dna and genetics y10
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
heredity
the process by which traits are passed from parents to offspring
structure of dna
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a double stranded molecule that forms a double helix shape
dna is a polymer made up of many monomer units called nucleotides
nucleotides
have three components:
a pentose, deoxyribose sugar
a nitrogenous base (ATGC)
a phosphate group
complementary base pairings
Adenine binds with thymine ( 2 hydrogen bonds)
cytosine binds with guanine (3hydrogen bonds)
DNA
provides a code for protein that organisms require to live
deoxyribose
ATGC - bases
Stores and transfers genetic information
found in nucleus, mitochondria
Gene
a section of DNA which codes for the synthesis of proteins
Chromosome
a thread like structure of tightly wound DNA and proteins
RNA
ribose
AUGC (base)
Messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA
odes for amino acids and makes proteins
found in nucleus, cytoplasm
protein synthesis
process of building proteins that perform a wide variety of functions in living organisms using the DNA code
each gene is a section of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein
protein synthesis stars at a specific gene and can be split into two main stages - transcription, translation
Transcription
RNA polymerase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two DNA strands (unzips)
template DNA strand is copied by another enzyme which builds a complementary mRNA
The DNA zips back up
the m RNA strand leaves the nucleus
Dna is far too large to leave the nucleus so only part of the DNA (gene) is unzipped and then copied into another nucleic acid
occurs inside the nucleus of cell
Translation
The mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome
ribosomes read three bases at a time (3 bases = 1 codon)
each codon in the mRNA specifies which amino acid is added to the polypeptide chain
transfer RNA molecules pick up the specific amino acid in the cytoplasm and join them to the polypeptide chain at the ribosome (complementary to mRNA)
at the end(when the stop codon is reached) the mRNA will detach from the ribosome as will the finished protein
occurs in the cytoplasm
amino acid chart
mRNA strands always should start with ‘start’ codon (A, U or G) which codes for the amino acid - methonine
There are several different stop codons all of which don’t code for an amino acid
homologous chromosomes
there are 46 chormosomes in every human body ( somatic) cell, 23 pairs
in these cells, each chromosome contains a mathcing pair
they are pairs of mathcing chromosomes as they have matching bonding patterns, genes and size
for each homologous pair there is 1 inherited from mum and 1 inherited from dad.
chromosome
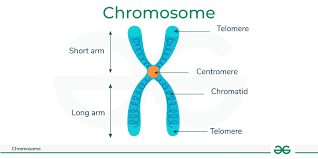
allele
a version of a gene
autotsomes
body chromosomes
any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
any chromosome that is in pairs 1 to 22
heterosomes
sex chromosomes
chromosomes that determine the sex of an organism
the 23rd pair in humans ( xx in femals, xy in males)
down syndrome
an extra chromosome on the 21st pair
trisomy 21 means an individual has 3 chromosomes instead of two for a homologous pair
replication in cells
all oragnisms replicate ( increase in number) in order to grow
DNA replication occurs in every cell before it divides
it doubles the amount of DNA required before the cell divides
sister chromatids ( which are genetically identical to each other) are joined at the centromere of the 46 chromosomes
after DNA replication occurs, the cell may enter into cell division. (mitosis or MEIosis)
how does DNA replicate
DNA unwinds and unzips - catalysed by DNA helicase
ne nucleotides are added following complementary base pairing rules - catalysed by DNA polymerase
result is two identical strands of DNA
mitosis
cell division of somatic cells
somatic cells are diploid (2n) as they contain 2 sets of chromosomes, 23 from mum, 23 from dad
occurs in humans for - growth, reapir and healing, tissue replacement ( from aging cells )
meiosis
cell division in animals and plants that produces gametes ( sex cells )
male gametes are sperm cells
female gametes are ova (ovum singular)
meiosis produces 4 daughter cells
the new daughter cells have only one set of chromosomes in each - therefore they are know as haploid (n)
heredity 2
the passing on of physical or mental characteristic genetically from one generation to another
homologous chromosomes have the same genes located at the same location of the chromosome ( location of gene is called the locus)
homologous chromosomes may have a different form of the gene (allele)
e.g. alleles for brown eyes or blue eyes
genotype
the combination of alleles an organism has for a particular gene
if 2 identical alleles are present in a persons genotype, they are homozygous
e.g. brown hair allele from mother and father
if 2 different alleles are present for the same trait, the person is heterozygous for that trait
phenotype
the observable characteristics of an organism
dominant
if this allele is present on either homologous chromosome, it’s physical appearance will be expressed ( masking the other allele)
recessive
this allele must be present on both homologous chromosomes in order to be physically expressed ( otherwise it will be masked by the dominant allele)
what are the three possible genotype
homozygous dominant
heterozygous
homozygous recessive
homozygous dominant
both chromosomes contain the dominant allele
BB
heterozygous
one chromosome contains the dominant allele, the other contains the recessive
Bb
homozygous recessive
both chromosomes contain the recessive allele
bb
sex linkage
all eggs=x
sperm=x or y
males are at a much greater risk for inheriting sex-linked disorders because they only inherit one x, so if the x has the allele for the disorder, they will suffer from the disorder
codominance
both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype
e.g. black chicken + white chicken =speckled
pedigree
a pedigree chart shows the relationships between family members and indicates which individuals have certain genetic traits
autosomal dominance
males and females can be equally affected, yet all of the affected individuals must have at least one parent affected
autosomal recessive
two unaffected parents can have an affected child
males and females are equally affected
stages of mitosis
interphase - chromosomes replicate( DNA replication), where cell spends most of its time, its job
prophase- chromosomes shorten and condense and become visible
metaphase - chromosomes align in the middle of cell ( equator), spindle fibres attach to the centromere
anaphase - chromatid moves to opposite side of cell ( poles)
telophase - nucleus of cell reforms
cytokenesis - cell membrane reforming, 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical