Exam 2
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio 1604
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Which of the following molecules could pass through cellular membranes w/o transporter proteins?
a. N2
b. Cl-
c. H2O
d. Glucose
a
Disrupted function in which of the following organelles would result in a dramatic decrease in ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells?
a. Lysosome
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Nucleus
d. Mitochondria
d
Which of the following statements best describe the sodium-potassium pump?
a. The pump moves 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 K+ ions into the cell and generates an ATP in each cycle
b. The pump moves 2 Na+ ions out of the cell and 3 K+ ions into the cell and generates an ATP in each cycle
c. The pump moves 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 K+ ions into the cell using energy from ATP hydrolysis
d. The pump moves 2 Na+ ions out of the cell and 3 K+ ions into the cell using energy from ATP hydrolysis
c
Which part of the amino acid gives it a unique identity?
a. Central carbon atom
b. Amino group
c. Carboxyl group
d. Variable R group
d
What is the difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis?
a. Pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules brought into the cell, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis
b. Pinocytosis concentrates substances from extracellular fluid, but receptor-mediated endocytosis cannot
c. Pinocytosis increases surface area of the plasma membrane, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis decreases the surface area of the plasma membrane
d. Pinocytosis only brings water molecules into the cell, but receptor-mediated endocytosis brings in other molecules as well
a
If a plant cell is in a hypertonic solution, the cell will be _________.
a. Turgid
b. Flaccid
c. Plasmolyzed
d. Shriveled
c
According to the endosymbiosis theory, an early ancestor of ________ cells engulfed a ________ cell, which eventually became an organelle.
a. Bacterial; protist
b. Protist; prokaryotic
c. Prokaryotic; eukaryotic
d. Eukaryotic; prokaryotic
d
Which of the following best compares dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis?
a. Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions assemble polymers from monomers
b. Hydrolysis assembles polymers; dehydration synthesis breaks polymers apart
c. Dehydration synthesis eliminates water from membranes; hydrolysis adds water to membranes
d. Dehydration synthesis assembles polymers; hydrolysis breaks polymers apart
d
Which of the following structures form cytoplasmic channels that connect adjacent animal cells?
a. Gap junctions
b. Tight junctions
c. Desmosomes
d. Integrin
a
Which of the following is not a membrane protein function?
a. Cell-surface identity markers
b. Cell-surface receptors
c. Cell-surface respiration
d. Cell-cell adhesion
c
Which of the following is not a component of cell membranes?
a. Phospholipid bilayer
b. Ribosomes
c. Integral proteins
d. Peripheral proteins
b
Ovalbumin, the protein found in egg whites, is denatured during cooking. Which level of protein structure is not affected by this denaturation?
a. Primary
b. Secondary
c. Tertiary
d. Quaternary
a
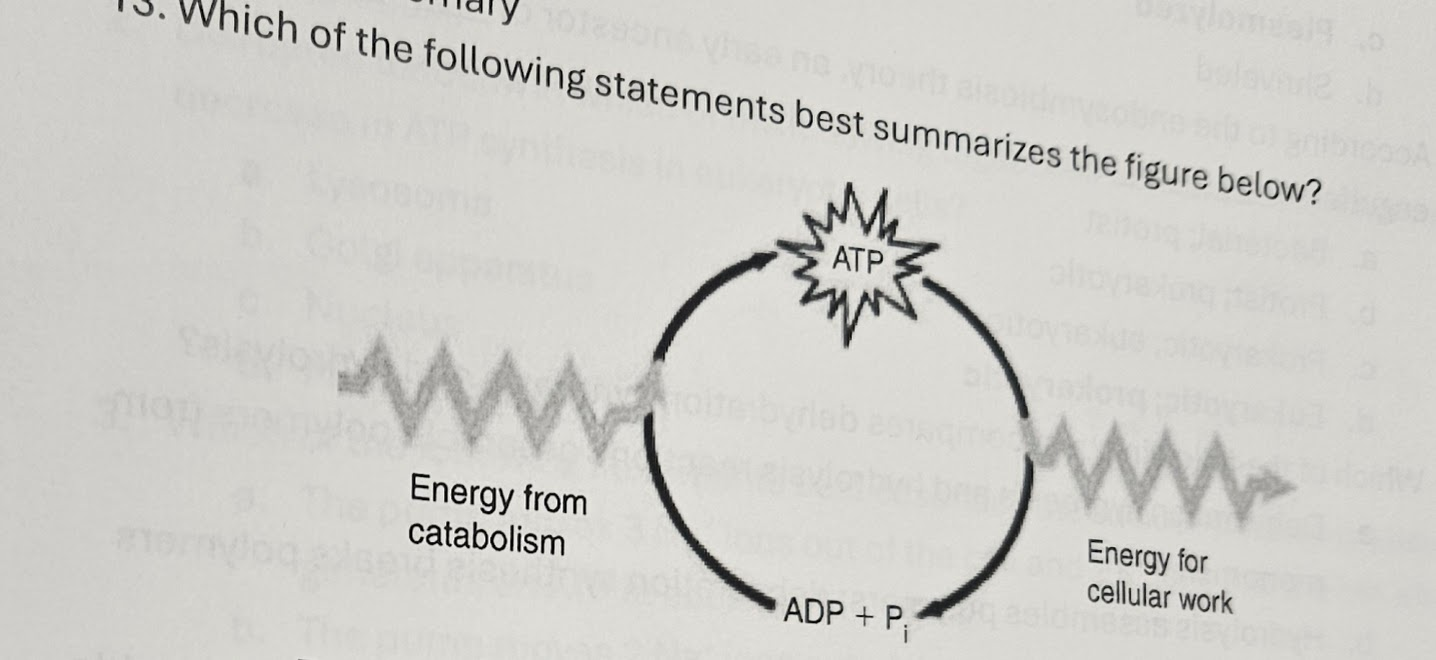
a. Energy from catabolism can be used directly for performing cellular work
b. ADP and Pi are molecules are molecules thar store energy for catabolism
c. ATP is a molecule that stores energy for cellular work
d. ADP has more energy than ATP
c
Which of the following statements best describes membrane structure?
a. The membrane is composed of a single layer of phospholipids between two layers of proteins
b. The membrane is composed of a fluid mosaic of phospholipids between two layers of proteins
c. The membrane is composed of a mosaic of fluid polysaccharides and proteins
d. The membrane is composed of a fluid bilayer of phospholipids with a mosaic of proteins
d
Why can humans digest starch but not cellulose?
a. Humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the α-glycosidic linkages of starch but not the β-glycosidic linkages of cellulose
b. Starch polymers are more branched than cellulose
c. Cellulose polymers are joined by ionic bonds while starch monomers are joined by covalent bonds
d. Cellulose cannot be digested by any organisms
a
Which monomer and structure type is observed with intermediate filaments?
a. Actin and hollow tube
b. Tubulin and hollow tube
c. Keratin and supercoiled cables
d. Actin and twisted chains
c
Living organisms increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in a decrease in the entropy of that organism. How does this relate to the second law of thermodynamics?
a. Living organisms do not obey the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of an organism increases with each energy transformation
b. The decrease in the entropy of a living organism is associated with a corresponding increase in the entropy of the universe
c. The decrease in the entropy of a living organism is associated with a corresponding decrease in the entropy of the universe
d. Living organisms cannot transform chemical energy into entropy
b
Penicillin is an antibiotic that kills bacteria by binding to the active site of an enzyme involved in synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Which of the following phenomena best describes the mechanism of action of penicillin?
a. Competitive inhibition
b. Noncompetitive inhibition
c. Feedback inhibition
d. Allosteric regulation
a
Which of the following statements describes the interaction between water molecules and phospholipids?
a. The polar heads avoid water; the nonpolar tails interact with water
b. Phospholipids do not interact with water because water is polar and lipids are nonpolar
c. The polar heads interact with water; the nonpolar tails avoid water
d. Phospholipids dissolve in water
c
Which of the following macromolecules cannot be found in polymer form?
a. Lipids
b. Nucleic acids
c. Proteins
d. Carbohydrates
a

21. Assuming only solute A can travel through the permeable membrane, which direction would solute A molecules diffuse?
a. Side 1 to Side 2
b. Side 2 to Side 1
c. Both directions
d. No diffusion occurs
22. Assuming only water can travel through the permeable membrane, which direction would water osmose (diffuse)?
a. Side 1 to Side 2
b. Side 2 to Side 1
c. Both directions
d. No osmosis occurs
23. Which of the following activities requires energy from ATP hydrolysis?
a. Facilitated diffusion of Cl ions through a channel protein
b. Movement of O2 molecules into a cell from a high concentration of O2 outside the cell
c. Movement of water through a channel protein from an environment with low concentration of solutes into a cell with high concentration of solutes
d. Movement of Na* ions from a low concentration in a cell to a high concentration in the extracellular fluid
a
b
d
Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory?
a. All organisms are composed of cells
b. Cells arise only from pre-existing cells
c. Cells are the smallest living things
d. A cell is the unit of genetic variation
a
Which of the following describes an exergonic reaction?
a. The products have more total energy than the reactants
b. Input of energy from the surroundings is required for the reaction to proceed
c. The reaction requires kinetic energy from energy coupling
d. The reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy
d
Which term best describes a reaction when AG is positive?
a. Exergonic
b. Spontaneous
c. Synergistic
d. Endergonic
d
Which of the following best describes glycogen?
a. A protein that helps in maintaining cellular structure
b. A polysaccharide found in animals
c. A nucleic acid for energy storage
d. A lipid found in cell membranes
b
Which of the following organelles often occupy most of the volume of a plant cell?
a. Lysosome
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Central vacuole
d. Chloroplast
c
Which of the following is similar between DNA and RNA?
a. Sugar
b. Pyrimidine bases
c. Purine bases
d. Number of strands
c
What is different between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
a. Eukaryotic cells have flagella; prokaryotic cell do not
b. Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles; prokaryotic cells do not
c. Prokaryotic cells have cell walls; eukaryotic cells do not
d. Prokaryotic cells have nuclei; eukaryotic cell do not
b
Which of the following statements correctly describes saturated fats?
a. They have multiple double bonds in their carbon chains
b. They are generally liquid at room temperature
c. They contain more hydrogen than unsaturated fats with the same
number of carbon atoms
d. They are more common in plants than in animals
c
Which statement best describes the first law of thermodynamics?
a. The entropy of the universe is constant
b. The entropy of the universe is increasing
c. Energy cannot be created or destroyed
d. Energy cannot be transferred or destroyed
c
If one strand of a DNA molecule has this sequence 5'-ATTGCA-3', what is the sequence of the complementary strand?
a. 5 ACGTTA-3
b. 5'-TGCAAT-3'
c. 5'-TAACGT-3'
d. 5-UGCAAU-3'
b
Which of the following is most likely to limit the maximum size of a cell?
a. The absence of a nucleus
b. The number of mitochondria
c. The ratio of surface area to volume
d. The volume of the endomembrane system
c
Which of the following terms best describes the process of breaking down large compounds into small molecules?
a. Dehydration
b. Anabolism
c. Catabolism
d. Polymerization
c
Microscopic examination of a cell shows high number of ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Based on this observation, which macromolecule is this cell actively producing?
a. Polysaccharides
b. Proteins
c. Lipids
d. Nucleic acids
b
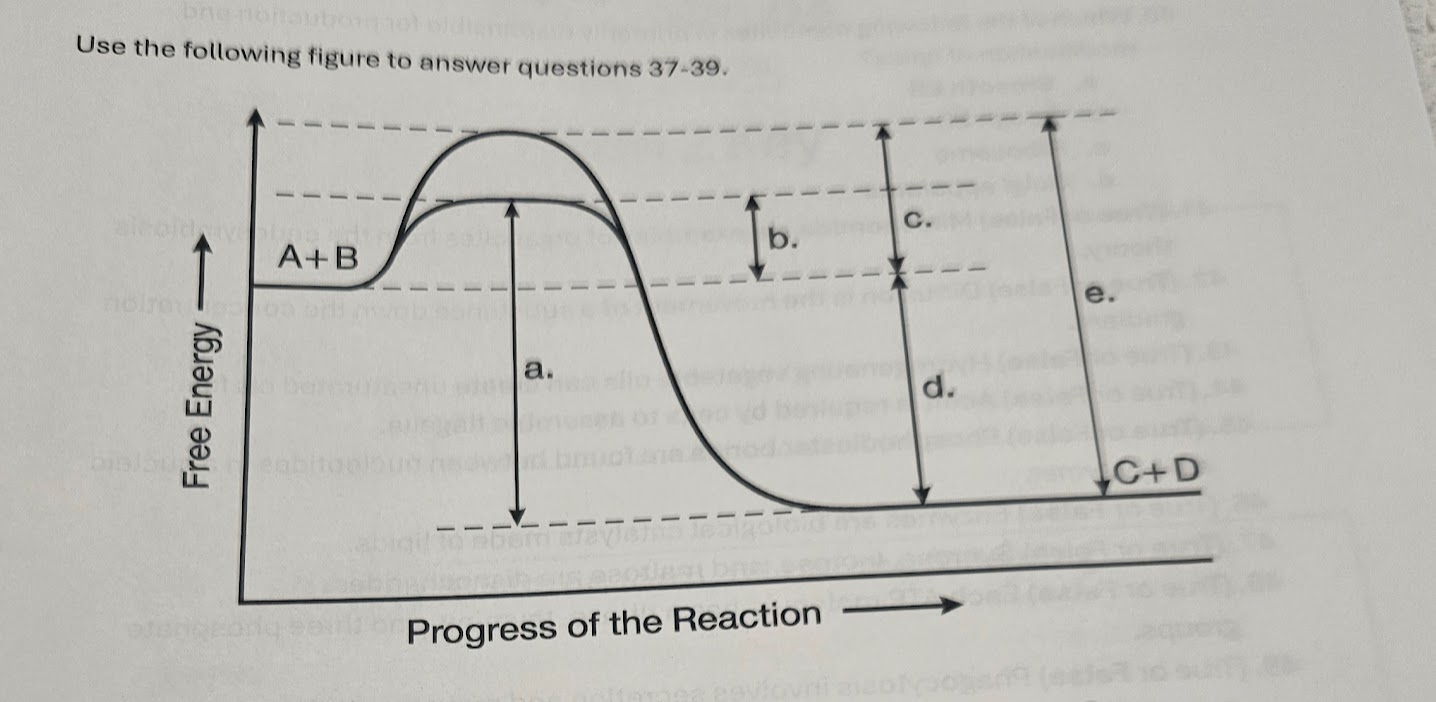
37. What best describes the forward reaction A + B -> C + D in the figure?
a. Endergonic, Delta*G > 0
b. Endergonic, Delta*G < 0
c. Exergonic, Delta*G > 0
d. Exergonic, Delta*G < 0
38. Which of the lower-case letters in the figure represents a free energy change that would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
a. a
b. b
C. C
d. d
39. Which of the lower-case letters represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
a. a
b. b
C. C
d. d
d
d
b
Which of the following organelles is primarily responsible for production and modification of lipids?
a. Smooth ER
b. Rough ER
c. Ribosome.
d. Golgi apparatus
a
(True or False) Mitochondria are examples of organelles from the endosymbiosis theory.
a. true
b. false
a
(True or False) Diffusion is the movement of a substance down the concentration gradient.
a. true
b. false
a
(True or False) Hydrogenating vegetable oils can create unsaturated cis fats.
a. true
b. false
b
(True or False) Actin is required by cells to assemble flagella.
a. true
b. false
b
(True or False) Phosphodiester bonds are found between nucleotides in a nucleic acid polymer.
a. true
b. false
a
(True or False) Enzymes are biological catalysts made of lipids.
a. true
b. false
b
(True or False) Sucrose, lactose, and maltose are disaccharides.
a. true
b. false
a
(True or False) Each ATP molecule has a ribose, thymine, and three phosphate groups.
a. true
b. false
b
(True or False) Phagocytosis involves secretion and movement of large particles out of the cell.
a. true
b. false
b
(True or False) The rate of reaction for an enzyme can be changed by a change in substrate concentration.
a. true
b. false
a