
7.3 Translation
Conversion of sequence of bases on mRNA into sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
Polypeptides are synthesized by ribosomes and tRNA.
tRNA
Delivers the amino acid to the ribosome as the polypeptide chain elongates.
70-90 nucleotides long.
Folds into a cloverleaf shape.
One arm of tRNA contains the anticodon, which is complementary to codon in mRNA.
The amino acids is attached to the opposite end of the tRNA molecule.
The Wobble Hypothesis
The anticodon only needs to match the first TWO bases in the codon, The third can be incorrect but still retrieve the correct amino acid.
Remember that multiple codons may encode for the same amino acid.
Aminoacylation
Amino acids are linked to tRNA in a process called aminoacylation.
This process is performed by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
There are 20 enzymes, one for each amino acid. The product is called an aminoacyl-tRNA
Ribosomes
Composed of 2 subunits: large ribosomal subunit and small ribosomal subunit, both composed of rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
mRNA moves through groove between subunits
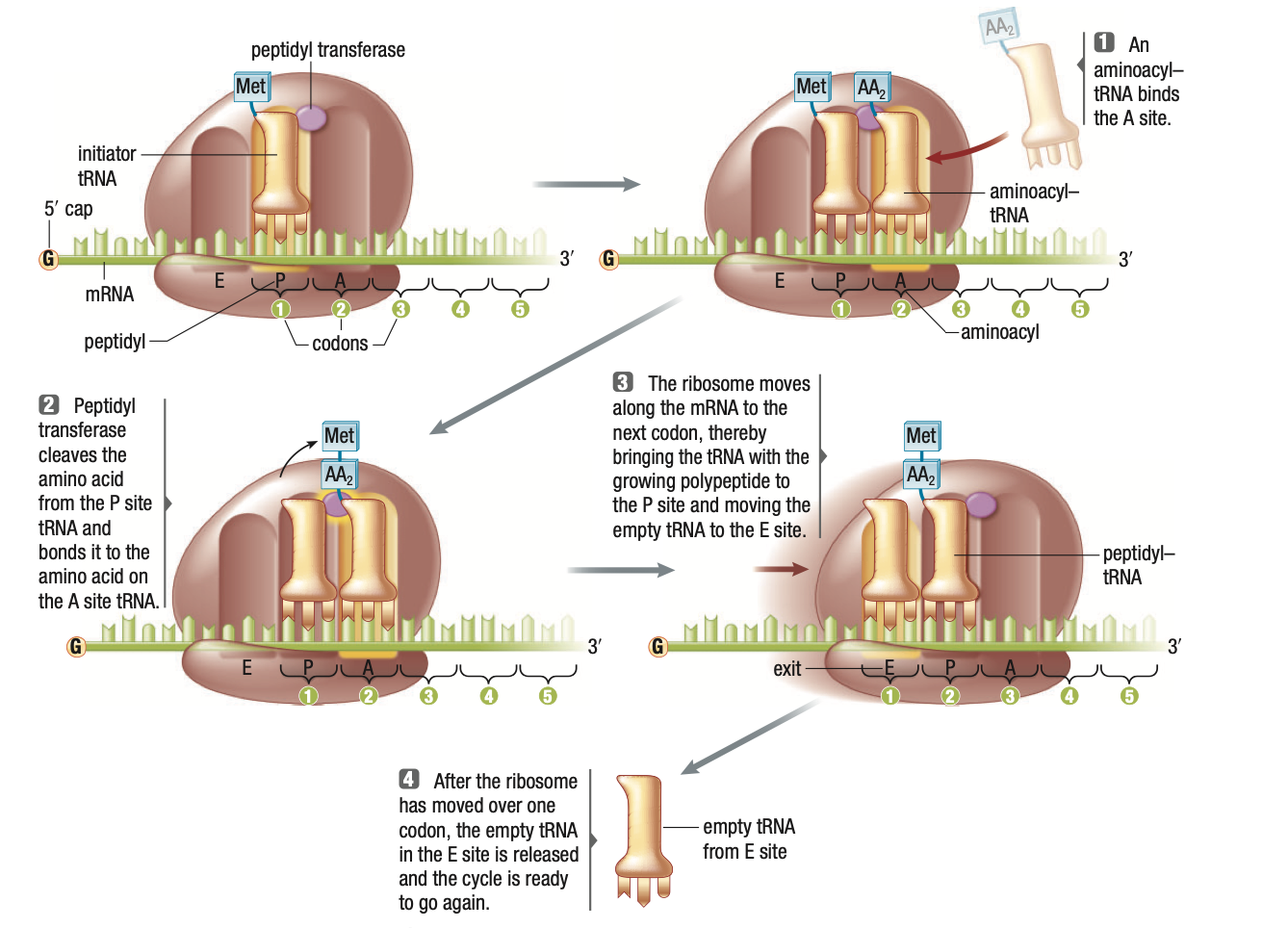
Contains 3 binding sites
A (aminoacyl) site – aminoacyl tRNA containing next amino acid binds to MRNA
P (peptidyl) site – TRNA binds to ribosome
E (exit) site – tRNA leaves ribosome

3 stages of translation:
Initiation
Translation begins at the start codon (AUG) on mRNA
AUG is the codon for the amino acid methionine
The aminoacyl-TRNA for methionine (the initiator tRNA) binds the small ribosomal subunit and scans the mRNA for the start codon
When met-tRNA recognizes the start codon, the large ribosomal subunit binds
A reading frame is established such that the bases are read 3 at a time from start codon.
Elongation
Begins with initiator tRNA bound to P site and empty A site
Aminoacyl-tRNA with next amino acid binds to A site
Amino acid in P site is removed from its tRNA and a peptide bond is formed with the amino acid in the A site
Ribosome moves to next codon, all tRNA’s shift (P --> E, A --> P)
A site is now ready to accept next aminoacyl-tRNA. E site ejects its tRNA.
Termination
Occurs when stop codons enter the A site (UAA, UAG, UGA)
Protein release factor binds instead of aminoacyl-tRNA (there are no corresponding amino acids for stop codons)
Polypeptide is released, ribosomal subunits detach.
7.3 Translation
Conversion of sequence of bases on mRNA into sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
Polypeptides are synthesized by ribosomes and tRNA.
tRNA
Delivers the amino acid to the ribosome as the polypeptide chain elongates.
70-90 nucleotides long.
Folds into a cloverleaf shape.
One arm of tRNA contains the anticodon, which is complementary to codon in mRNA.
The amino acids is attached to the opposite end of the tRNA molecule.
The Wobble Hypothesis
The anticodon only needs to match the first TWO bases in the codon, The third can be incorrect but still retrieve the correct amino acid.
Remember that multiple codons may encode for the same amino acid.
Aminoacylation
Amino acids are linked to tRNA in a process called aminoacylation.
This process is performed by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
There are 20 enzymes, one for each amino acid. The product is called an aminoacyl-tRNA
Ribosomes
Composed of 2 subunits: large ribosomal subunit and small ribosomal subunit, both composed of rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
mRNA moves through groove between subunits
Contains 3 binding sites
A (aminoacyl) site – aminoacyl tRNA containing next amino acid binds to MRNA
P (peptidyl) site – TRNA binds to ribosome
E (exit) site – tRNA leaves ribosome

3 stages of translation:
Initiation
Translation begins at the start codon (AUG) on mRNA
AUG is the codon for the amino acid methionine
The aminoacyl-TRNA for methionine (the initiator tRNA) binds the small ribosomal subunit and scans the mRNA for the start codon
When met-tRNA recognizes the start codon, the large ribosomal subunit binds
A reading frame is established such that the bases are read 3 at a time from start codon.
Elongation
Begins with initiator tRNA bound to P site and empty A site
Aminoacyl-tRNA with next amino acid binds to A site
Amino acid in P site is removed from its tRNA and a peptide bond is formed with the amino acid in the A site
Ribosome moves to next codon, all tRNA’s shift (P --> E, A --> P)
A site is now ready to accept next aminoacyl-tRNA. E site ejects its tRNA.
Termination
Occurs when stop codons enter the A site (UAA, UAG, UGA)
Protein release factor binds instead of aminoacyl-tRNA (there are no corresponding amino acids for stop codons)
Polypeptide is released, ribosomal subunits detach.


