Ch 11: Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
fertilization
combines cells (gametes) from 2 parents
does mixing chromosomes from 2 individuals increase or decrease genetic diversity?
increase
how is an organism’s sex determined?
it is an inherited phenotype characteristic determined in large by the presence or absence of certain chromosomes
phenotype
physical manifestations: what you can see, hormones in the body, etc.
what is SRY (sex determining region Y) required for?
testicular development
2 varieties of sex chromosomes
X and Y
true or false. sex cells are diploid.
false. sex cells are haploid.
by how much does meiosis reduce the number of chromosomes by?
half
the process of meiosis resembles mitosis but goes through how many rounds of division?
2: meiosis I and meiosis II
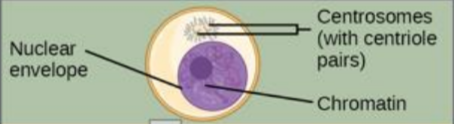
S Phase
chromosomes are duplicated during interphase. the resulting sister chromatids are held together at the centromere. the centrosomes are also duplicated

prophase I
chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope fragments. homologous chromosomes bind firmly together along their length, forming a tetrad. chiasmata form between non sister chromatids. crossing over occurs at the chiasmata. spindle fibers emerge from the centromeres
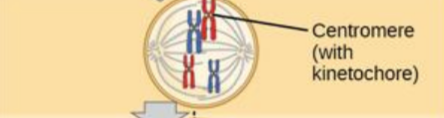
prometaphase I
homologous chromosomes are attached to spindle microtubules at the fused kinetochore shared by the sister chromatids. chromosomes continue to condense, and the nuclear envelope completely disappears

metaphase I
homologous chromosomes randomly assemble at the metaphase plate, where they have been maneuvered into place by the microtubules
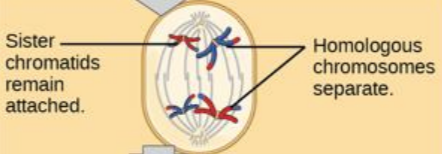
anaphase I
spindle microtubules pull the homologous chromosomes apart. the sister chromatids are still attached at the centromere
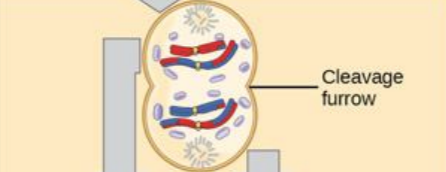
telophase I and cytokinesis
sister chromatids arrive at the poles of the cell and begin to decondense. a nuclear envelope forms around each nucleus, and the cytoplasm is divided by a cleavage furrow. the result is two haploid cells. each cell contains one duplicated copy of each homologous chromosome pair
prophase I: homologous chromosomes pair and __________________ complex holds them close together in __________
synaptonemal, synapsis
prophase I: crossing over
segments of chromosomes can be exchanged
prophase i: visible structures at cross over points are called ____________
chiasmata
prophase I: the 4 chromatids held together by chiasmata are called a _______
tetrad
prometaphase I: spindle fiber microtubules attach to kinetochore proteins at _______________
centromeres
prometaphase I: homologous chromosomes are still held together at the ____________
chiasmata
prometaphase I: __________ membrane is completely broken down
nuclear
metaphase I: homologous chromosomes are arranged at cell equator with _____________ facing opposite poles
kinetochores
metaphase I: independent assortment
maternal and paternal chromatids orient randomly mixed when they migrate to poles
2 primary mechanisms for genetic variation in meiosis
crossing over and independent assortment
anaphase I: the microtubules pull the _______ apart
tetrads
anaphase I: ____________ are broken but sister chromatids remain attached at the ______________
chiasmata, centromere
telophase I and cytokinesis: separated chromosomes arrive at ___________ poles
opposite
telophase I and cytokinesis: if cytokinesis does occur, ______ do not reform
nuclei
cytokinesis in animal and fungal cells
occurs via a cleavage furrow that constricts
cytokinesis in plant cells
form a cell plate that ultimately produces cell walls that separate the daughter cells
3 injections of genetic variation
crossing over, independent assortment, fertilization
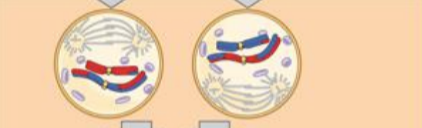
prophase II
sister chromatids condense. a new spindle begins to form. the nuclear envelope starts to fragment
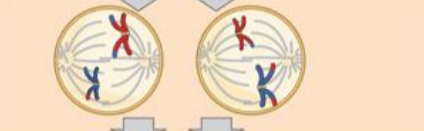
prometaphase II
the nuclear envelope disappears, and the spindle fibers engage the individual kinetochores on the sister chromatids.
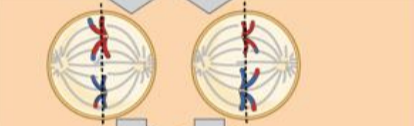
metaphase II
sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate
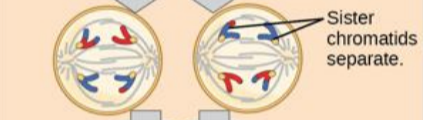
anaphase II
sister chromatids are pulled apart by the shortening of the kinetochore microtubules. non kinetochore microtubules lengthen the cell
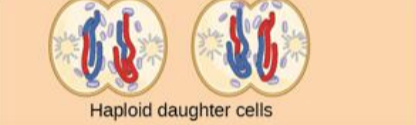
telophase II and cytokinesis
chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell and decondense. nuclear envelope surrounds the four nuclei. cleavage furrows divide the two cells into four haploid cells
prophase II: if chromosomes decondensed in telophase I, they _____________ now
recondense
true or false. prophase II: if centrosomes were duplicated, they migrate to opposite poles and new spindles form
true
prometaphase II: nuclear envelopes completely ____________
disappear
prometaphase II: _______ is fully formed
spindle
prometaphase II: each sister chromatid forms a ______________ and attached to __________ from opposite poles
chromatid, microtubules
metaphase II and anaphase II: events process as in mitosis and sister _________ separate and move toward opposite ______
chromatids, poles
telophase II and cytokinesis: the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and ____________
decondense
telophase II and cytokinesis: nuclear ____________ form around chromosomes
envelopes
telophase II and cytokinesis: cytokinesis separates the two cells into ______ unique ________ cells
four, haploid
which produces genetically unique cells: mitosis or meiosis?
meiosis
in what process do homologous chromosomes pair to form tetrads?
meiosis
which process produces genetically identical clones?
mitosis