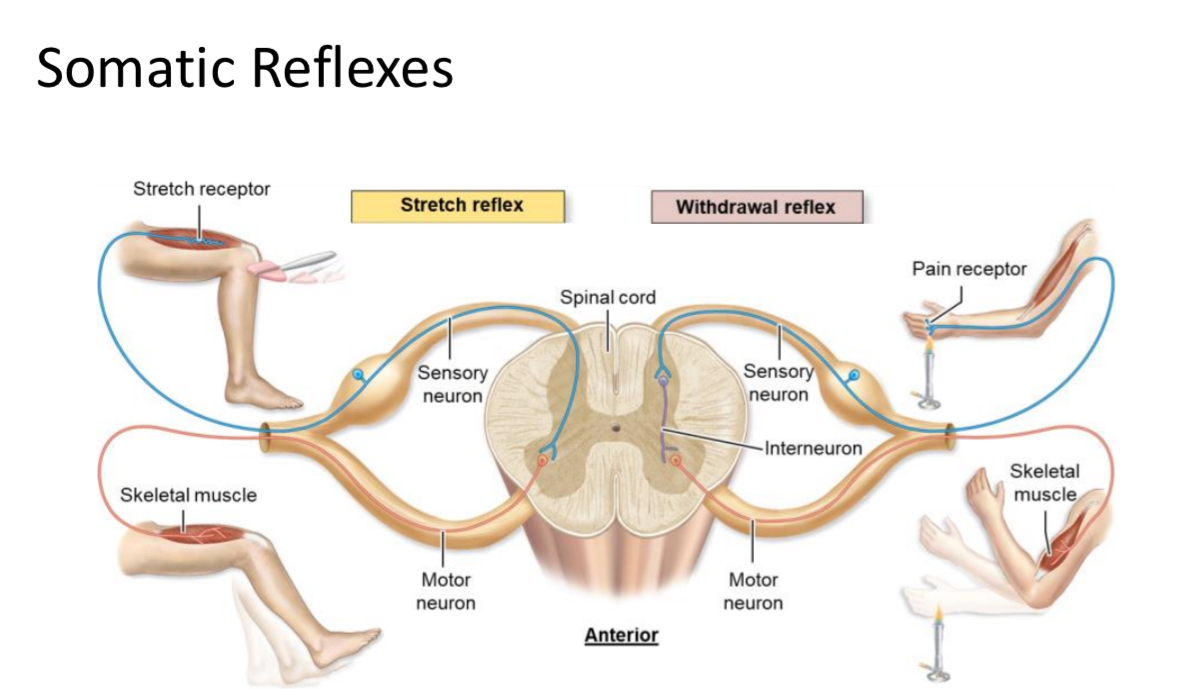
Somatic Reflex
Reflex that activates skeletal muscle, such as stretch and withdrawal reflexes.
Autonomic Reflex
Reflex that activates cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands
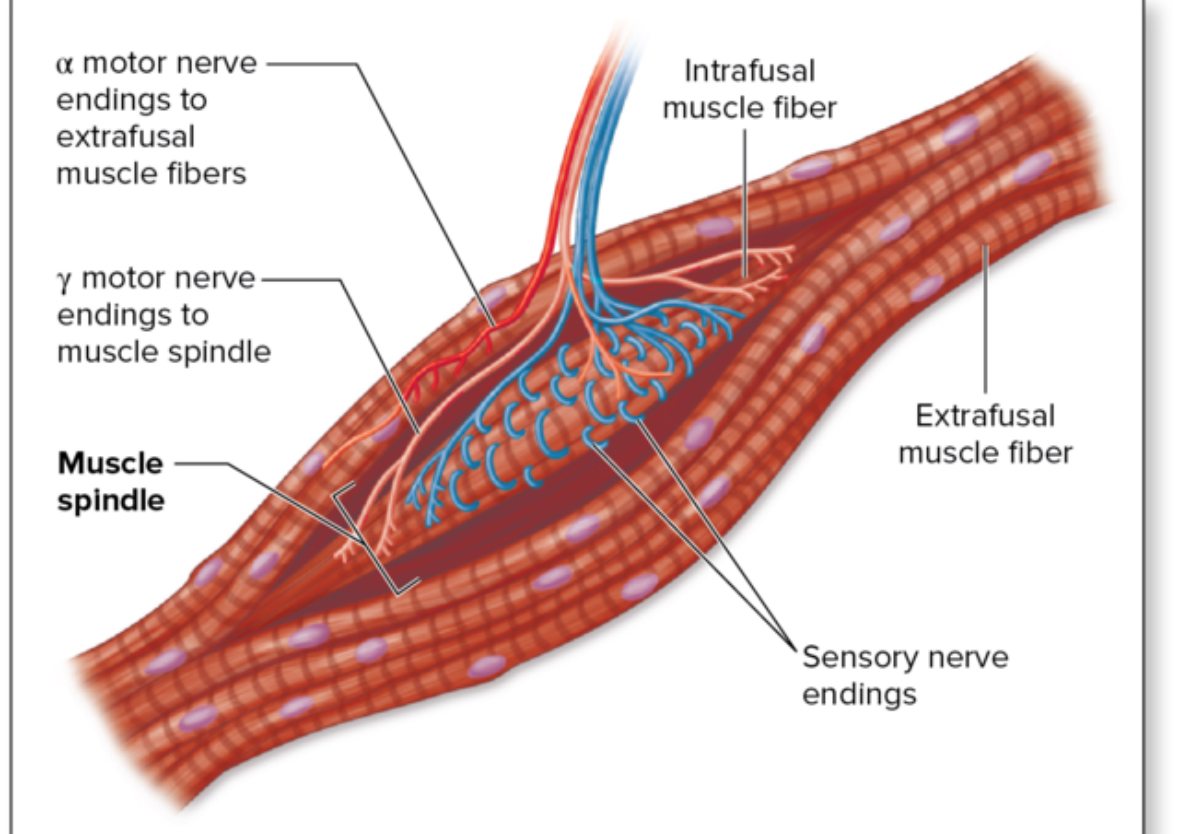
Stretch Reflex
Muscle contraction in response to muscle stretching; prevents overstretching (e.g., knee-jerk).
Withdrawal Reflex
Muscle contraction pulling a limb away from painful stimuli; protects tissues from damage.