Chapter 19: Advertising, Public Relations, and Sales Promotions
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
advertising
A paid form of communication delivered through media from an identifiable source about an organization, product, service, or idea designed to persuade the receiver
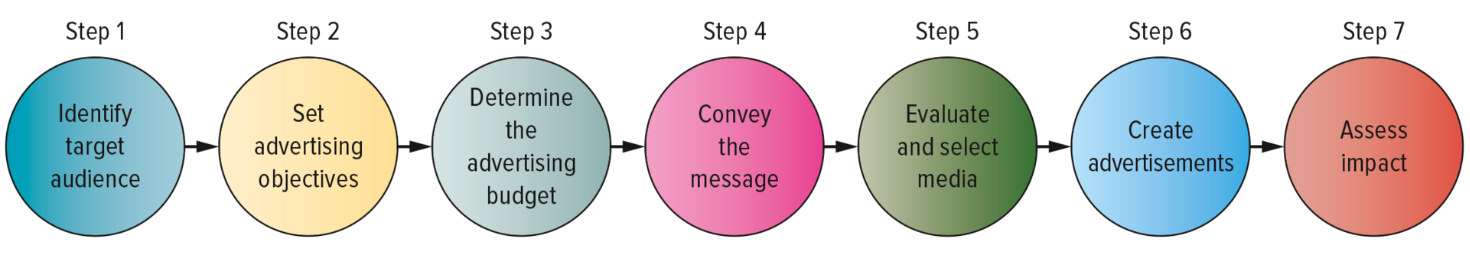
7 Steps in Planning and Executive an Ad Campaign
Identify target audience
Set advertising objectives
Determine the advertising budget
Convey the message
Evaluate and select media
Create advertisements
Assess impact using marketing metrics
Step 1: Identify Target Audience
Firms conduct research to identify target audience, then use the information to set the tone and select the media they will use

Step 2: Set Advertising Objectives
The objectives of an ad campaign are derived from the overall objectives of the marketing program
Pull strategy for consumers; push strategy for sellers
advertising plan
A subsection of the firm’s overall marketing plan that explicitly analyzes the marketing and advertising situation, identifies the objectives of the ad campaign, and indicates how the firm can determine whether the campaign was successful
pull strategy
Strategy in which the goal is to get consumers to pull the product through the marketing channel by demanding it
push strategy
Strategy designed to increase demand by motivating sellers—wholesalers, distributors, or salespeople—to highlight the product over competitors and push the product to consumers
3 Objectives of Advertising
Inform
Persuade
Remind
informative advertising
Communication used to create and build brand awareness, with the ultimate goal of moving the consumer through the buying cycle to a purchase
persuasive advertising
Communication used to motivate consumers to take action
reminder advertising
Communication used to remind consumers of a product or to prompt repurchases, especially for products in the maturity stage of their life cycle
product-focused advertisements
Advertisements used to inform, persuade, or remind consumers about a specific product or service
institutional advertisement
Type of advertising that promotes a company, corporation, business, institution, or organization; not intended to sell a particular product or service
public service advertising (PSA)
Advertising that focuses on public welfare and is generally sponsored by nonprofit institutions, civic groups, religious organizations, or political groups
social marketing
The content distributed through online and mobile technologies to facilitate interpersonal interactions
Step 3: Determine the Advertising Budget
Firms must consider:
The role that advertising plays in its overall promotional objectives
Expenditures vary over the course of the product life cycle
Nature of the market and the product influence the size of budget

Step 4: Convey the Message
Marketers determine what they want to convey about the product or service with a key message and an appeal
Often uses a unique selling proposition (USP)

unique selling proposition (USP)
A strategy of differentiating a product by communicating its unique attributes in the entire advertising campaign
informational appeal
Helps consumers make purchase decisions by offering factual information
emotional appeal
Aims to satisfy consumers’ emotional desires rather than their utilitarian needs
Step 5: Evaluate and Select Media
Firms must engage in media planning to select the media mix that will deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message to the intended audience

media planning
The process of evaluating and selecting the media mix that will deliver a clear, consistent, compelling message to the intended audience
media mix
The combination of the media used and the frequency of advertising in each medium
media buy
The actual purchase of airtime or print pages
mass media
Channels ideal for reaching large, anonymous audiences; includes billboards, newspapers, magazines, radio, and television
niche media
Channels that are more focused and used to reach narrower segments, often with unique demographic characteristics or interests
advertising schedule
The specification of the timing and duration of advertising
continuous advertising schedule
Runs steadily throughout the year and is suited to products and services that are consumed continually at relatively steady rates that require persuasive or reminder advertising
flighting advertising schedule
Implemented in spurts, with periods of heavy advertising followed by periods of no advertising for products whose demand fluctuates
pulsing advertising schedule
Combines the continuous and flighting schedules by maintaining a base level of advertising but increasing intensity during certain periods
Step 6: Create Advertisements
After the advertiser has decided on the message, type of ad, and appeal, they create the advertisement by creatively translating the message and appeal into words, pictures, colors, and/or music

headline
The large type in an ad that is designed to draw attention
subhead
A smaller headline that provides a great deal of information through short and simple words
body copy
The main text portion of an ad
brand elements
Characteristics that identify the sponsor of a specific ad
Step 7: Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics
The effectiveness of an advertising campaign must be assessed before, during, and after the campaign has run using pretesting, tracking, and posttesting
pretesting
Assessments performed before an ad campaign is implemented to ensure that the various elements are working in an integrated fashion and doing what they are intended to do
tracking
Assessments that monitor key indicators, such as daily or weekly sales volume, while the advertisement is running to identify any problems with the message or medium
posttesting
The evaluation of an IMC campaign’s impact after it has been implemented
public relations (PR)
Managing communication and relationships to achieve the objectives of building and maintaining a positive image of the firm, handling unfavorable stories and events, and maintaining positive relationships with the media
cause-related marketing
Commercial activity in which businesses and charities form a partnership to market an image, product, or service for their mutual benefit
event sponsorship
When corporations support various activities (financially or otherwise) usually in the cultural or sports and entertainment sectors
Elements of a Public Relations Toolkit
Print, broadcast, Internet, and out of home media
print media
Informs stakeholders and creates greater awareness around the brand
ex: press release, newsletters, annual reports
broadcast media
Creates awareness of causes brand supports and informs stakeholders of activities the brand is engaging in
ex: PSAs, YouTube videos
Internet media
Websites contain similar functions as print and broadcast media; email directs PR efforts to specific groups
ex: websites, email campaigns, social media sites
out of home media
Allows the brand to inform stakeholders and garner greater awareness
ex: billboards, speech conferences, event appearances
sales promotions
Special incentives or excitement-building programs that encourage the purchase of a product or service
Types of Sales Promotions
Coupons, deals, premiums, contests, sweepstakes, samples, loyalty programs, POP displays, rebates, and product placement
coupon
Offers a discount on the price of specific items when the items are purchased and is used to stimulate demand
deal
Short-term price reduction that can take several forms, such as a featured price, a reduced price, or BOGO
premium
An item offered for free or at a bargain price to reward some type of behavior, such as buying, sampling, or testing
contest
A brand-sponsored competition that requires some form of skill or effort
sweepstake
A form of sales promotion that offers prizes based on a chance drawing of entrants’ names
sampling
Offers potential customers the opportunity to try a product or service before they make a buying decision
loyalty program
Specifically designed to retain customers by offering premiums or other incentives to those who make multiple purchases over time
point-of-purchase (POP) display
A merchandise display located at the point of purchase, such as the checkout counter
product placement
Inclusion of a product in nontraditional situations, such as a TV or movie scene