Sub-Surface Test 2
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Wireline+Perforating+Wellbore Integrity & CBLs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
What is the primary objective of a perforating gun?
To provide effective flow communication between a cased wellbore and a productive reservoir
What types of logs are used to correlate perforation depth?
Gamma Ray
Casing Collar Locator (CCL) Logs
Name the 2 methods of perforating
Jet perforation
most common
shaped charge; high velocity gas
Bullet perforation
Name 1 benefit and 1 drawback of jet perforating
Benefit: minimizes casing and cement damage (compared to bullet perforation)
Drawback: can leave debris in the formation
TorF: Bullet perforating is mainly used to perforate in deep formations
False
it is used in moderately compressed (ie. shallow) formations
it produces shorter, smaller-diameter perforations and can’t effectively penetrate deep, compact, or high-pressure formations
Name 5 methods of perforating gun actuation (ie. triggering)
Electronic signal on e-line
Drop bar (mechanical)
Ball drop
Hydraulic delay
Programmable firing head
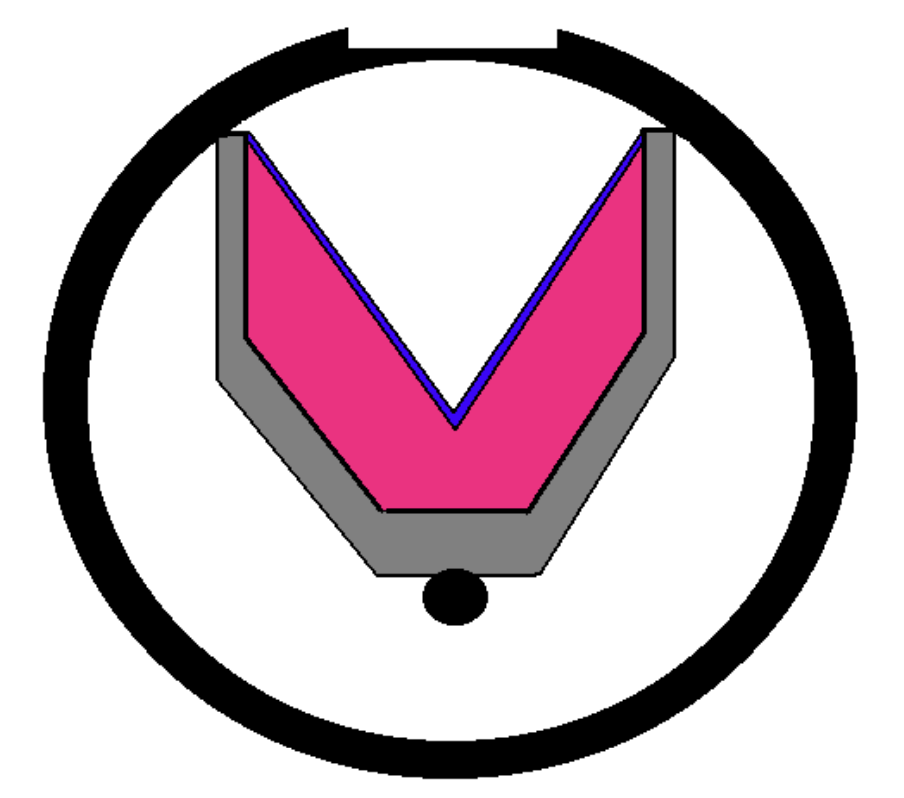
In the picture of a shaped charge shown, in which direction does the shot fire?
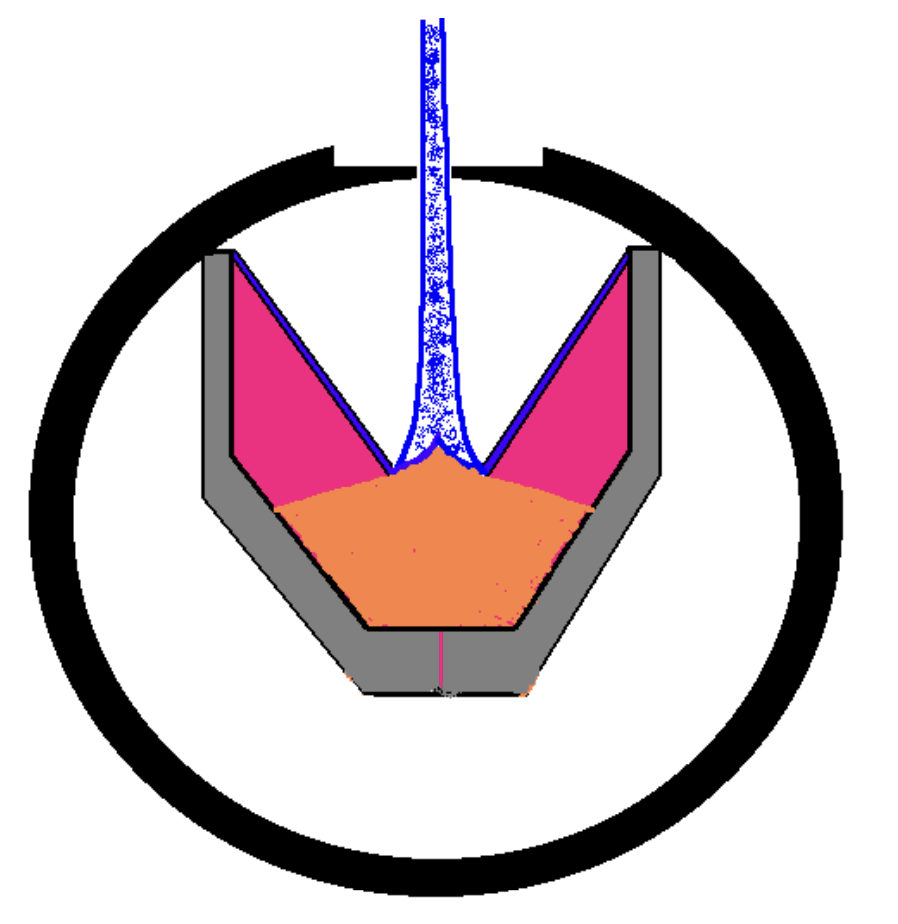
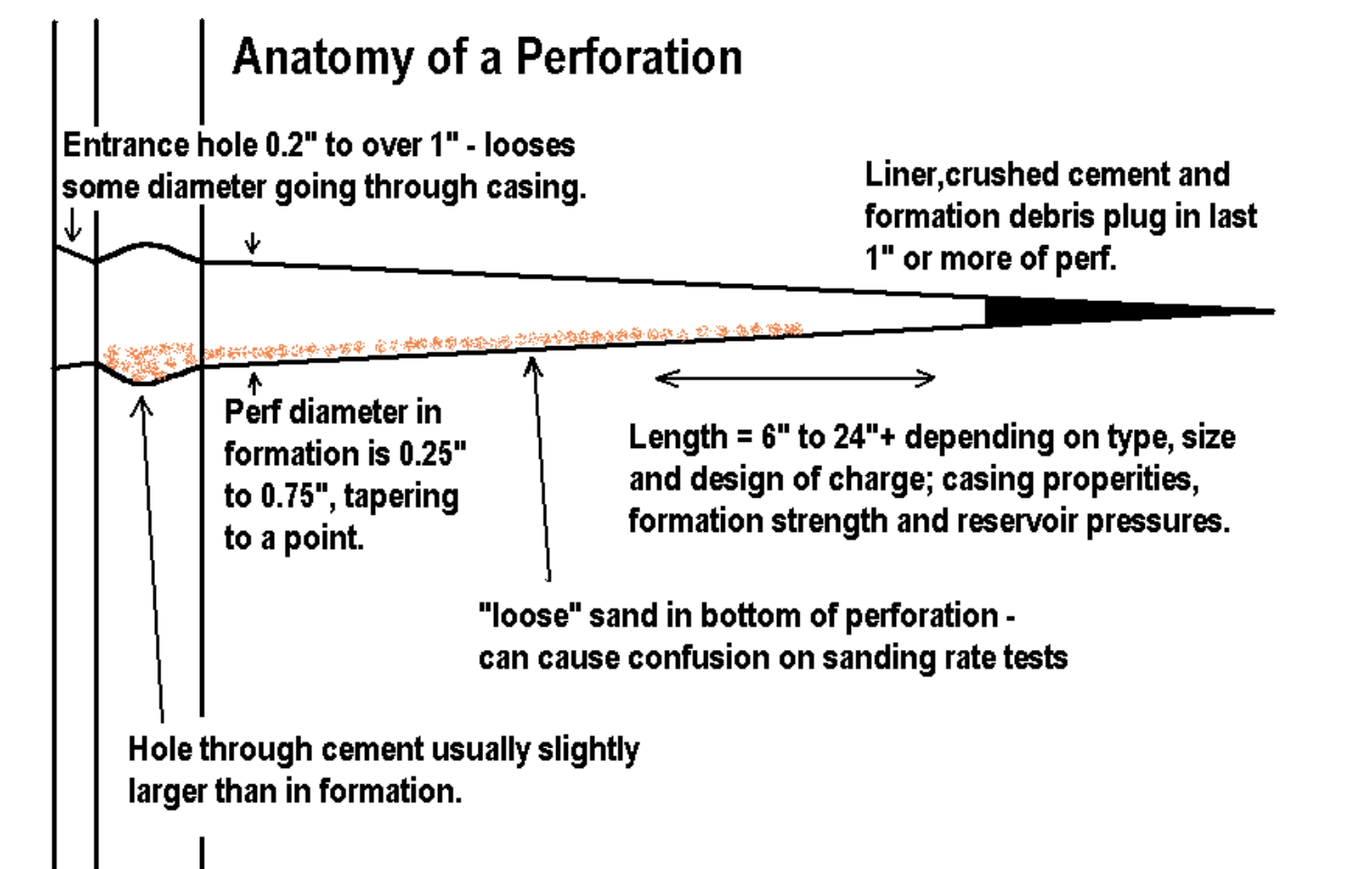
What is a typical range of perforation lengths?
6” to 24”
depending on type; size and design of charge; casing properties; formation strength; reservoir pressure
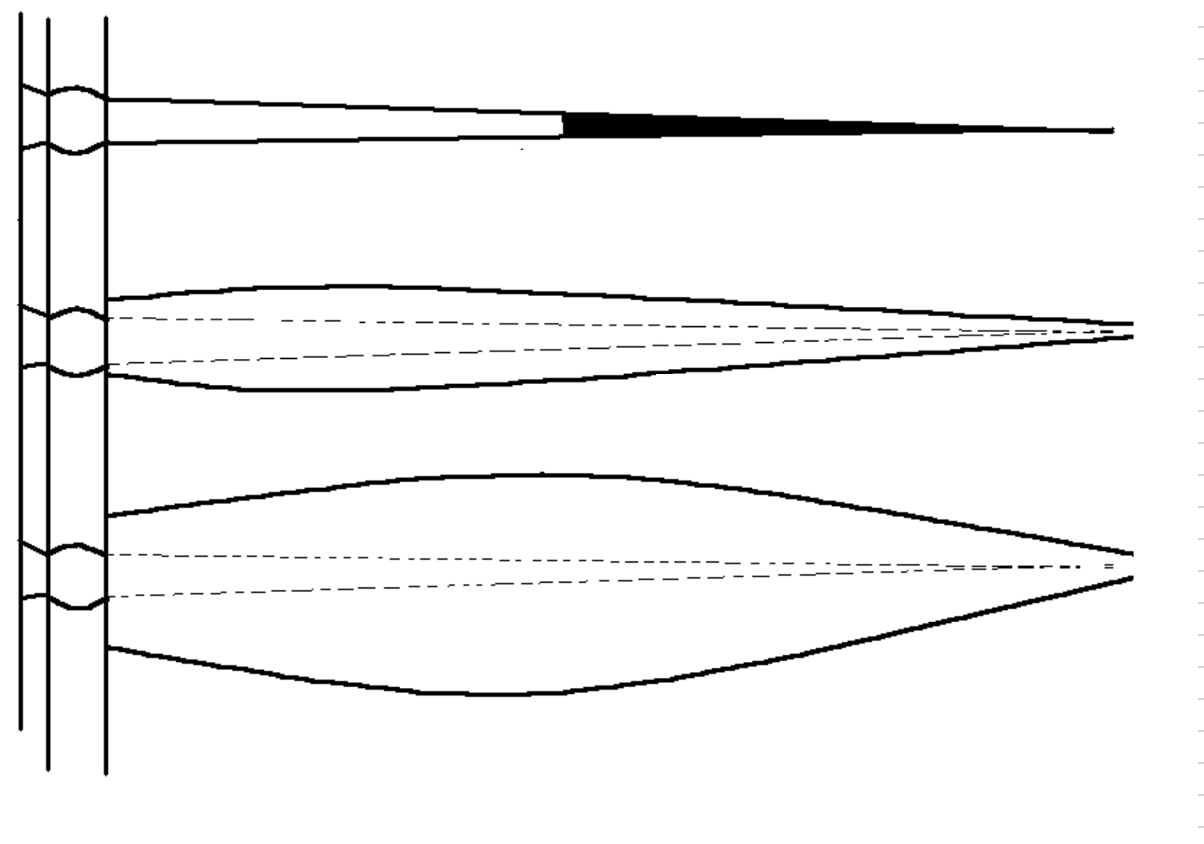
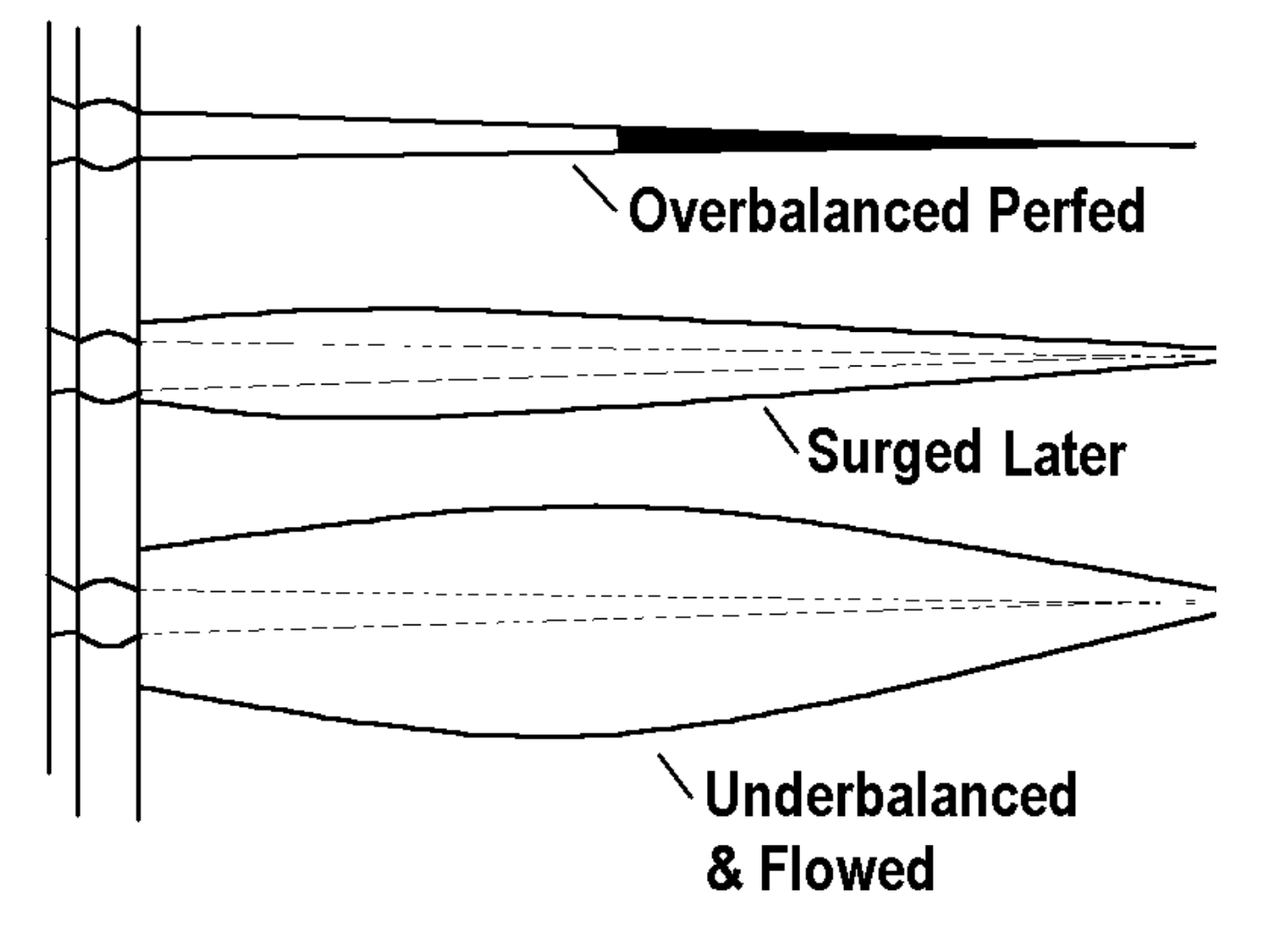
Of the 3 perforations shown, which one was shot ‘underbalanced and flowed’ ?
While perforating underbalanced, the pressure differential from the formation to the wellbore (ie. inflow) helps remove the crushed formation from the perforation and provides an improved flow channel
TorF: It is common to see a loss of permeability in the rock immediately surrounding a perforation tunnel
True
When a perforation is created — whether by bullet or jet — the shock, heat, and pressure from the explosive event damage the formation near the tunnel. This creates what’s called a “crushed zone” or “compacted zone.”
The grains in this zone are fractured and compacted, reducing pore space and blocking flow paths.
Fine particles can also be smeared or melted, plugging pore throats.
As a result, permeability near the perforation is lower than the native formation permeability.
Name 5 types of conveyance methods for perforating guns
• Wireline conveyed (vertical)
• Pump down perforating
• Tractor conveyed (on wireline; horizontal)
• Tubing conveyed perforating (TCP)
• Coiled tubing perforating
TorF: A dropbar is used to detonate a perforating gun run on e-line
False
Dropbars are solid steel bars that can be dropped through tubing or on slickline to set off an impact detonator
The most cost-effective and quickest method of perforating, which should be used in vertical and low deviated wells
Wireline perforating
Which perforating technique would best be used in horizontal multi-stage treatments?
a) Wireline perforating
b) Pump-down perforating
b) Pump-down perforating
can’t push a wire
Commonly used to perforate the toe intervals of wells that then use pump down for the remaining intervals
Tractor perforating
Which perforating technique is the most likely to create open, undamaged perforations?
a) Underbalanced
b) Balanced
c) Extreme Overbalanced
a) Underbalanced
the pressure differential from the formation to the wellbore (ie. inflow) helps remove the crushed formation from the perforation and provides improved flow channels
used on natural completions where stimulation is not planned
On a perforating job for a horizontal shale gas well that will eventually be fraced, what type of perforation technique would most likely be used?
a) Underbalanced
b) Balanced or Extreme Overbalanced
b) Balanced or Extreme Overbalanced
you will be fracturing through the perfs anyway, so there is no need for immediate flow into the well (which you’d get w/ underbalanced)
your main goal is to maintain control of the well, which balanced (usually slightly overbalanced) or extreme overbalanced achieves
A well has been perforated from 2304.5-2306.5m at 60° phasing, shot at 7 spm. How many total perforation holes are there?
2m x 7 shots/m = 14 shots = 14 holes
Name three types of perforating carriers (there are two specific types, with one having a sub-category)
1) Expendable
2) Retrievable
Scalloped
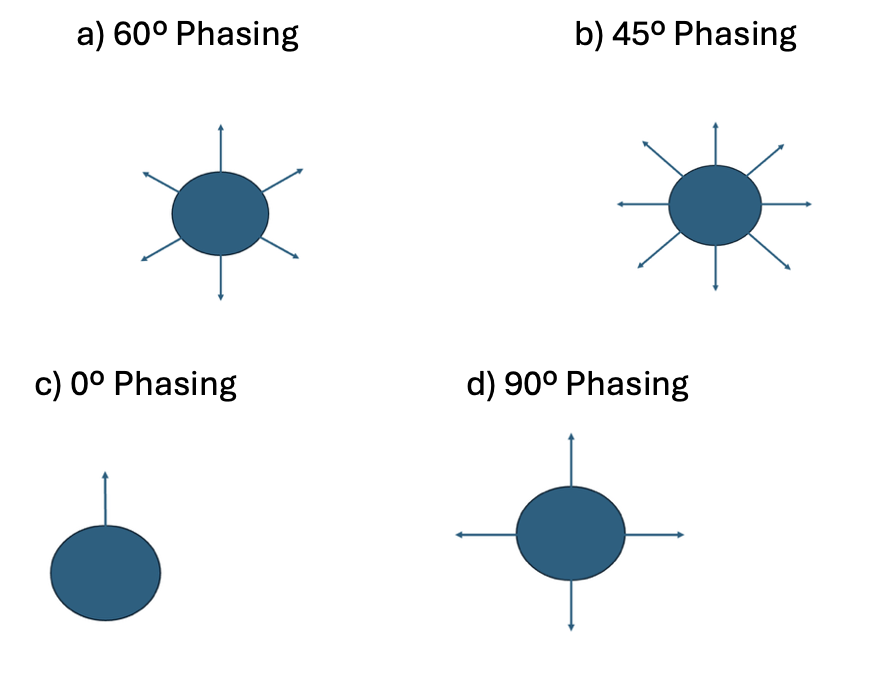
Sketch top view pictures of the following phasing setups:
a) 60°
b) 45°
c) 0°
d) 90°
When designing a perforating program, what resource would you use to determine the length of the interval to perforate?
You only want to perforate the productive zone, so therefore you would use formation evaluation logs:
Gamma Ray Logs
Porosity/Resistivity Logs
A precisely machined tool used to confirm the internal diameter of downhole tubulars like casing, tubing, and drill pipe, ensuring they meet operational specifications and are free from obstructions or deformations.
Drift gauge
A tool run on e-line or slickline that is used to place small volumes of cement slurry in a wellbore
Dump bailer
A type of well test designed to measure the pressure gradient within the wellbore when the well is not flowing. It helps determine the bottomhole pressure and the presence of fluids downhole.
Static Gradient
To what depth below the lowest water-bearing zone must surface casing be cemented for injection or disposal wells?
25m
A method used to detect gas migration from oil and gas wells. Performed at the wellhead, it evaluates the integrity of the well and identifies any leaks or gas emissions
Surface Casing Vent Flow (SCVF) test
Tests for the flow of gas or liquid that is detectable at surface outside of the outermost casing string
Gas Migration Test
A pressure test of the tubing and casing annulus that is designed to evaluate the integrity of the wellhead, casing, tubing, and packer
Packer Isolation Test
To prep for a perf job, a company wants to perform a formation property analysis (ex: stress, rock strength, etc.) to optimize perforation design. Which open-hole log should be performed?
Sonic (Acoustic) Log
Why run a Gamma Ray log when placing a bridge plug?
To correlate depth accurately.
The gamma ray log records natural radioactivity in the formations, giving a unique “fingerprint” vs. depth.
By matching gamma ray trace with a previous open-hole gamma ray log, the operator can:
Confirm exact depth inside the wellbore, and
Ensure the bridge plug is set at the intended formation or zone boundary (e.g., above perforations, water zone, or pay interval).
What is the first thing you do to a newly drilled and cemented well?
In other words, what is the first step in any completion?
Install the tubing head
What type of fluid would you expect to find left in a newly drilled and cemented well?
Whatever the drilling company left in it
typically drilling mud or completion fluid
A company plans to reverse circulate in order to kill a flowing oil well. At what point on the wellhead would they hook up in order to kill the well?
Into the flow tee on the tubing spool
reverse circulate means you’re pumping down the annulus
For an abandonment, when would a cement retainer be run?
On a sour well
Nipples have profiles. Describe what profiles are and what their function is.
A precisely machined internal shape inside the nipple that allows for engagement with tools
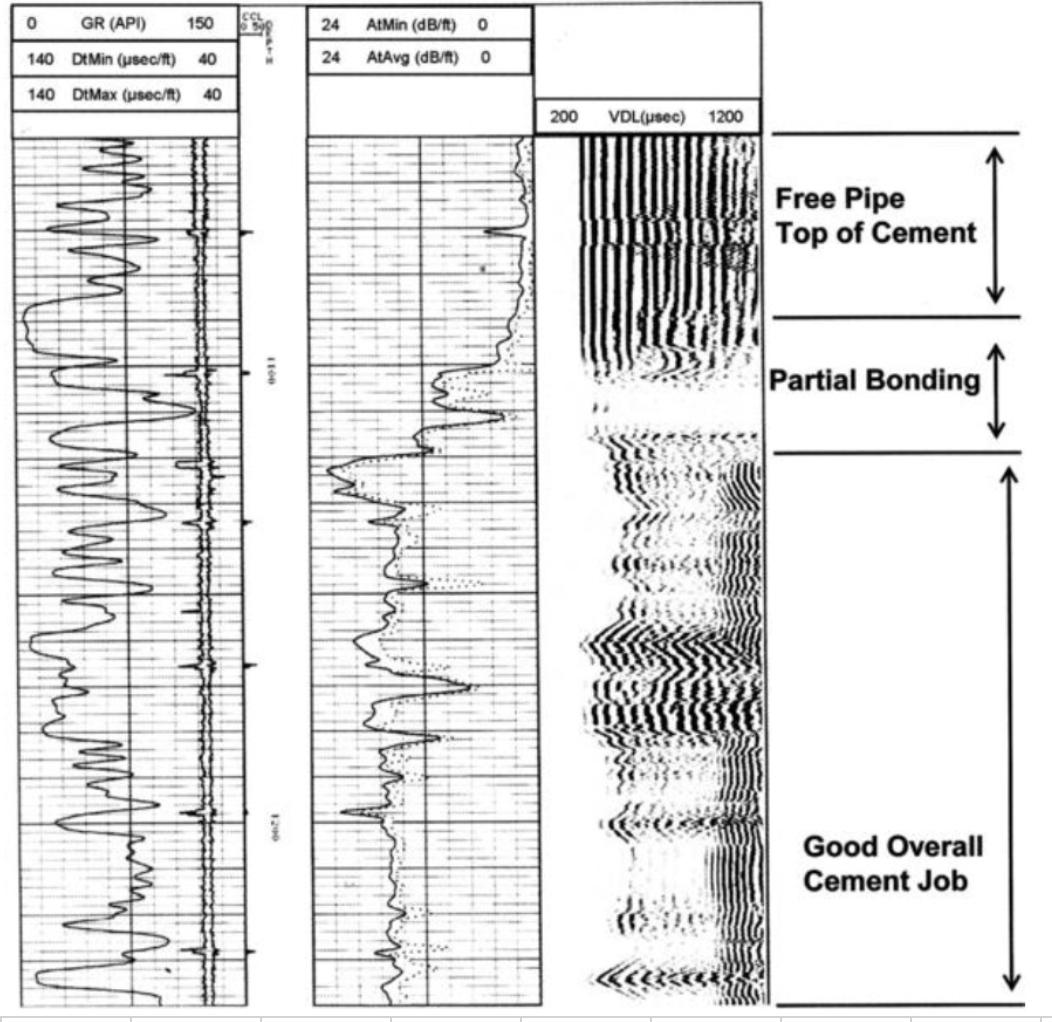
Name the 4 curves typically found on a Cement Bond Log
Gamma Ray
Casing Collar
Variable Density
Attenuation/Amplitude (Bond Log)
This log shows natural radioactivity vs. depth
Gamma Ray
On a cement bond log, what would be indicated by:
a) High amplitude
b) Low amplitude
The amplitude curve shows the strength of the returning sonic signal received by the tool
High amplitude = strong returning signal → poor cement bond (sound travels freely - cement too shitty to absorb it)
Low amplitude = weak returning signal → good cement bond (sound energy absorbed by cement and formation)
On a cement bond log, what would be indicated by:
a) High attenuation?
b) Low attenuation?
Attenuation measures how much sonic energy is absorbed or lost as it travels from the transmitter, through the casing, cement, and into the formation.
High attenuation = high energy loss → good bond (energy absorbed by cement/formation)
Low attenuation = low energy loss → poor bond (energy mostly reflects back b/c cement too shitty to absorb it)
A company wants to measure the amount of flow coming from different sets of perforations within the wellbore. What type of log should they run? What type of conveyance would be used?
Spinner log
Spinner logs are run on wireline
A non-sonic log that is run in producing wells to locate production sources downhole. Can also detect flow channels behind casing, as well as areas within a formation that are accepting injected fluids.
Temperature logs
Temperature surveys operate on the principle that temperature increases with depth below the surface (the geothermal gradient).
When a temperature survey measures a temperature in a well that is significantly deviated from the geothermal profile, that temperature anomaly is a possible point of fluid flow, entry or injection.
The anomaly could be confirmed as fluid with a noise log
These logs use microphones to detect fluid movement downhole
Noise log
Noise logs depend upon fluid moving at sufficient velocities to create turbulence so that the movement can be heard
Often run in conjunction with temperature logs
Which log can be run while moving through the wellbore - temperature logs or noise logs?
Temperature logs
Noise logs are run by wireline and position the tool against the casing at a predetermined spot.
Noise logs cannot be run while the tool is moving, because tool and cable movement noise will drown out all other sounds.
Therefore, noise logs are more of a diagnostic tool than an investigative tool, because they cannot locate the problem areas, but can be positioned in a suspected problem area to confirm whether there is a problem.
As a result, noise logs are usually run in conjunction with a temperature log.
The temperature log can record while moving, so it can isolate areas of fluid movement that can later be verified with a noise log.
What is the foundation of the wellhead assembly?
Casing head
When running wireline, at what point on the wellhead is the lubricator connected?
Top of the christmas tree
Which is stronger, slickline or braided line?
Braided line
used in deep wells or for fishing
On wireline operations, this is a device used to deploy tools in horizontal wellbores
Tractor

Which of the following logs is more suited to diagnostics, and which more suited as an investigative test?
Temperature log
Noise log
Temperature log → investigative (can run while moving to find fluid flow)
Noise log → diagnostic (cannot run while moving, so is often used as a confirmation test once the temperature log detects an area of interest
In perforating, this is the angle differential between shots
Phasing
What is the most common SPM in Westen Canadian perf jobs?
13 SPM
What is the purpose of the scallops on a perforating gun?
Primarily to contain the metal burr around the perforation exit hole, preventing damage or scoring to polished bore surfaces, such as those on packers and profiles.
also reduces the thickness of the gun body through which the charge must penetrate
Are packers typically used in pumping oil wells? Why or why not?
Never
Multi-phase flow in an oil well requires an open annular space to offload the solution gas (necessary to prevent pump lock-up)
This component, installed as part of the production string, is used for the safe re-entry of wireline tools from the casing back into the tubing string
Wireline re-entry guide
Name 3 ways that perf charges can be detonated
Electric charge (electrically)
Pressure (hydraulically)
Impact (mechanically)
Name two methods of conveying wireline over horizontal sections
Fluid conveyance (pump-down)
Tractor conveyance
A well service operation that uses the drilling rig’s hoisting and/or power systems to assist the service
Rig-Assist Servicing
For a wireline operation in which advanced logging tools that require multiple data channels will be run downhole (ie. formation evaluation logging), what type of wireline would be used?
Multiconductor E-line
What are the three main types of casing inspection logging tools?
1. Mechanical
Multi-finger cased-hole calipers
measures ID only
2. Electromagnetic
Induced electric current creates magnetic field
Magnetic field is sensed and variations correspond to irregularities
Detects internal and external corrosion (wall thickness)
Cannot detect scale or wax buildup
3. Ultrasonic
Rotating ultrasonic transducer emits high frequency sonic signal
Travel time for signal to return is indicative of casing ID
Frequency of signal is proportional to wall thickness
Can determine casing ID, ovality, thickness
Requires fluid filled borehole
What are the 2 main applications of production logs?
Assessing well flow profile and fluid type
Diagnose wellbore production problems (unproductive perf clusters, etc.)
TorF: A service rig is necessary in order to run production logging tools
False
They are run on:
e-line
slickline
coiled tubing
TorF: Running a logging tool on a slickline is very convenient, as a real-time surface readout can be obtained
False
Nothing through which to send the signal on a slickline for a surface read-out
would need e-line
Any logging on slickline would be run in memory mode
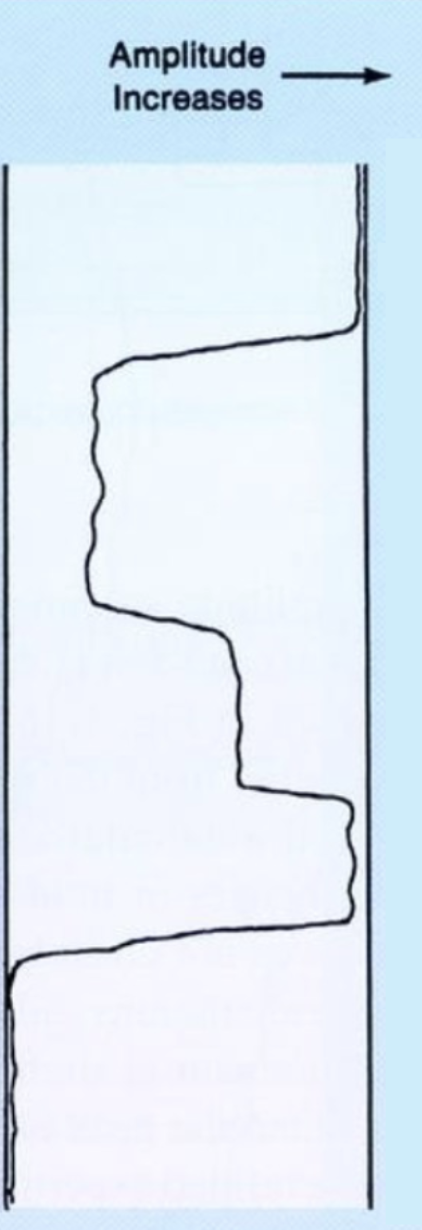
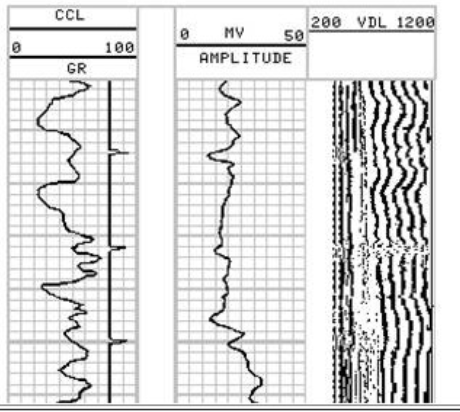
On the cement bond log shown, identify each of the 5 distinct readings as either:
Free Pipe
No Cement
Partial Bond
Effectively Cemented
Poorly Cemented
High amplitude = bad/no cement
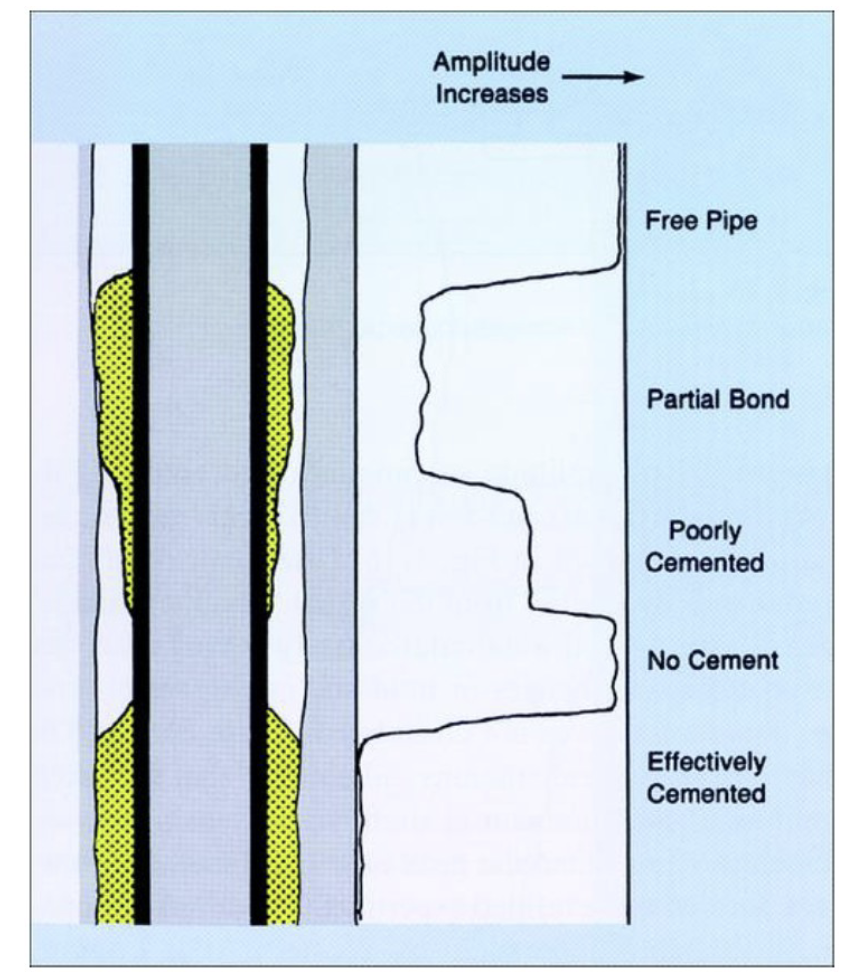
TorF: Electromagnetic casing inspection logs can be used to detect wax/scale build-up
False
they rely on electromagnetic induction
wax/scale is non-metallic
Caliper logs could be used, as these will mechanically detect inner diameter reductions (which could be wax or scale)
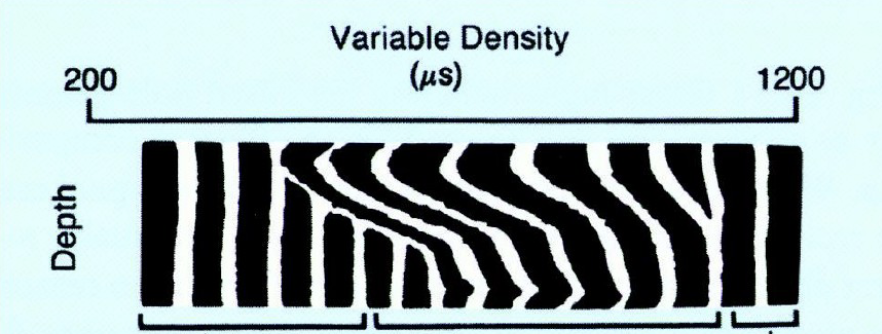
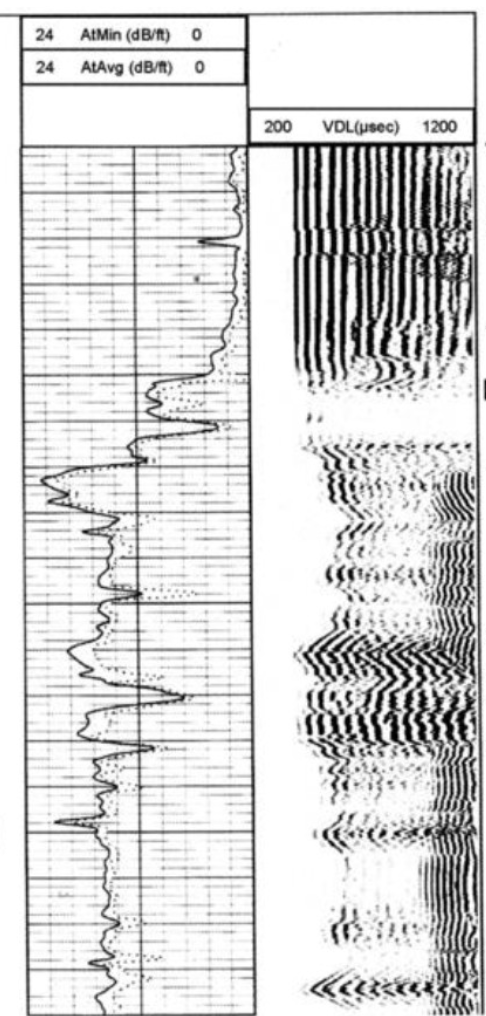
On the VDL read-off shown, identify:
Pipe arrivals
Mud arrivals
Formation arrivals
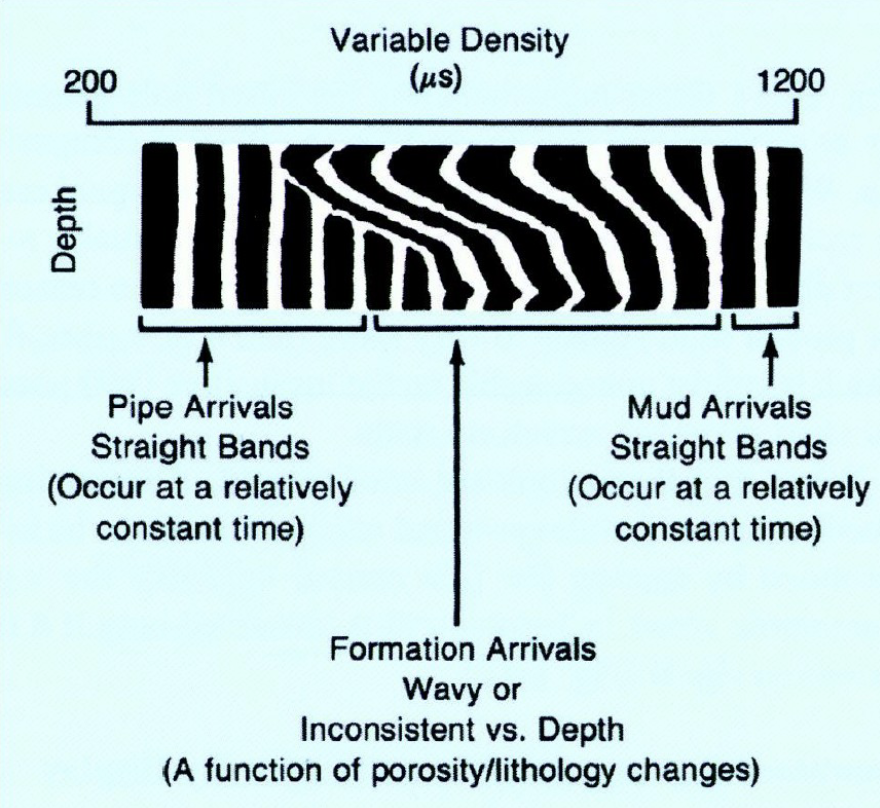
The first, sharp sonic reflections that are recorded by a variable density log correspond to:
a) Formation arrivals
b) Mud arrivals
c) Pipe arrivals
c) Pipe arrivals
Name 2 ways that a micro annulus can form
Temperature/pressure changes
casing can contract following temperture/pressure changes, which may open up a micro annulus b/w the cement and casing
Cement shrinkage
cement shrinks slightly as it cures, which could cause it to pull away from the casing or formation, forming a micro annulus
TorF: Micro annuli are normally less than 1mm across
True
TorF: A standard CBL log will detect small channels in the cement
False
The sonic signal averages over the circumference of the casing
Tiny or thin channels (less than a few mm) may not change the overall signal enough
Would have to run a Radial Bond Tool to detect small channels
Provides circumferential imaging, not just an averaged response
TorF: Production logs are normally run on producing wells and through tubing
True
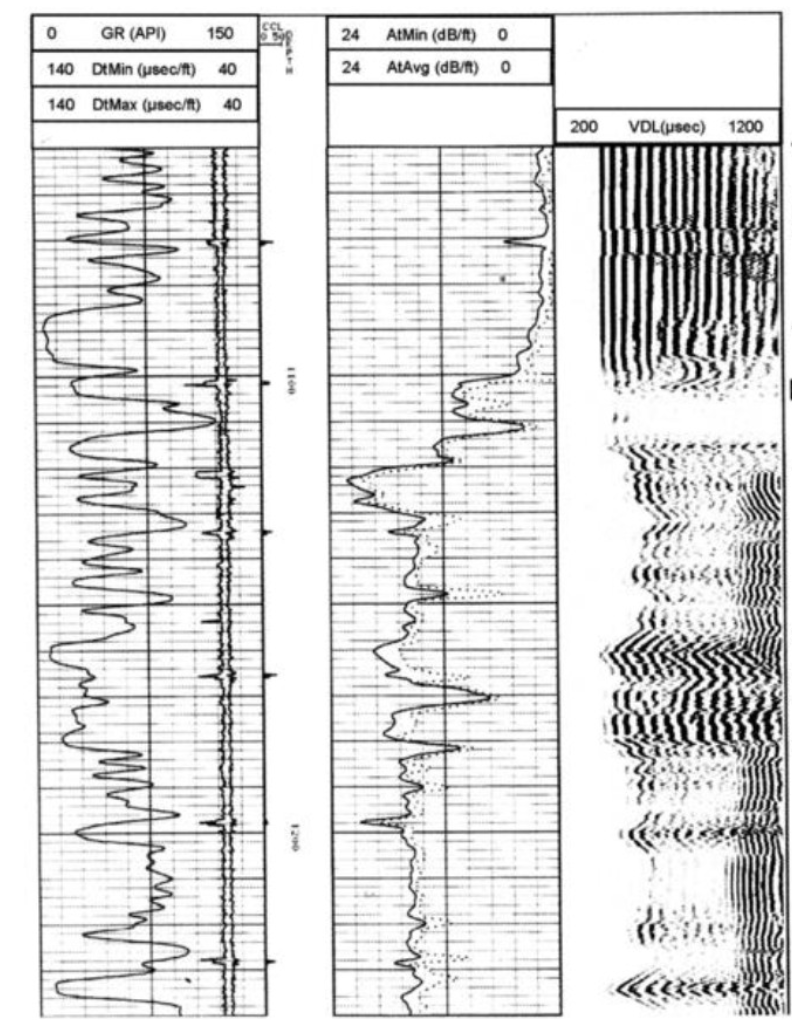
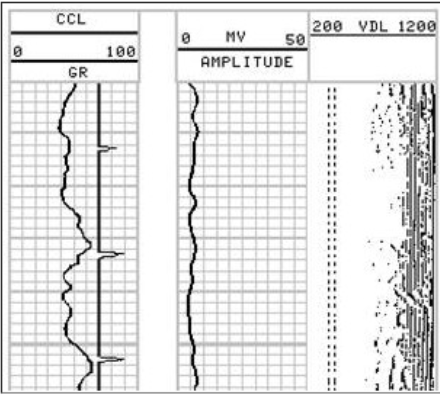
Identify the following areas:
partial bonding
good cement
free pipe
Of the following common cement problems, which is the one most likely to be misinterpreted as free pipe?
a) Microannulus
b) Channeling
c) Poor centralization
d) Gas cut
a) Microannulus
Per AER guidelines, when abandoning a sour well, what height of cement is required above the cement retainer?
30m
According to Espo - couldn’t find that in Directive 20
Per AER guidelines, when abandoning a sweet well, what height of cement is required above the cement retainer?
8m
What, specifically, does a spinner log measure?
Fluid velocity
Which of the following casing inspection logging tools requires a fluid filled wellbore?
a) Caliper
b) Ultrasonic
c) Electromagnetic
b) Ultrasonic
Requires a fluid-filled wellbore to transmit the signal between the tool and the casing wall.
Without fluid, sound waves cannot travel effectively — you’d get no return signal.
Which type of perforating carrier can be run in a well under pressure?
Hollow Carrier gun
Hollow carrier perforating guns are pressure-tight, with the shaped charges sealed inside a steel housing (the carrier)
Because the explosives and wiring are isolated from well fluids and pressure, the gun can be safely run and fired in a well under pressure

What is the difference between a SCVF test and a gas migration test?
Surface Casing Vent Flow (SCVF) Test
Detects gas or liquid flow that is venting to surface through the surface casing vent (i.e. inside the annulus between the surface casing and the next casing string).
Indicates:
The cement job b/w the surface and next casing string has failed to isolate one or more formations - gas is migrating through channels, micro-annuli, or poor bond zones in that cement column
Test method:
The surface casing vent is opened to measure flow rate and composition, or pressure buildup is monitored when closed
Gas Migration (GM) Test
Detects gas leaking outside the surface casing, through the surrounding soil, to the ground surface.
Indicates:
The cement b/w the surface casing and formation is not providing full isolation — gas is migrating through channels, micro-annuli, or poor bond zones in that cement column
Test method:
Gas detectors or probes are placed in the soil near the wellhead to measure methane concentration or bubbling in water
Which curve on the Casing Bond Log should be referenced in order to discern the quality of the bond between the cement and the formation?
Variable Density Log (VDL)
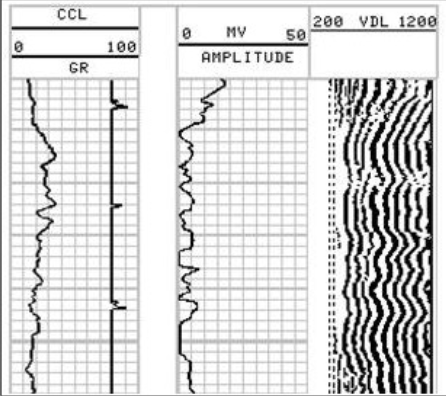
Good Cement
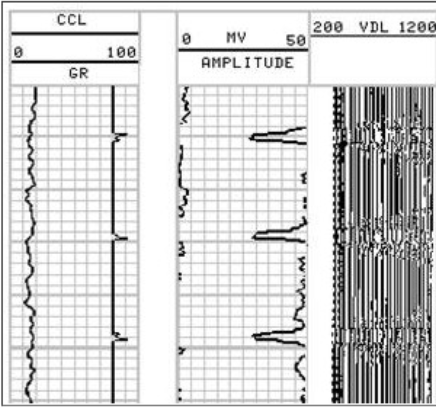
No Cement
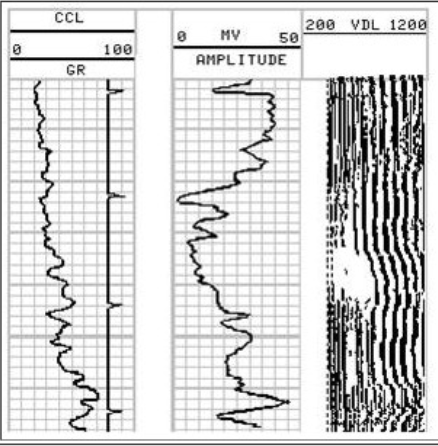
Partial Cement
Micro annulus
Cement w/o bond to formation
Once a retrievable perforating gun has been fired and brought back to surface, what remains?
Hollow steel carrier
Can the pipe to cement bond be reliably measured in a fast formation?
No
A fast formation (like limestone or dolomite) transmits the sonic signal very quickly.
The formation arrival (the signal that travels through cement and formation) can overlap or arrive almost simultaneously with the first casing arrival.
This interference makes it difficult to distinguish between:
Energy traveling through the casing (free pipe), and
Energy traveling through the bonded cement and into the formation.
As a result, the log might falsely indicate poor bonding even when a good bond exists
TorF: The CBL amplitude can be used to reliably indicate the quality of the bond between the cement and the formation
False
The CBL amplitude curve shows the amplitude of the first signal to arrive → and hence primarily reflects the quality of the cement-to-casing bond
for insight into the cement-to-formation bond, check the VDL
For CBL amplitude:
High amplitude → poor casing-to-cement bond (or free pipe)
Low amplitude → good casing-to-cement bond
Your plan is to abandon a non-producing zone in a pumping oil well and perforate a separate zone of interest in order to bring production back online. Arrange the following steps in the order that the operation would be carried out:
Swab well down to +/-1060mKB
MU and RIH with casing guns and perforate zone of interest from 1035.0 - 1037.0 mKB and 1043.0 to 1046.0 mKB
RU tubing inspection equipment, pull and inspect 73.0mm tubing
MORU service rig
MORU Wireline unit and set permanent bridge plug at +/-2465mKB
Kill well, pull pump and rods
RU pressure truck and PT BP to 7 mPa
Cap with 8 linear meters of cement on top of plug
MORU service rig
Kill well, pull pump and rods
RU tubing inspection equipment, pull and inspect 73.0mm tubing
MORU Wireline unit and set permanent bridge plug at +/-2465mKB
RU pressure truck and PT BP to 7 mPa
Cap with 8 linear meters of cement on top of plug
Swab well down to +/-1060mKB
MU and RIH with casing guns and perforate zone of interest from 1035.0 - 1037.0 mKB and 1043.0 to 1046.0 mKB
TorF: Typically the casing is swabbed prior to performing a thru-tubing perf job
False
If you are swabbing the casing, it means that there is no tubing in the well, and so therefore the perf job will not be thru-tubing
Your CBL is showing free pipe, and now you must decide whether or not to order a remedial cement squeeze. But as a SAIT student you know that a micro annulus (no squeeze required) can often be misinterpreted as free pipe (squeeze required). How would you decide whether or not to do a squeeze?
Perform a pressure pass
Pump fluid into the casing to increase internal pressure
The casing expands slightly
This compresses the microannulus, forcing the casing into better contact with the cement.
Run the CBL again while the pressure is applied
If CBL shows good casing-to-cement bond you have confirmed a micro annulus, and not free pipe
confirmation of a micro annulus means no remedial squeeze is needed, whereas with free pipe, a remedial squeeze would be required
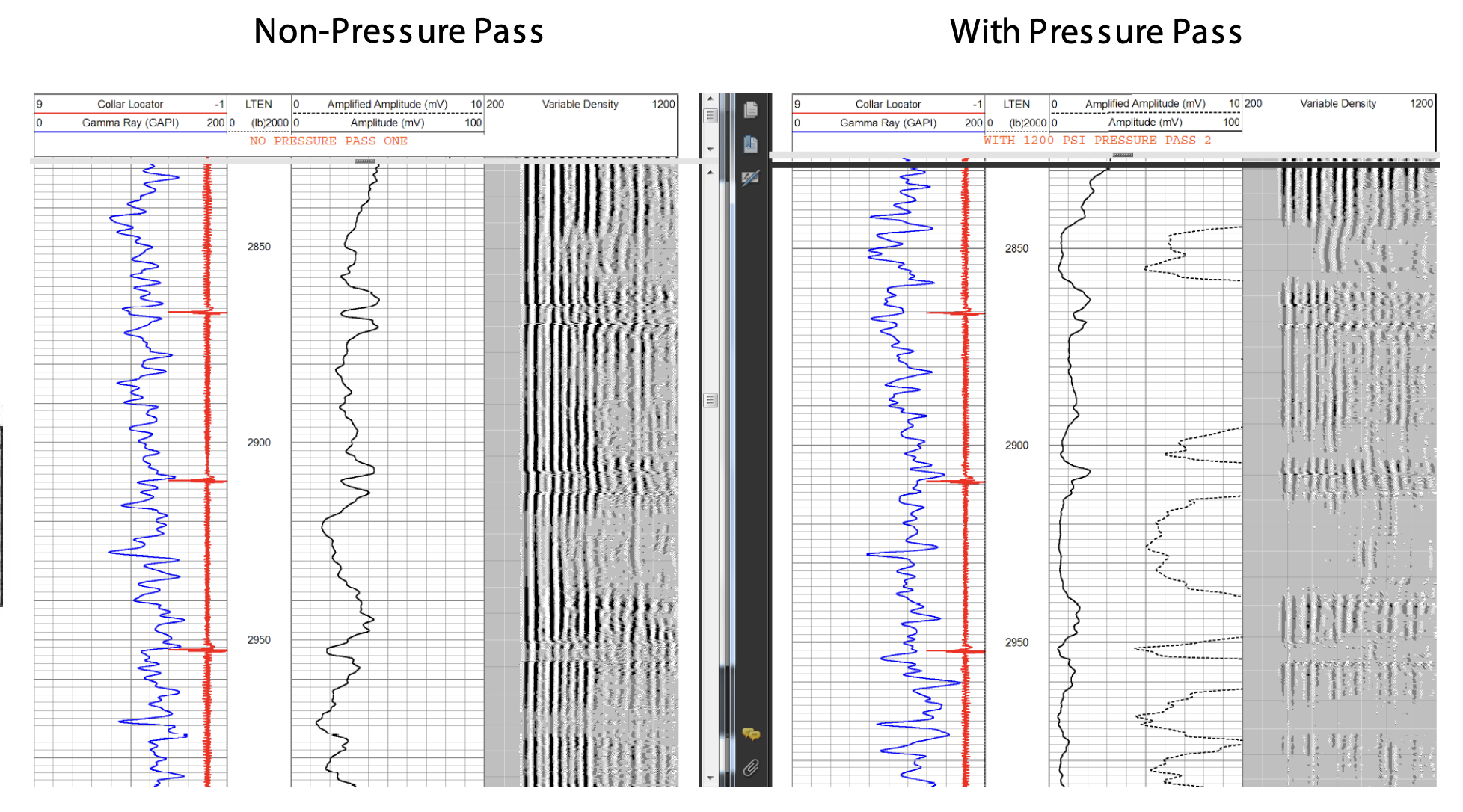
How is a micro annulus different than free pipe?

Indicate the top of cement
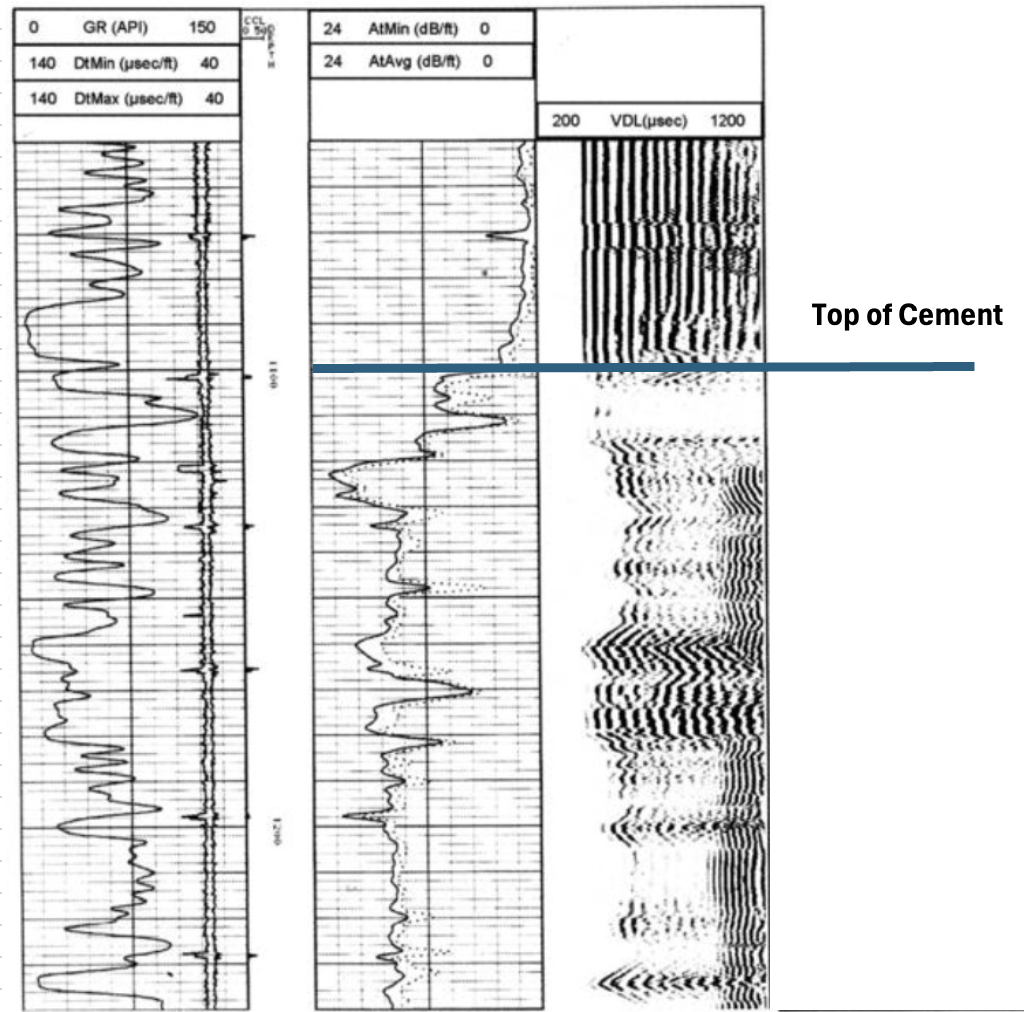
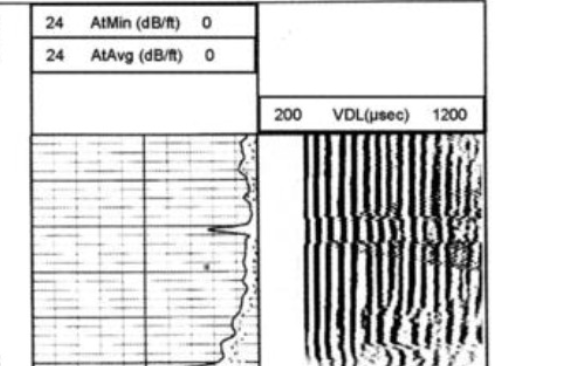
Free pipe
Which of the following could be used for ram-to-ram pipe injection?
a) Service rig
b) Wireline unit
c) Coiled tubing unit
a) Service rig
ram-to-ram pipe injection → it’s a snubbing operation → could be a rig-assist snubbing operation → therefore, answer is service rig
neither wireline or CT use ram-to-ram pipe injection
Which type of conveyance would be used to perform open hole logging?
a) slickline
b) coiled tubing
c) pump-down
d) e-line
d) e-line
for open-hole logging specifically, you want to have real-time transmission, so slickline is not used
slickline could be used to run memory logs for cased-hole logging
Which operation unit would typically use a crane?
a) wireline
b) service rig
c) coiled tubing
c) coiled tubing
Uses a crane to hoist the injector head
On a wireline unit, where would the top sheave be connected?
On top of the lubricator
wireline passes over the top sheave, through the lubricator and into the well
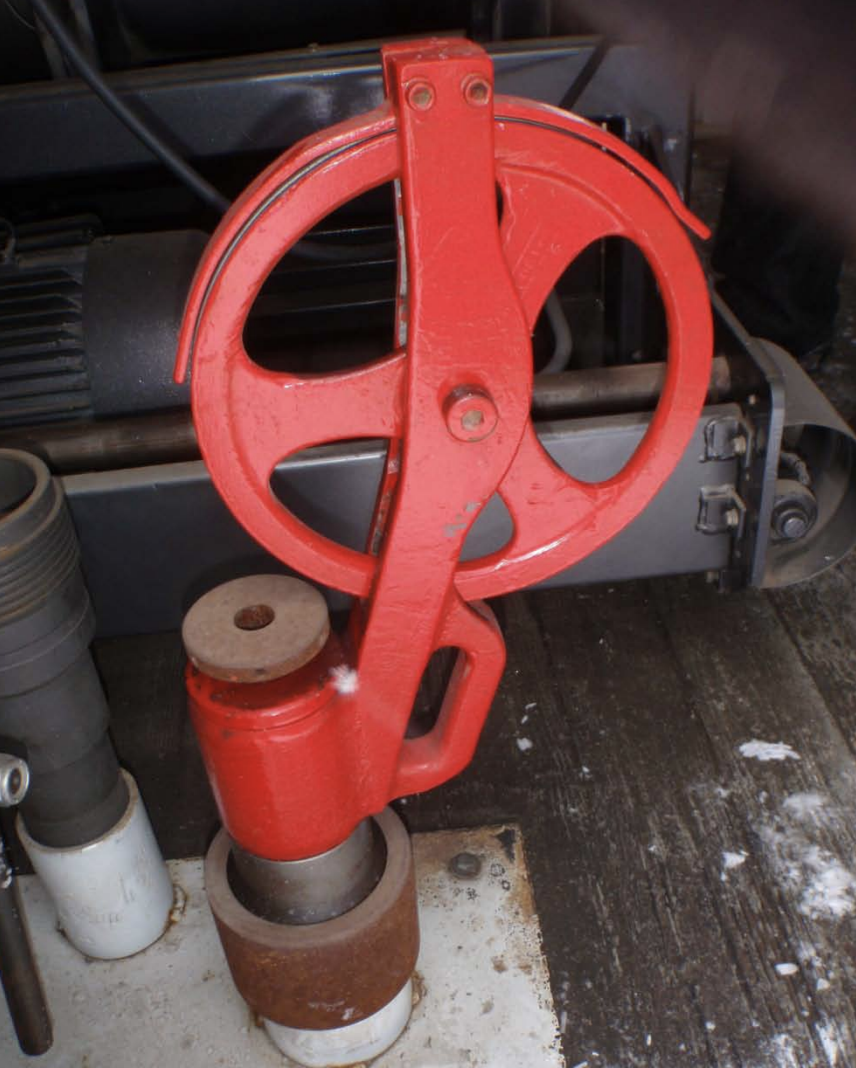

What is the designated weak point on a wireline?
Cable heads
so that wireline will detach if tool gets stuck
What are the 3 main types of prep-work that must be done before a perf job?
Determine the interval to perforate.
Based on log parameters, relation to zone top, g/o & o/w interfaces
Determine the type of perforating gun to run.
Retrievable, expendable, shots/m, phasing
Estimate the reservoir pressure and corresponding fluid level to have in the wellbore to allow the well to be perforated slightly underbalanced
Which type of casing inspection logging tool could be used to identify external corrosion?
a) caliper
b) acoustic tools
c) ultrasonic tools
c) ultrasonic tools
can measure internal wear/corrosion directly - while also measuring wall thickness
therefore, external wear/corrosion can be inferred if there is a reduction in wall thickness at point x while there is also no indication of internal wear/corrosion at x
TorF: Downhole imaging tools are often used to detect problem areas downhole
False (operative word = detect)
expensive to run so not used to detect → used for inspection at a specific point after another type of tool detects a problem area