Grand Pracs
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
1
New cards
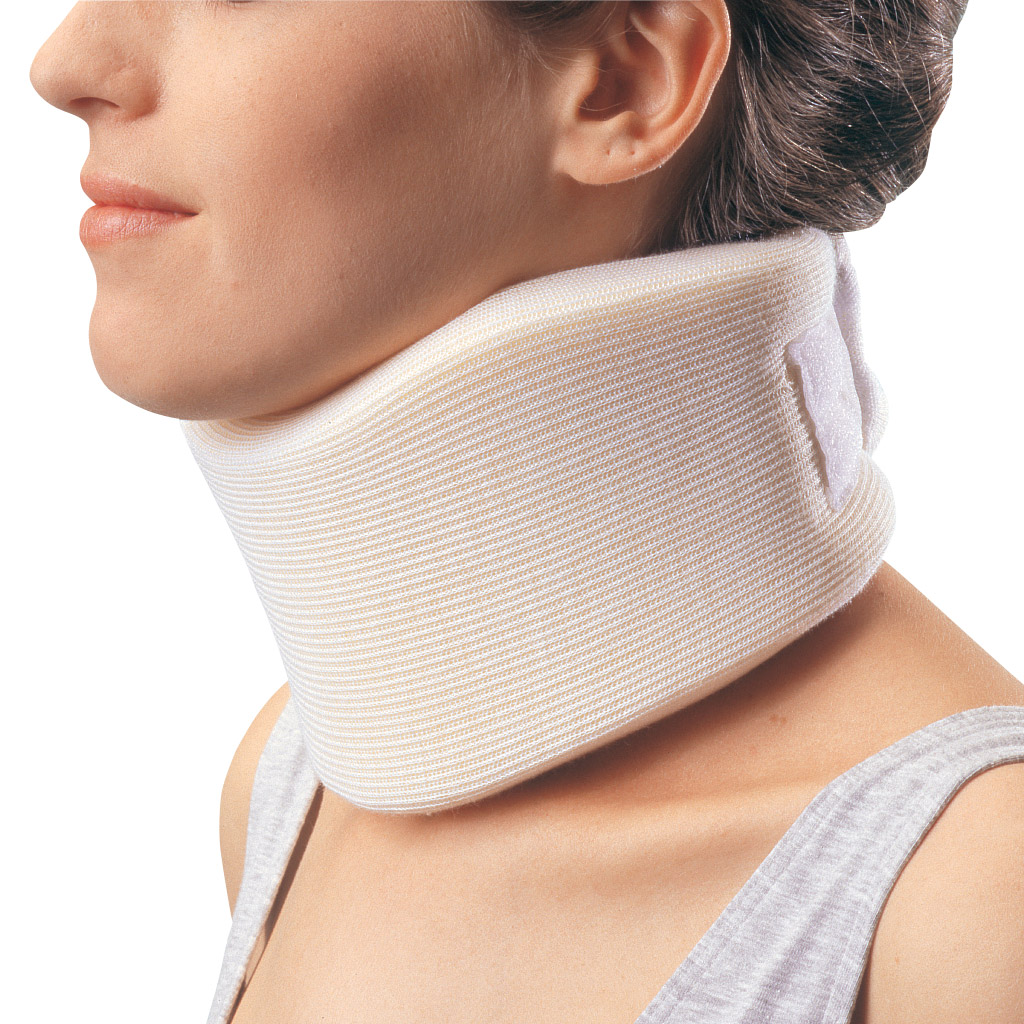
Soft Collar
\- most comfortable of the available cervical collars
\- this type of cervical orthosis does little to restrict motions
\- kinesthetic function of only
\- the collar is usually a narrow block of foam rubber material covered with stockinette or knitted material, and it is closed around the neck with velcro
\- it is used primarily as a comfortable reminder to the patient to limit exaggerated neck movements
\- this type of cervical orthosis does little to restrict motions
\- kinesthetic function of only
\- the collar is usually a narrow block of foam rubber material covered with stockinette or knitted material, and it is closed around the neck with velcro
\- it is used primarily as a comfortable reminder to the patient to limit exaggerated neck movements
2
New cards
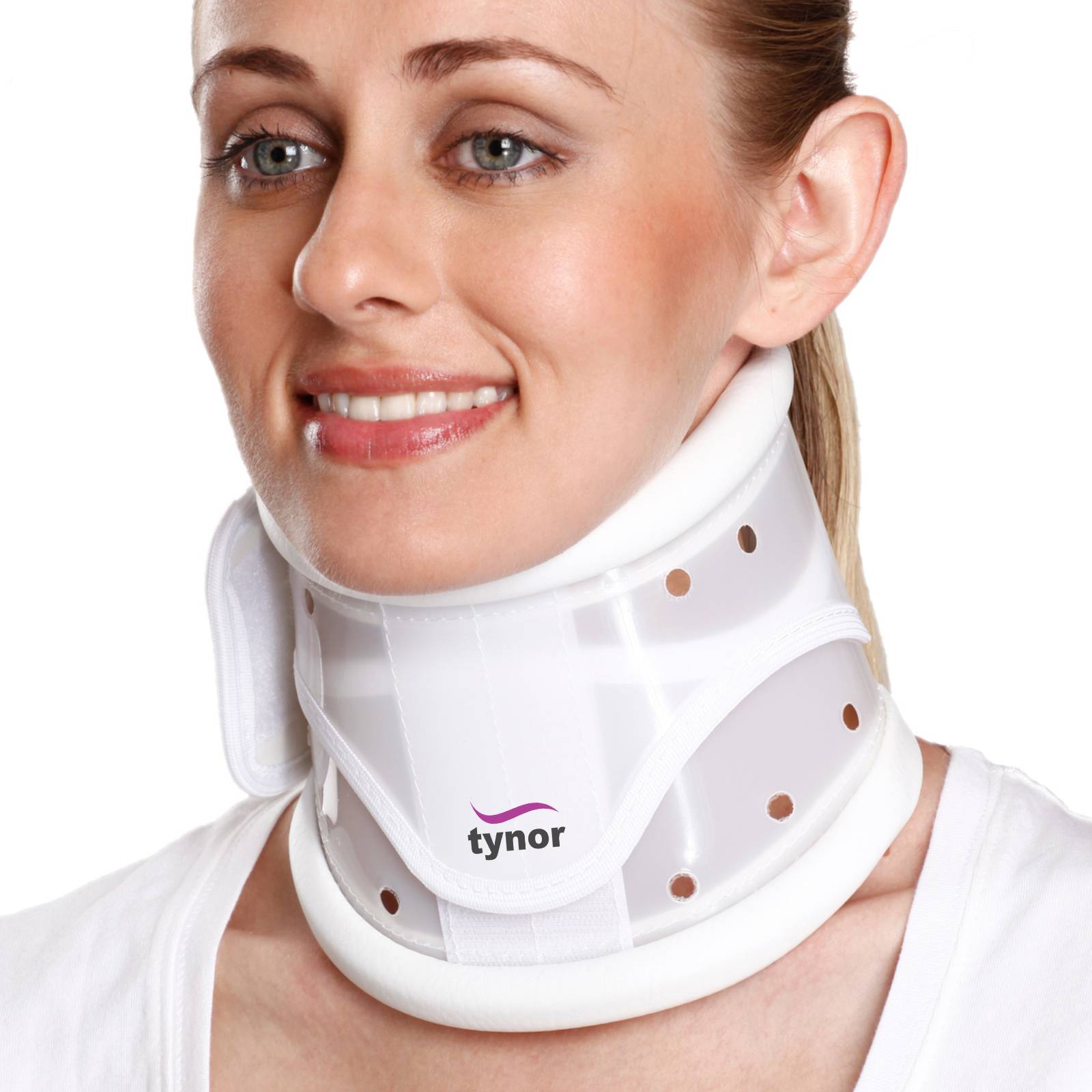
Reinforced Collar
\- has an outer plastic/semi regid frame and an inner soft pad or closed cell foam shell that interfaces with the skin
\- functions:
* mechanical restriction
* sensory feedback
* retains body heat which may aid healing of soft tissue and reduce muscle spasm
\- functions:
* mechanical restriction
* sensory feedback
* retains body heat which may aid healing of soft tissue and reduce muscle spasm
3
New cards
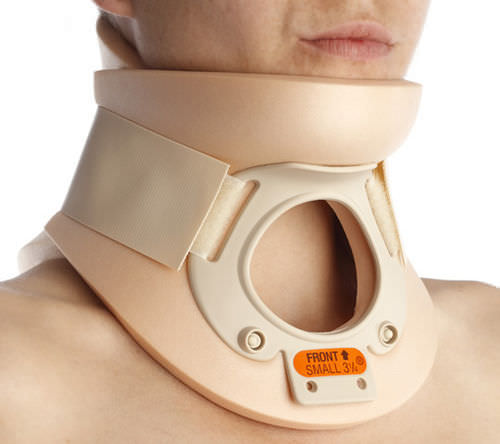
Philadelphia Collar
\
\- designed to control motion
\- composed of:
* rigid anterior and posterior plastic strips that covers more part of the head and neck
* terminates superiorly over the mandible and occiput
* terminates inferiorly at at the thorax
\- functions:
* limit neck motions and retains body heat
* greater restriction against cervical flexion and extension
* more selective adjustment of head position than soft collar
\- designed to control motion
\- composed of:
* rigid anterior and posterior plastic strips that covers more part of the head and neck
* terminates superiorly over the mandible and occiput
* terminates inferiorly at at the thorax
\- functions:
* limit neck motions and retains body heat
* greater restriction against cervical flexion and extension
* more selective adjustment of head position than soft collar
4
New cards
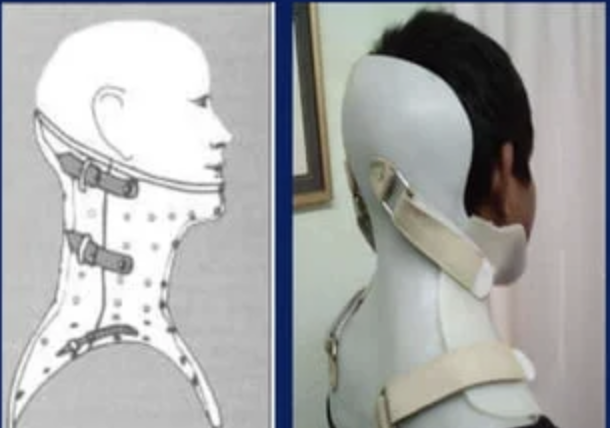
Cuirass
\- extend superiorly over the chin, mandible and occiput
\- inferiorly may extend up to 1 inc above IAS or further downward towards the inferior coastal margin
\- inferiorly may extend up to 1 inc above IAS or further downward towards the inferior coastal margin
5
New cards
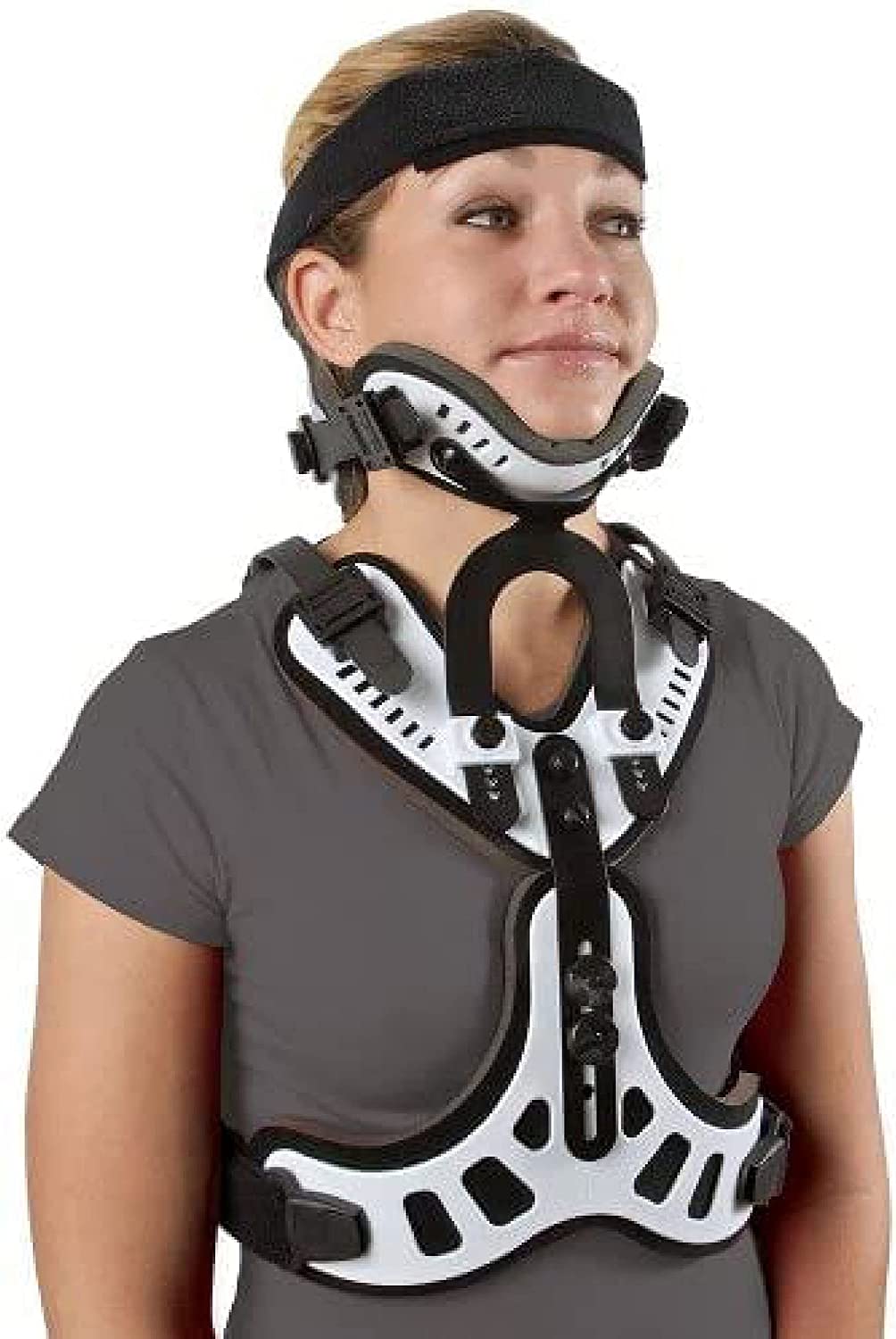
Minerva
\- orthosis that encloses the skull
\- it also includes: forehead band and body jacket
\- light weights than the halo vest; no pins (no “invasive” support)
\- less restriction of motion compared to halo vest
\- it also includes: forehead band and body jacket
\- light weights than the halo vest; no pins (no “invasive” support)
\- less restriction of motion compared to halo vest

6
New cards
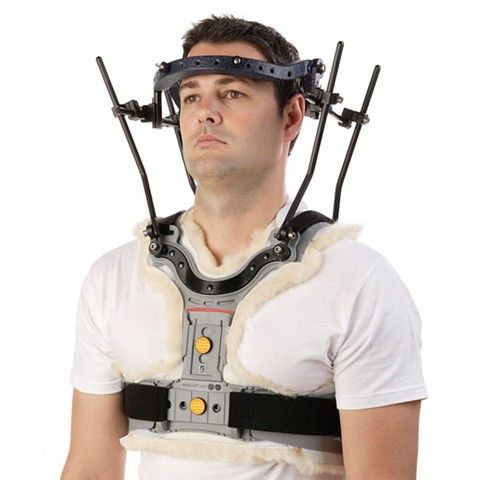
Halo
\- provides greatest control of all cervical appliances
\- composed of:
* halo ring
* distraction rods
* shoulder bars
* distal fixation
\- functions:
* rigidly fixates the head with respect to thorax
* spinal stabilization
* reduces the load of the head
\- composed of:
* halo ring
* distraction rods
* shoulder bars
* distal fixation
\- functions:
* rigidly fixates the head with respect to thorax
* spinal stabilization
* reduces the load of the head

7
New cards
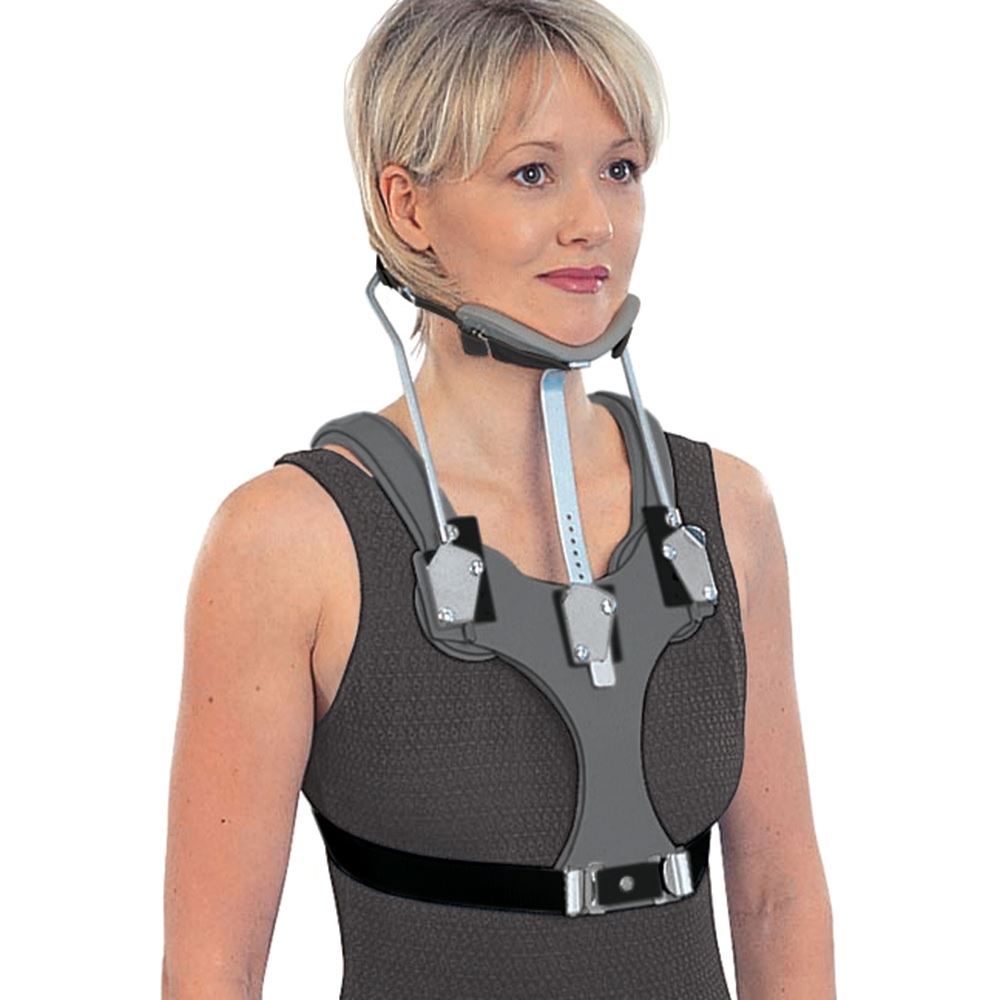
Sterno Occipital Mandibular Immobilizer
\- composed of:
* occipital support
* anterior upright
\- can be easily applied even when patient is in supine position
\- control flexion, rotation, extension (although significantly less)
\- modified version: polyethylene and dacron skull strap substitute mandibular support
\- modification in spina jacket for increasing control over the vertebral column
* occipital support
* anterior upright
\- can be easily applied even when patient is in supine position
\- control flexion, rotation, extension (although significantly less)
\- modified version: polyethylene and dacron skull strap substitute mandibular support
\- modification in spina jacket for increasing control over the vertebral column
8
New cards
Posterior Appliance
\
\- composed of:
* sternal plate
* one or two upright anteriorly
* mandibular support
* interscapular plate
* one or two uprights posteriorly
* occipital support
* axillary straps for added stability
\- functions:
* restrict flexion and extension of the head and cervical spine by forces from the mandible and occiput
* limits lateral flexion and rotation by forces at the mandibular and occipital support
* relieve of weight from the head
\- composed of:
* sternal plate
* one or two upright anteriorly
* mandibular support
* interscapular plate
* one or two uprights posteriorly
* occipital support
* axillary straps for added stability
\- functions:
* restrict flexion and extension of the head and cervical spine by forces from the mandible and occiput
* limits lateral flexion and rotation by forces at the mandibular and occipital support
* relieve of weight from the head

9
New cards
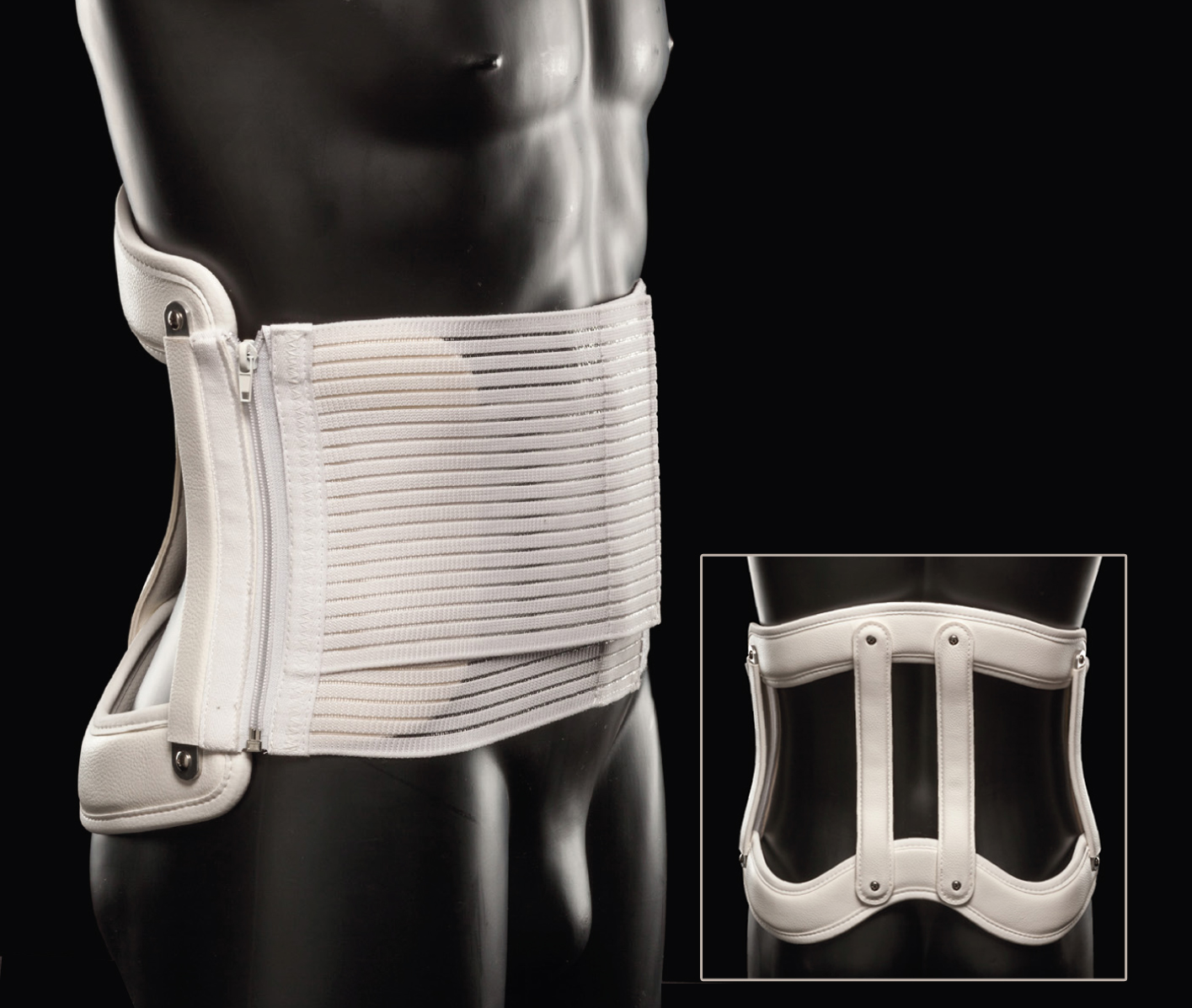
Chairback
\- components:
* lumbosacral posterior uprights
* pelvic and thoracic band
* full front abdominal support
\- functions:
* restrict trunk flexion and extension
* lumbosacral posterior uprights
* pelvic and thoracic band
* full front abdominal support
\- functions:
* restrict trunk flexion and extension
10
New cards
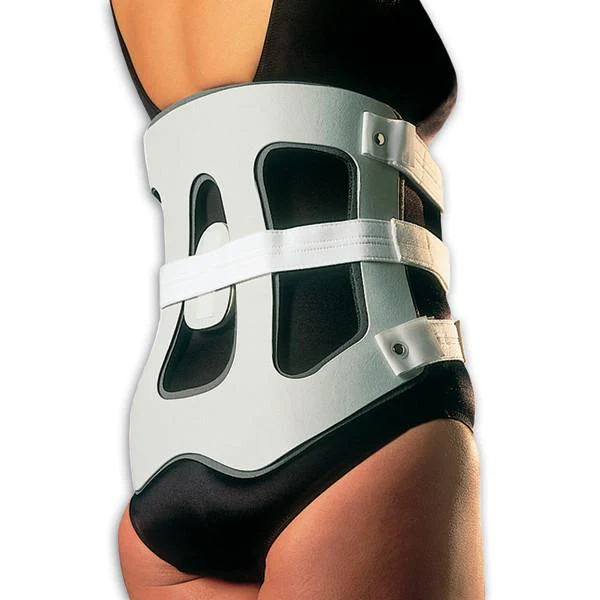
Knight
\- components:
* lumbosacral posterior uprights
* pelvic and thoracic band
* full front abdominal support
* lateral uprights
\- functions:
* restrict flexion, extension, and lateral flexion
* lumbosacral posterior uprights
* pelvic and thoracic band
* full front abdominal support
* lateral uprights
\- functions:
* restrict flexion, extension, and lateral flexion

11
New cards
Williams
\- components:
* pelvic and thoracic band
* lateral uprights
* oblique lateral uprights
* abdominal pads
\- functions:
* restrict extension and lateral flexion
* pelvic and thoracic band
* lateral uprights
* oblique lateral uprights
* abdominal pads
\- functions:
* restrict extension and lateral flexion

12
New cards
Taylor
\- components:
* TLS posterior uprights
* intrascapular band
* full front abdominal support
* axillary straps
\- functions:
* restrict flexion and extension
* TLS posterior uprights
* intrascapular band
* full front abdominal support
* axillary straps
\- functions:
* restrict flexion and extension
13
New cards
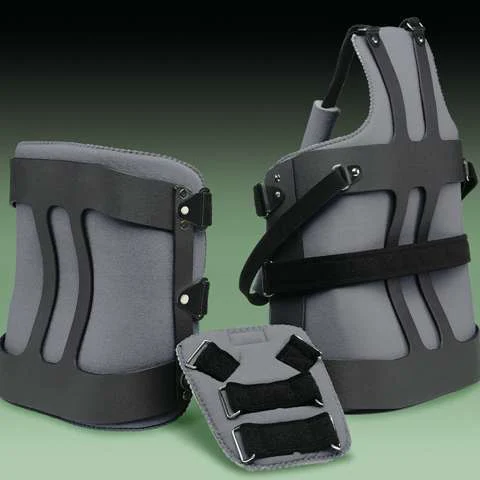
Knight Taylor
\- components:
* TLS posterior uprights
* intrascapular band
* full front abdominal support
* axillary straps
* lateral uprights
\- functions:
* restrict flexion, extension, and lateral flexion
* TLS posterior uprights
* intrascapular band
* full front abdominal support
* axillary straps
* lateral uprights
\- functions:
* restrict flexion, extension, and lateral flexion

14
New cards
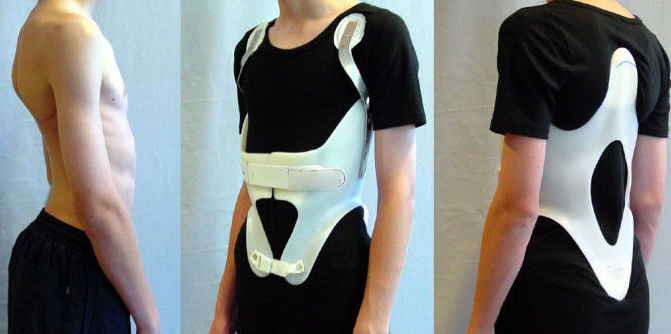
Cowhorn
\- components:
* pelvic and thoracic band
* posterior uprights
* lateral uprights
* abdominal support
* cowhorn extension
\- functions:
* restrict flexion, extension (lumbar only), lateral flexion, and rotation
* pelvic and thoracic band
* posterior uprights
* lateral uprights
* abdominal support
* cowhorn extension
\- functions:
* restrict flexion, extension (lumbar only), lateral flexion, and rotation
15
New cards
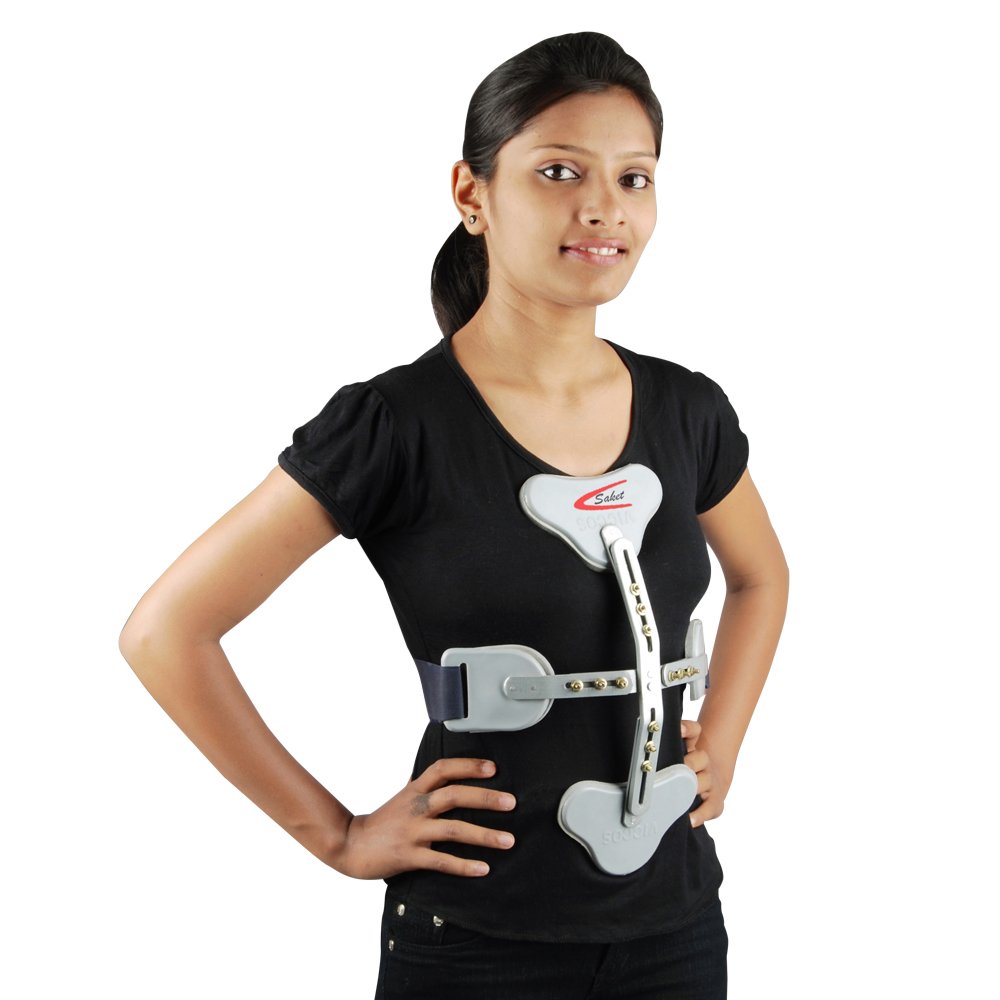
Ant. Hyperextension (Jewett or CASH)
\- components:
* anterior and lateral torso grame
* lateral, sternal, suprapubic, and thoracolumbar pads
\- functions:
* restrict flexion
* anterior and lateral torso grame
* lateral, sternal, suprapubic, and thoracolumbar pads
\- functions:
* restrict flexion

16
New cards
Plastic Body Jacket
\- restrict all motion of the trunk
\- provides maximum/highest orthotic immobilization and control of the spine
\- provides maximum/highest orthotic immobilization and control of the spine

17
New cards
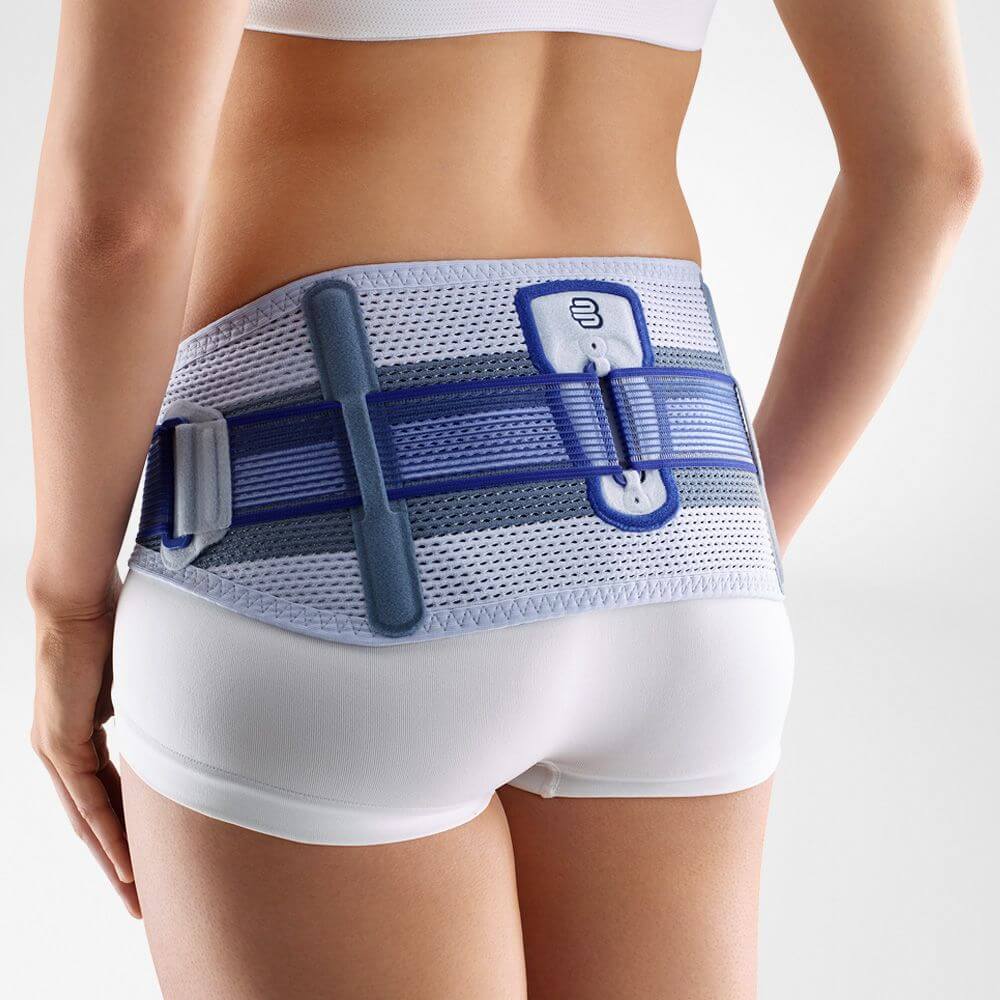
Sacroiliac Orthosis
\- provides anterior and lateral containment and assists in the restriction of some pelvic flexion and extension
\- compresses the pelvis
\- compresses the pelvis

18
New cards
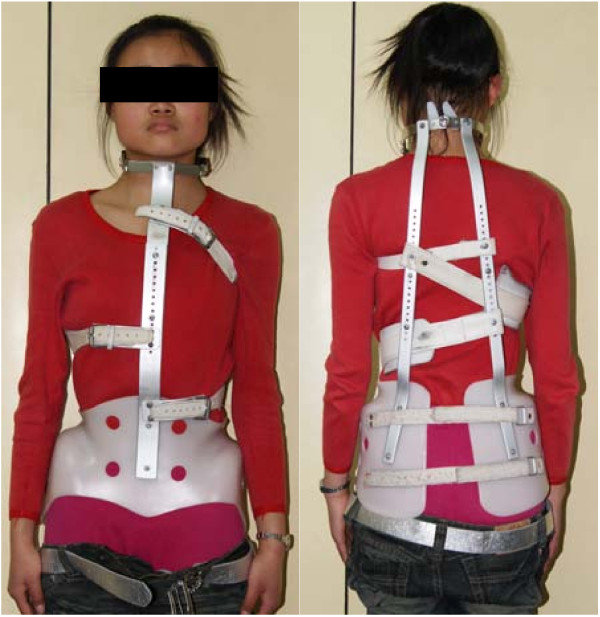
Milwaukee
\- control or correct spinal curvature
\- for curves above T7 and 25-40 degrees superior to T8
\- for curves above T7 and 25-40 degrees superior to T8
19
New cards
Boston and Wilmington
\- prevent curve progression
\- stabilize the spine
\- for curves below T8 and 25-35 degrees with apex of T7
\- stabilize the spine
\- for curves below T8 and 25-35 degrees with apex of T7
20
New cards
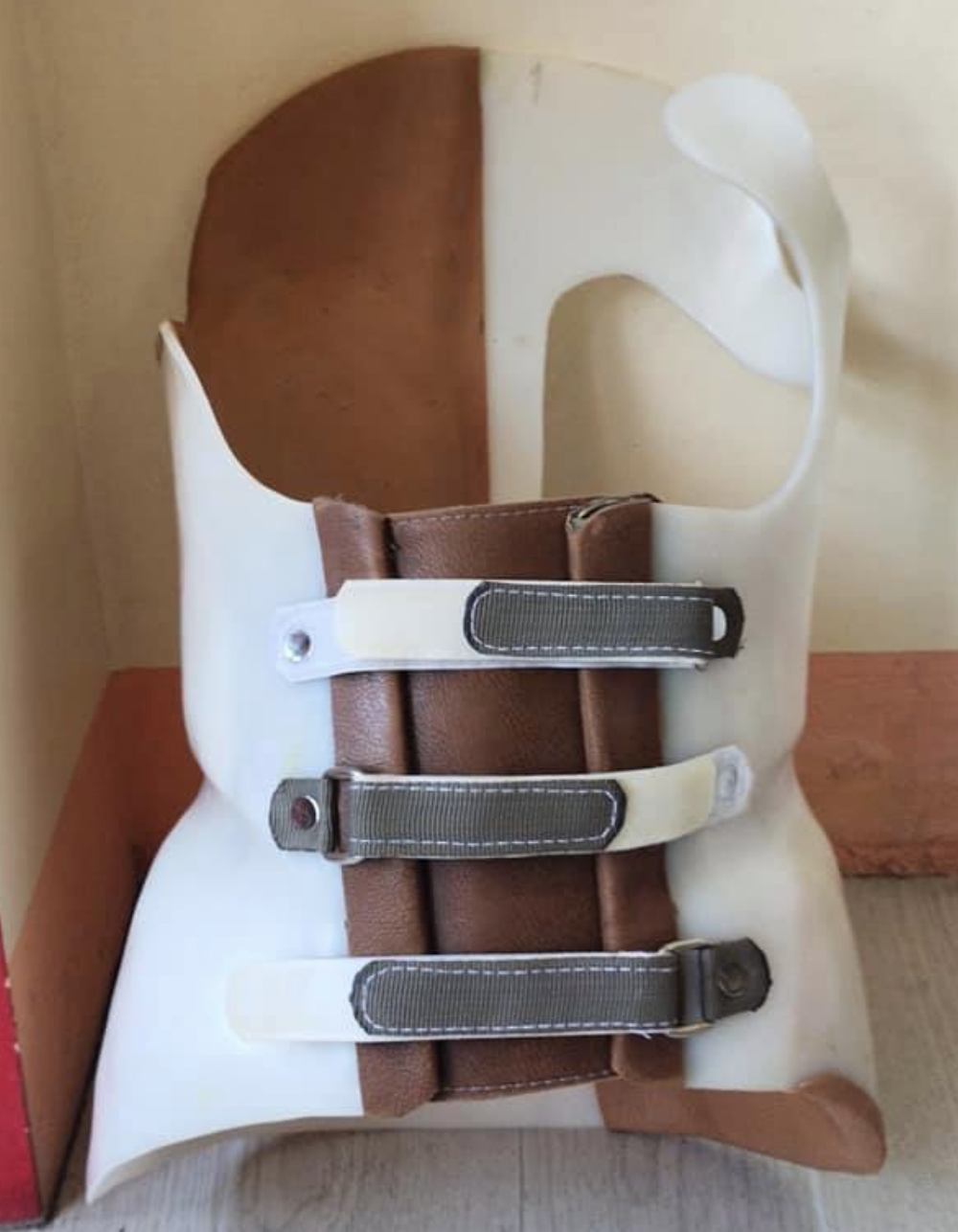
Miami
\- to reduce and prevent the progression of thoracolumbar and thoracic curves
\- for curves of 25-35 degrees with apex T7 or lower
\- for curves of 25-35 degrees with apex T7 or lower

21
New cards
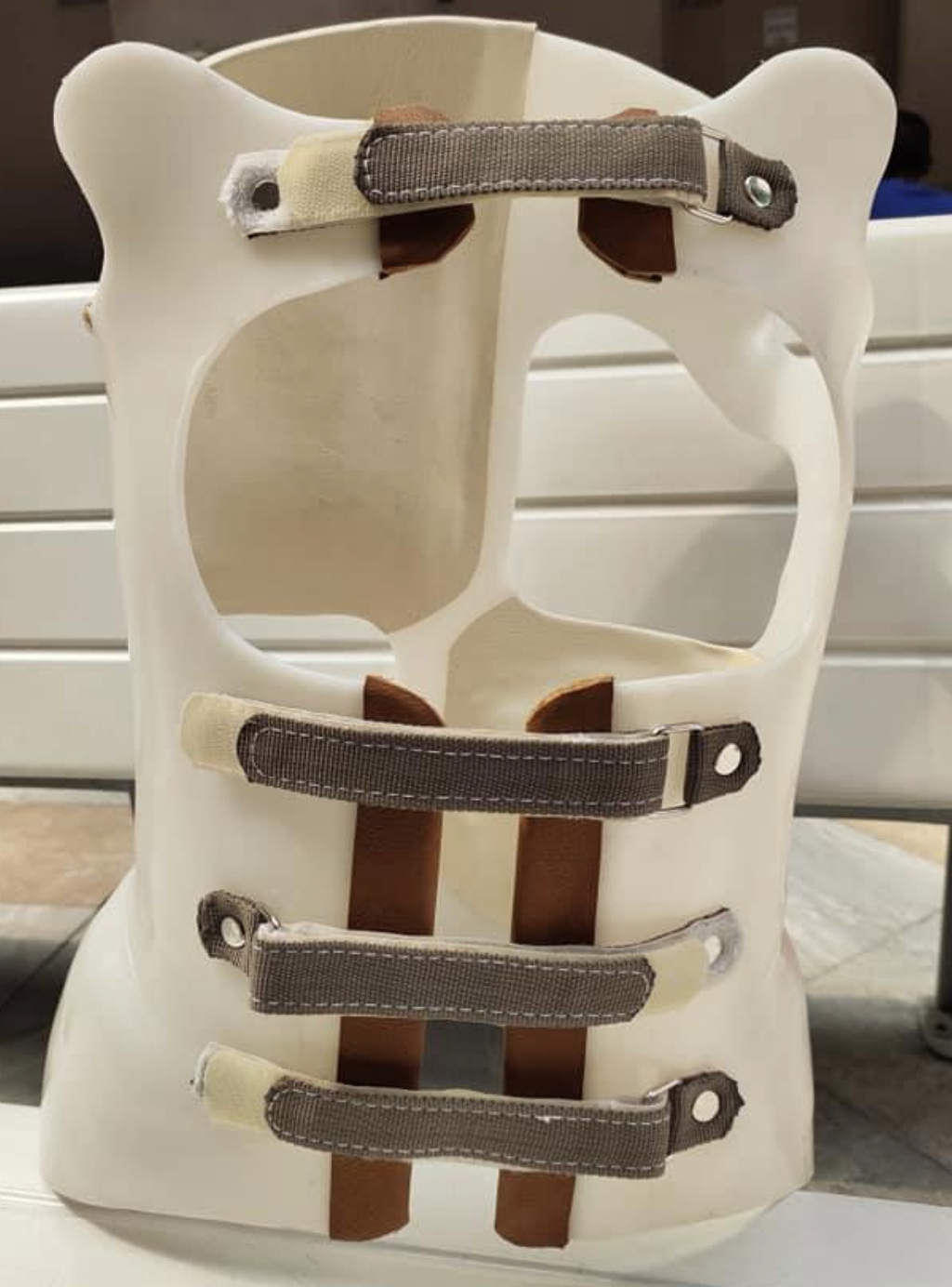
NYOH
\- to reduce and prevent the progression of curves
\- for low thoracic curve
\- for low thoracic curve

22
New cards
Shoe Inserts
\- permits the pt. to transfer the orthosis from shoe to shoe
\- may also reduce the gait unsteadiness
\- may also reduce the gait unsteadiness

23
New cards
Tapered Heels
\- reduces impact shock and shear, thus protecting painful or insensitive feet
\- limits longitudinal arch and prevent pes planus
\- limits longitudinal arch and prevent pes planus

24
New cards
University of California Biomechanics Laboratory Foot Orthosis
controls hindfoot valgus and limits subtalar motion.
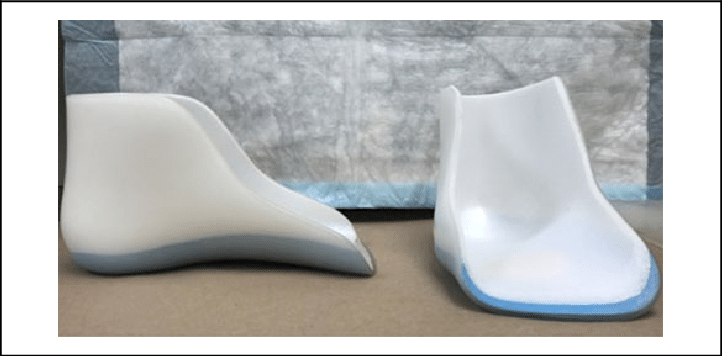
25
New cards
Metatarsal Pad
\- it provides support to the arches
\- reduces the pressure on the ball of the foot, and sometimes on the arches
\- reduces the pressure on the ball of the foot, and sometimes on the arches
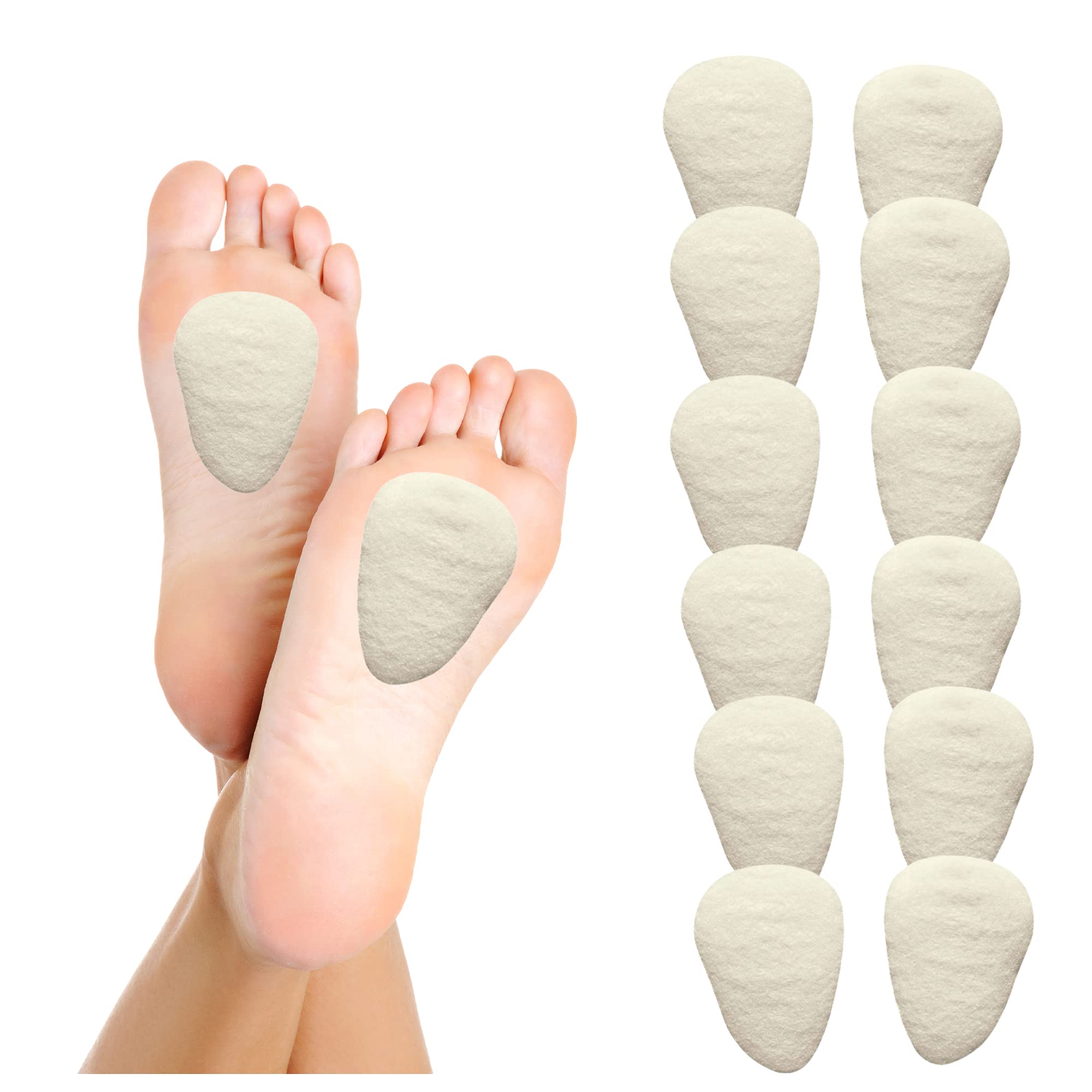
26
New cards
Metatarsal Bar
at a late stance, the bar transfers stress from the MTP joints to the metatarsal shaft.
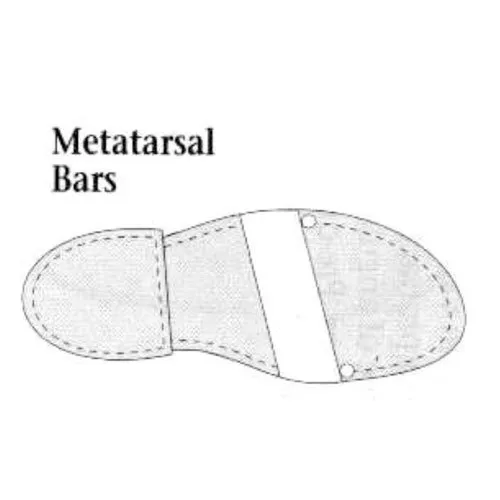
27
New cards
Rocker Bar
reduces the distance the wearer must travel during stance phase, improving late stance, as well as shifting load from the MTP joints to the metatarsal shaft.
28
New cards
Heel Wedge
\- alters alignment of the rear foot
\- realigns pes valgus and pes varus
\- realigns pes valgus and pes varus
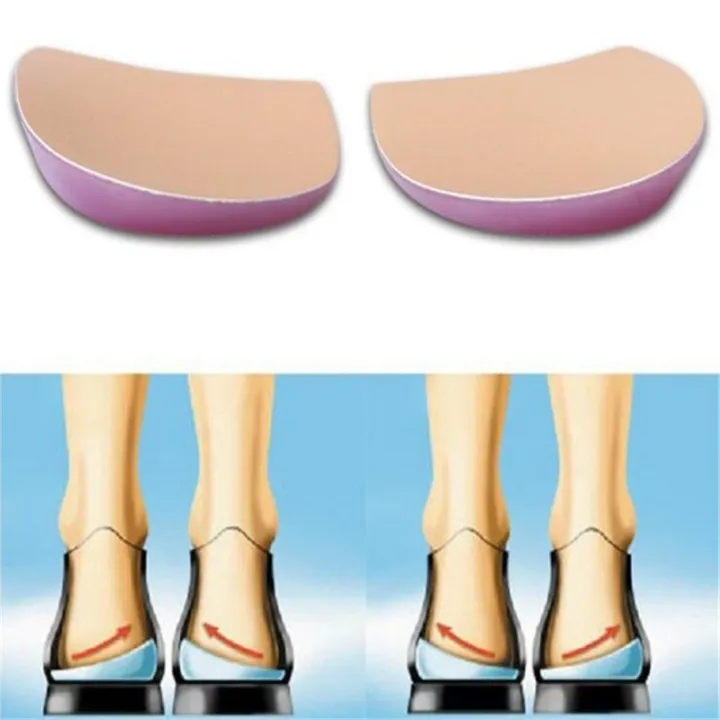
29
New cards
Flare
\- not intended to correct deformity but to control motion
\- provide support for the foot to prevent it from collapsing to the ground
\- provide support for the foot to prevent it from collapsing to the ground

30
New cards
Solid Ankle Cushion Heel
absorb more impact and limit ankle and tarsal motion better; it will make the transition between heel strike to foot-flat slower.
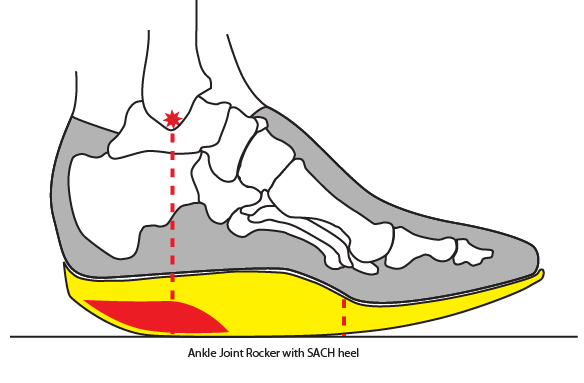
31
New cards
Thomas Heel and Reverse Thomas Heel
produce inversion of the forefoot.
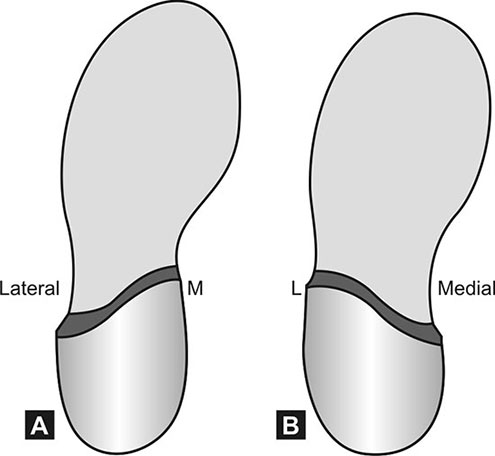
32
New cards
Finger Orthosis (DIP)
\- limit the motion
* either static or dynamic
* volar, dorsal, or joint crossed
* either static or dynamic
* volar, dorsal, or joint crossed
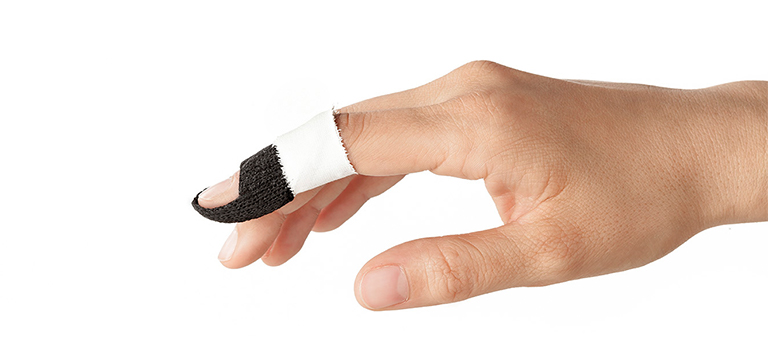
33
New cards
Finger Orthosis (PIP)
\- provide three point static control to prevent certain position and allow movement in the opposite position
\- the combination of static control in both surfaces immobilizes the finger
\- the combination of static control in both surfaces immobilizes the finger
34
New cards
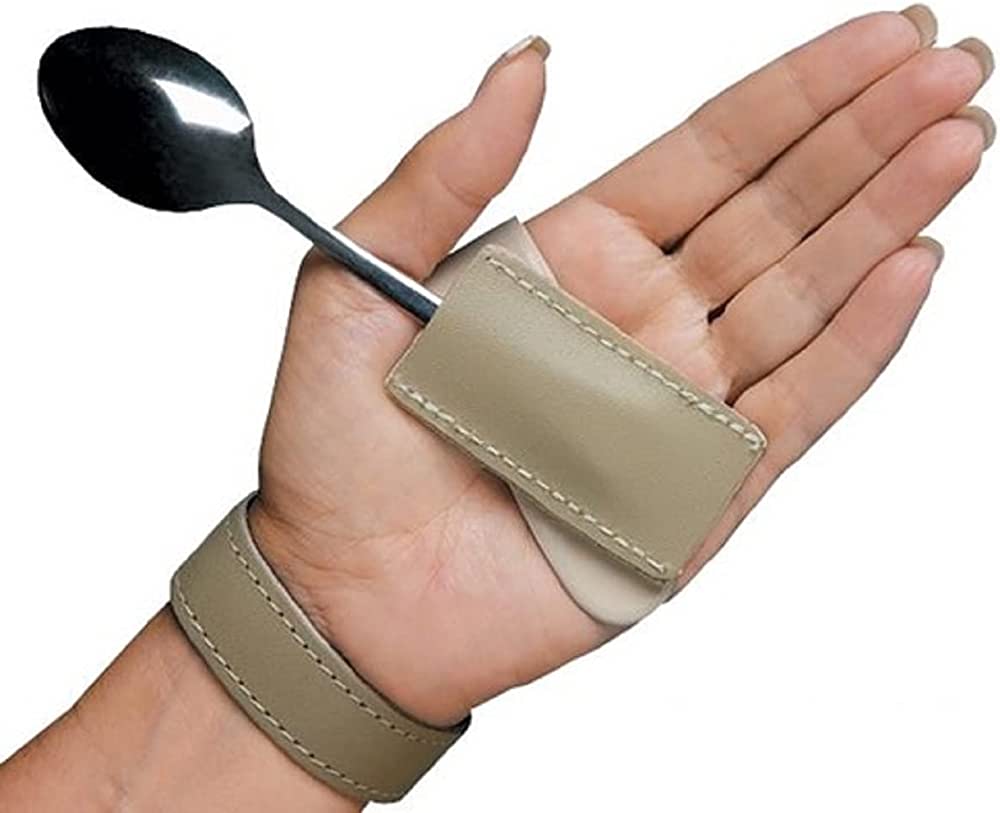
Universal Cuff
\- can be used associate to devices (e.g. spoon assistive device)
\- accommodates eating utensils and writing instruments, assisting with daily functions
\- accommodates eating utensils and writing instruments, assisting with daily functions

35
New cards
Wrist Cock Up Splint
\- maintain the wrist in the neutral or mildly extended position
\- immobilizes the wrist while allowing MCP flexion and thumb mobility
\- allows for functional mobility/activities
\- immobilizes the wrist while allowing MCP flexion and thumb mobility
\- allows for functional mobility/activities
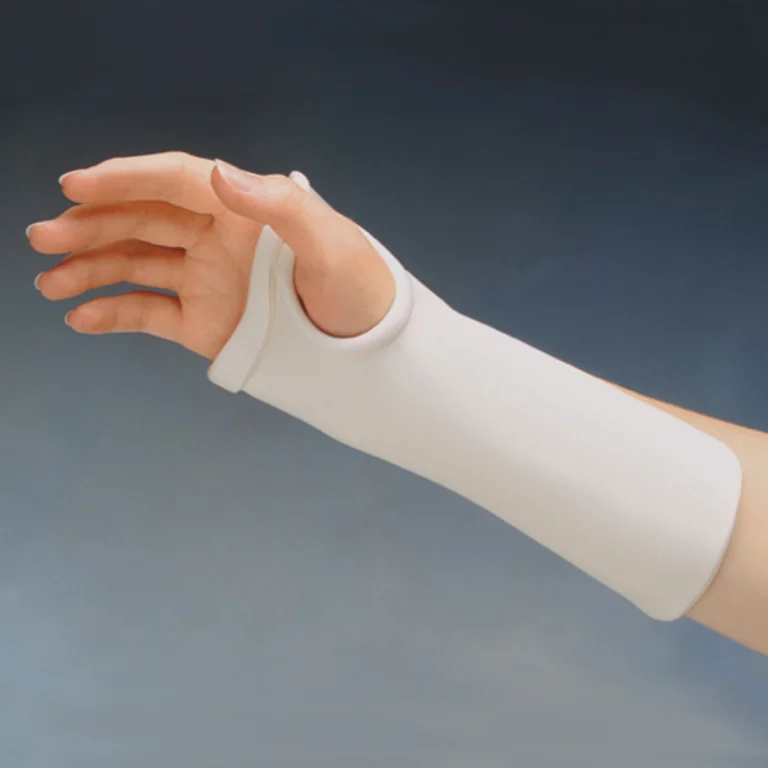
36
New cards
Dorsal Wrist Cock Up Splint
\- stronger mechanical support of wrist and freeing up some of the palmar pressure for sensory input
\- distributes pressure over the larger dorsal wrist surface area
\- better tolerated by edematous hand
\- distributes pressure over the larger dorsal wrist surface area
\- better tolerated by edematous hand
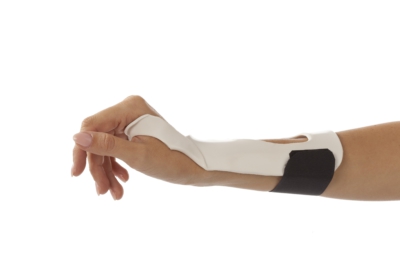
37
New cards
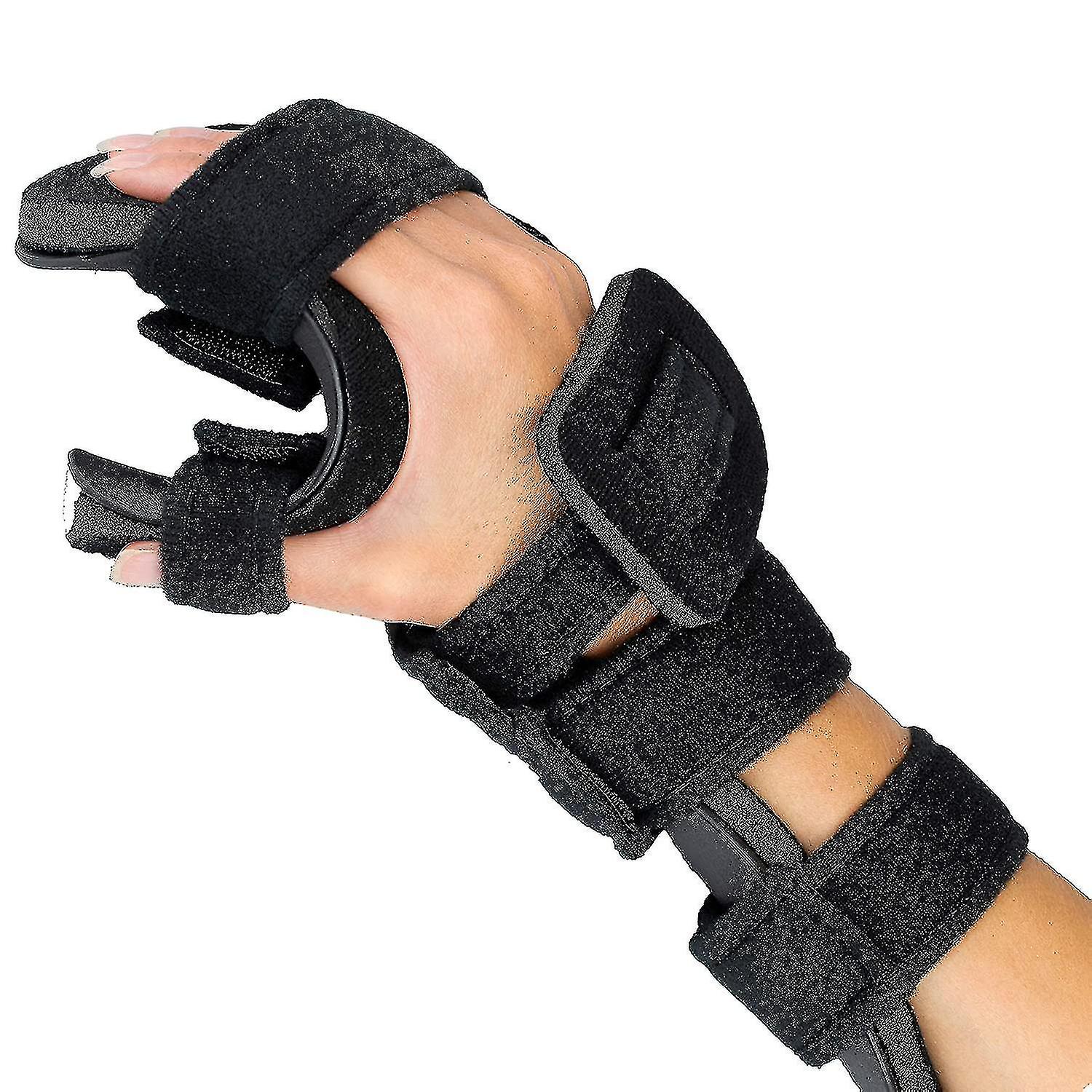
Resting Hand Splint
\- immobilizes to reduce symptoms during wrist movements like radial and ulnar deviation
\- retard further deformity
\- retard further deformity

38
New cards
Thumb Spica Splint
\- help stabilize CMC, MCP, and IP joints
\- resists flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and opposition of the thumb
\- resists flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and opposition of the thumb
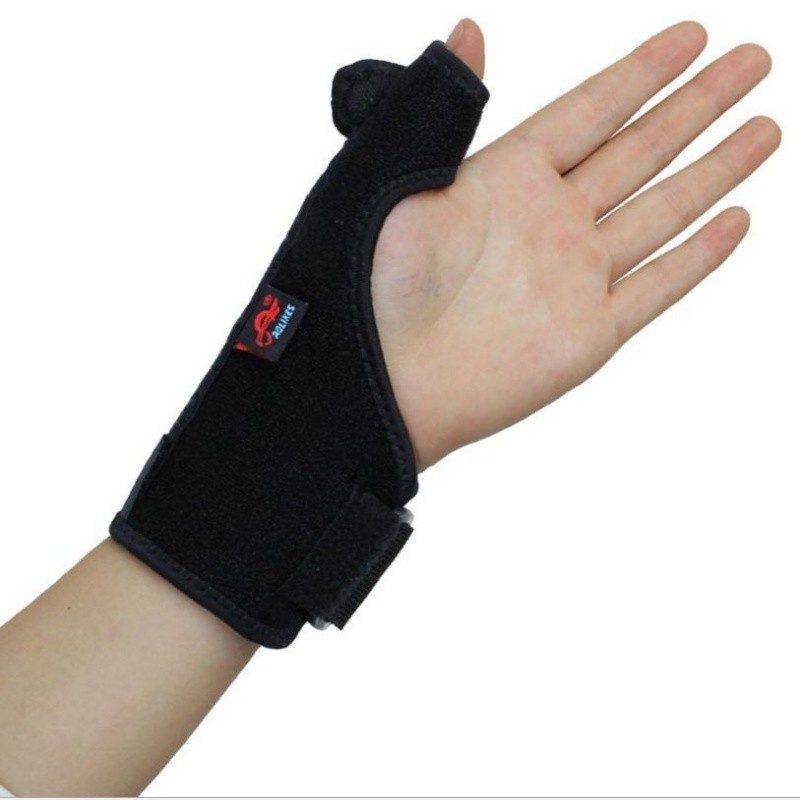
39
New cards
Antispasticity Splint
\- allows space for the fingers and thumb to move (finger spreader)
\- provides holding position to the certain joints (cones)
\- provides holding position to the certain joints (cones)

40
New cards
Dynamic Finger Extension Splint
\- immobilizes the wrist in functional position
\- passively extend the MCP to 0
\- permits full active MCP flexion and unrestricted IP motion
\- passively extend the MCP to 0
\- permits full active MCP flexion and unrestricted IP motion
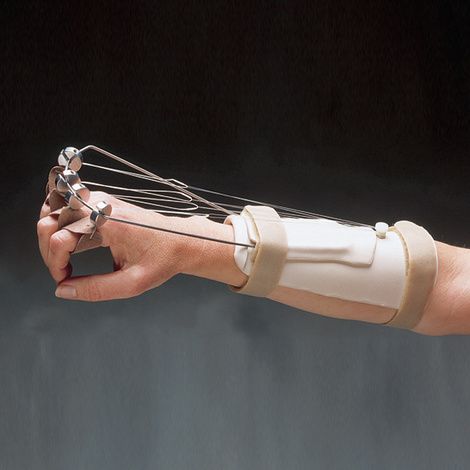
41
New cards
Dynamic Wrist Extension Splint
\- passively extends the wrist while allowing wrist flexion
\- to prevent contracture of unopposed, innervated wrist flexors
\- to prevent contracture of unopposed, innervated wrist flexors
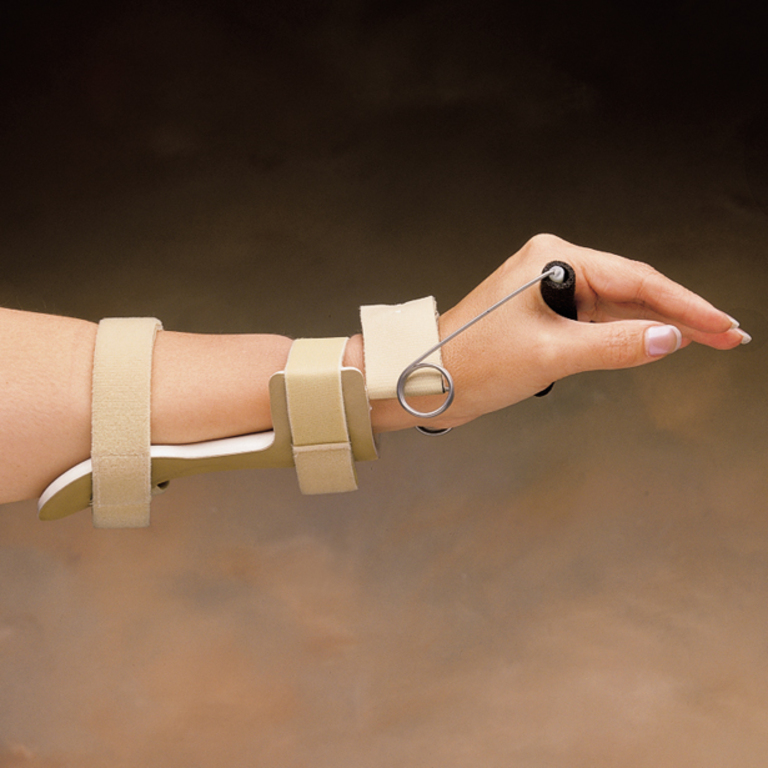
42
New cards
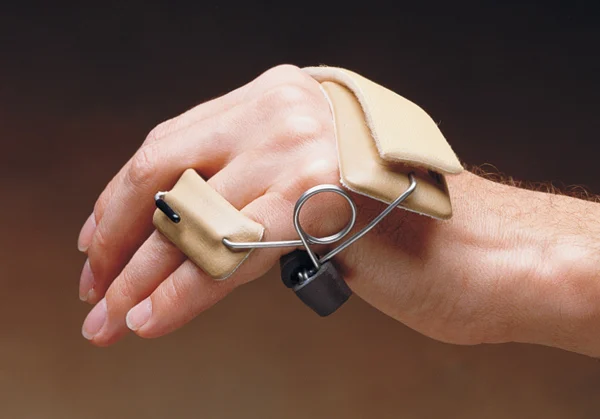
Dynamic Ulnar Nerve Splint
\- passively flex the 4th and 5th MCPs
\- prevent shortening of the MCP collateral ligament
\- promote active IP flexion
\- prevent shortening of the MCP collateral ligament
\- promote active IP flexion

43
New cards
Capener Splint
\- passively extend the PIP’
\- allows active IP flexion
\- provide stability to PIP
\- allows active IP flexion
\- provide stability to PIP
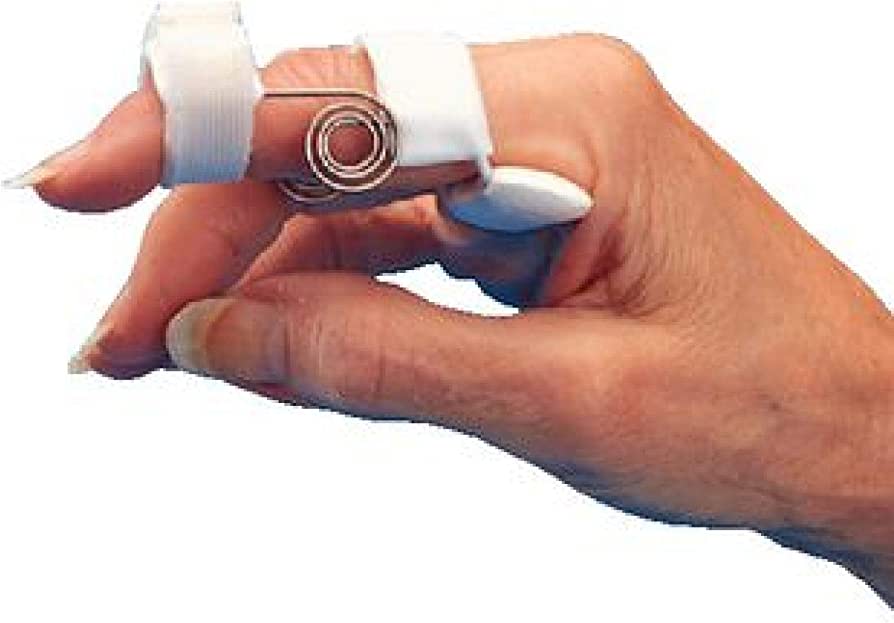
44
New cards
Anti Microstomial Splint
\- apply stretch to tissues surrounding the oral cavity while permitting speech
\- to prevent contracture of lip and buccal tissues
\- to prevent contracture of lip and buccal tissues
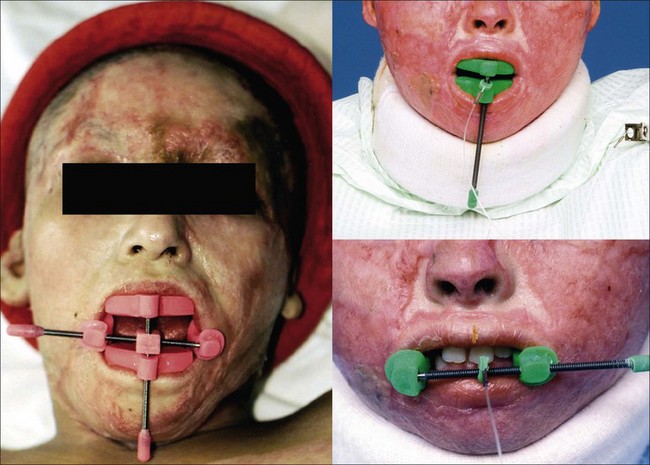
45
New cards
Static Dorsal Elbow Orthosis
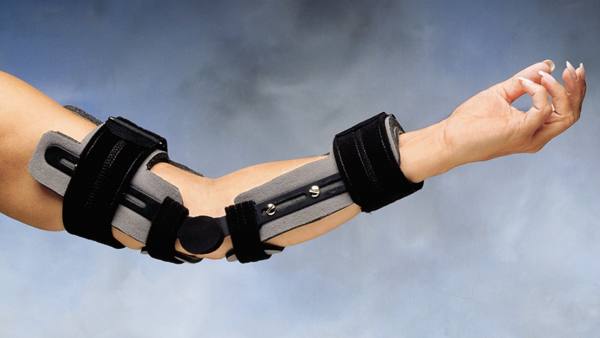
46
New cards
Shoulder Slings
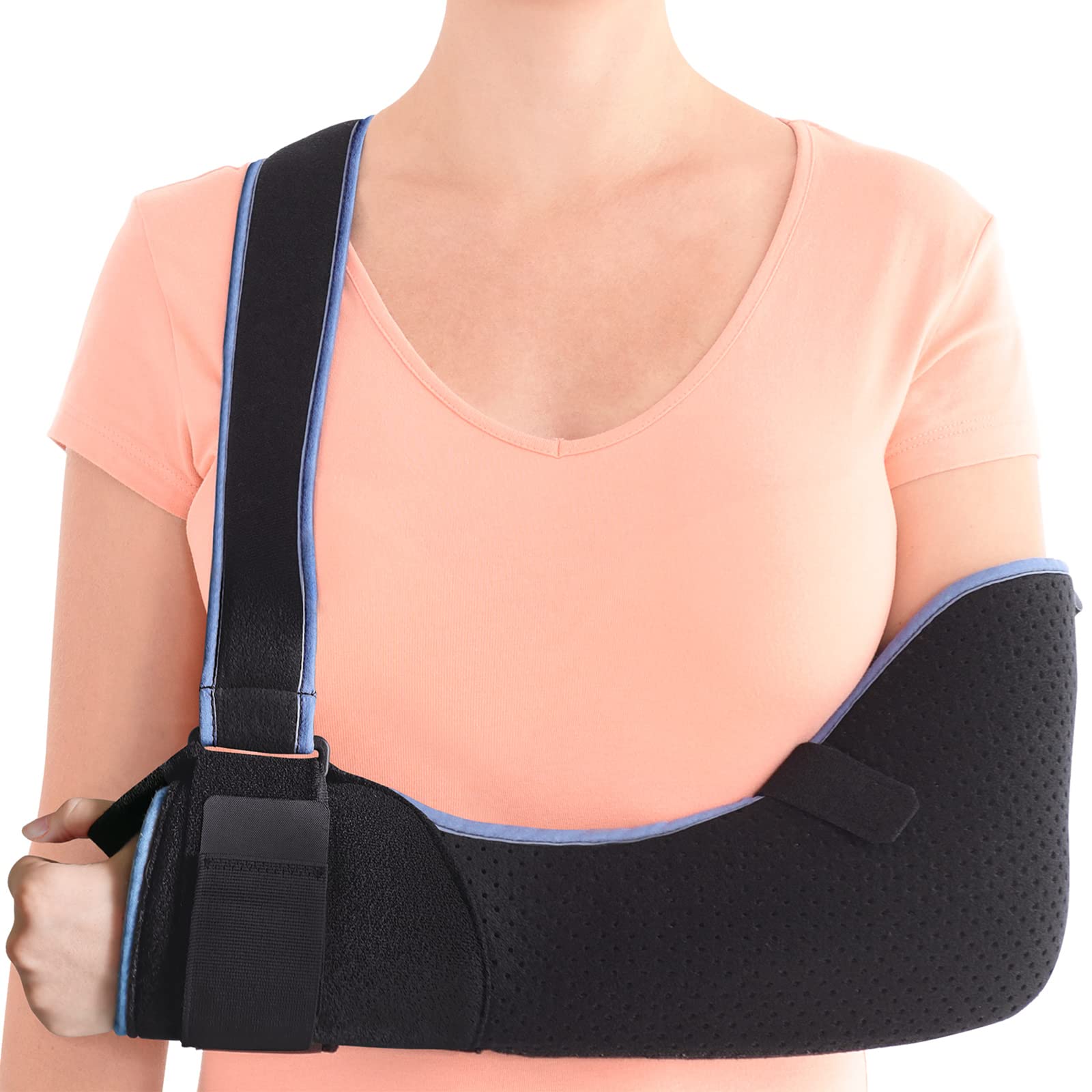
47
New cards
Humeral Fracture Brace
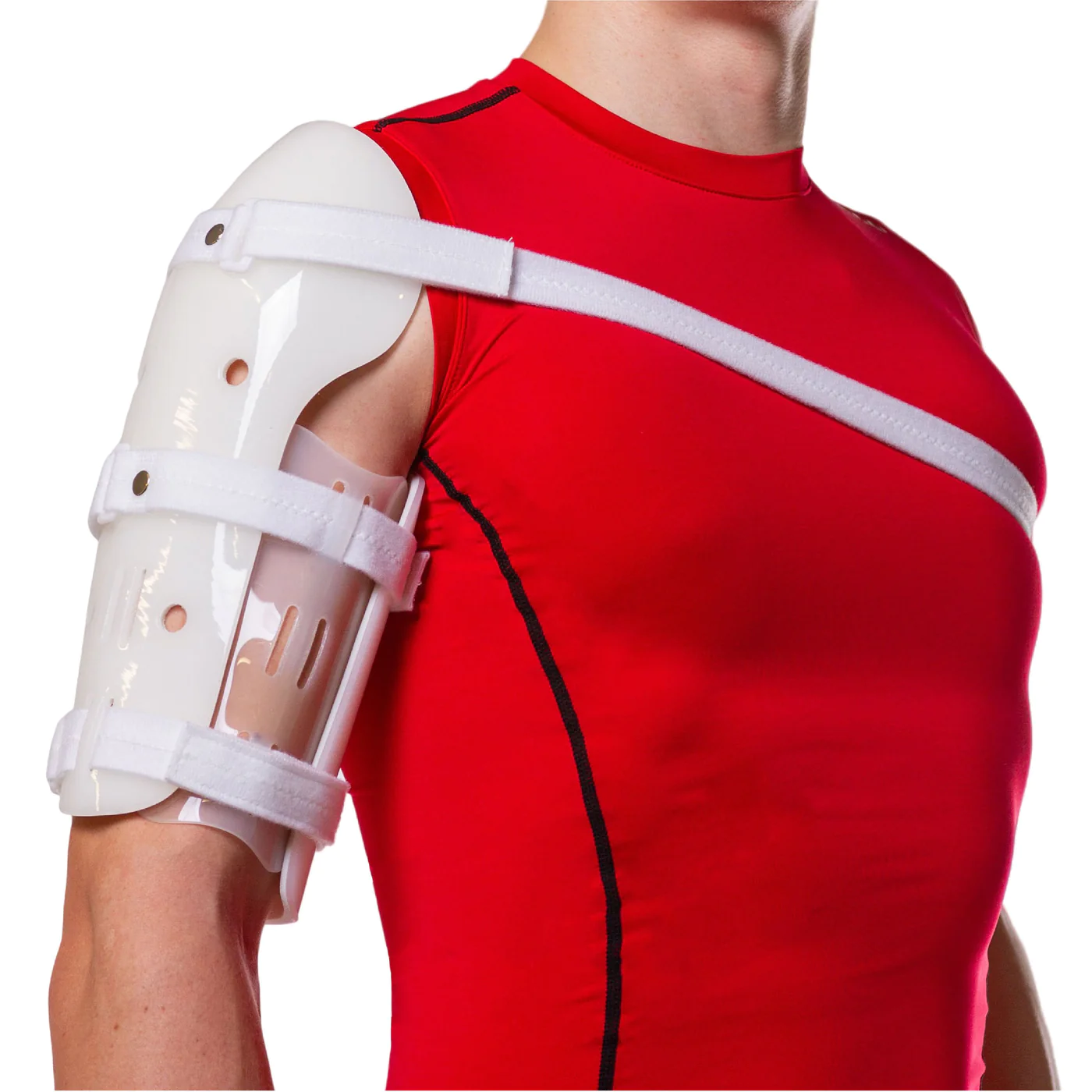
48
New cards
Airplane Splint
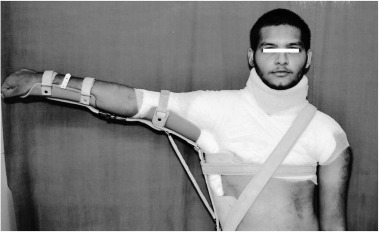
49
New cards
Foot Plate
\- provides best control of the foot because internal modifications can be incorporated
\- permits interchanging of shoes
\- facilitates donning
\- permits interchanging of shoes
\- facilitates donning
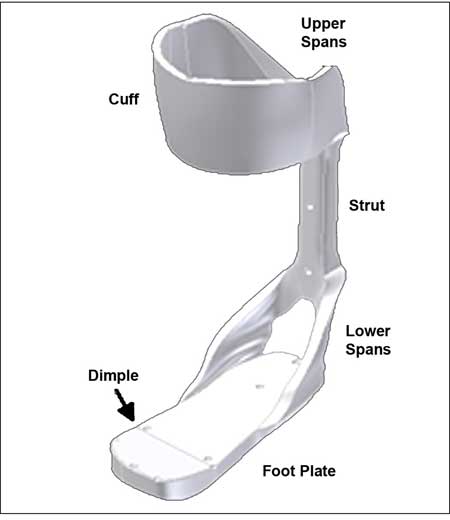
50
New cards
Stirrup
\- types:
* solid - provides maximum stability of the orthosis to the shoe; not movable
* split - 3 segments: 1 sole plate, 2 calipers; simplifies donning and doffing of orthosis
* solid - provides maximum stability of the orthosis to the shoe; not movable
* split - 3 segments: 1 sole plate, 2 calipers; simplifies donning and doffing of orthosis
51
New cards
Foot Control (Valgus/Varus Correction Strap)
for varus or valgus correction of the foot
52
New cards
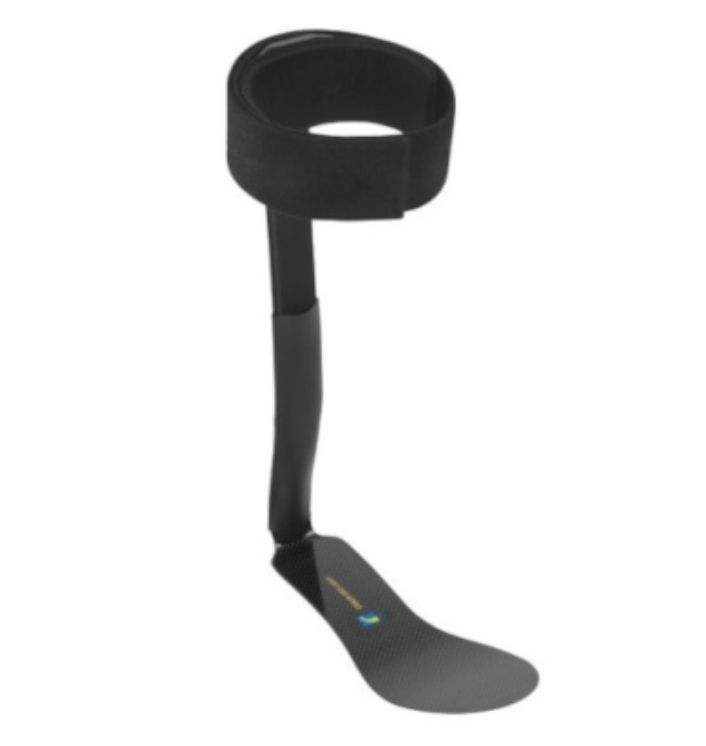
Posterior Leaf Spring
\- address weak dorsiflexion
\- resists plantarflexion at heel strike and swing
\- resists plantarflexion at heel strike and swing

53
New cards
Solid Ankle Foot Orthosis
\- excellent stability anterior and posterior
\- for plantarflexion spasticity, genu recurvatum, and knee instability
\- for plantarflexion spasticity, genu recurvatum, and knee instability
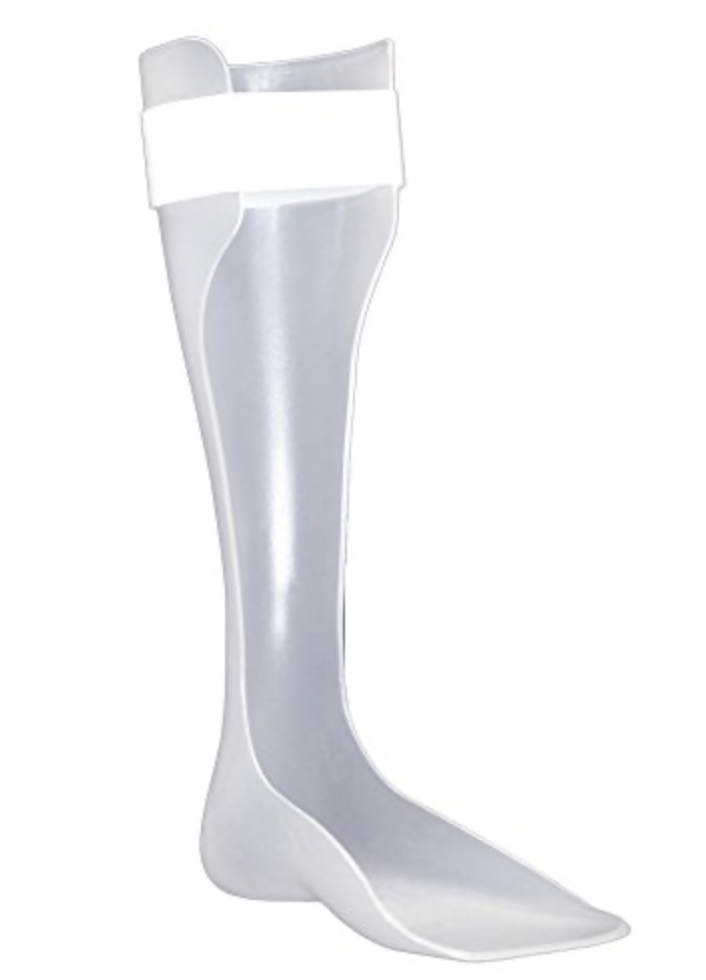

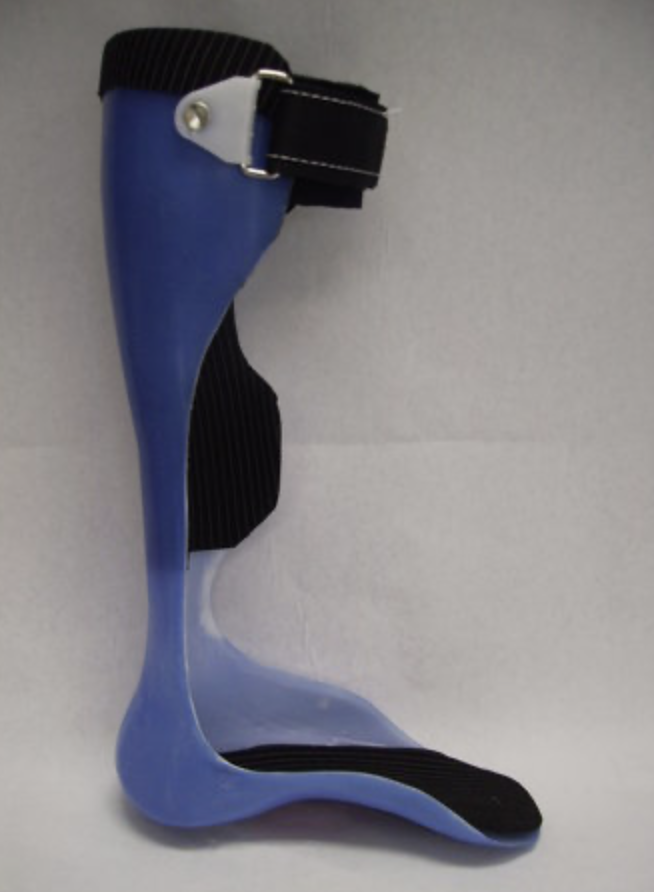
54
New cards
Spiral
\- controls all motion, allows leg to rotate in transverse plane
\- mediodistal
\- mediodistal
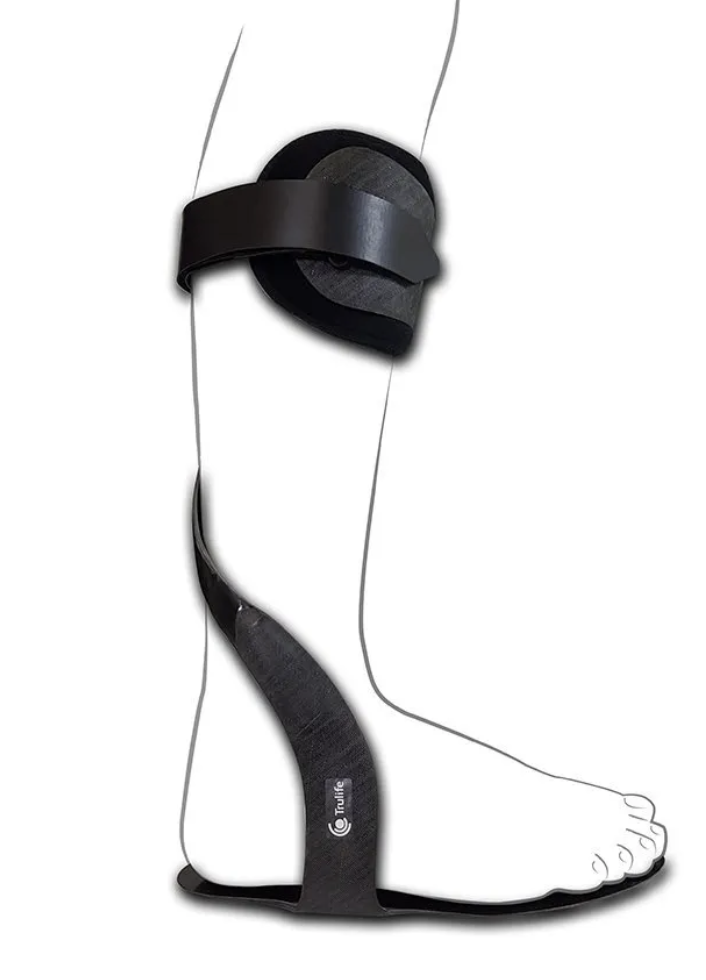

55
New cards
Hemispiral
\- greater control in equinovarus (club foot) foot
\- laterodistal
\- laterodistal
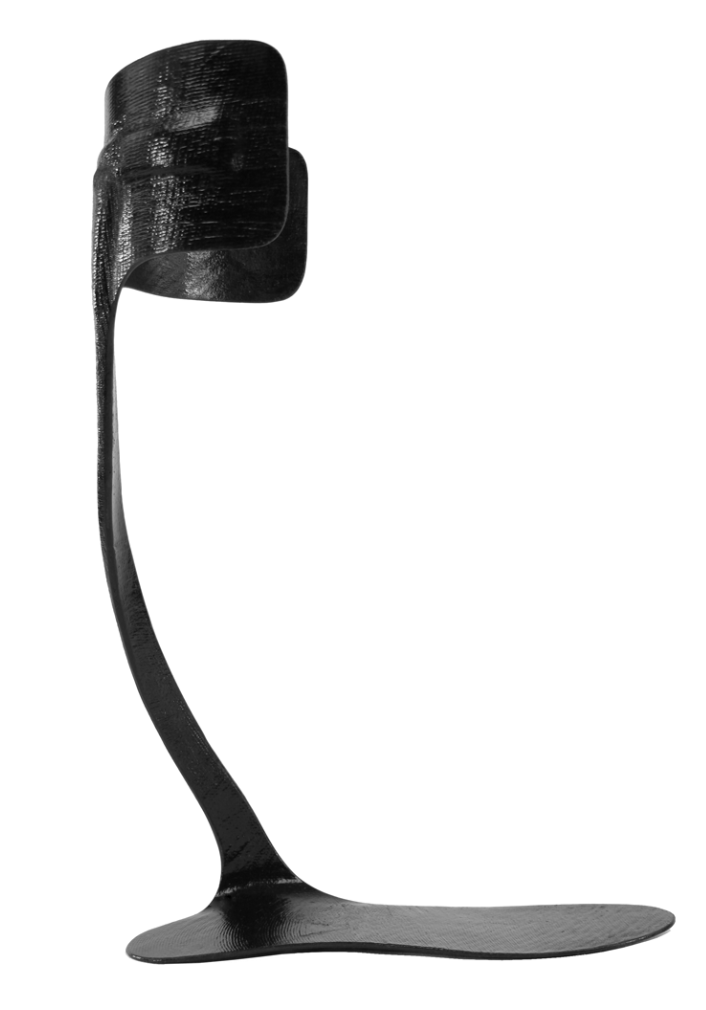

56
New cards
Ankle Foot Orthosis with Flange
provides maximum valgus or varus control.

57
New cards
Ground Reaction Ankle Foot Orthosis
proximal portion influences knee throughout gait.
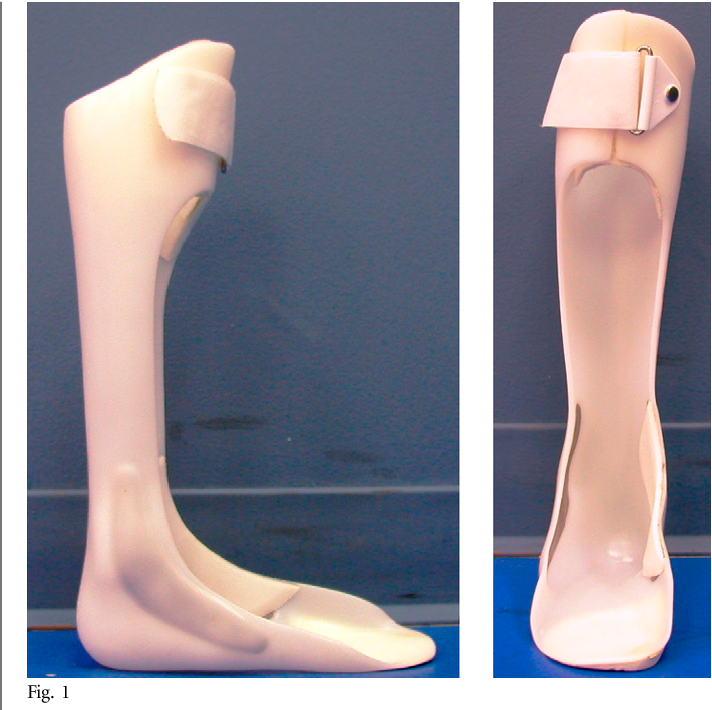
58
New cards
Orthotic Oregon System
with corrugations, and BICAAL ankle joints.

59
New cards
Tone Reducing Ankle Foot Orthosis
modify reflex hypertonicity by constant pressure to plantarflexors and inverters
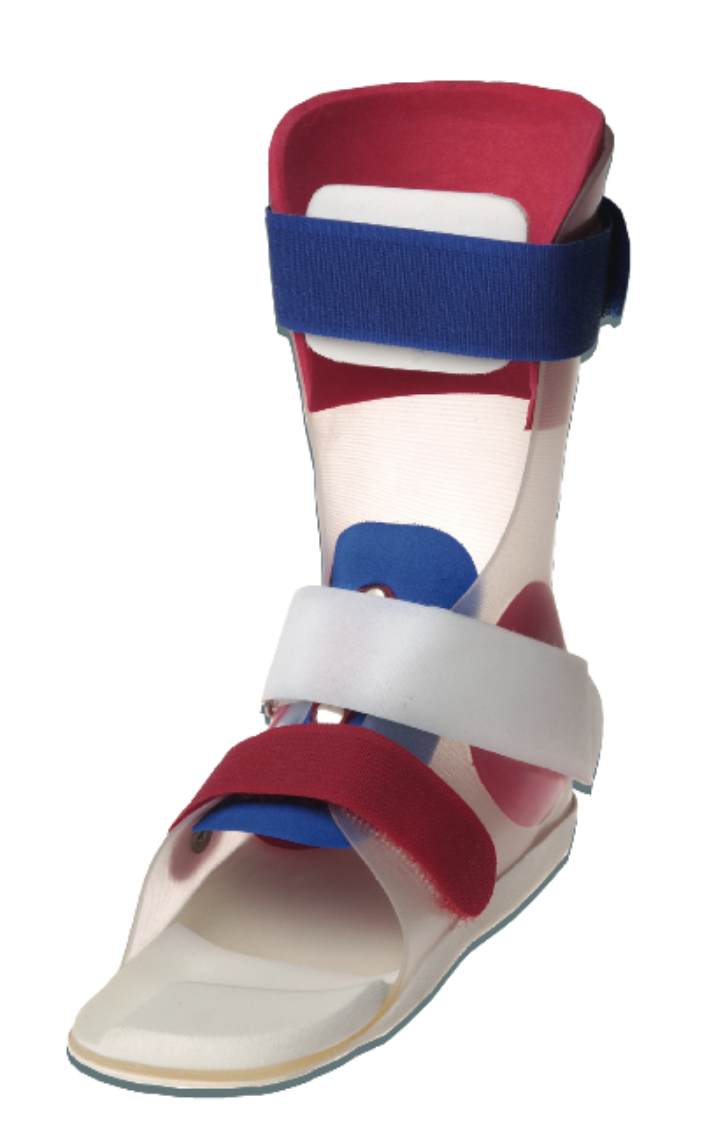
60
New cards
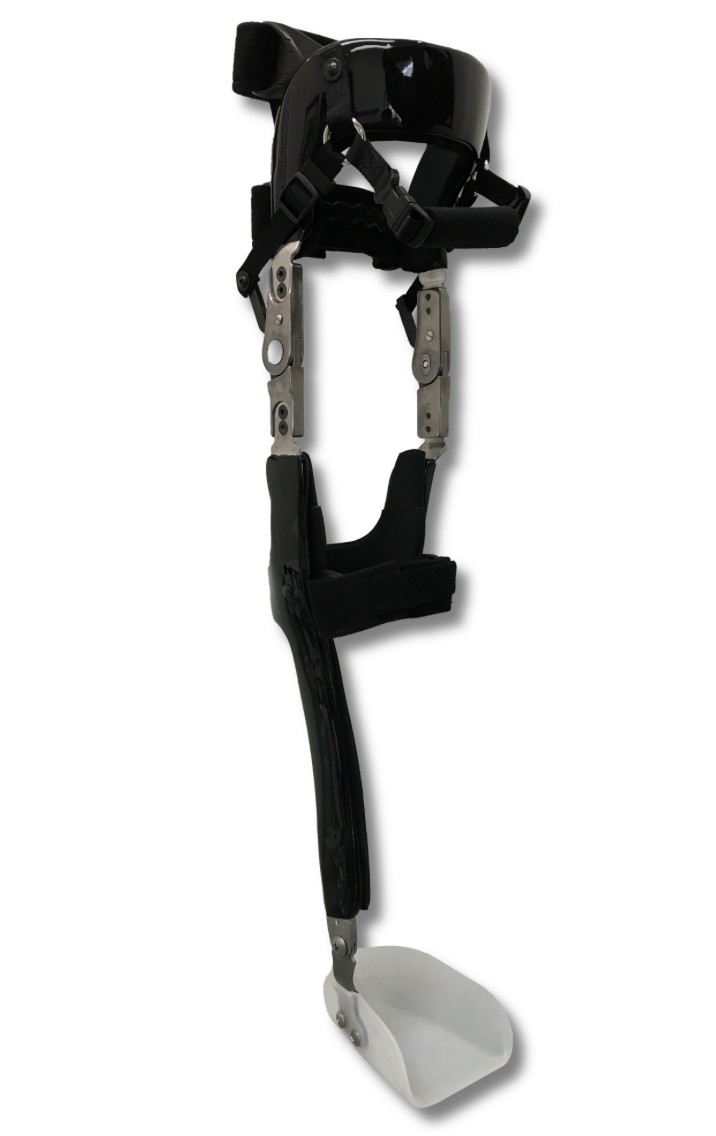
Single Upright Orthosis
has thigh and pretibial cuffs made of molded plastic.

61
New cards
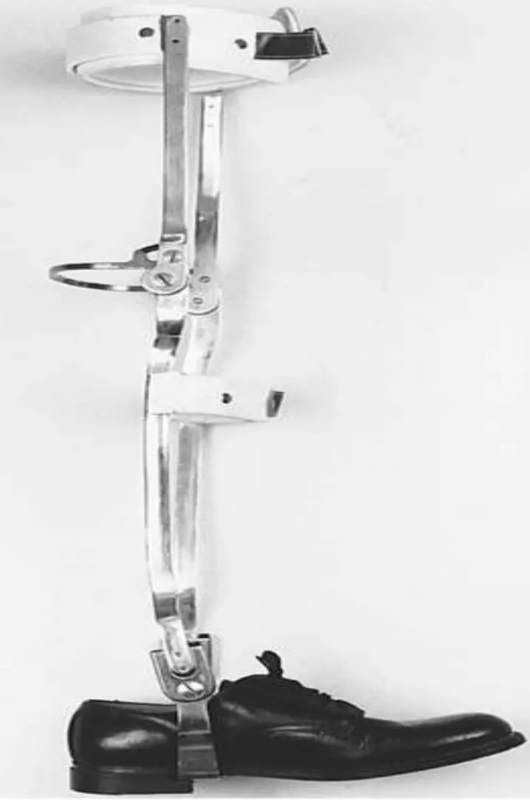
Scott Craig Orthosis
for paraplegic patient L1 level or higher.

62
New cards
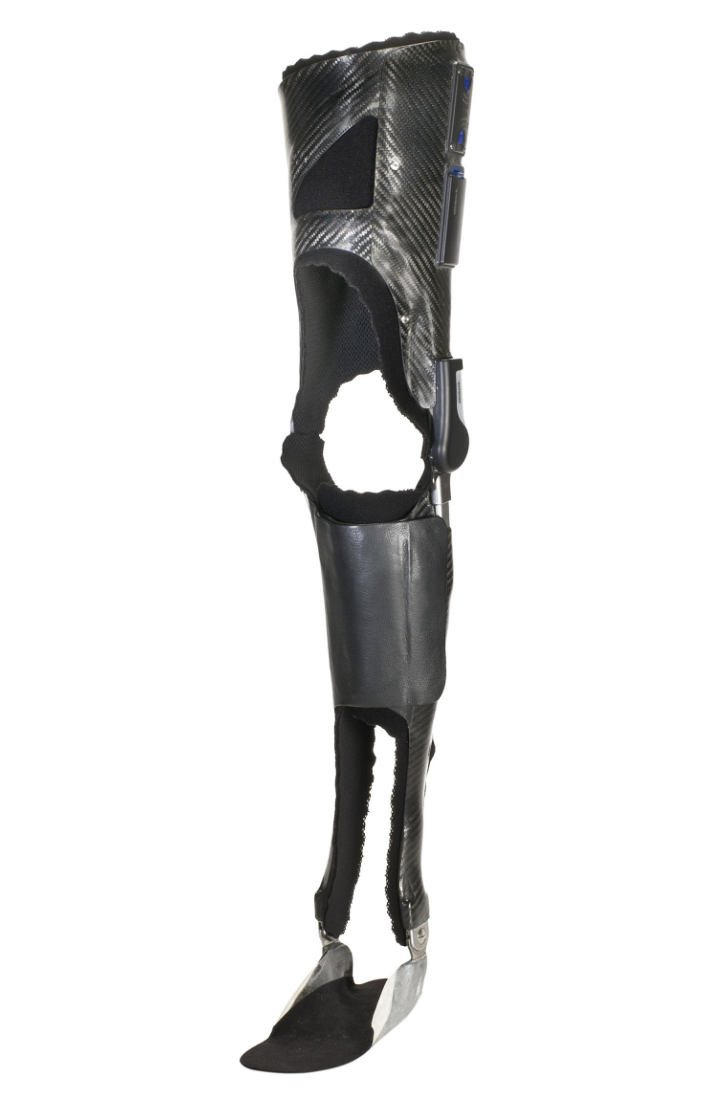
Supracondylar Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis
\- resists recurvatum and provide mediolateral stability
\- limits subtalar motion and immobilizes ankle into slight equinus
\- cannot be used bilaterally
\- limits subtalar motion and immobilizes ankle into slight equinus
\- cannot be used bilaterally

63
New cards
THKAFO
\- LSO + KAFO
\- very difficult to done and cumbersome = poor pt. compliance
\- very difficult to done and cumbersome = poor pt. compliance
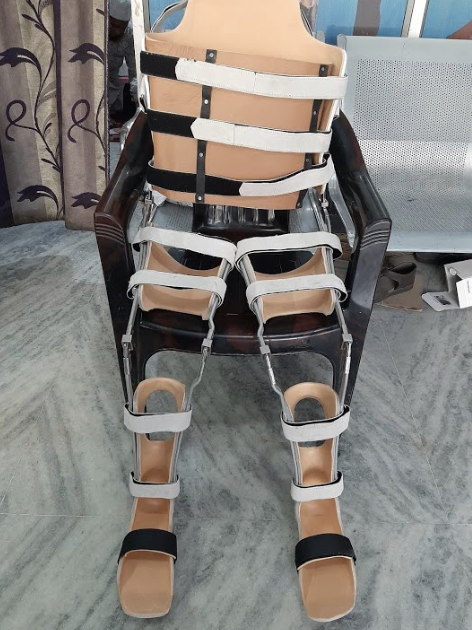
64
New cards
Chopat Brace
foam padded infrapatellar strap encircles the knee below the patella.
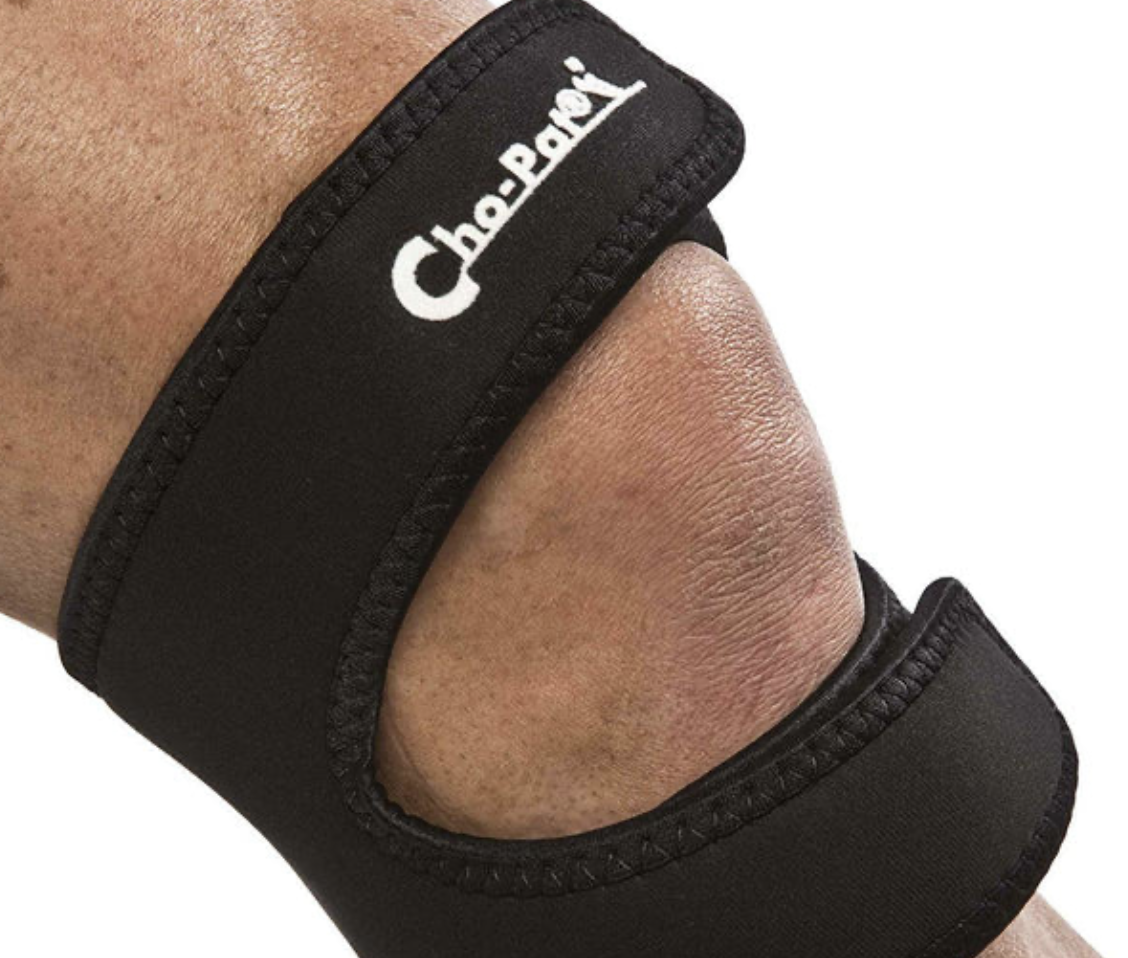
65
New cards
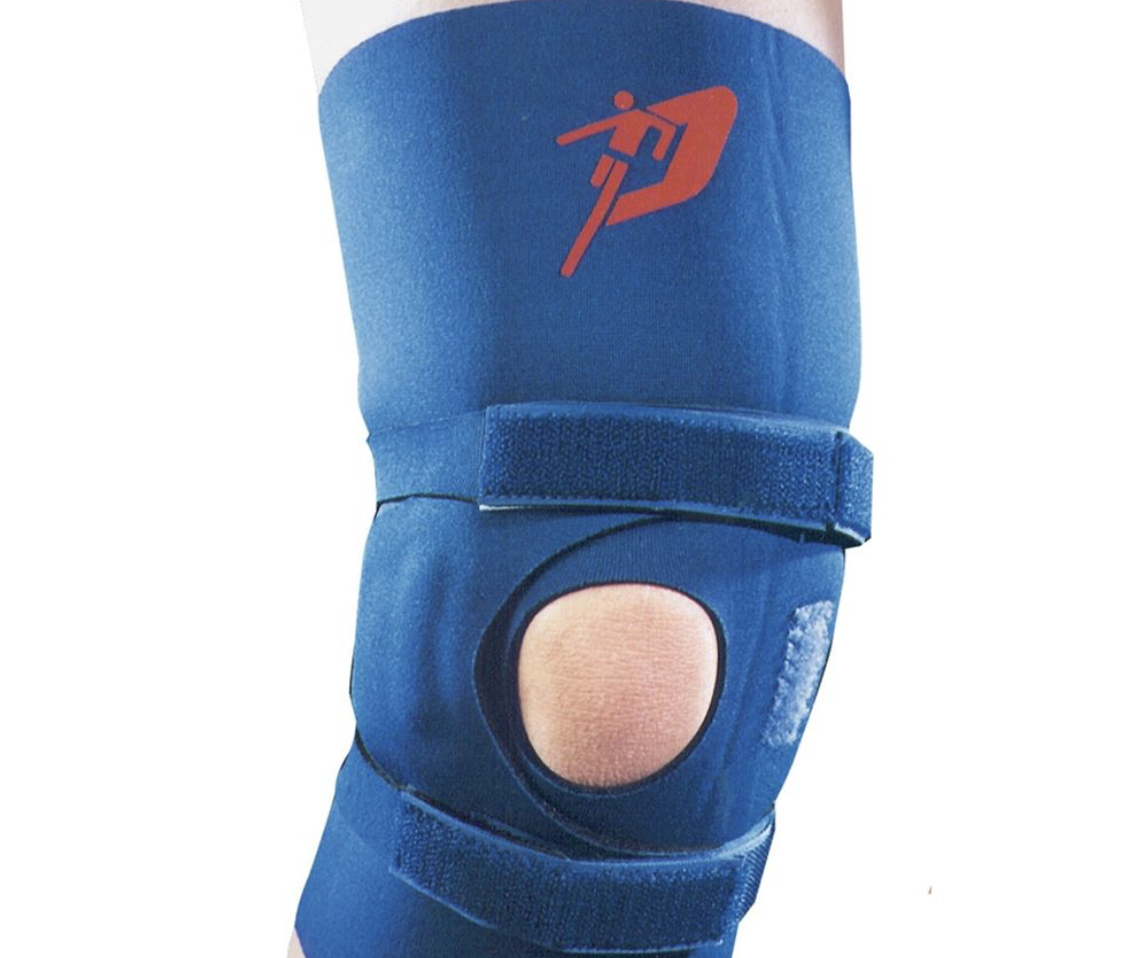
Palumbo
\- elastic sleeve with patella cutout
\- 2 rubber straps provide tension to the crescent shaped patellar pad and elastic counterforce strap to maintain pad position and prevent axial rotation of the device
\- 2 rubber straps provide tension to the crescent shaped patellar pad and elastic counterforce strap to maintain pad position and prevent axial rotation of the device
66
New cards
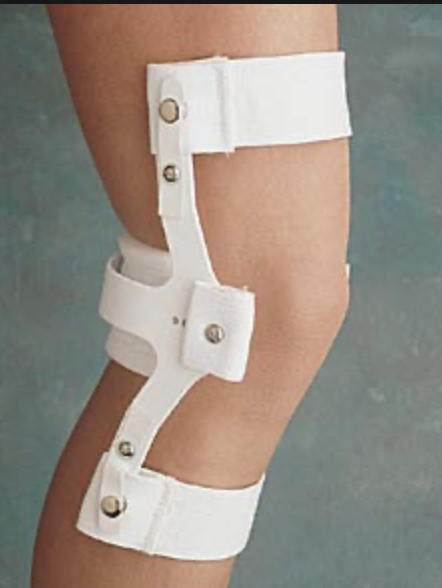
Swedish Knee Cage
\- for genu recurvatum
\- has 2 anterior and 1 posterior straps
\- has 2 anterior and 1 posterior straps
67
New cards
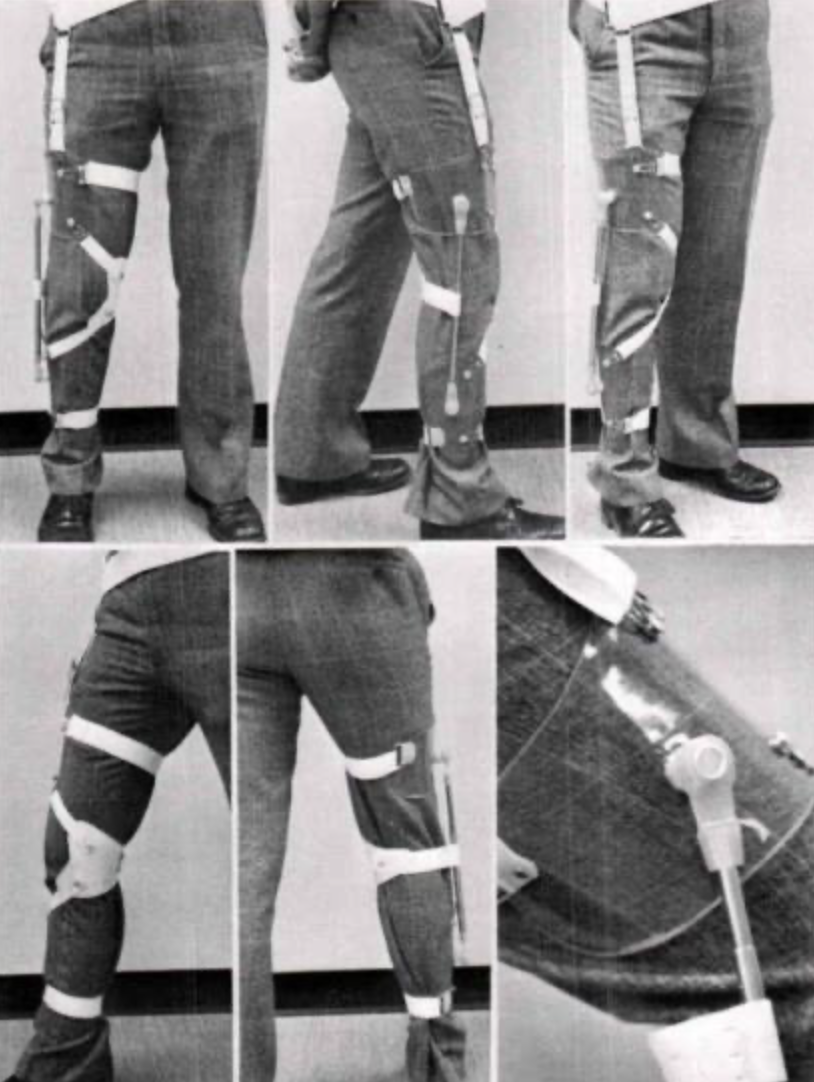
CARS UBC Orthosis
\- for genu valgum/varum
\- support is provided by lateral/medial telescoping rods with straps in the opposite sides respectively
\- support is provided by lateral/medial telescoping rods with straps in the opposite sides respectively
68
New cards
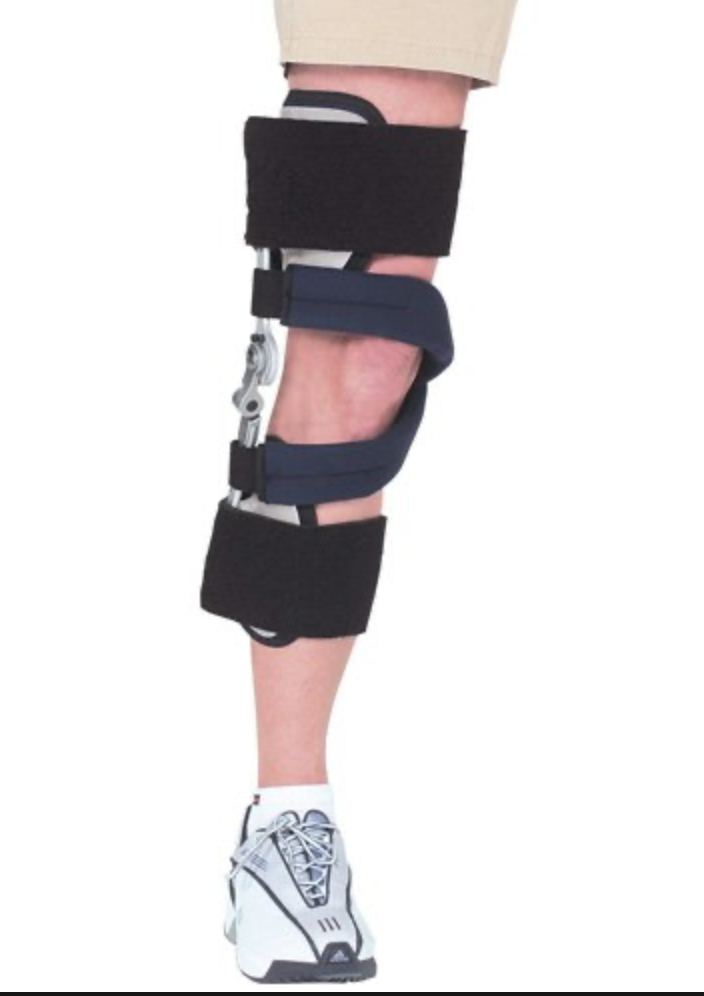
Lerman Multigamentous Knee Control Orthosis
both utilize elastic straps that encircle the leg and thigh and provide forces to provide rotational control.
69
New cards
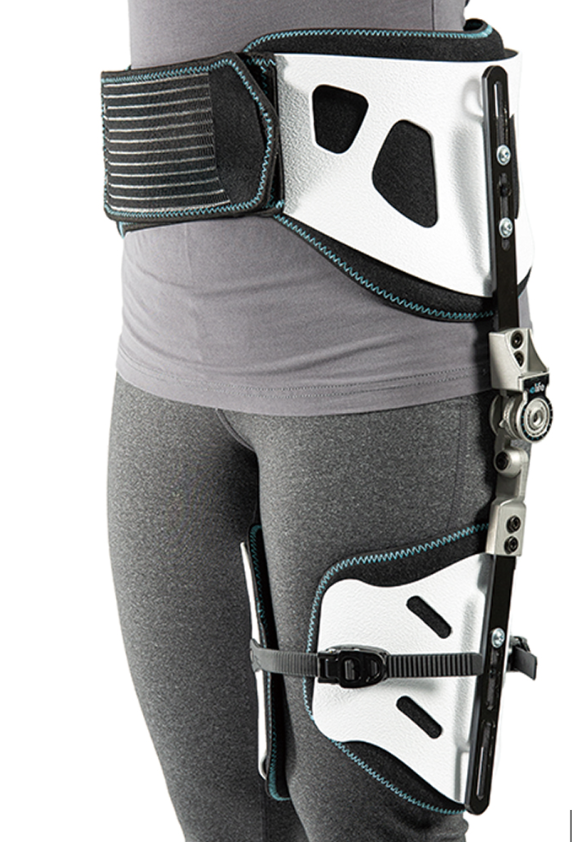
Hip Orthosis
\- usual design address adductor spasticity
\- also used by patient that had hip replacement during convalescence
\- also used by patient that had hip replacement during convalescence

70
New cards
Patellar Tendon Bearing Orthosis
pressure on the patellar tendon and tibial flare.
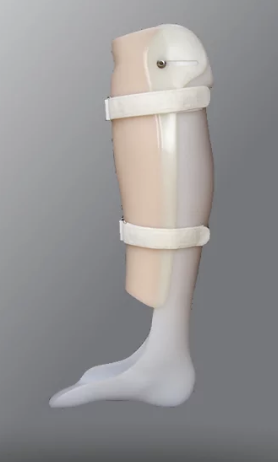
71
New cards
Ischial Weight Bearing Orthosis
pressure is on the ischial tuberosity.
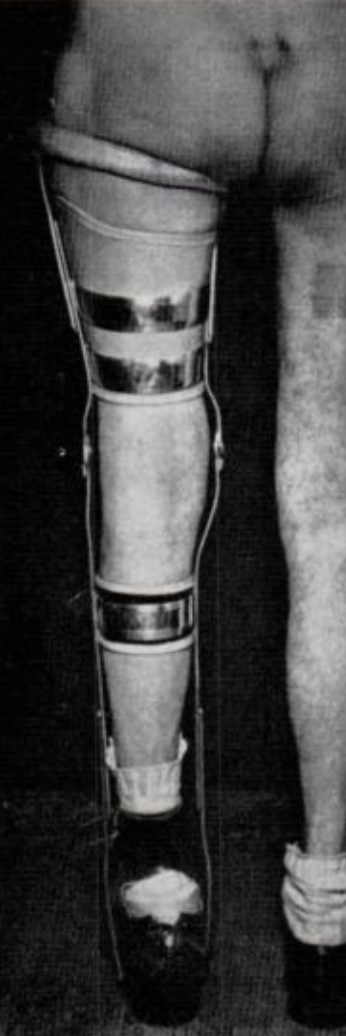
72
New cards
Patten Bottom
for elimination of weight bearing.

73
New cards
Dennis Browne Splint
correct angular and rotational deformities.
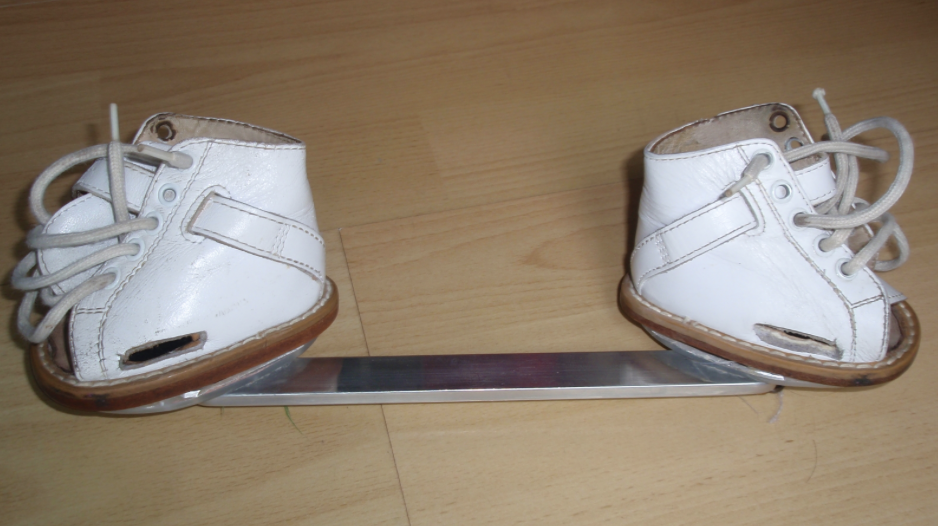

74
New cards
A frame
correct angular and rotational deformities.

75
New cards
Torsion Shaft Orthosis
correct angular and rotational deformities.
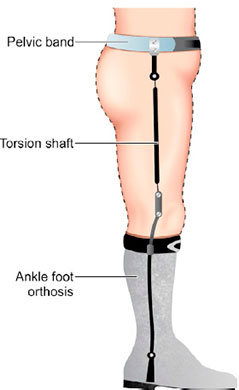
76
New cards
Van Rosen Splint
for hip control.
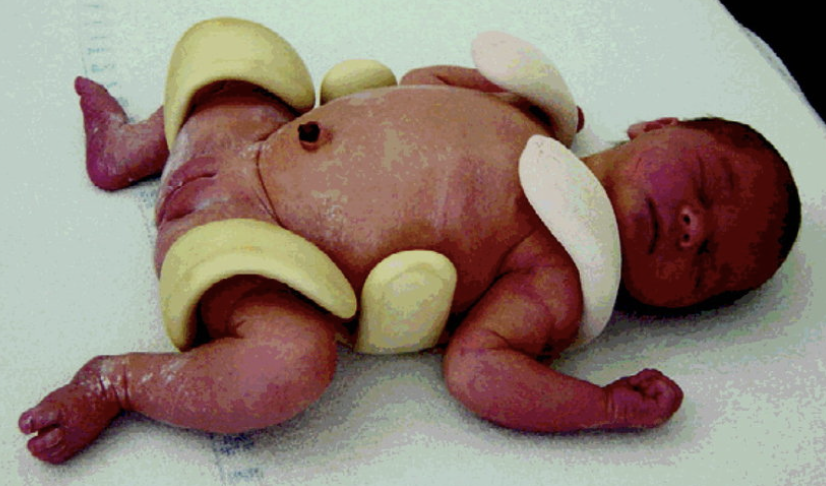
77
New cards
ILFELD Splint
for hip control.
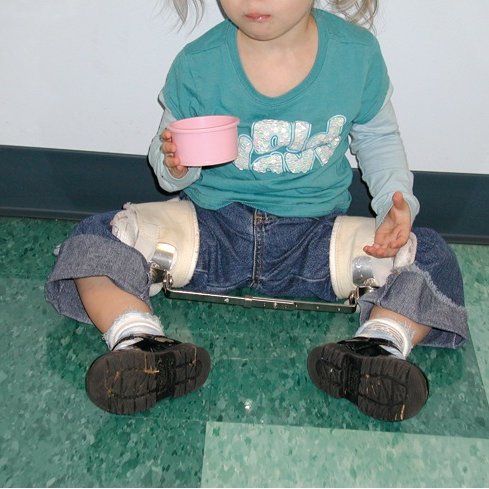
78
New cards
Pavlik Harness
for hip control.
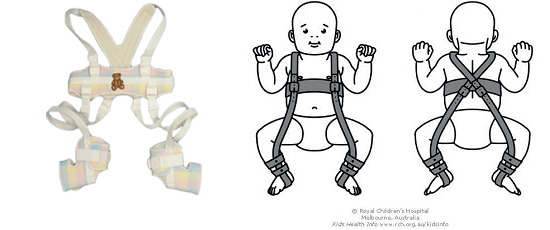
79
New cards
Trilateral Orthosis
to prevent and counter the impairments of LCPD.
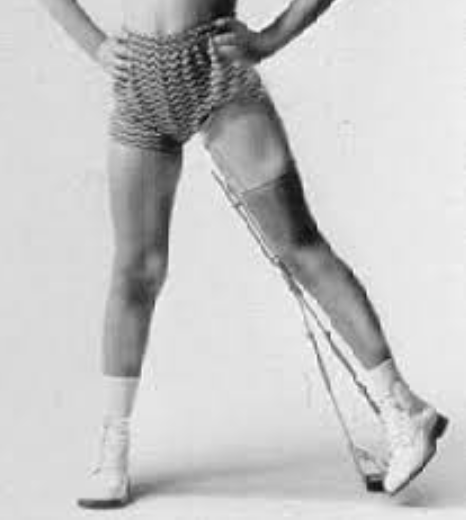

80
New cards
Toronto Orthosis
to prevent and counter the impairments of LCPD.
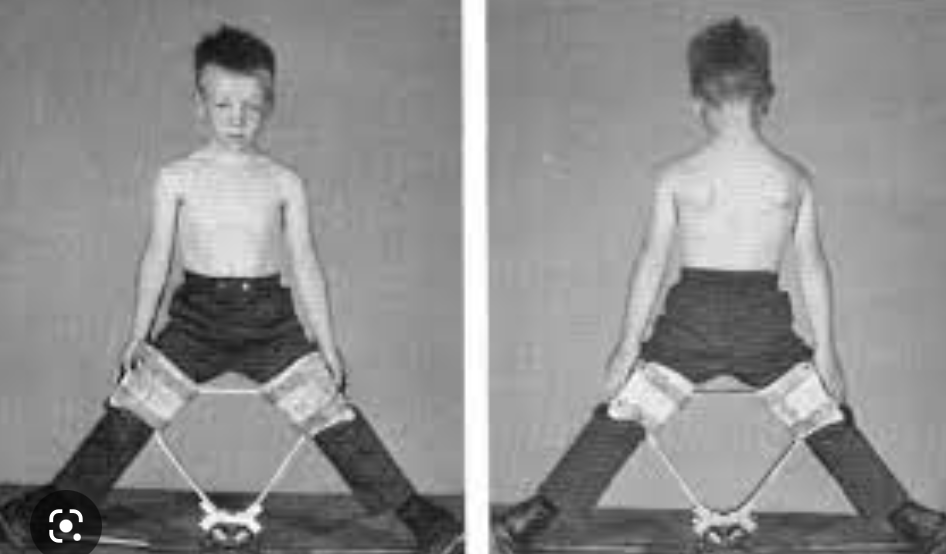
81
New cards
Scottish Rite Orthosis
to prevent and counter the impairments of LCPD.
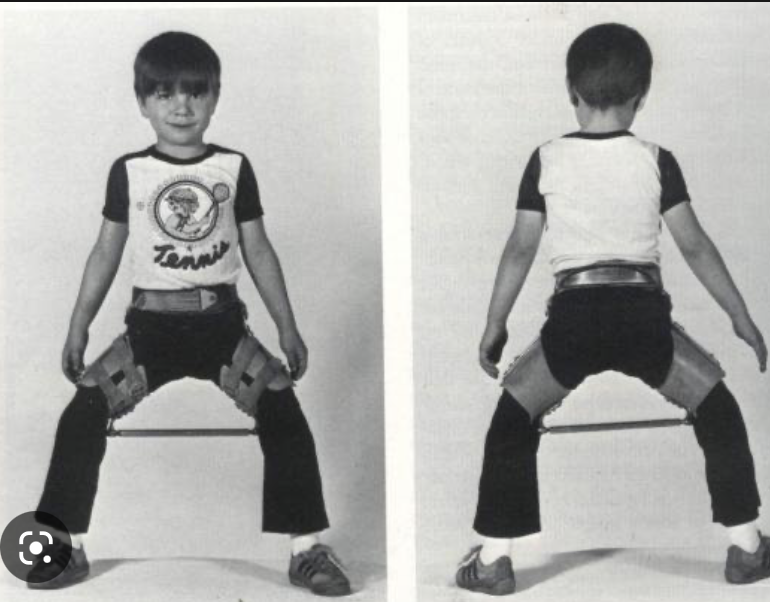
82
New cards
Standing Frame
\- initial use: 8-15 months
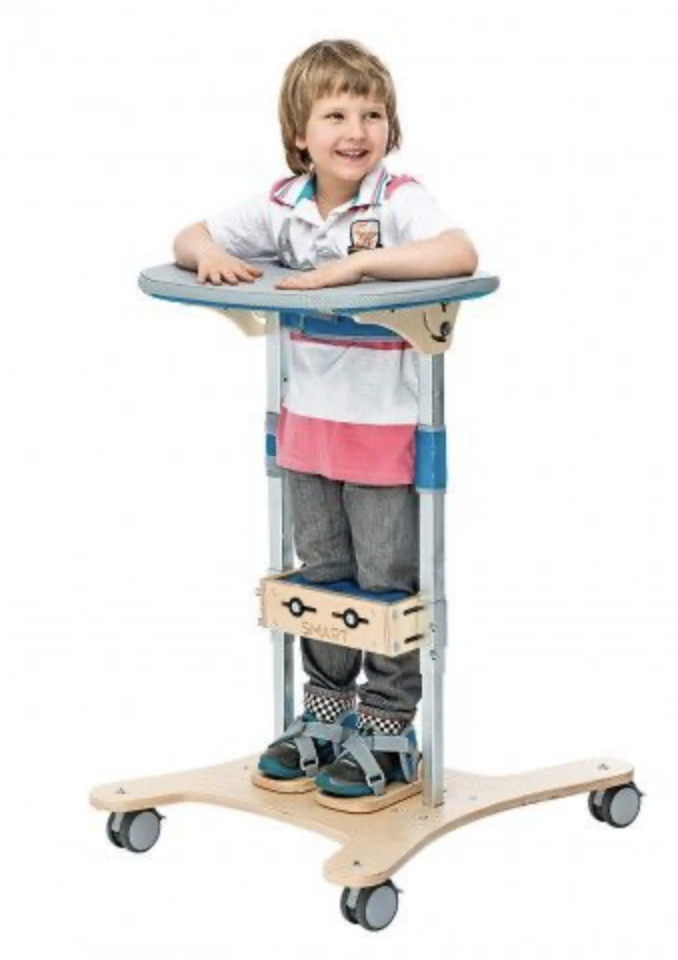

83
New cards
Swivel Walker
for both children and adult
84
New cards
Parapodium
\- initial use: 2-5 years
\- it permits the wearer to sit
\- may keep the knees locked while the child unlock the hip for leaning forward
\- it permits the wearer to sit
\- may keep the knees locked while the child unlock the hip for leaning forward
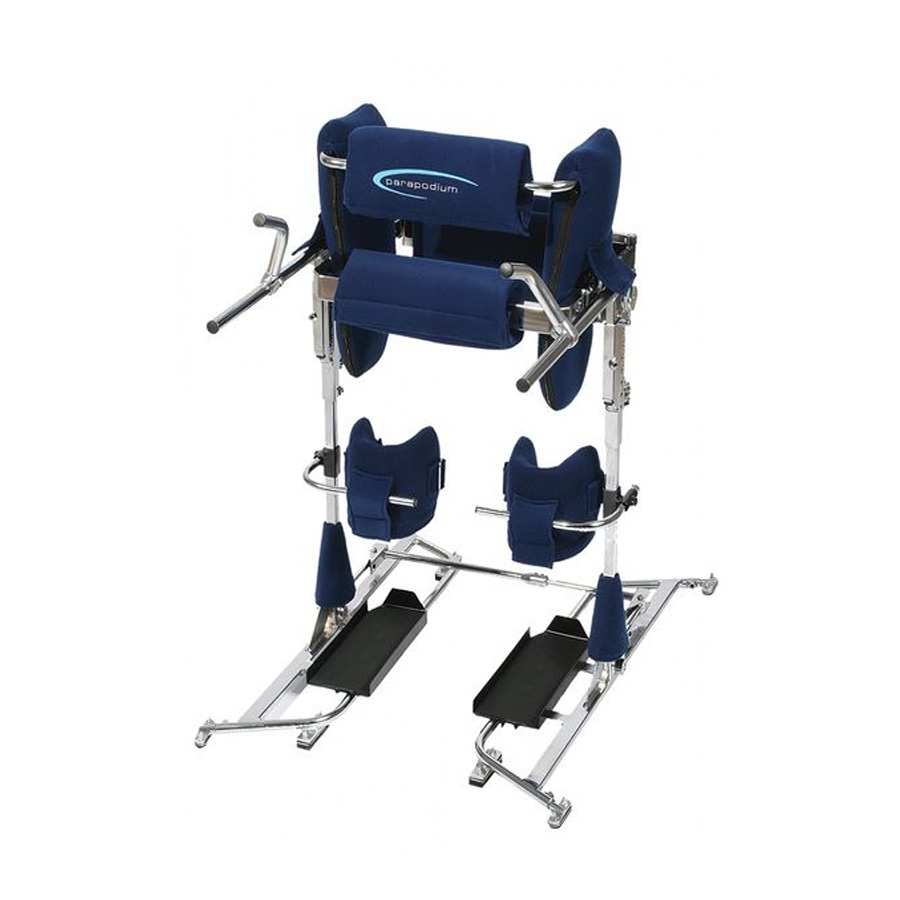

85
New cards
Reciprocating Gait Orthosis
\- initial use: 3-6 years
\- provide contralateral hip extension with ipsilateral hip flexion
\- provide contralateral hip extension with ipsilateral hip flexion