Chem
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:02 PM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
Name the 7 diatomic ions
(H)- hydrogen
(N)- Nitrogen
(O)- oxygen
(F)-Fluorine
(Cl)- Chlorine
(Br)-Bromine
(I)-Iodine
(N)- Nitrogen
(O)- oxygen
(F)-Fluorine
(Cl)- Chlorine
(Br)-Bromine
(I)-Iodine
2
New cards
hydroxide
OH-
3
New cards
Nitrate
NO3-
4
New cards
Carbonate
CO32-
5
New cards
Hydrogen carbonate
HCO3-
6
New cards
Ethanoate
CH3COO-
7
New cards
Sulphate
SO42-
8
New cards
Phosphate
PO43-
9
New cards
Ammonium
NH4+
10
New cards
copper (II) ion
Cu2+
11
New cards
Copper (I)
Cu+
12
New cards
Iron (II) ion
Fe2+
13
New cards
Iron (III)
Fe3+
14
New cards
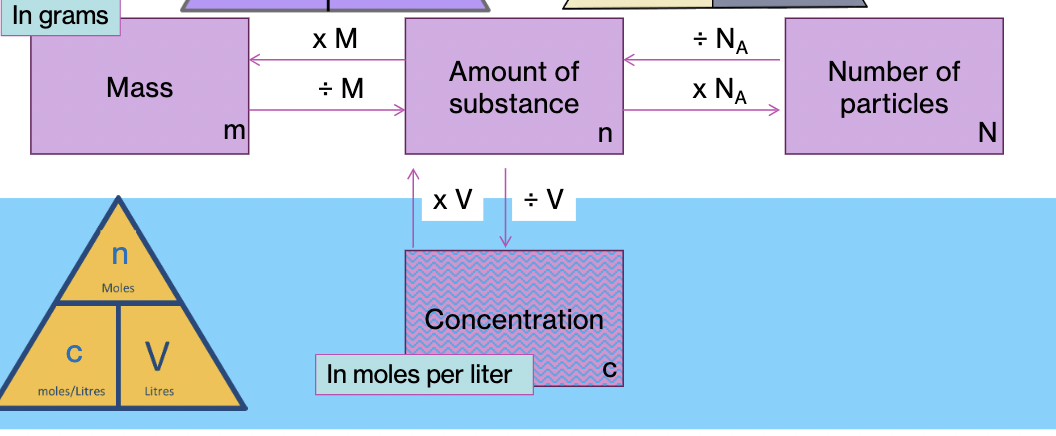
Name the formulas in stoichiometry
15
New cards
Mole
**A mole of a substance is the amount that contains the same number of units as the number of carbon atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12.**
16
New cards
Avogadro’s number
12 g of carbon-12 contains, **6.02x10^23 (How many atoms are there? Number of particles)**
17
New cards
How do you get dm^3 from cm^3
divide cm by 1000 to get dm
18
New cards
Zinc
Zn2+
19
New cards
Common acids
Hydrochloric acid- HCl
Sulfuric acid- H2SO4
Nitric acid- HNO3
Ethanoic acid- CH3C00H
Sulfuric acid- H2SO4
Nitric acid- HNO3
Ethanoic acid- CH3C00H
20
New cards
Common Alkalis
Sodium Hydroxide- NaOH
Potassium hydroxide- KOH
Calcium hydroxide- Ca (OH)2
Ammonia- NH3
Potassium hydroxide- KOH
Calcium hydroxide- Ca (OH)2
Ammonia- NH3
21
New cards
Strong acids
Hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, Nitric acid
22
New cards
Weak acids
Methanoic acid, Ethanoic acid, Citric acid
23
New cards
Strong alkali
Sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide
24
New cards
Weak alkali
Ammonia solution
25
New cards
What is always produced when acids react with metals, bases, or carbonates
Salt
26
New cards
What is a neutralisation reaction
Reaction with acid that gives water and salt
27
New cards
what is neutralised in a neutralisation reaction, and which reactions are considered neutralisation reactions
The acid, Reactions of bases and carbonates with acids
28
New cards
What are the typical acid reactions
Acid+metal→Salt+ hydrogen
Acid+base→Salt+Water
Acid+carbonate→Salt+water+carbon dioxide
Acid+base→Salt+Water
Acid+carbonate→Salt+water+carbon dioxide
29
New cards
Effect of acid on litmus paper?
Acid turns litmus red
30
New cards
Properties of alkalis
Also must be handled carefully, pure alkalis are solid but used in lab as aqueous solutions (except ammonia which is a gas). Alkalis are bases soluble in water.
31
New cards
What are indicators
Shows wether something is an acid or base through colour change
32
New cards
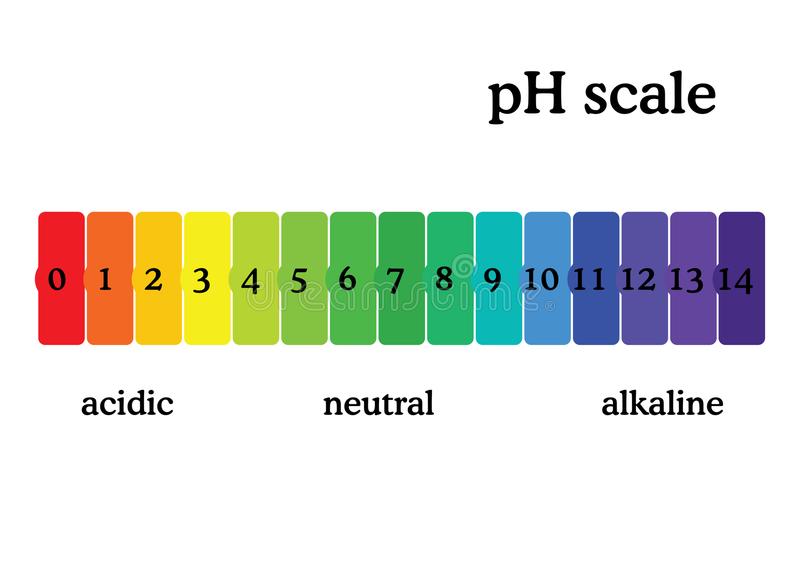
Neutral substances
Not an acid or a base, pH of 7, for example water
33
New cards
pH for acids and bases?
Under 7 is an acid. Over 7 is a base
34
New cards
Universal indicator paper
Can be used to find the pH of any solution. Mixture of dyes, can be used as a solution or a paper strip, Colour will change with pH.
35
New cards
What do acids produce
Hydrogen ions
36
New cards
What do acids contain
Hydrogen ions that gives the acidity
37
New cards
What happens with strong acids
All molecules become ions, therefore conduct better because more ions are present, lower pH as there are more hydrogen ions present.
38
New cards
What happens with weak acids
Less than 100% of molecules become ions, so conduct worse with less ions and have a higher pH as there are less hydrogen ions present
39
New cards
What do alkalis produce
Hydroxide ions
40
New cards
What do alkali solutions contain
Hydroxide ions
41
New cards
What happens with strong alkalis
High conductivity because all molecules become ions, so more ions present, and higher pH as there are more hydroxide ions present
42
New cards
What happens with weak alkalis
Lower conductivity because not all molecules become ions, so there is a lower concentration of ions, so less conductivity, pH is lower as there are less hydroxide ions.
43
New cards
Why are ions good conductors
Because they are able to move freely
44
New cards
What is an ionic equation
Best way to show what is going on in a neutralisation reaction
45
New cards
What are the three steps in writing a net ionic equation
1\. Write down all ions and charges present in the equation
2. Cross out any ions that appear unchanged, on both sides of the equation. These are called spectator ions, they do not take part in the reaction
3. You are left with the ionic equation for the reaction
2. Cross out any ions that appear unchanged, on both sides of the equation. These are called spectator ions, they do not take part in the reaction
3. You are left with the ionic equation for the reaction
46
New cards
Which is proton donor and which is proton acceptor
Acid is a proton donor and alkali is a proton acceptor, H gives a proton to OH to form H2O
47
New cards
Only seperate this in ionic equations
AQ substances that are not polyatomic, solids that are ionic
48
New cards
Potassium oxide
K2O
49
New cards
Name the 4 acid and metal reactions
Acid+metal→salt+hydrogen gas
Acid+Metal oxide→ salt+water
Acid +metal hydroxide→ Salt+ water
Acid+Metal oxide→ salt+water
Acid +metal hydroxide→ Salt+ water
50
New cards
Hydrogen flouride
HF
51
New cards
Potassium carbonate
K(CO3)2
52
New cards
Phosphoric acid
H3PO4
53
New cards
Magnesium hydroxide
Mg(OH)2
54
New cards
Lithium oxide
Li2O
55
New cards
How to write dissolution reaction
Take out what makes it a base or an acid and balance the rest together
56
New cards
When looking at molar mass
Only account for the subscripts when calculating
57
New cards
What stays together and what doesn’t
covalent stays together (H2O, CO2, NH3)
58
New cards
Base and water equation we need to know
NH3+H2O → NH4+ + OH-
59
New cards
CO3 charge
\-2
60
New cards
When it asks to show something dissolving in water, except for NH3 which you just do a reaction with water
Just split it up
61
New cards
Covalent bonds and ionic bonds
Non- metal Nonmetal, metal nonmetal